图书管理系统 (单链表实现,C++及文件操作,超详细)
大家好!这里是小张,五一即将到来,小张在这里提前祝大家劳动节快乐!那么今天小张给大家带来的是由单链表,C++以及文件操作实现的图书信息管理系统。
另外小张给大家推荐一款什么阶段都适用的刷题神器和模拟面试好用神器点击这里进入神器****
目录
图书管理系统菜单
单链表的实现?
图书类
图书管理系统单链表的创建
文件操作
陈列信息
根据编号查找图书
根据书名查找
通过图书编号删除图书信息
插入图书信息
修改图书信息
switch语句实现功能
整体代码
结果展示
结束语
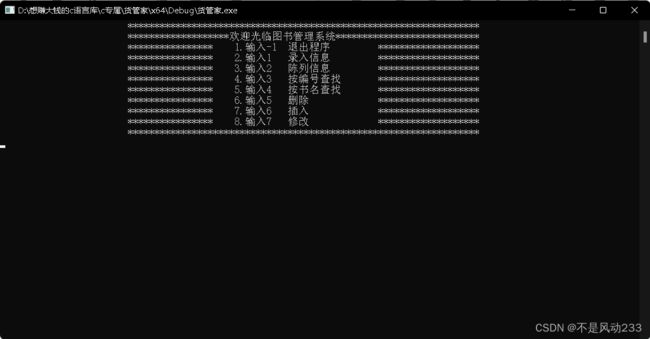
图书管理系统菜单
void menu()
{
cout << " ******************************************************************" << endl;
cout << " *******************欢迎光临图书管理系统***************************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 1.输入-1 退出程序 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 2.输入1 录入信息 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 3.输入2 陈列信息 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 4.输入3 按编号查找 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 5.输入4 按书名查找 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 6.输入5 删除 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 7.输入6 插入 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 8.输入7 修改 *******************" << endl;
cout << " ******************************************************************" << endl;
}
单链表的实现
ypedef struct londe
{
admin data;//数据域
struct londe *next;//指针域
}londe, *strlonde;
图书类
class admin
{
public:
char name[100];
char num[100];
char tel[100];
char name1[100];
char adress[100];
};
图书管理系统单链表的创建
void londecreat(strlonde&L,int n)
{
L = (strlonde)malloc(sizeof(londe));
L->next = NULL;
strlonde p, q;
q = L;
int i =0;
cout << "请您依次输入图书编号,图书名,图书作者,图书出版社,价格" << endl;
for(i=0;i> p->data.name;
cin >> p->data.num;
cin >> p->data.tel;
cin >> p->data.name1;
cin >> p->data.adress;
p->next = NULL;
q->next = p;
q = p;
}
ofstream ofs;//创建文件流
ofs.open("text.txt", ios::out);//指定打开方式(在双引号里,可以根据自行情况进行更改)
strlonde S;
S = L->next;
while (S)
{
ofs << S->data.name << " " << S->data.num << " " << S->data.tel << " " <data.name1<<" "<data.adress<<" "<< endl;
S = S->next;
}
ofs.close();//关闭文件
}
文件操作
我们为什么要使用文件操作,是因为“许多程序在实现过程中,依赖于把数据保存到变量中,而变量是通过内存单元存储数据的,数据的处理完全由程序控制。当一个程序运行完成或者终止的时候,所有变量的值不再保存。另外,当输入输出数据量较大时,就会受限,带来不便。文件是解决这些问题的有效办法,他通过把数据存储在磁盘文件中,得以长久保存。当有大量数据输入时,可通过编辑工具事先建立输入数据的文件,程序运行时将不再从键盘输入,而是从指定的文件上读入,从而实现数据的一次输入多次使用。”
写文件分为五步操作:
1.包含头文件
#include
2.创建流对象
ofstream ofs;
3.打开文件
ofs.open(“文件路径”,打开方式);
4.写数据
ofs<<“写入的数据”;
5.关闭文件
ofs.close();
读文件也是五步操作:
1.包含头文件
#include
2.创建流对象
ifstream ifs;
3.打开文件并判断是否成功
ifs.open(“文件路径”,打开方式);
4.读数据
四种方式读取
5.关闭文件
ifs.close();
具体的代码在图书信息管理系统中实现
陈列信息
void display(strlonde&L)
{
ifstream ifs;//创建流对象
ifs.open("text.txt",ios::in);//打开文件
char buf[10000] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
cout << "下面是您录入的信息" << endl;
while (ifs >> buf)//读取文件中数据
{
if (i % 5 == 0)
{
cout <根据编号查找图书
void findname(char *arr)
{
char a[100];
strcpy_s(a, arr);
ifstream ifs;//创建流对象
ifs.open("text.txt", ios::in);//打开文件
char buf[1000] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
while (ifs >> buf)//读入文件
{
int n = strcmp(a, buf);
if (n == 0)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
continue;
}
if (i > 5)
{
return;
}
if (i <=5 && i >=1)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
}
}
ifs.close();//关闭文件
}
根据书名查找
void findnum(char *arr)
{
char a[100];
strcpy_s(a, arr);
ifstream ifs;
ifs.open("text.txt", ios::in);
char buf[10000] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
while (ifs >> buf)
{
if (i == 3)
{
cout << buf << " ";
return;
}
if (i==2)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
}
if (i == 1)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
}
int n = strcmp(a, buf);
if (n == 0)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
}
}
ifs.close();
}
通过图书编号删除图书信息
void delete1(strlonde&L,char *arr)
{
char a[100], b[100];
int i = 0, j = 0, count = 0;
strcpy_s(a, arr);
while (*arr != '')
{
count++;
arr++;
}
strlonde p, q, r;
q = L;
p = L->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
strcpy_s(b, p->data.name);
i = 0, j = 0;
while (a[i] == b[j] && a[i] != ''&&b[j] != '')
{
i++;
j++;
}
if (i == count)
{
r = p;
while (q)
{
while (q->next == r)
{
q->next = q->next->next;
free(r);
cout << "删除图书信息成功!" << endl;
ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("text.txt", ios::out);
strlonde S;
S = L->next;
while (S)
{
ofs << S->data.name << " " << S->data.num << " " << S->data.tel << " " << S->data.name1 << " " << S->data.adress << " " << endl;
S = S->next;
}
ofs.close();
return;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
p = p->next;
}
}
插入图书信息
void insert(strlonde&L, char*arr, char*arr2, char*arr3, char*arr4,char*arr5,char*arr6)
{ strlonde p, q, s;
char a[100], b[100];
int count = 0, i = 0, j = 0;
s = (strlonde)malloc(sizeof(londe));
strcpy_s(s->data.name, arr3);
strcpy_s(s->data.num, arr2);
strcpy_s(s->data.tel, arr4);
strcpy_s(s->data.name1, arr5);
strcpy_s(s->data.adress, arr6);
strcpy_s(a, arr);
while (*arr != '')
{
count++;
arr++;
}
q = L;
p = L->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
strcpy_s(b, p->data.name);
i = 0, j = 0;
while (a[i] == b[j] && a[i] != ''&&b[j] != '')
{
i++;
j++;
}
if (i == count)
{
while (q)
{
while (q->next == p)
{
q->next = s;
s->next = p;
cout << "插入成功" << endl;
ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("text.txt", ios::out);
strlonde S;
S = L->next;
while (S)
{
ofs << S->data.name << " " << S->data.num << " " << S->data.tel << " " << S->data.name1 << " " << S->data.adress << " " << endl;
S = S->next;
}
ofs.close();
return;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
p = p->next;
}
}
修改图书信息
void modify(strlonde&L, char*arr,char*arr1,char*arr2,char*arr3,char*arr4,char*arr5)
{
char a[100], b[100];
strcpy_s(a, arr);
strlonde p;
int count = 0, i = 0, j = 0;
while (*arr != '')
{
count++;
arr++;
}
p = L->next;
while (p)
{
strcpy_s(b, p->data.name);
i = 0, j = 0;
while (a[i] == b[j] && a[i] != ''&&b[j] != '')
{
i++;
j++;
}
if (i == count)
{
strcpy_s(p->data.num, arr1);
strcpy_s(p->data.name, arr2);
strcpy_s(p->data.tel, arr3);
strcpy_s(p->data.name1, arr4);
strcpy_s(p->data.adress, arr5);
cout << "修改成功" << endl;
ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("text.txt", ios::out);
strlonde S;
S = L->next;
while (S)
{
ofs << S->data.name << " " << S->data.num << " " << S->data.tel << " " << S->data.name1 << " " << S->data.adress << " " << endl;
S = S->next;
}
ofs.close();
return;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
switch语句实现功能
switch (x)
{
case 1:
cout << "现在开始录入信息,请输入您要录入几本书的信息" << endl;
cin >> n;
londecreat(L, n);
cout << "录入完成" << endl;
break;
case 2:
display(L);
break;
case 3:
cout << "请输入您要进行查找的图书的编号" << endl;
cin >> arr;
findname(arr);
break;
case 4:
cout << "请输入您要进行查找图书名" << endl;
cin >> arr2;
findnum(arr2);
break;
case 5:
cout << "请输入您要删除图书的编号" << endl;
cin >> arr4;
delete1(L, arr4);
break;
case 6:
cout << "请输入您要进行插入地方图书的编号以及插入的图书编号,图书名,图书作者,图书出版社,价格" << endl;
cin >> arr5 >> arr6 >> arr7 >> arr8 >> arr13 >> arr14;
insert(L, arr5, arr6, arr7, arr8,arr13,arr14);
break;
case 7:
cout << "请输入您要进行修改的用户的编号以及您需要修改的信息" << endl;
cin >> arr9 >> arr10 >> arr11 >> arr12 >> arr15 >> arr16;
modify(L, arr9, arr10, arr11, arr12,arr15,arr16);
break;
default:
cout << "您的输入有误,请重新输入" << endl;
}
}
整体代码
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define Max 1000
using namespace std;
class admin
{
public:
char name[100];
char num[100];
char tel[100];
char name1[100];
char adress[100];
};
typedef struct londe
{
admin data;
struct londe *next;
}londe, *strlonde;
void londecreat(strlonde&L,int n)
{
L = (strlonde)malloc(sizeof(londe));
L->next = NULL;
strlonde p, q;
q = L;
int i =0;
cout << "请您依次输入图书编号,图书名,图书作者,图书出版社,价格" << endl;
for(i=0;i> p->data.name;
cin >> p->data.num;
cin >> p->data.tel;
cin >> p->data.name1;
cin >> p->data.adress;
p->next = NULL;
q->next = p;
q = p;
}
ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("text.txt", ios::out);
strlonde S;
S = L->next;
while (S)
{
ofs << S->data.name << " " << S->data.num << " " << S->data.tel << " " <data.name1<<" "<data.adress<<" "<< endl;
S = S->next;
}
ofs.close();
}
void display(strlonde&L)
{
ifstream ifs;
ifs.open("text.txt",ios::in);
char buf[10000] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
cout << "下面是您录入的信息" << endl;
while (ifs >> buf)
{
if (i % 5 == 0)
{
cout <> buf)
{
int n = strcmp(a, buf);
if (n == 0)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
continue;
}
if (i > 5)
{
return;
}
if (i <=5 && i >=1)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
}
}
ifs.close();
}
void findnum(char *arr)
{
char a[100];
strcpy_s(a, arr);
ifstream ifs;
ifs.open("text.txt", ios::in);
char buf[10000] = { 0 };
int i = 0;
while (ifs >> buf)
{
if (i == 3)
{
cout << buf << " ";
return;
}
if (i==2)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
}
if (i == 1)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
}
int n = strcmp(a, buf);
if (n == 0)
{
cout << buf << " ";
i++;
}
}
ifs.close();
}
void delete1(strlonde&L,char *arr)
{
char a[100], b[100];
int i = 0, j = 0, count = 0;
strcpy_s(a, arr);
while (*arr != '')
{
count++;
arr++;
}
strlonde p, q, r;
q = L;
p = L->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
strcpy_s(b, p->data.name);
i = 0, j = 0;
while (a[i] == b[j] && a[i] != ''&&b[j] != '')
{
i++;
j++;
}
if (i == count)
{
r = p;
while (q)
{
while (q->next == r)
{
q->next = q->next->next;
free(r);
cout << "删除图书信息成功!" << endl;
ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("text.txt", ios::out);
strlonde S;
S = L->next;
while (S)
{
ofs << S->data.name << " " << S->data.num << " " << S->data.tel << " " << S->data.name1 << " " << S->data.adress << " " << endl;
S = S->next;
}
ofs.close();
return;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
p = p->next;
}
}
void insert(strlonde&L, char*arr, char*arr2, char*arr3, char*arr4,char*arr5,char*arr6)
{ strlonde p, q, s;
char a[100], b[100];
int count = 0, i = 0, j = 0;
s = (strlonde)malloc(sizeof(londe));
strcpy_s(s->data.name, arr3);
strcpy_s(s->data.num, arr2);
strcpy_s(s->data.tel, arr4);
strcpy_s(s->data.name1, arr5);
strcpy_s(s->data.adress, arr6);
strcpy_s(a, arr);
while (*arr != '')
{
count++;
arr++;
}
q = L;
p = L->next;
while (p != NULL)
{
strcpy_s(b, p->data.name);
i = 0, j = 0;
while (a[i] == b[j] && a[i] != ''&&b[j] != '')
{
i++;
j++;
}
if (i == count)
{
while (q)
{
while (q->next == p)
{
q->next = s;
s->next = p;
cout << "插入成功" << endl;
ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("text.txt", ios::out);
strlonde S;
S = L->next;
while (S)
{
ofs << S->data.name << " " << S->data.num << " " << S->data.tel << " " << S->data.name1 << " " << S->data.adress << " " << endl;
S = S->next;
}
ofs.close();
return;
}
q = q->next;
}
}
p = p->next;
}
}
void modify(strlonde&L, char*arr,char*arr1,char*arr2,char*arr3,char*arr4,char*arr5)
{
char a[100], b[100];
strcpy_s(a, arr);
strlonde p;
int count = 0, i = 0, j = 0;
while (*arr != '')
{
count++;
arr++;
}
p = L->next;
while (p)
{
strcpy_s(b, p->data.name);
i = 0, j = 0;
while (a[i] == b[j] && a[i] != ''&&b[j] != '')
{
i++;
j++;
}
if (i == count)
{
strcpy_s(p->data.num, arr1);
strcpy_s(p->data.name, arr2);
strcpy_s(p->data.tel, arr3);
strcpy_s(p->data.name1, arr4);
strcpy_s(p->data.adress, arr5);
cout << "修改成功" << endl;
ofstream ofs;
ofs.open("text.txt", ios::out);
strlonde S;
S = L->next;
while (S)
{
ofs << S->data.name << " " << S->data.num << " " << S->data.tel << " " << S->data.name1 << " " << S->data.adress << " " << endl;
S = S->next;
}
ofs.close();
return;
}
p = p->next;
}
}
void menu()
{
cout << " ******************************************************************" << endl;
cout << " *******************欢迎光临图书管理系统***************************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 1.输入-1 退出程序 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 2.输入1 录入信息 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 3.输入2 陈列信息 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 4.输入3 按编号查找 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 5.输入4 按书名查找 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 6.输入5 删除 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 7.输入6 插入 *******************" << endl;
cout << " **************** 8.输入7 修改 *******************" << endl;
cout << " ******************************************************************" << endl;
}
int main()
{
strlonde L;
char arr[100], arr2[100], arr4[100], arr5[100], arr6[100], arr7[100], arr8[100], arr9[100], arr10[100], arr11[100], arr12[100], arr13[100], arr14[100], arr15[100], arr16[100];
int n = 0;
int x = 0;
menu();
while (cin >> x)
{
if (x < 0)
{
break;
}
switch (x)
{
case 1:
cout << "现在开始录入信息,请输入您要录入几本书的信息" << endl;
cin >> n;
londecreat(L, n);
cout << "录入完成" << endl;
break;
case 2:
display(L);
break;
case 3:
cout << "请输入您要进行查找的图书的编号" << endl;
cin >> arr;
findname(arr);
break;
case 4:
cout << "请输入您要进行查找图书名" << endl;
cin >> arr2;
findnum(arr2);
break;
case 5:
cout << "请输入您要删除图书的编号" << endl;
cin >> arr4;
delete1(L, arr4);
break;
case 6:
cout << "请输入您要进行插入地方图书的编号以及插入的图书编号,图书名,图书作者,图书出版社,价格" << endl;
cin >> arr5 >> arr6 >> arr7 >> arr8 >> arr13 >> arr14;
insert(L, arr5, arr6, arr7, arr8,arr13,arr14);
break;
case 7:
cout << "请输入您要进行修改的用户的编号以及您需要修改的信息" << endl;
cin >> arr9 >> arr10 >> arr11 >> arr12 >> arr15 >> arr16;
modify(L, arr9, arr10, arr11, arr12,arr15,arr16);
break;
default:
cout << "您的输入有误,请重新输入" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
到这里,这个图书信息管理系统的基本功能就已经全部实现了,下面我们来看看运行后是什么样子:
结果展示
这里是刚刚打开时的界面
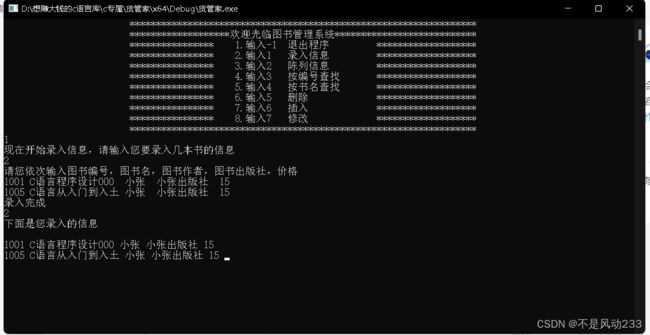
录入及陈列信息
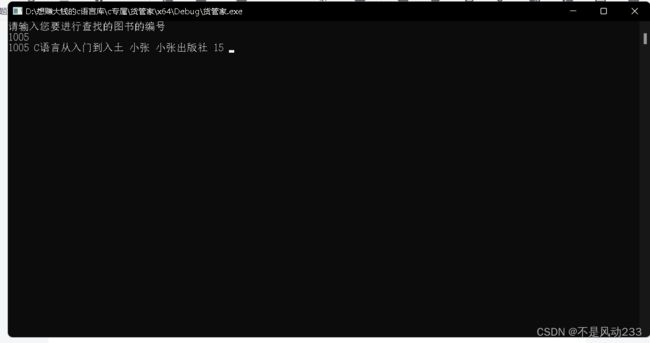
按照编号查找
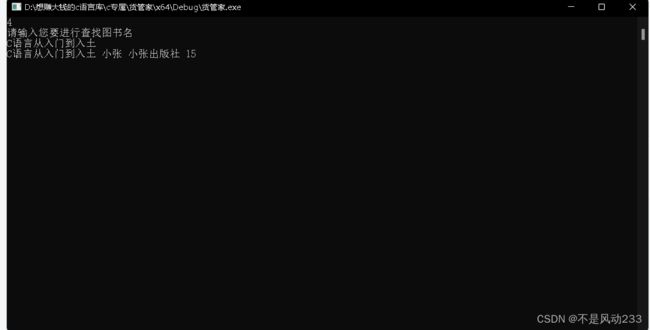
按照书名查找
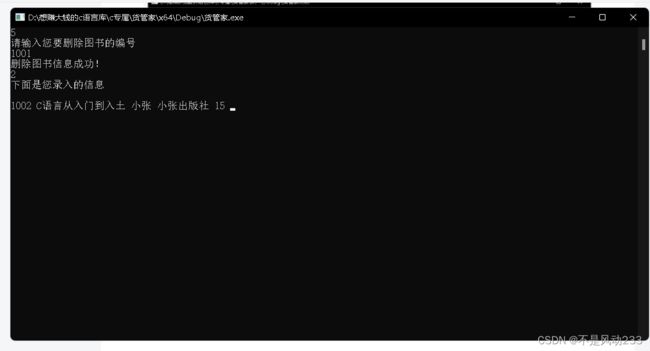
根据编号删除图书
插入操作
保存到txt文件中的样子
结束语
到了这里今天的内容就已经全部的结束了,希望小张的图书信息管理系统可以给大家带来帮助,同时也希望大家可以多多支持支持小张,小张在这里提前谢谢大家啦!