python中format函数的用法
在python2.6以前,格式化字符串还是以%来处理,在python2.6之后,python增加了新的格式化字符串的方式,那就是format函数。format函数增强了字符串格式化的功能。基本语法是通过 {} 和 : 来代替以前的 %
str.format() 方法的基本用法如下所示:在这里只例举了常用的方法
一:对字符串的操作
1.没有设置指定位置的参数
print('We are the {} who say "{}!"'.format('knights', 'Ni'))
We are the knights who say “Ni!”
2.设置指定位置的参数,花括号中的数字可用来表示传递给 str.format() 方法的对象的位置。
print('{0} {1}'.format('hello', 'python'))
hello python
3.在 str.format() 方法中使用关键字参数,则使用参数的名称引用它们的值
print('This {food} is {adjective}.'.format(food='beef', adjective='delicious'))
This beef is delicious.
二:分别通过列表索引,元祖索引和字典设置参数
# 通过列表索引设置参数
list1 = ["fish","beef","chicken"]
print("{0}, {1},{2}".format(*list1))
#通过元祖索引设置参数
tup1 = ("apple","banana","pear")
print("{0}, {1},{2}".format(*tup1))
# 通过字典设置参数
site = {"name": "tom", "age": "18"}
print("姓名:{name}, 年龄 {age}".format(**site))
fish, beef,chicken
apple, banana,pear
姓名:tom, 年龄 18
三:format对数值型的格式化
保留3位小数和使用用来做金额的千分位分割符
print('The value of pi is approximately {:.3f}'.format(math.pi))
print('{:,}'.format(1548762659552623))
The value of pi is approximately 3.142
1,548,762,659,552,623
另外python还提供了字符串前加上 f 或 F 并将表达式写成 {expression} 来在字符串中包含 Python 表达式的值。
例如:
a=3.1415926
print(f’The value of pi is approximately {a:.3f}.’)
The value of pi is approximately 3.142.
我们可以使用大括号 {} 来转义大括号,如下实例:
print ("{} 第一个字母是 {{h}}".format(“hello”))
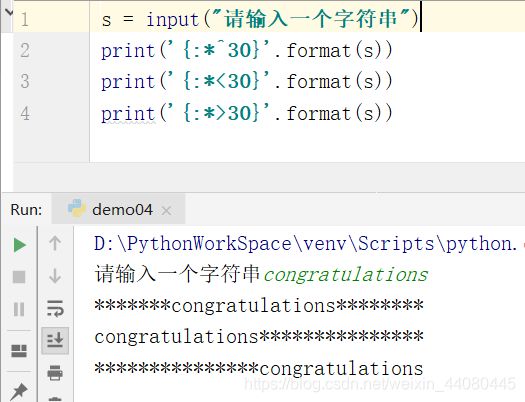
四:填充与对齐
填充常跟对齐一起使用
^、< 、 > 分别是居中、左对齐、右对齐,后面带宽度
: 号后面带填充的字符,只能是一个字符,不指定的话默认是用空格填充