人工智能 | ShowMeAI资讯日报 #2022.06.07
ShowMeAI日报系列全新升级!覆盖AI人工智能 工具&框架 | 项目&代码 | 博文&分享 | 数据&资源 | 研究&论文 等方向。点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
1.工具&框架
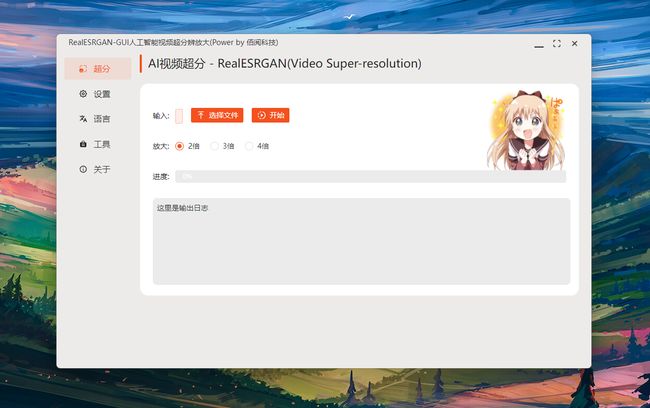
工具:QualityScaler - Windows下的图像/视频深度学习超分辨率App
tags:[AI,工具库,图像,视频,超分辨率]
‘QualityScaler - Image/video deep learning upscaler app for Windows - BRSGAN & RealSR_JPEG’ by Annunziata Gianluca
GitHub:http://github.com/Djdefrag/QualityScaler
工具:Codex CLI - 用Codex将自然语言命令转换成Bash/ZShell/PowerShell脚本的命令行工具
tags:[AI,工具,命令行,自然语言,命令转换]
‘Codex CLI - Natural Language Command Line Interface - CLI tool that uses Codex to turn natural language commands into their Bash/ZShell/PowerShell equivalents’ by Microsoft
GitHub:http://github.com/microsoft/Codex-CLI
工具:paper2gui - 面向普通人的 AI 桌面APP工具箱**
tags:[AI,工具库]
免安装即开即用,已支持15+AI模型,内容涵盖语音合成、视频补帧、视频超分、目标检测、图片风格化、图片OCR识别等领域.
‘paper2gui - Convert AI papers to GUI,Make it easy and convenient for everyone to use artificial intelligence technology’ by Baiyuetribe
GitHub:http://github.com/Baiyuetribe/paper2gui
工具库:codex_py2cpp - 用OpenAI Codex将Python脚本转换成C++代码
tags:[python,C++]
‘codex_py2cpp - Converts python code into c++ by using OpenAI CODEX.’ by Alexander
GitHub:http://github.com/alxschwrz/codex_py2cpp
工具库:lineapy - 从开发到生产的全链数据工程工具库
tags:[数据工程,数据开发]
lineapy - Data engineering, simplified. LineaPy creates a frictionless path for taking your data science artifact from development to production.’
GitHub:http://github.com/LineaLabs/lineapy
工具库:Colossal-AI - 整合高效并行技术的 AI 大模型训练系统
tags:[大模型,训练,部署]
它提供了一系列并行训练组件,目标是分布式AI模型训练像普通的单GPU模型一样简单
‘Colossal-AI - Colossal-AI: A Unified Deep Learning System for Large-Scale Parallel Training’ by HPC-AI Tech
GitHub:http://github.com/hpcaitech/ColossalAI
2.项目&代码
![]()
项目:语义分割实战
tags:[语义分割]
‘Semantic segmentation - In this tutorial, you will perform inference across 10 well-known pre-trained semantic segmentors and fine-tune on a custom dataset. Design and train your own segmentor.’ by Ibrahim Sobh
GitHub:http://github.com/IbrahimSobh/Segmentation
![]()
3.博文&分享
![]()
书籍代码:《Transformers自然语言处理(第二版)》随书代码
tags:[transformers,GPT-3 ,DeBERTa,Hugging Face,OpenAI,AllenNLP]
《Transformers自然语言处理(第二版)》随书代码,内容覆盖各种前沿主流模型transformers,GPT-3 ,DeBERTa,vision models等,也覆盖Hugging Face、OpenAI API、Trax和 AllenNLP等NLP平台。
‘Transformers-for-NLP-2nd-Edition - Under the hood working of transformers, fine-tuning GPT-3 models, DeBERTa, vision models, and the start of Metaverse, using a variety of NLP platforms: Hugging Face, OpenAI API, Trax, and AllenNLP’ by Denis Rothman
GitHub:http://github.com/Denis2054/Transformers-for-NLP-2nd-Edition
教程:( ACL 2022 Tutorial Slides)有限数据学习
tags:[有限数据,有限数据学习]
‘ACL 2022 Limited Data Learning Tutorial’ by diyiy
GitHub:http://github.com/diyiy/ACL2022_Limited_Data_Learning_Tutorial
教程:Web3_Tutorial - Web3科学家极简入门指南
tags:[web3]
GitHub:http://github.com/gm365/Web3_Tutorial
教程:机器学习论文撰写简要指南
tags:[机器学习,论文,写作]
《How to ML Paper - A brief Guide - Google Docs》by Jakob Foerster
Link:https://docs.google.com/document/d/16R1E2ExKUCP5SlXWHr-KzbVDx9DBUclra-EbU8IB-iE
4.数据&资源
![]()
资源列表:gtrick: 图神经网络技巧集
tags:[图神经网络,GNN]
‘gtrick: Bag of Tricks for Graph Neural Networks’ by Yunxin Sang
GitHub:http://github.com/sangyx/gtrick
资源列表:非自回归应用概览
tags:[非自回归]
‘Overview-of-Non-autoregressive-Applications’ by LitterBrother-Xiao
GitHub:http://github.com/LitterBrother-Xiao/Overview-of-Non-autoregressive-Applications
资源列表:DeltaPapers:预训练模型参数高效方法必读论文列表
tags:[预训练,参数]
‘DeltaPapers - Must-read Papers of Parameter Efficient Methods on Pre-trained Models (Delta Tuning).’ by THUNLP
GitHub:http://github.com/thunlp/DeltaPapers
资源列表:《地理空间数据科学》课程资料
tags:[GIS,地理信息,数据科学]
‘Course materials for: Geospatial Data Science - Course materials for: Geospatial Data Science’ by Michael Szell
GitHub:http://github.com/mszell/geospatialdatascience
5.研究&论文
![]()
可以点击 这里 回复关键字 日报,免费获取整理好的6月论文合辑。
论文:CogVideo: Large-scale Pretraining for Text-to-Video Generation via Transformers
论文标题:CogVideo: Large-scale Pretraining for Text-to-Video Generation via Transformers
论文时间:29 May 2022
所属领域:自然语言处理,计算机视觉
对应任务:Text-to-Video Generation,Video Generation,文字约束视频生成,视频生成
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.15868
代码实现:https://github.com/thudm/cogvideo
论文作者:Wenyi Hong, Ming Ding, Wendi Zheng, Xinghan Liu, Jie Tang
论文简介:Large-scale pretrained transformers have created milestones in text (GPT-3) and text-to-image (DALL-E and CogView) generation. / 大规模预训练transformer在文本 (GPT-3) 和文本到图像 (DALL-E 和 CogView) 生成方面创造了里程碑。
论文摘要:Large-scale pretrained transformers have created milestones in text (GPT-3) and text-to-image (DALL-E and CogView) generation. Its application to video generation is still facing many challenges: The potential huge computation cost makes the training from scratch unaffordable; The scarcity and weak relevance of text-video datasets hinder the model understanding complex movement semantics. In this work, we present 9B-parameter transformer CogVideo, trained by inheriting a pretrained text-to-image model, CogView2. We also propose multi-frame-rate hierarchical training strategy to better align text and video clips. As (probably) the first open-source large-scale pretrained text-to-video model, CogVideo outperforms all publicly available models at a large margin in machine and human evaluations.
大规模预训练transformer在文本(GPT-3)和文本到图像(DALL-E 和 CogView)生成方面创造了里程碑。它在视频生成中的应用仍然面临许多挑战:潜在的巨大计算成本使得从头开始的训练难以承受;文本视频数据集的稀缺性和弱相关性阻碍了模型理解复杂的图像动作语义。在这项工作中,我们提出了 9B 参数转换器 CogVideo,在预训练的文本到图像模型 CogView2 的基础上进行训练。我们还提出了多帧率分层训练策略,以更好地对齐文本和视频剪辑。作为(可能)第一个开源的大规模预训练文本到视频模型,CogVideo 在机器和人工评估中大大优于所有公开可用的模型。
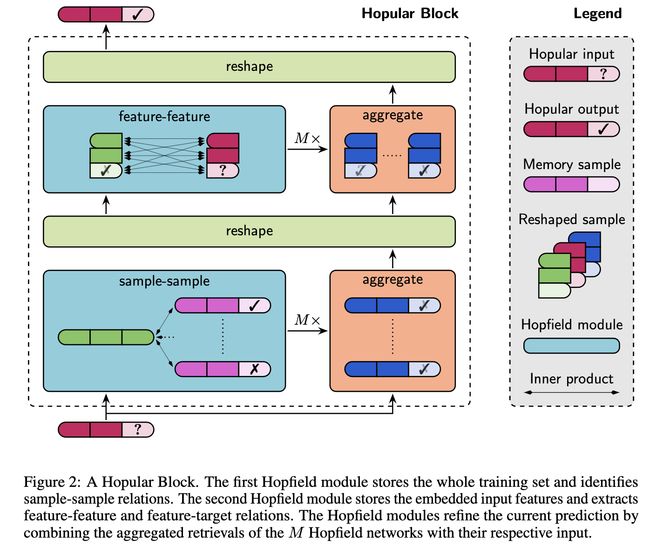
论文:Hopular: Modern Hopfield Networks for Tabular Data
论文标题:Hopular: Modern Hopfield Networks for Tabular Data
论文时间:1 Jun 2022
所属领域:结构化数据
对应任务:表格数据建模,结构化数据建模
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00664
代码实现:https://github.com/ml-jku/hopular
论文作者:Bernhard Schäfl, Lukas Gruber, Angela Bitto-Nemling, Sepp Hochreiter
论文简介:In experiments on small-sized tabular datasets with less than 1, 000 samples, Hopular surpasses Gradient Boosting, Random Forests, SVMs, and in particular several Deep Learning methods. / 在对少于 1,000 个样本的小型表格数据集的实验中,Hopular 超越了梯度提升、随机森林、SVM,尤其是几种深度学习方法。
论文摘要:While Deep Learning excels in structured data as encountered in vision and natural language processing, it failed to meet its expectations on tabular data. For tabular data, Support Vector Machines (SVMs), Random Forests, and Gradient Boosting are the best performing techniques with Gradient Boosting in the lead. Recently, we saw a surge of Deep Learning methods that were tailored to tabular data but still underperform compared to Gradient Boosting on small-sized datasets. We suggest “Hopular”, a novel Deep Learning architecture for medium- and small-sized datasets, where each layer is equipped with continuous modern Hopfield networks. The modern Hopfield networks use stored data to identify feature-feature, feature-target, and sample-sample dependencies. Hopular’s novelty is that every layer can directly access the original input as well as the whole training set via stored data in the Hopfield networks. Therefore, Hopular can step-wise update its current model and the resulting prediction at every layer like standard iterative learning algorithms. In experiments on small-sized tabular datasets with less than 1,000 samples, Hopular surpasses Gradient Boosting, Random Forests, SVMs, and in particular several Deep Learning methods. In experiments on medium-sized tabular data with about 10,000 samples, Hopular outperforms XGBoost, CatBoost, LightGBM and a state-of-the art Deep Learning method designed for tabular data. Thus, Hopular is a strong alternative to these methods on tabular data.
虽然深度学习在视觉和自然语言处理中遇到的结构化数据方面表现出色,但它未能满足其对表格数据(结构化数据)的期望。对于表格数据,支持向量机 (SVM)、随机森林和梯度提升是性能最好的技术,其中梯度提升处于领先地位。最近,我们看到了大量针对表格数据量身定制的深度学习方法,但与在小型数据集上的梯度提升相比仍然表现不佳。我们提出“Hopular”,一种用于中小型数据集的新型深度学习架构,其中每一层都配备了连续的现代 Hopfield 网络。现代 Hopfield 网络使用存储的数据来识别特征-特征、特征-目标和样本-样本依赖关系。 Hopular 的新颖之处在于,每一层都可以通过 Hopfield 网络中存储的数据直接访问原始输入以及整个训练集。因此,Hopular 可以像标准迭代学习算法一样逐步更新其当前模型和每一层的预测结果。在对少于 1,000 个样本的小型表格数据集的实验中,Hopular 超越了梯度提升、随机森林、SVM,尤其是几种深度学习方法。在大约 10,000 个样本的中型表格数据的实验中,Hopular 优于 XGBoost、CatBoost、LightGBM 和专为表格数据设计的最先进的深度学习方法。Hopular 是这些表格数据方法的强大替代方案。
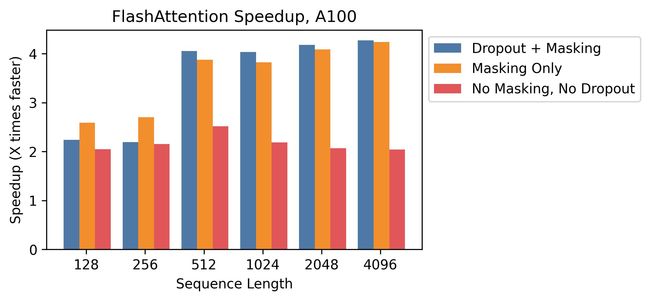
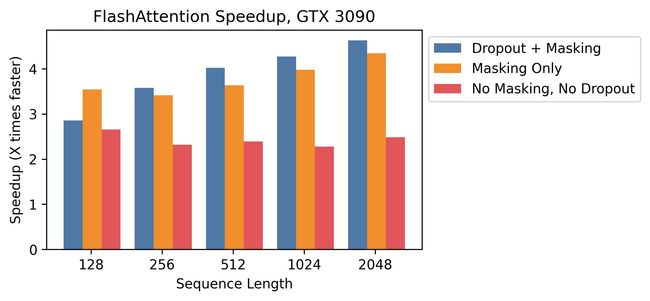
论文:FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness
论文标题:FlashAttention: Fast and Memory-Efficient Exact Attention with IO-Awareness
论文时间:27 May 2022
所属领域:Natural Language Processing/自然语言处理
对应任务:Document Classification,文本分类,文档分类
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14135
代码实现:https://github.com/hazyresearch/flash-attention
论文作者:Tri Dao, Daniel Y. Fu, Stefano Ermon, Atri Rudra, Christopher Ré
论文简介:We also extend FlashAttention to block-sparse attention, yielding an approximate attention algorithm that is faster than any existing approximate attention method. / 我们还将 FlashAttention 扩展到块稀疏注意力,产生了一种比任何现有的近似注意力方法都快的近似注意力算法。
论文摘要:Transformers are slow and memory-hungry on long sequences, since the time and memory complexity of self-attention are quadratic in sequence length. Approximate attention methods have attempted to address this problem by trading off model quality to reduce the compute complexity, but often do not achieve wall-clock speedup. We argue that a missing principle is making attention algorithms IO-aware – accounting for reads and writes between levels of GPU memory. We propose FlashAttention, an IO-aware exact attention algorithm that uses tiling to reduce the number of memory reads/writes between GPU high bandwidth memory (HBM) and GPU on-chip SRAM. We analyze the IO complexity of FlashAttention, showing that it requires fewer HBM accesses than standard attention, and is optimal for a range of SRAM sizes. We also extend FlashAttention to block-sparse attention, yielding an approximate attention algorithm that is faster than any existing approximate attention method. FlashAttention trains Transformers faster than existing baselines: 15% end-to-end wall-clock speedup on BERT-large (seq. length 512) compared to the MLPerf 1.1 training speed record, 3× speedup on GPT-2 (seq. length 1K), and 2.4× speedup on long-range arena (seq. length 1K-4K). FlashAttention and block-sparse FlashAttention enable longer context in Transformers, yielding higher quality models (0.7 better perplexity on GPT-2 and 6.4 points of lift on long-document classification) and entirely new capabilities: the first Transformers to achieve better-than-chance performance on the Path-X challenge (seq. length 16K, 61.4% accuracy) and Path-256 (seq. length 64K, 63.1% accuracy).
在长序列上,Transformer速度慢且需要内存,因为 self-attention 的时间和内存复杂度在序列长度上是平方的。近似注意力方法试图通过权衡模型质量来降低计算复杂性来解决这个问题,但通常不能实现计算加速。我们认为一个缺失的原则是让注意力算法具有 IO 感知能力 - 考虑 GPU 内存级别之间的读取和写入。我们提出了 FlashAttention,这是一种 IO 感知的精确注意力算法,它使用平铺来减少 GPU 高带宽内存 (HBM) 和 GPU 片上 SRAM 之间的内存读/写次数。我们分析了 FlashAttention 的 IO 复杂性,表明它比标准注意力需要更少的 HBM 访问,并且对于一系列 SRAM 大小是最佳的。我们还将 FlashAttention 扩展到块稀疏注意力,产生一种比任何现有近似注意力方法都快的近似注意力算法。 FlashAttention 比现有基线更快地训练 Transformer:与 MLPerf 1.1 训练速度记录相比,BERT-large(序列长度 512)的端到端挂钟加速 15%,GPT-2 的 3 倍加速(序列长度 1K) ),以及 2.4 倍的远程竞技场加速(序列长度 1K-4K)。 FlashAttention 和块稀疏 FlashAttention 可以在 Transformer 中实现更长的上下文,产生更高质量的模型(GPT-2 的困惑度提高 0.7,长文档分类的提升点提高 6.4 点)和全新的功能:第一个实现优于机会的 Transformer在 Path-X 挑战(序列长度 16K,61.4% 准确度)和 Path-256(序列长度 64K,63.1% 准确度)上的表现。
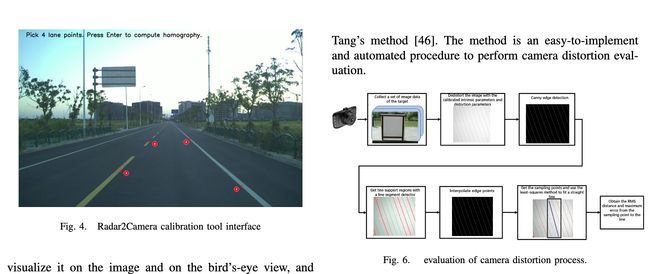
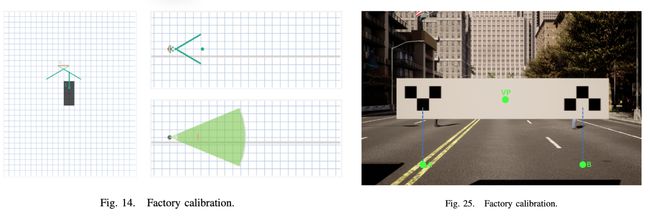
论文:OpenCalib: A Multi-sensor Calibration Toolbox for Autonomous Driving
论文标题:OpenCalib: A Multi-sensor Calibration Toolbox for Autonomous Driving
论文时间:27 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision,计算机视觉
对应任务:Autonomous Driving,Autonomous Vehicles,自动驾驶,无人驾驶,自动驾驶汽车
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.14087
代码实现:https://github.com/pjlab-adg/sensorscalibration
论文作者:Guohang Yan, Liu Zhuochun, Chengjie Wang, Chunlei Shi, Pengjin Wei, Xinyu Cai, Tao Ma, Zhizheng Liu, Zebin Zhong, Yuqian Liu, Ming Zhao, Zheng Ma, Yikang Li
论文简介:To this end, we present OpenCalib, a calibration toolbox that contains a rich set of various sensor calibration methods. / 为此,我们提出了 OpenCalib,这是一个校准工具箱,包含丰富的各种传感器校准方法。
论文摘要:Accurate sensor calibration is a prerequisite for multi-sensor perception and localization systems for autonomous vehicles. The intrinsic parameter calibration of the sensor is to obtain the mapping relationship inside the sensor, and the extrinsic parameter calibration is to transform two or more sensors into a unified spatial coordinate system. Most sensors need to be calibrated after installation to ensure the accuracy of sensor measurements. To this end, we present OpenCalib, a calibration toolbox that contains a rich set of various sensor calibration methods. OpenCalib covers manual calibration tools, automatic calibration tools, factory calibration tools, and online calibration tools for different application scenarios. At the same time, to evaluate the calibration accuracy and subsequently improve the accuracy of the calibration algorithm, we released a corresponding benchmark dataset. This paper introduces various features and calibration methods of this toolbox. To our knowledge, this is the first open-sourced calibration codebase containing the full set of autonomous-driving-related calibration approaches in this area. We wish that the toolbox could be helpful to autonomous driving researchers. We have open-sourced our code on GitHub to benefit the community. Code is available at https://github.com/PJLab-ADG/SensorsCalibration .
准确的传感器校准是自动驾驶汽车多传感器感知和定位系统的先决条件。传感器的内参标定是获取传感器内部的映射关系,外参标定是将两个或多个传感器转换成统一的空间坐标系。大多数传感器在安装后都需要进行校准,以确保传感器测量的准确性。为此,我们提出了 OpenCalib,这是一个校准工具箱,其中包含一组丰富的各种传感器校准方法。 OpenCalib涵盖了针对不同应用场景的手动校准工具、自动校准工具、工厂校准工具和在线校准工具。同时,为了评估标定精度,进而提高标定算法的精度,我们发布了相应的基准数据集。本文介绍了该工具箱的各种特性和校准方法。据我们所知,这是第一个包含该领域自动驾驶相关校准方法的全套开源校准代码库。我们希望该工具箱对自动驾驶研究人员有所帮助。我们已经在 GitHub 上开源了我们的代码,代码可在 https://github.com/PJLab-ADG/SensorsCalibration 获得。
论文:EfficientFormer: Vision Transformers at MobileNet Speed
论文标题:EfficientFormer: Vision Transformers at MobileNet Speed
论文时间:2 Jun 2022
所属领域:计算机视觉
对应任务:图像识别,图像分类
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.01191
代码实现:https://github.com/snap-research/efficientformer
论文作者:Yanyu Li, Geng Yuan, Yang Wen, Eric Hu, Georgios Evangelidis, Sergey Tulyakov, Yanzhi Wang, Jian Ren
论文简介:Our work proves that properly designed transformers can reach extremely low latency on mobile devices while maintaining high performance. / 我们的工作证明,正确设计的transformer可以在移动设备上达到极低的延迟,同时保持高性能。
论文摘要:Vision Transformers (ViT) have shown rapid progress in computer vision tasks, achieving promising results on various benchmarks. However, due to the massive number of parameters and model design, e.g., attention mechanism, ViT-based models are generally times slower than lightweight convolutional networks. Therefore, the deployment of ViT for real-time applications is particularly challenging, especially on resource-constrained hardware such as mobile devices. Recent efforts try to reduce the computation complexity of ViT through network architecture search or hybrid design with MobileNet block, yet the inference speed is still unsatisfactory. This leads to an important question: can transformers run as fast as MobileNet while obtaining high performance? To answer this, we first revisit the network architecture and operators used in ViT-based models and identify inefficient designs. Then we introduce a dimension-consistent pure transformer (without MobileNet blocks) as design paradigm. Finally, we perform latency-driven slimming to get a series of final models dubbed EfficientFormer. Extensive experiments show the superiority of EfficientFormer in performance and speed on mobile devices. Our fastest model, EfficientFormer-L1, achieves 79.2% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet-1K with only 1.6 ms inference latency on iPhone 12 (compiled with CoreML), which is even a bit faster than MobileNetV2 (1.7 ms, 71.8% top-1), and our largest model, EfficientFormer-L7, obtains 83.3% accuracy with only 7.0 ms latency. Our work proves that properly designed transformers can reach extremely low latency on mobile devices while maintaining high performance.
视觉transformer(ViT)在计算机视觉任务中取得了快速进展,在各种基准测试中取得了可喜的成果。然而,由于大量的参数和模型设计,例如注意力机制,基于 ViT 的模型通常比轻量级卷积网络慢几倍。因此,为实时应用部署 ViT 尤其具有挑战性,尤其是在移动设备等资源受限的硬件上。最近的努力试图通过网络架构搜索或与 MobileNet 块的混合设计来降低 ViT 的计算复杂度,但推理速度仍然不能令人满意。这就引出了一个重要的问题:Transformer 能否在获得高性能的同时运行得像 MobileNet 一样快?为了回答这个问题,我们首先重新审视基于 ViT 的模型中使用的网络架构和操作算子(operators),并确定低效的设计。然后我们引入了一个维度一致的纯transformer(没有 MobileNet 块)作为设计范式。最后,我们执行延迟驱动的瘦身以获得一系列最终模型,称为 EfficientFormer。大量实验表明 EfficientFormer 在移动设备上的性能和速度方面具有优势。我们最快的模型 EfficientFormer-L1 在 ImageNet-1K 上实现了 79.2% 的 top-1 准确率,在 iPhone 12(使用 CoreML 编译)上只有 1.6 ms 的推理延迟,这甚至比 MobileNetV2(1.7 ms,71.8% top- 1) 要快一点,我们最大的模型 EfficientFormer-L7 获得了 83.3% 的准确率,延迟仅为 7.0 ms。我们的工作证明,正确设计的transformer可以在移动设备上达到极低的延迟,同时保持高性能。
论文:Text2Human: Text-Driven Controllable Human Image Generation
论文标题:Text2Human: Text-Driven Controllable Human Image Generation
论文时间:31 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision,计算机视觉
对应任务:Human Parsing,Image Generation,人体(形态)解析,图像生成
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.15996
代码实现:https://github.com/yumingj/Text2Human ,https://github.com/yumingj/deepfashion-multimodal , https://github.com/stylegan-human/stylegan-human
论文作者:Yuming Jiang, Shuai Yang, Haonan Qiu, Wayne Wu, Chen Change Loy, Ziwei Liu
论文简介:In this work, we present a text-driven controllable framework, Text2Human, for a high-quality and diverse human generation. / 在这项工作中,我们提出了一个文本驱动的可控框架 Text2Human,用于高质量和多样化的人体形态生成。
论文摘要:Generating high-quality and diverse human images is an important yet challenging task in vision and graphics. However, existing generative models often fall short under the high diversity of clothing shapes and textures. Furthermore, the generation process is even desired to be intuitively controllable for layman users. In this work, we present a text-driven controllable framework, Text2Human, for a high-quality and diverse human generation. We synthesize full-body human images starting from a given human pose with two dedicated steps. 1) With some texts describing the shapes of clothes, the given human pose is first translated to a human parsing map. 2) The final human image is then generated by providing the system with more attributes about the textures of clothes. Specifically, to model the diversity of clothing textures, we build a hierarchical texture-aware codebook that stores multi-scale neural representations for each type of texture. The codebook at the coarse level includes the structural representations of textures, while the codebook at the fine level focuses on the details of textures. To make use of the learned hierarchical codebook to synthesize desired images, a diffusion-based transformer sampler with mixture of experts is firstly employed to sample indices from the coarsest level of the codebook, which then is used to predict the indices of the codebook at finer levels. The predicted indices at different levels are translated to human images by the decoder learned accompanied with hierarchical codebooks. The use of mixture-of-experts allows for the generated image conditioned on the fine-grained text input. The prediction for finer level indices refines the quality of clothing textures. Extensive quantitative and qualitative evaluations demonstrate that our proposed framework can generate more diverse and realistic human images compared to state-of-the-art methods.
生成高质量和多样化的人体图像是视觉和图形学中一项重要但具有挑战性的任务。然而,现有的生成模型往往在服装形状和纹理的高度多样性下达不到要求。此外,甚至希望生成过程对于外行用户来说是直观可控的。在这项工作中,我们提出了一个文本驱动的可控框架 Text2Human,用于高质量和多样化的人体图像生成。我们从给定的人体姿势开始通过两个专用步骤合成全身人体图像。 1)对于一些描述衣服形状的文本,首先将给定的人体姿势转换为人体解析图。 2)然后通过为系统提供更多关于衣服纹理的属性来生成最终的人体图像。具体来说,为了对服装纹理的多样性进行建模,我们构建了一个分层纹理感知码本,用于存储每种纹理的多尺度神经表示。粗略级别的码本包括纹理的结构表示,而精细级别的码本侧重于纹理的细节。为了利用学习到的分层码本来合成所需的图像,首先采用混合专家的基于扩散的Transformer采样器从码本的最粗略级别采样索引,然后用于更精细地预测码本的索引水平。解码器将不同级别的预测索引转换为人类图像,并结合分层码本进行学习。基于混合专家的实现,能完成以细粒度文本输入为条件的图像生成。对更精细级别指数的预测改进了服装纹理的质量。广泛的定量和定性评估表明,与最先进的方法相比,我们提出的框架可以生成更多样化和更逼真的人类图像。
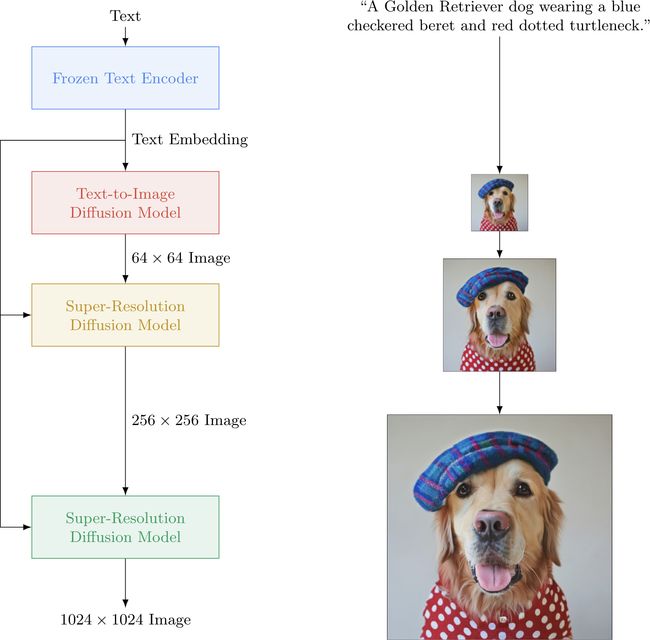
论文:Photorealistic Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Deep Language Understanding
论文标题:Photorealistic Text-to-Image Diffusion Models with Deep Language Understanding
论文时间:23 May 2022
所属领域:自然语言处理,计算机视觉
对应任务:Image Generation,Language Modelling,Text-to-Image Generation,图像生成,语言建模,基于文本的图像生成
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.11487
代码实现:https://github.com/lucidrains/imagen-pytorch , https://github.com/cene555/Imagen-pytorch
论文作者:Chitwan Saharia, William Chan, Saurabh Saxena, Lala Li, Jay Whang, Emily Denton, Seyed Kamyar Seyed Ghasemipour, Burcu Karagol Ayan, S. Sara Mahdavi, Rapha Gontijo Lopes, Tim Salimans, Jonathan Ho, David J Fleet, Mohammad Norouzi
论文简介:We present Imagen, a text-to-image diffusion model with an unprecedented degree of photorealism and a deep level of language understanding. / 我们展示了 Imagen,这是一种文本到图像的扩散模型,具有前所未有的真实感和深度的语言理解。
论文摘要:We present Imagen, a text-to-image diffusion model with an unprecedented degree of photorealism and a deep level of language understanding. Imagen builds on the power of large transformer language models in understanding text and hinges on the strength of diffusion models in high-fidelity image generation. Our key discovery is that generic large language models (e.g. T5), pretrained on text-only corpora, are surprisingly effective at encoding text for image synthesis: increasing the size of the language model in Imagen boosts both sample fidelity and image-text alignment much more than increasing the size of the image diffusion model. Imagen achieves a new state-of-the-art FID score of 7.27 on the COCO dataset, without ever training on COCO, and human raters find Imagen samples to be on par with the COCO data itself in image-text alignment. To assess text-to-image models in greater depth, we introduce DrawBench, a comprehensive and challenging benchmark for text-to-image models. With DrawBench, we compare Imagen with recent methods including VQ-GAN+CLIP, Latent Diffusion Models, and DALL-E 2, and find that human raters prefer Imagen over other models in side-by-side comparisons, both in terms of sample quality and image-text alignment. See https://imagen.research.google/ for an overview of the results.
我们提出了 Imagen,这是一种文本到图像的扩散模型,具有前所未有的逼真度和深度的语言理解。 Imagen 建立在大型 Transformer 语言模型在理解文本方面的强大功能之上,并依赖于扩散模型在高保真图像生成方面的优势。我们的关键发现是,在纯文本语料库上预训练的通用大型语言模型(例如 T5)在为图像合成编码文本方面非常有效:增加 Imagen 中语言模型的大小可以大大提高样本保真度和图像-文本对齐不仅仅是增加图像扩散模型的大小。 Imagen 在 COCO 数据集上获得了 7.27 的最新 FID 分数,而且并没有在 COCO数据集上训练过,并且人类评估者发现 Imagen 样本在图像-文本对齐方面与 COCO 数据本身相当。为了更深入地评估文本到图像模型,我们引入了 DrawBench,这是一个用于文本到图像模型的全面且具有挑战性的基准。使用 DrawBench,我们将 Imagen 与最近的方法(包括 VQ-GAN+CLIP、潜在扩散模型和 DALL-E 2)进行比较,发现人类评分者在并排比较中更喜欢 Imagen,无论是在样本质量方面和图文对齐。有关结果的概述,请参阅 https://imagen.research.google/]()。
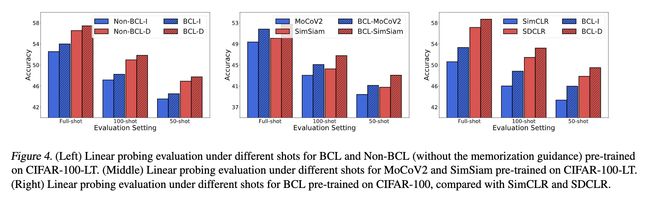
论文:Contrastive Learning with Boosted Memorization
论文标题:Contrastive Learning with Boosted Memorization
论文时间:25 May 2022
所属领域:Computer Vision,计算机视觉
对应任务:Contrastive Learning,Long-tailed Learning,Representation Learning,Self-Supervised Learning,对比学习,长尾学习,表征学习,自监督学习
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.12693
代码实现:https://github.com/MediaBrain-SJTU/BCL
论文作者:Zhihan Zhou, Jiangchao Yao, Yanfeng Wang, Bo Han, Ya zhang
论文简介:Different from previous works, we explore this direction from an alternative perspective, i. e., the data perspective, and propose a novel Boosted Contrastive Learning (BCL) method. / 与以往的作品不同,我们从另一个角度探索这个方向,即数据视角,我们也提出了一种新颖的增强对比学习(BCL)方法。
论文摘要:Self-supervised learning has achieved a great success in the representation learning of visual and textual data. However, the current methods are mainly validated on the well-curated datasets, which do not exhibit the real-world long-tailed distribution. Recent attempts to consider self-supervised long-tailed learning are made by rebalancing in the loss perspective or the model perspective, resembling the paradigms in the supervised long-tailed learning. Nevertheless, without the aid of labels, these explorations have not shown the expected significant promise due to the limitation in tail sample discovery or the heuristic structure design. Different from previous works, we explore this direction from an alternative perspective, i.e., the data perspective, and propose a novel Boosted Contrastive Learning (BCL) method. Specifically, BCL leverages the memorization effect of deep neural networks to automatically drive the information discrepancy of the sample views in contrastive learning, which is more efficient to enhance the long-tailed learning in the label-unaware context. Extensive experiments on a range of benchmark datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of BCL over several state-of-the-art methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/MediaBrain-SJTU/BCL .
自监督学习在视觉和文本数据的表示学习方面取得了巨大成功。然而,目前的方法主要在精心准备的数据集上进行验证,这些数据集没有表现出真实世界的长尾分布。最近考虑自监督长尾学习的尝试是通过重新平衡损失视角或模型视角来进行的,类似于监督长尾学习中的范式。然而,在没有标签的帮助下,由于尾样本发现或启发式结构设计的限制,这些探索并未显示出很有效的预期。与之前的工作不同,我们从另一个角度探索这个方向,即数据视角,并提出了一种新颖的增强对比学习(BCL)方法。具体来说,BCL利用深度神经网络的记忆效应,自动驱动对比学习中样本视图的信息差异,更有效地增强了无标签上下文中的长尾学习。在一系列基准数据集上进行的大量实验证明了 BCL 在几种最先进的方法上的有效性。我们的代码可在 https://github.com/MediaBrain-SJTU/BCL 获得。
论文:DoWhy: Addressing Challenges in Expressing and Validating Causal Assumptions
论文标题:DoWhy: Addressing Challenges in Expressing and Validating Causal Assumptions
论文时间:27 Aug 2021
所属领域:Knowledge Base,知识库
对应任务:Causal Discovery,因果发现,因果推理
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.13518
代码实现:https://github.com/microsoft/dowhy
论文作者:Amit Sharma, Vasilis Syrgkanis, Cheng Zhang, Emre Kiciman
论文简介:Estimation of causal effects involves crucial assumptions about the data-generating process, such as directionality of effect, presence of instrumental variables or mediators, and whether all relevant confounders are observed. / 因果效应的估计涉及关于数据生成过程的关键假设,例如效应的方向性、工具变量或中介的存在,以及是否观察到所有相关的混杂因素。
论文摘要:Estimation of causal effects involves crucial assumptions about the data-generating process, such as directionality of effect, presence of instrumental variables or mediators, and whether all relevant confounders are observed. Violation of any of these assumptions leads to significant error in the effect estimate. However, unlike cross-validation for predictive models, there is no global validator method for a causal estimate. As a result, expressing different causal assumptions formally and validating them (to the extent possible) becomes critical for any analysis. We present DoWhy, a framework that allows explicit declaration of assumptions through a causal graph and provides multiple validation tests to check a subset of these assumptions. Our experience with DoWhy highlights a number of open questions for future research: developing new ways beyond causal graphs to express assumptions, the role of causal discovery in learning relevant parts of the graph, and developing validation tests that can better detect errors, both for average and conditional treatment effects. DoWhy is available at https://github.com/microsoft/dowhy .
因果效应的估计涉及关于数据生成过程的关键假设,例如效应的方向性、工具变量或中介的存在,以及是否观察到所有相关的混杂因素。违反任何这些假设都会导致效应估计出现重大错误。然而,与预测模型的交叉验证不同,没有用于因果估计的全局验证器方法。因此,正式表达不同的因果假设并(尽可能)验证它们对于任何分析都至关重要。我们提出了 DoWhy,这是一个允许通过因果图明确声明假设并提供多个验证测试来检查这些假设的子集的框架。我们在 DoWhy 方面的经验突出了未来研究的一些悬而未决的问题:开发因果图之外的新方法来表达假设、因果发现在学习图的相关部分中的作用,以及开发可以更好地检测错误的验证测试,两者都适用于平均和有条件的治疗效果。 DoWhy 位于 https://github.com/microsoft/dowhy 。
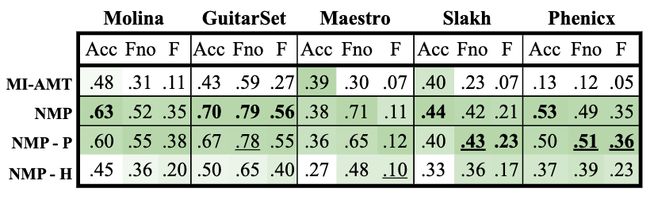
论文:A Lightweight Instrument-Agnostic Model for Polyphonic Note Transcription and Multipitch Estimation
论文标题:A Lightweight Instrument-Agnostic Model for Polyphonic Note Transcription and Multipitch Estimation
论文时间:18 Mar 2022
所属领域:Music,音乐
对应任务:Music Transcription,音乐转录
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.09893
代码实现:https://github.com/spotify/basic-pitch
论文作者:Rachel M. Bittner, Juan José Bosch, David Rubinstein, Gabriel Meseguer-Brocal, Sebastian Ewert
论文简介:Despite its simplicity, benchmark results show our system’s note estimation to be substantially better than a comparable baseline, and its frame-level accuracy to be only marginally below those of specialized state-of-the-art AMT systems. / 尽管它很简单,但基准测试结果表明我们的系统的音符估计大大优于可比较的基线,并且其帧级精度仅略低于专门的最先进的 AMT 系统。
论文摘要:Automatic Music Transcription (AMT) has been recognized as a key enabling technology with a wide range of applications. Given the task’s complexity, best results have typically been reported for systems focusing on specific settings, e.g. instrument-specific systems tend to yield improved results over instrument-agnostic methods. Similarly, higher accuracy can be obtained when only estimating frame-wise f0 values and neglecting the harder note event detection. Despite their high accuracy, such specialized systems often cannot be deployed in the real-world. Storage and network constraints prohibit the use of multiple specialized models, while memory and run-time constraints limit their complexity. In this paper, we propose a lightweight neural network for musical instrument transcription, which supports polyphonic outputs and generalizes to a wide variety of instruments (including vocals). Our model is trained to jointly predict frame-wise onsets, multipitch and note activations, and we experimentally show that this multi-output structure improves the resulting frame-level note accuracy. Despite its simplicity, benchmark results show our system’s note estimation to be substantially better than a comparable baseline, and its frame-level accuracy to be only marginally below those of specialized state-of-the-art AMT systems. With this work we hope to encourage the community to further investigate low-resource, instrument-agnostic AMT systems.
自动音乐转录(AMT)已被公认为具有广泛应用的关键使能技术。鉴于任务的复杂性,通常会针对专注于特定设置的系统报告最佳结果,例如与仪器无关的方法相比,仪器特定的系统往往会产生更好的结果。类似地,当仅估计逐帧 f0 值并忽略更难的音符事件检测时,可以获得更高的准确度。尽管它们的准确性很高,但这种专门的系统通常无法在现实世界中部署。存储和网络限制禁止使用多个专用模型,而内存和运行时限制了它们的复杂性。在本文中,我们提出了一种用于乐器转录的轻量级神经网络,它支持复音输出并泛化到各种乐器(包括人声)。我们的模型经过训练,可以联合预测逐帧起始、多音高和音符激活,我们通过实验证明这种多输出结构提高了最终的帧级音符精度。尽管它很简单,但基准测试结果表明我们的系统的音符估计大大优于可比较的基线,并且其帧级精度仅略低于专门的最先进的 AMT 系统。通过这项工作,我们希望鼓励社区进一步研究低资源、与仪器无关的 AMT 系统。
我们是 ShowMeAI,致力于传播AI优质内容,分享行业解决方案,用知识加速每一次技术成长!点击查看 历史文章列表,在公众号内订阅话题 #ShowMeAI资讯日报,可接收每日最新推送。点击 专题合辑&电子月刊 快速浏览各专题全集。点击 这里 回复关键字 日报 免费获取AI电子月刊与资料包。
- 作者:韩信子@ShowMeAI
- 历史文章列表
- 专题合辑&电子月刊
- 声明:版权所有,转载请联系平台与作者并注明出处
- 欢迎回复,拜托点赞,留言推荐中有价值的文章、工具或建议,我们都会尽快回复哒~