SpringBoot启动流程
本文以调试一个实际的SpringBoot启动程序为例,参考流程中主要类类图,来分析其启动逻辑和自动化配置原理。
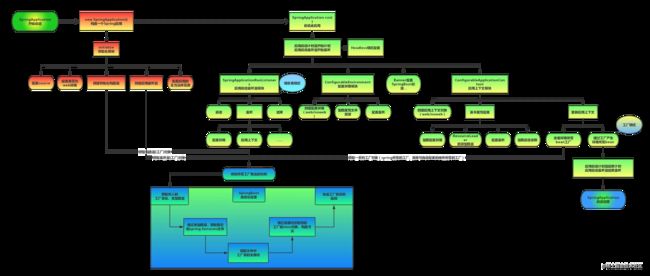
一、SpringBoot启动流程图
二、SpringBoot启动入口
@EnableScheduling
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {
"cn.gov.zcy.demand",
"cn.gov.zcy.id.util",
"cn.gov.zcy.backlog.sdk",
"com.dtdream.vanyar",
"cn.gov.zcy.base.server.gateway",
"cn.gov.zcy.workflow.sdk"})
@ImportResource(value = "classpath:/spring/*.xml")
@MapperScan(basePackages = {"cn.gov.zcy.demand.dao","cn.gov.zcy.workflow.sdk.dao","cn.gov.zcy.springboot.workflow.core"})
@ImportAutoConfiguration(value = { ExternalAutoConfiguration.class })
public class CenterApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CenterApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public RestTemplate restTemplate(){
return new RestTemplate();
}
@Bean
public WorkflowSdkConfig workflowSdkConfig(){
WorkflowSdkConfig config = new WorkflowSdkConfig();
config.defaultTaskLogComp(Boolean.FALSE);
config.defaultTimelineComp(Boolean.FALSE);
return config;
}
}
复制代码
SpringBoot 有自己独立的启动类。
三、SpringBoot执行流程
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
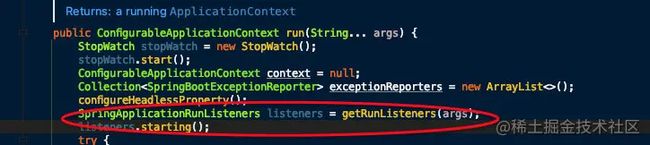
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
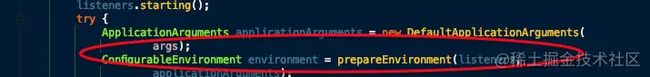
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
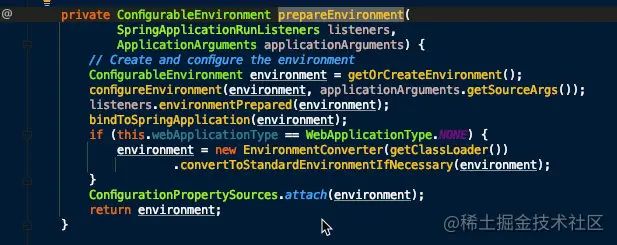
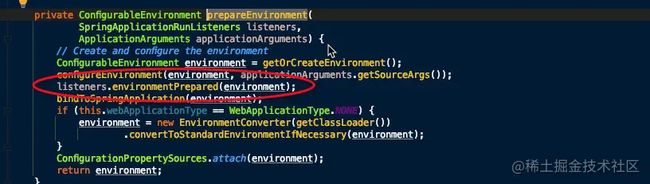
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
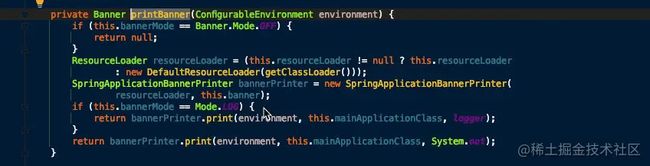
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
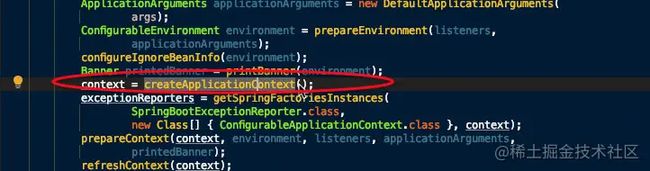
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
复制代码
SpringApplication.run() 执行的整个流程索引代码。
1.调用 SpringApplication 的静态 run 方法之前,需要进行实例化,实例化需要做下面几件事:
-
根据 classpath 里面是否存在某个特征类(org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext)来决定是否应该创建一个为 Web 应用使用的 ApplicationContext 类型。
-
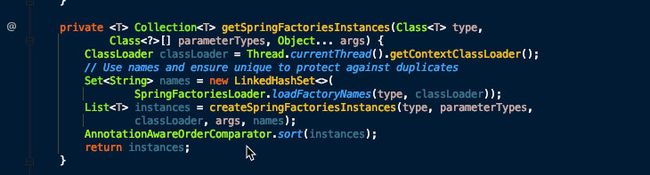
使用 SpringFactoriesLoader 在应用的 classpath 中查找并加载所有可用的 ApplicationContextInitializer。
-
使用 SpringFactoriesLoader 在应用的 classpath 中查找并加载所有可用的 ApplicationListener。
-
推断并设置 main 方法的定义类。
/**
- Create a new {@link SpringApplication} instance. The application context will load
- beans from the specified primary sources (see {@link SpringApplication class-level}
- documentation for details. The instance can be customized before calling
- {@link #run(String…)}.
- @param resourceLoader the resource loader to use
- @param primarySources the primary bean sources
- @see #run(Class, String[])
- @see #setSources(Set)
*/
@SuppressWarnings({ “unchecked”, “rawtypes” })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class… primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, “PrimarySources must not be null”);
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = deduceWebApplicationType();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(
ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
复制代码
- SpringApplication 实例初始化完成并且完成设置后,就开始执行 run 方法的逻辑了,方法执行伊始,首先遍历执行所有通过 SpringFactoriesLoader 可以查找到并加载的 SpringApplicationRunListener。 调用它们的 started() 方法,告诉这些 SpringApplicationRunListener,“嘿,SpringBoot 应用要开始执行咯!”。
- 创建并配置当前 Spring Boot 应用将要使用的 Environment(包括配置要使用的 PropertySource 以及 Profile )。
- 遍历调用所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 的 environmentPrepared() 的方法,告诉他们:“当前 SpringBoot 应用使用的 Environment 准备好了咯!”。
- 如果 SpringApplication 的 showBanner 属性被设置为 true ,则打印 banner。
- 根据用户是否明确设置了 applicationContextClass 类型以及初始化阶段的推断结果,决定该为当前 SpringBoot 应用创建什么类型的 ApplicationContext 并创建完成,然后根据条件决定是否添加 ShutdownHook ,决定是否使用自定义的 BeanNameGenerator,决定是否使用自定义的 ResourceLoader,当然,最重要的,将之前准备好的 Environment 设置给创建好的 ApplicationContext 使用。
- ApplicationContext 创建好之后,SpringApplication 会再次借助 Spring-FactoriesLoader,查找并加载 classpath 中所有可用的 ApplicationContext-Initializer,然后遍历调用这些 ApplicationContextInitializer 的 initialize(applicationContext)方法来对已经创建好的 ApplicationContext 进行进一步的处理。
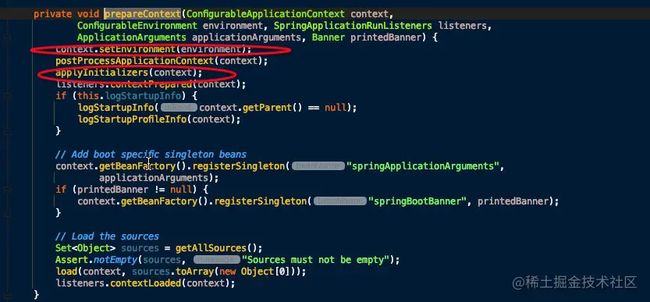
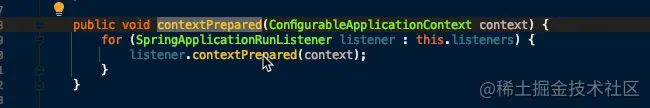
- 遍历调用所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 的 contextPrepared() 方法。
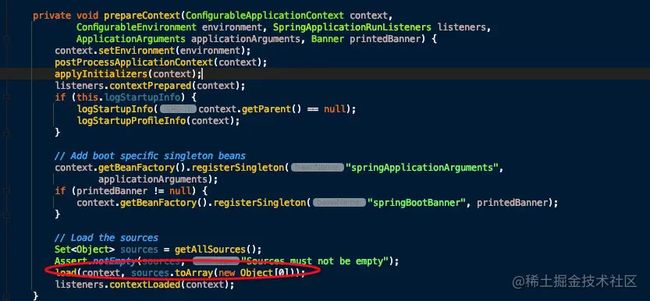
- 最核心的一步,将之前通过 @EnableAutoConfiguration 获取的所有配置以及其他形式的 IoC 容器配置加载到已经准备完毕的 ApplicationContext。
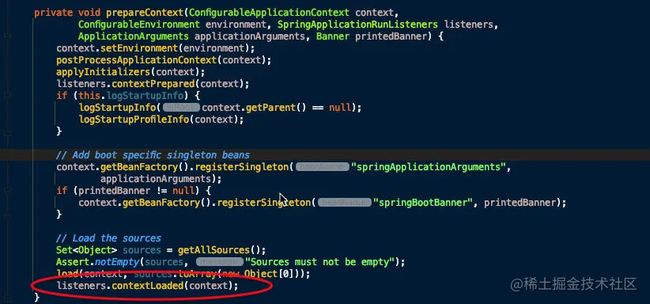
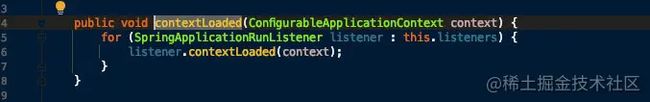
- 遍历调用所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 的 contextLoaded() 方法。
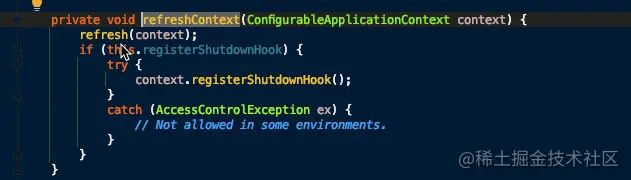
- 调用 ApplicationContext 的 refresh() 方法,完成 IoC 容器可用的最后一道工序。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.===>从Spring容器中找出BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的实现类并按照一定的规则顺序进行执行。 其中ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这个BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor优先级最高,它会对项目中的@Configuration注解修饰的类(@Component、@ComponentScan、@Import、@ImportResource修饰的类也会被处理)进行解析,解析完成之后把这些bean注册到BeanFactory中。需要注意的是这个时候注册进来的bean还没有实例化。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
复制代码
- 查找当前 ApplicationContext 中是否注册有 CommandLineRunner、ApplicationRunner,如果有,则遍历执行它们。
- 正常情况下,遍历执行 SpringApplicationRunListener 的 finished() 方法,(如果整个过程出现异常,则依然调用所有 SpringApplicationRunListener 的 finished() 方法,只不过这种情况下会将异常信息一并传入处理)。
参考文档:www.cnblogs.com/trgl/p/7353…
)