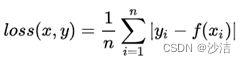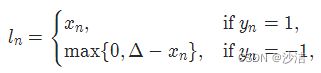损失函数-pytorch
损失函数的作用: 主要用于深度学习中predict与True label “距离”度量或者“相似度度量”,并通过反向传播求梯度,进而通过梯度下降算法更新网络参数,周而复始,通过损失值和评估值反映模型的好坏。
损失函数的种类:主要分为分类损失函数和回归损失函数。
| 分类损失函数 |
|
| 回归损失函数 |
|
|
|
补充知识:
- 分类损失函数:
(2.1) NLL Loss(Negative Log Likelihood Loss, 负对数似然函数)
作用:对预测正确但是预测概率不高的情况进行惩罚(这种情况的损失值更大)。
公式:
计算过程:
- Batch_size=N,x是全连接层的输出,是个N*c的向量;
- 先对输入x计算softmax,此时,softmax(x)的取值范围是0-1;
- 再求对数-log,此时-log(softmax(x))的取值范围是(0, +∞ ); softmax(x)越小,-log(softmax(x))则越大;
- 通过labels将(N*C)中的N个样本对应的正确类别的预测得分取出来,组成(N,1)的向量,最后求和取均值。 yi表示第i个样本的标签。
代码-pytorch
torch.nn.NLLLoss(weight=None,size_average=None,ignore_index=-100,reduce=None,
reduction='mean')
weight:用于数据集类别不均衡问题。
import torch
from torch import nn
m = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
loss = nn.NLLLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.tensor([1, 0, 4])
output = loss(m(input), target)
output.backward
(2.1)Cross Entropy Loss-交叉熵损失
公式:
softmax(y)指的就是预测标签的概率。![]() 是真实类别标签的one-hot的形式.
是真实类别标签的one-hot的形式.
计算过程:
- y是神经网络全连接层的输出shape=(N, C);
- 对y经过sigmoid或softmax处理输出概率值,shape=(N, C);
- 将预测的概率值(shape=(N,C))与
 真实类别标签的one-hot的形式(shape=(N,C))进行交叉熵计算。
真实类别标签的one-hot的形式(shape=(N,C))进行交叉熵计算。
代码:
nn.CrossEntropyLoss (input, target)
参数:input.shape=(N, C),target.shape为(N)或者概率形式的target(N,C)。
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.randn(3, 5).softmax(dim=1)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()
(2.3) BCE Loss-二分类交叉熵损失,Binary Cross Entropy Loss
可用于二分类、多标签分类,即判断每一个标签是否是前景、背景。
公式:
y为预测当前标签的概率值。使用BCE前,需要通过sigmoid将score转换为预测的概率。
代码:nn.BCELoss(input, target), input和target的shape一致。
# 1. 在放入BCE Loss前需要对输入使用sigmoid转换为概率,
m = nn.Sigmoid()
loss = nn.BCELoss()
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
output = loss(m(input), target)
output.backward()
(2.4)BCE With Logits Loss
可用于多标签分类,即判断每一个标签是否是前景、背景。
BCEWithLogitsLoss损失函数把 Sigmoid 层集成到了 BCELoss 类中。
![]()
代码:nn.BC EWithLogitsLoss(input, target)
参数:input和target的shape一致。
loss = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
input = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
output = loss(input, target)
output.backward()(2.5)Focal Loss
(2.6)arcface loss
(2.7)magface loss
3.回归损失函数
(3.1) L1Loss-L1范数损失
它是把目标值yi与模型输出(估计值)f(xi) 做绝对值得到的误差
代码:torch.nn.L1Loss(reduction='mean')
参数:reduction有三个值可选:none: 不使用约简;mean:返回loss和的平均值;sum:返回loss的和。默认:mean。
(3.2) MSELoss-均方误差损失
它是把目标值yi与模型输出(估计值)f(xi)做差然后平方得到的误差公式:
torch.nn.MSELoss(reduction='mean')
参数:reduction有三个值可选:none: 不使用约简;mean:返回loss和的平均值;sum:返回loss的和。默认:mean。
(3.3) SmoothL1Loss
简单来说就是平滑版的L1 Loss。
公式:
torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(reduction='mean')
SooothL1Loss其实是L2Loss和L1Loss的结合,它同时拥有L2 Loss和L1 Loss的部分优点:
(1)当预测值和ground truth差别较小的时候(绝对值差小于1),使用的是L2 Loss,梯度不至于太大。(损失函数相较L1 Loss比较圆滑)
(2)当差别大的时候,使用的是L1 Loss,梯度值足够小(较稳定,不容易梯度爆炸)。
(6) MarginRankingLoss
torch.nn.MarginRankingLoss(margin=0.0, reduction='mean') 对于 mini-batch(小批量) 中每个实例的损失函数如下:
参数:margin:默认值0
(7) HingeEmbeddingLoss
torch.nn.HingeEmbeddingLoss(margin=1.0, reduction='mean') 对于 mini-batch(小批量) 中每个实例的损失函数如下:
参数:margin:默认值1