lecture 9:分类变量回归
先学习这个这个资料
分类变量回归——Probit和Logit(附代码)
以下两个网页上均有heckman的代码,以日本教师的优先考虑。
https://pypi.org/project/py4etrics/官方安装地址
https://github.com/Py4Etrics
https://github.com/vnery5/Econometria
https://lost-stats.github.io/Model_Estimation/GLS/heckman_correction_model.html
https://rlhick.people.wm.edu/stories/econ_407_notes_heckman.html
https://econ.pages.code.wm.edu/407/notes/docs/mle_heckman.html
Heckman 两阶段模型:
Heckman两阶段模型解决的是样本选择偏差(sample selection bias)的问题。样本选择偏差指的是我们在回归方程中估计出的参数是基于那些被选择进样本了的数据点(或者说是能够观测得到的数据点)而得出的。如果说一个数据点(观测值)是不是被选择进样本是一个外生的、纯随机的事件,那么我们据此得出的参数并不会有偏差(bias)——这个估计结果就不会有问题。
可是,一个数据点是不是能被选择进样本、或者说是不是能够被观测到,这个过程在很多时候并不是随机、外生的。比如说,就拿Wooldridge 教材中的一个经典例子来讲:研究者试图估计出受教育程度以及工作经验对于女职工工资的影响。在一个753名女性的大样本中,428名女性是有工作的,所以这项研究只能在这428名有工作(有收入)的样本中展开。那么问题来了:因为我们无法观测到那325个没有工作的样本中受教育程度以及经验对于收入的影响,并且一个人选择工作或不工作并非是随机的——人们会根据潜在的收入水平、自身条件、家庭情况、年龄等等因素综合来决定是否参加工作,于是,我们仅从那428个有工作的人身上找出的统计学结果将是有偏差的,因为样本的选择并非随机及外生的。
Heckman两阶段模型的功能就是试图纠正这种偏差导致的估计偏误。第一阶段的模型,是一个包括全样本(753人)的Probit模型,用来估计一个人参加工作与否的概率。这里的因变量是二元的,表示是否参加工作;自变量是一些会影响个人决定工作与否的外生变量,比如其他收入来源、年龄、有几个未成年子女,等等。这些自变量类似工具变量——他们会影响个人是否参加工作的决策,但不太可能影响参加工作后的收入水平。然后根据这个Probit模型,我们为每一个样本计算出逆米尔斯比率(Inverse Mills Ratio)。这个比率的作用是为每一个样本计算出一个用于修正样本选择偏差的值。
然后第二步,只需要在原来的回归方程——即对于428个有工作的样本,基于她们受教育程度和经验的回归中加入一个额外的自变量——逆米尔斯比率即可,然后估计出回归参数。
最后,观察在第二阶段方程中,逆米尔斯比率这个自变量的显著性。如果该变量不显著,则说明最一开始的回归方程并不具有样本选择偏差,研究者可以根据原来的系数来做出统计推断;但如果尼米尔比率这个参数是显著的,则说明样本选择偏差是存在的,研究者应当根据第二阶段方程里的回归系数来做出统计推断。
Heckman两阶段模型适用于解决由样本选择偏差(sample selection bias)造成的内生性问题。在经济学领域,样本选择偏差的典型例子是研究女性的受教育情况对女性工资的影响。按照这个思路,一般会去问卷收集或在哪个网站下载部分女性的受教育情况,工资,及其他特征数据,例如年龄,毕业院校等级等个人特征,然后做回归。不过这样做有一个问题,就是登记的女性,都是在工作的,但是许多受教育程度较高的女性不工作,选择做家庭主妇,这部分样本就没有算在内,样本失去随机性。这就导致模型只是用到了在工作的女性,这样得出的结论是有偏差的。在管理学领域,一个典型的问题是企业的某个特征,或者董事/CEO的某个特征,对企业R&D投入的影响。也是同样的问题,企业的R&D投入是企业自愿披露的内容,有的企业不披露,这时你做回归时就不能包括这部分样本,也会造成样本选择偏差,结果有偏。
对于这种情况,Heckman提出了一个方法,赫克曼矫正法(Heckman Correction,又称两阶段方法)。赫克曼矫正法分两个步骤进行:第一步骤,研究者根据管理学理论设计出一个计算企业披露R&D投入概率的模型,而该模型的统计估计结果可以用来预测每个个体的概率;第二步骤,研究者将这些被预测个体概率合并为一个额外的解释变量,与其他控制变量等变量一起来矫正自选择问题。这个比率叫逆米尔斯比率,inverse Mills ration, imr,也就是说,在第一步计算出imr,在第二步把imr当作一个控制变量。
以企业R&D投入问题为例,假设全样本是1000家公司,其中800家公司披露了其R&D投入。
第一阶段的模型,是一个包括全样本(1000家)的Probit模型,用来估计一家公司是否会披露其R&D投入的概率。这里的因变量是二元的,表示是否披露R&D投入;自变量是一些会影响是否披露R&D的外生变量,比如其他收入营业收入,杠杆率,公司规模,所属行业等等。然后根据这个Probit模型,为每一个样本计算出imr,imr作用是为每一个样本计算出一个用于修正样本选择偏差的值。
第二阶段,在原来的回归方程,也就是原来只有800家公司的样本的方程假如imr作为控制变量,其他都不变,然后估计出回归参数。这时不管imr显著不显著都不重要,imr显著说明样本选择偏差的确影响了你最初模型的估计,这正表明了使用Heckman两步法纠正样本选择偏差的必要性。imr不显著说明原模型不存在严重的样本选择偏差,这时Heckman第二步得到的结果应该与原模型得到的结果差不多。(关于imr的显著性是否说明样本选择偏差存在目前还有争议,不过imr不是关注的变量)。第二步关注的对象是核心解释变量是否显著。只要核心解释变量显著,就说明结果稳健。
在stata上的实现,还是刚才的例子。假设问题是研究董事会的连锁懂事比例对企业R&D投入的影响,各变量如下:
因变量:企业R&D投入额度(rd)
自变量:董事会连锁懂事比例 (interlockratio)
控制变量:公司规模(firmsize),杠杆率(leverage), 公司成长性(growth),公司年龄(age),行业R&D投入(industryrd),行业集中度(cr4),行业净资产收益率(industryroa)等。其中前三个控制变量还会影响企业R&D投入的概率。
总样本数1000家,其中800家披露了R&D投入,不考虑其他变量的缺失值。
Heckman两步法
第一步,命名一个新的因变量,企业是否披露R&D投入,ifrd
xi: probit ifrd firmsize leverage growth i.year i.ind r//Heckman两阶段的第一阶段回归,这里的r可加可不加,看需不需要控制异方差问题。
estimate store First
predict y_hat, xb
gen pdf = normalden(y_hat)
gen cdf = normal(y_hat)
gen imr = pdf/cdf//生成imr
第二步回归,把imr当作控制变量加入原模型,用原来的数据。
reg rd interlockratio leverage growth industryrd cr4 industryroa imr i.year i.ind , r if ifrd==1
需要注意的是,在第一步,确定哪些变量会影响企业披露其R&D数据时,这些变量不一定是原模型的因变量,可以是可以不是,是不是要说明理由。
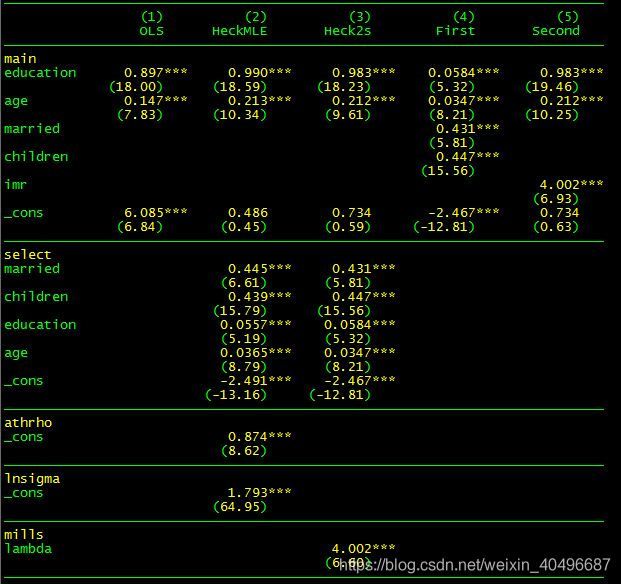
例二:
数据地址:点击下载
*数据来源: https://gitee.com/arlionn/data
use womenwk.dta, clear
*描述性统计数据
sum age educ married children wage
*简单的ols模型,存在选择性偏误
reg wage educ age
est store OLS
*第一种方法 heckman maximum likelihood
heckman wage educ age, select(married children educ age) //默认最大似然估计
est store HeckMLE
*第二种方法 heckman two-step all-in-one 不可以进行cluster调整
heckman wage educ age, select(married children educ age) twostep
est store Heck2s
*第二种方法 heckman two-step step-by-step 可以进行cluster调整
probit work married children educ age
est store First
predict y_hat, xb
gen pdf = normalden(y_hat) //概率密度函数
gen cdf = normal(y_hat) //累积分布函数
gen imr = pdf/cdf //计算逆米尔斯比率
reg wage educ age imr if work == 1 //女性工作子样本
est store Second
vif //方差膨胀因子
*对比结果
local m "OLS HeckMLE Heck2s First Second"
esttab `m', mtitle(`m') nogap compress pr2 ar2
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# true parameters
rho_t = np.array([0.8])
rho_x_w_t = np.array([0.8])
gamma_t = np.array([.5,1.0])
beta_t = np.array([-2.0,0.5])
sigma_e_t = np.array([1.0])
N =5000
# generate toy data consistent with heckman:
# generate potentially correlated x,w data
mean_x_w = np.array([0,0])
cov_x_w = np.array([[1,rho_x_w_t[0]],[rho_x_w_t[0], 1]])
w, x = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean_x_w, cov_x_w, N).T
# add constant to first position and convert to DataFrame
w_ = pd.DataFrame(np.c_[np.ones(N),w],columns=['Constant (Selection)','Slope (Selection)'])
x_ = pd.DataFrame(np.c_[np.ones(N),x], columns=['Constant','Slope'])
# generate errors
mean_u_eps = np.array([0,0])
cov_u_eps = np.array([[1,rho_t[0]],[rho_t[0],sigma_e_t]])
u, epsilon = np.random.multivariate_normal(mean_u_eps, cov_u_eps, N).T
# generate latent zstar
zstar = w_.dot(gamma_t) + u
# generate observed z (indicator=1 if zstar is positive)
z = zstar > 0
# generate latent ystar
ystar = x_.dot(beta_t) + epsilon
y=ystar.copy()
# generate observed y [if z=0, set y to NaN]
y[~z] = np.nan
stata_data = pd.DataFrame(np.c_[y,z,x,w], columns=['y','z','x','w'])
stata_data.to_stata('/tmp/heckman_data.dta')
print(stata_data.head())
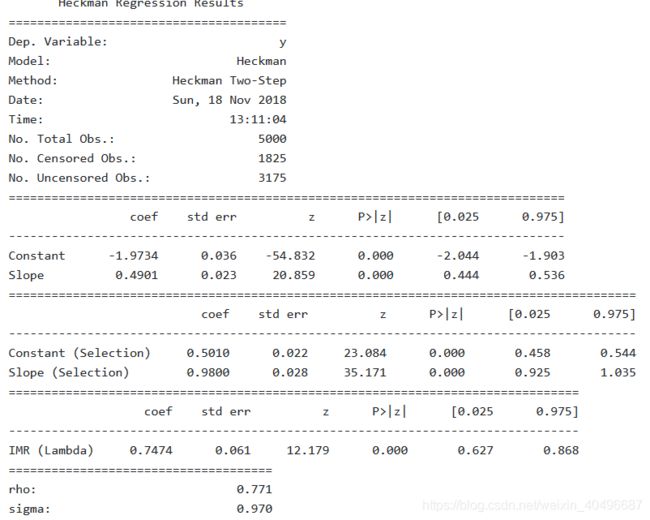
import heckman as heckman
res = heckman.Heckman(y, x_, w_).fit(method='twostep')
print(res.summary())
"""
Heckman correction for sample selection bias (the Heckit procedure).
Original Code Created August 19, 2014 by B.I.
Last modified February 26, 2017 by B.I.
NO warranty is provided for this software.
"""
import numpy as np
import statsmodels.api as sm
import statsmodels.base.model as base
from statsmodels.iolib import summary
from statsmodels.tools.numdiff import approx_fprime
from scipy.stats import norm
import warnings
import pandas as pd
class Heckman(base.LikelihoodModel):
"""
Class for Heckman correction for sample selection bias model.
Parameters
----------
endog : 1darray
Data for the dependent variable. Should be set to np.nan for
censored observations.
exog : 2darray
Data for the regression (response) equation. If a constant
term is desired, the user should directly add the constant
column to the data before using it as an argument here.
exog_select : 2darray
Data for the selection equation. If a constant
term is desired, the user should directly add the constant
column to the data before using it as an argument here.
**kwargs:
missing=, which can be 'none', 'drop', or 'raise'
Notes
-----
The selection equation should contain at least one variable that
is not in the regression (response) equation, i.e. the selection
equation should contain at least one instrument. However, this
module should still work if the user chooses not to do this.
"""
def __init__(self, endog, exog, exog_select, **kwargs):
# check that Z has same index as X (and consequently Y through super().__init__)
if pd.__name__ in type(endog).__module__ and pd.__name__ in type(exog).__module__:
if not all(endog.index==exog_select.index):
raise ValueError("Z indices need to be the same as X and Y indices")
# shape checks
if (len(endog) == len(exog)) and (len(endog) == len(exog_select)):
pass
else:
raise ValueError("Y, X, and Z data shapes do not conform with each other.")
try:
if (endog.ndim == 1) and (exog.ndim <= 2) and (exog_select.ndim <= 2):
pass
else:
raise ValueError("Y, X, and Z data shapes do not conform with each other.")
except AttributeError:
if (np.asarray(endog).ndim == 1) and (np.asarray(exog).ndim <= 2) and (np.asarray(exog_select).ndim <= 2):
pass
else:
raise ValueError("Y, X, and Z data shapes do not conform with each other.")
# give missing (treated) values in endog variable finite values so that super().__init__
# does not strip them out -- they will be put back after the call to super().__init__
treated = np.asarray(~np.isnan(endog))
try:
endog_nomissing = endog.copy()
endog_nomissing[~treated] = -99999
except (TypeError, AttributeError):
endog_nomissing = [endog[i] if treated[i] else -99999 for i in range(len(treated))]
# create 1-D array that will be np.nan for every row of exog_select that has any missing
# values and a finite value otherwise for the call to super().__init__ so that it can
# strip out rows where exog_select has missing data if missing option is set
if np.asarray(exog_select).ndim==2:
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder = \
[np.nan if any(np.isnan(row)) else 1 for row in np.asarray(exog_select)]
else: # assume ==1
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder = [np.nan if np.isnan(row) else 1 for row in np.asarray(exog_select)]
if pd.__name__ in type(endog).__module__:
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder = pd.Series(exog_select_1dnan_placeholder, index=endog.index)
else:
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder = np.array(exog_select_1dnan_placeholder)
# create array of sequential row positions so that rows of exog_select that have missing
# data can be identified after call to super().__init__
obsno = np.array(list(range(len(endog))))
# call super().__init__
super(Heckman, self).__init__(
endog_nomissing, exog=exog,
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder=exog_select_1dnan_placeholder, obsno=obsno,
treated=treated,
**kwargs)
# put np.nan back into endog for treated rows
self.endog = self.data.endog = \
np.asarray(
[self.endog[i] if self.treated[i] else np.nan for i in range(len(self.treated))]
)
# strip out rows stripped out by call to super().__init__ in Z variable
self.exog_select = np.asarray([np.asarray(exog_select)[obs] for obs in self.obsno])
# store variable names of exog_select
try:
self.exog_select_names = exog_select.columns.tolist()
except AttributeError:
self.exog_select_names = None
# delete attributes created by the call to super().__init__ that are no longer needed
del self.exog_select_1dnan_placeholder
del self.obsno
# store observation counts
self.nobs_total = len(endog)
self.nobs_uncensored = self.nobs = np.sum(self.treated)
self.nobs_censored = self.nobs_total - self.nobs_uncensored
def initialize(self):
self.wendog = self.endog
self.wexog = self.exog
def whiten(self, data):
"""
Model whitener for Heckman correction model does nothing.
"""
return data
def get_datamats(self):
Y = np.asarray(self.endog)
Y = Y[self.treated]
X = np.asarray(self.exog)
X = X[self.treated,:]
if X.ndim==1:
X = np.atleast_2d(X).T
Z = np.asarray(self.exog_select)
if Z.ndim==1:
Z = np.atleast_2d(Z).T
return Y, X, Z
def fit(self, method='twostep', start_params_mle=None, method_mle=None, maxiter_mle=None, **kwargs_mle):
"""
Fit the Heckman selection model.
Parameters
----------
method : str
Can only be "2step", which uses Heckman's two-step method.
start_params_mle: 1darray
If using MLE, starting parameters.
method_mle: str
If using MLE, the MLE estimation method.
maxiter_mle: scalar
If using MLE, the maximum number of iterations for MLE estimation.
**kwargs_mle:
Other arguments to pass to optimizer for MLE estimation.
Returns
-------
A HeckmanResults class instance.
See Also
---------
HeckmanResults
"""
## Show warning to user if estimation is by two-step but MLE arguments were also provided
if method=='twostep':
if start_params_mle is not None or method_mle is not None or maxiter_mle is not None or \
len(kwargs_mle.keys())>0:
warnings.warn('The user chose to estimate the Heckman model by Two-Step,' + \
' but MLE arguments were provided. Extraneous MLE arguments will be ignored.')
## fit
if method=='twostep':
results = self._fit_twostep()
elif method=='mle':
results = self._fit_mle(
start_params_mle=start_params_mle, method_mle=method_mle, maxiter_mle=maxiter_mle,
**kwargs_mle)
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid choice for estimation method.")
## return fitted Heckman model
return results
def _fit_twostep(self):
########################################################################
# PRIVATE METHOD
# Fits using Heckman two-step from Heckman (1979).
########################################################################
## prep data
Y, X, Z = self.get_datamats()
## Step 1
step1model = sm.Probit(self.treated, Z)
step1res = step1model.fit(disp=False)
step1_fitted = np.atleast_2d(step1res.fittedvalues).T
step1_varcov = step1res.cov_params()
inverse_mills = norm.pdf(step1_fitted)/norm.cdf(step1_fitted)
## Step 2
W = np.hstack((X, inverse_mills[self.treated] ) )
step2model = sm.OLS(Y, W)
step2res = step2model.fit()
params = step2res.params[:-1]
betaHat_inverse_mills = step2res.params[-1]
## Compute standard errors
# Compute estimated error variance of censored regression
delta = np.multiply(inverse_mills, inverse_mills + step1_fitted)[self.treated]
sigma2Hat = step2res.resid.dot(step2res.resid) / self.nobs_uncensored + \
(betaHat_inverse_mills**2 * sum(delta)) / self.nobs_uncensored
sigma2Hat = sigma2Hat[0]
sigmaHat = np.sqrt(sigma2Hat)
rhoHat = betaHat_inverse_mills / sigmaHat
# compute standard errors of beta estimates of censored regression
delta_1d = delta.T[0]
Q = rhoHat**2 * ((W.T*delta_1d).dot(Z[self.treated])).dot(step1_varcov).dot((Z[self.treated].T*delta_1d).dot(W))
WT_W_inv = np.linalg.inv(W.T.dot(W))
WT_R = W.T*(1 - rhoHat**2 * delta_1d)
normalized_varcov_all = WT_W_inv.dot(WT_R.dot(W)+Q).dot(WT_W_inv)
del WT_W_inv
del WT_R
del delta_1d
normalized_varcov = normalized_varcov_all[:-1,:-1]
varcov_all = sigma2Hat * normalized_varcov_all
varcov = varcov_all[:-1,:-1]
stderr_all = np.sqrt(np.diag(varcov_all))
stderr = stderr_all[:-1]
stderr_betaHat_inverse_mills = stderr_all[-1]
## store results
results = HeckmanResults(self, params, normalized_varcov, sigma2Hat,
select_res=step1res,
params_inverse_mills=betaHat_inverse_mills, stderr_inverse_mills=stderr_betaHat_inverse_mills,
var_reg_error=sigma2Hat, corr_eqnerrors=rhoHat,
method='twostep')
return results
def _fit_mle(self, start_params_mle=None, method_mle=None, maxiter_mle=None, **kwargs_mle):
# get number of X parameters and number of Z parameters
Y, X, Z = self.get_datamats()
num_xvars = X.shape[1]
num_zvars = Z.shape[1]
del Y, X, Z
# let the Heckman two-step parameter estimates be the starting values
# of the the optimizer of the Heckman MLE estimate if not specified by user
if start_params_mle is None:
twostep_res = self._fit_twostep()
xparams = np.asarray(twostep_res.params)
zparams = np.asarray(twostep_res.select_res.params)
params_all = np.append(xparams, zparams)
params_all = np.append(params_all,
np.log(np.sqrt(twostep_res.var_reg_error)))
params_all = np.append(params_all,
(1./2.)*np.log((1+twostep_res.corr_eqnerrors)/(1-twostep_res.corr_eqnerrors)))
start_params_mle = params_all
# fit Heckman parameters by MLE
results_mle = super(Heckman, self).fit(
start_params=start_params_mle, method=method_mle, maxiter=maxiter_mle,
**kwargs_mle
)
xbeta_hat = np.asarray(results_mle.params[:num_xvars]) # reg eqn coefs
zbeta_hat = np.asarray(results_mle.params[num_xvars:num_xvars+num_zvars]) # selection eqn coefs
log_sigma_hat = results_mle.params[-2]
atanh_rho_hat = results_mle.params[-1]
sigma_hat = np.exp(log_sigma_hat)
rho_hat = np.tanh(atanh_rho_hat)
scale = results_mle.scale
xbeta_ncov_hat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[:num_xvars,:num_xvars]
zbeta_ncov_hat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[
num_xvars:(num_xvars+num_zvars),num_xvars:(num_xvars+num_zvars)
]
imr_hat = rho_hat*sigma_hat
# use the Delta method to compute the variance of lambda (the inverse Mills ratio)
log_sigma_var_hat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[-2,-2] * scale
atanh_rho_var_hat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[-1,-1] * scale
def grad_lambda(log_sigma, atanh_rho):
return np.array([atanh_rho, log_sigma])
grad_lambda_hat = np.atleast_2d(grad_lambda(sigma_hat, rho_hat))
covmat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[-2:,-2:] * scale
imr_stderr_hat = np.sqrt(
grad_lambda_hat.dot(covmat).dot(grad_lambda_hat.T)[0,0]
)
del grad_lambda_hat
del covmat
# fill in results for this fit, and return
DUMMY_COEF_STDERR_IMR = 0.
results = HeckmanResults(self, xbeta_hat,
xbeta_ncov_hat, scale,
select_res=base.LikelihoodModelResults(None, zbeta_hat, zbeta_ncov_hat, scale),
params_inverse_mills=imr_hat, stderr_inverse_mills=imr_stderr_hat,
var_reg_error=sigma_hat**2, corr_eqnerrors=rho_hat,
method='mle')
return results
def loglike(self, params):
return self.loglikeobs(params).sum(axis=0)
def nloglike(self, params):
return -self.loglikeobs(params).sum(axis=0)
def loglikeobs(self, params_all):
"""
Log-likelihood of model.
Parameters
----------
params_all : array-like
Parameter estimates, with the parameters for the regression
equation coming first, then the parameters for the
selection equation, then log sigma, then atanh rho.
Returns
-------
loglike : float
The value of the log-likelihood function for a Heckman correction model.
"""
# set up data and parameters needed to compute log likelihood
Y, X, Z = self.get_datamats()
D = self.treated
num_xvars = X.shape[1]
num_zvars = Z.shape[1]
xbeta = np.asarray(params_all[:num_xvars]) # reg eqn coefs
zbeta = np.asarray(params_all[num_xvars:num_xvars+num_zvars]) # selection eqn coefs
log_sigma = params_all[-2]
atanh_rho = params_all[-1]
sigma = np.exp(log_sigma)
rho = np.tanh(atanh_rho)
# line the data vectors up
Z_zbeta_aligned = Z.dot(zbeta)
X_xbeta = X.dot(xbeta)
X_xbeta_aligned = np.empty(self.nobs_total)
X_xbeta_aligned[:] = np.nan
X_xbeta_aligned[D] = X_xbeta
del X_xbeta
Y_aligned = np.empty(self.nobs_total)
Y_aligned[:] = np.nan
Y_aligned[D] = Y
# create an array where each row is the log likelihood for the corresponding observation
norm_cdf_input = (Z_zbeta_aligned+(Y_aligned-X_xbeta_aligned)*rho/sigma) / np.sqrt(1-rho**2)
norm_cdf_input[~D] = 0 # dummy value
ll_obs_observed = \
np.multiply(D,
norm.logcdf(norm_cdf_input) - \
(1./2.)*((Y_aligned-X_xbeta_aligned)/sigma)**2 - \
np.log(np.sqrt(2*np.pi)*sigma))
ll_obs_observed[~D] = 0
ll_obs_notobserved = \
np.multiply(1-D,
norm.logcdf(-Z_zbeta_aligned))
ll_obs = ll_obs_observed + ll_obs_notobserved
# return log likelihood by observation vector
return ll_obs
def score(self, params):
'''
Gradient of log-likelihood evaluated at params
'''
#this is the numerical approx func taken from
# base.model.GenericLikelihoodModel
kwds = {}
kwds.setdefault('centered', True)
return approx_fprime(params, self.loglike, **kwds).ravel()
def jac(self, params, **kwds):
'''
Jacobian/Gradient of log-likelihood evaluated at params for each
observation.
'''
#this is the numerical approx func taken from
# base.model.GenericLikelihoodModel
#kwds.setdefault('epsilon', 1e-4)
kwds.setdefault('centered', True)
return approx_fprime(params, self.loglikeobs, **kwds)
def hessian(self, params):
'''
Hessian of log-likelihood evaluated at params
'''
#this is the numerical approx func taken from
# base.model.GenericLikelihoodModel
from statsmodels.tools.numdiff import approx_hess
# need options for hess (epsilon)
return approx_hess(params, self.loglike)
def predict(self, params, exog=None):
"""
Return linear predicted values from a design matrix.
Parameters
----------
exog : array-like
Design / exogenous data
params : array-like, optional after fit has been called
Parameters of a linear model
Returns
-------
An array of fitted values
Notes
-----
If the model has not yet been fit, params is not optional.
"""
if exog is None:
exog = self.exog
return np.dot(exog, params)
if self._results is None and params is None:
raise ValueError("If the model has not been fit, then you must specify the params argument.")
if self._results is not None:
return np.dot(exog, self._results.params)
else:
return np.dot(exog, params)
class HeckmanResults(base.LikelihoodModelResults):
"""
Class to represent results/fits for Heckman model.
Attributes
----------
select_res : ProbitResult object
The ProbitResult object created when estimating the selection equation.
params_inverse_mills : scalar
Parameter estimate of the coef on the inverse Mills term in the second step.
stderr_inverse_mills : scalar
Standard error of the parameter estimate of the coef on the inverse Mills
term in the second step.
var_reg_error : scalar
Estimate of the "sigma" term, i.e. the error variance estimate of the
regression (response) equation
corr_eqnerrors : scalar
Estimate of the "rho" term, i.e. the correlation estimate of the errors between the
regression (response) equation and the selection equation
method : string
The method used to produce the estimates, i.e. 'twostep', 'mle'
"""
def __init__(self, model, params, normalized_cov_params=None, scale=1.,
select_res=None,
params_inverse_mills=None, stderr_inverse_mills=None,
var_reg_error=None, corr_eqnerrors=None,
method=None):
super(HeckmanResults, self).__init__(model, params,
normalized_cov_params,
scale)
self.select_res = select_res
self.params_inverse_mills = params_inverse_mills
self.stderr_inverse_mills = stderr_inverse_mills
self.var_reg_error = var_reg_error
self.corr_eqnerrors = corr_eqnerrors
self.method = method
if not hasattr(self, 'use_t'):
self.use_t = False
if not hasattr(self.select_res, 'use_t'):
self.select_res.use_t = False
def summary(self, yname=None, xname=None, zname=None, title=None, alpha=.05):
"""Summarize the Heckman model Results
Parameters
-----------
yname : string, optional
Default is `y`
xname : list of strings, optional
Default is `x_##` for ## in p the number of regressors
in the regression (response) equation.
zname : list of strings, optional
Default is `z_##` for ## in p the number of regressors
in the selection equation.
title : string, optional
Title for the top table. If not None, then this replaces the
default title
alpha : float
significance level for the confidence intervals
Returns
-------
smry : Summary instance
this holds the summary tables and text, which can be printed or
converted to various output formats.
See Also
--------
statsmodels.iolib.summary.Summary : class to hold summary
results
"""
## Put in Z name detected from data if none supplied, unless that too could not be
## inferred from data, then put in generic names
if zname is None and self.model.exog_select_names is not None:
zname=self.model.exog_select_names
elif zname is None and self.model.exog_select_names is None:
try:
zname = ['z' + str(i) for i in range(len(self.model.exog_select[0]))]
zname[0] = 'z0_or_zconst'
except TypeError:
zname = 'z0_or_zconst'
try: # for Python 3
if isinstance(zname, str):
zname = [zname]
except NameError: # for Python 2
if isinstance(zname, basestring):
zname = [zname]
## create summary object
# instantiate the object
smry = summary.Summary()
# add top info
if self.method=='twostep':
methodstr = 'Heckman Two-Step'
elif self.method=='mle':
methodstr = 'Heckman MLE'
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid method set")
top_left = [('Dep. Variable:', None),
('Model:', None),
('Method:', [methodstr]),
('Date:', None),
('Time:', None),
('No. Total Obs.:', ["%#i" % self.model.nobs_total]),
('No. Censored Obs.:', ["%#i" % self.model.nobs_censored]),
('No. Uncensored Obs.:', ["%#i" % self.model.nobs_uncensored]),
]
if hasattr(self, 'cov_type'):
top_left.append(('Covariance Type:', [self.cov_type]))
top_right = [
]
if title is None:
title = self.model.__class__.__name__ + ' ' + "Regression Results"
smry.add_table_2cols(self, gleft=top_left, gright=top_right,
yname=yname, xname=xname, title=title)
# add the Heckman-corrected regression table
smry.add_table_params(self, yname=yname, xname=xname, alpha=alpha,
use_t=self.use_t)
# add the selection equation estimates table
smry.add_table_params(self.select_res, yname=yname, xname=zname, alpha=alpha,
use_t=self.select_res.use_t)
# add the estimate to the inverse Mills estimate (z-score)
smry.add_table_params(
base.LikelihoodModelResults(None, np.atleast_1d(self.params_inverse_mills),
normalized_cov_params=np.atleast_1d(self.stderr_inverse_mills**2), scale=1.),
yname=None, xname=['IMR (Lambda)'], alpha=alpha,
use_t=False)
# add point estimates for rho and sigma
diagn_left = [('rho:', ["%#6.3f" % self.corr_eqnerrors]),
('sigma:', ["%#6.3f" % np.sqrt(self.var_reg_error)]),
]
diagn_right = [
]
smry.add_table_2cols(self, gleft=diagn_left, gright=diagn_right,
yname=yname, xname=xname,
title="")
# add text at end
smry.add_extra_txt(['First table are the estimates for the regression (response) equation.',
'Second table are the estimates for the selection equation.',
'Third table is the estimate for the coef of the inverse Mills ratio (Heckman\'s Lambda).'])
## return
return smry
https://github.com/vnery5/Econometria/blob/main/Heckman.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sun Dec 19 14:08:43 2021
@author: Administrator
"""
##Importando os pacotes e módulos necessários
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import math
#Para Regressão Linear Múltipla (OLS, GLS e WLS) e Testes Estatísticos
import statsmodels.api as sm
import econtools
import econtools.metrics as mt
from scipy import stats
#Pacotes de fórmula patsy no SM
from statsmodels.formula.api import logit, probit, poisson, ols, wls
#Pacotes para tabelas
from statsmodels.iolib.summary2 import summary_col
#Pacotes para fazer a coleta dos dados armazenados no mesmo diretório e outros pacotes gerais
import os
import pathlib
import glob
from IPython.display import clear_output
import gc
import subprocess #permite a cópia para o clipboard das equações gerados com as funções equation()
## Outros Pacotes
import statsmodels.base.model as base
from statsmodels.iolib import summary
from statsmodels.tools.numdiff import approx_fprime
from scipy.stats import norm
from scipy.optimize import minimize
from scipy.special import log_ndtr
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, mean_absolute_error
import warnings
class Heckman(base.LikelihoodModel):
"""
Class for Heckman correction for sample selection bias model.
Parameters
----------
endog : 1darray
Data for the dependent variable. Should be set to np.nan for
censored observations.
exog : 2darray
Data for the regression (response) equation. If a constant
term is desired, the user should directly add the constant
column to the data before using it as an argument here.
exog_select : 2darray
Data for the selection equation. If a constant
term is desired, the user should directly add the constant
column to the data before using it as an argument here.
**kwargs:
missing=, which can be 'none', 'drop', or 'raise'
Notes
-----
The selection equation should contain at least one variable that
is not in the regression (response) equation, i.e. the selection
equation should contain at least one instrument. However, this
module should still work if the user chooses not to do this.
"""
def __init__(self, endog, exog, exog_select, **kwargs):
# check that Z has same index as X (and consequently Y through super().__init__)
if pd.__name__ in type(endog).__module__ and pd.__name__ in type(exog).__module__:
if not all(endog.index==exog_select.index):
raise ValueError("Z indices need to be the same as X and Y indices")
# shape checks
if (len(endog) == len(exog)) and (len(endog) == len(exog_select)):
pass
else:
raise ValueError("Y, X, and Z data shapes do not conform with each other.")
try:
if (endog.ndim == 1) and (exog.ndim <= 2) and (exog_select.ndim <= 2):
pass
else:
raise ValueError("Y, X, and Z data shapes do not conform with each other.")
except AttributeError:
if (np.asarray(endog).ndim == 1) and (np.asarray(exog).ndim <= 2) and (np.asarray(exog_select).ndim <= 2):
pass
else:
raise ValueError("Y, X, and Z data shapes do not conform with each other.")
# give missing (treated) values in endog variable finite values so that super().__init__
# does not strip them out -- they will be put back after the call to super().__init__
treated = np.asarray(~np.isnan(endog))
try:
endog_nomissing = endog.copy()
endog_nomissing[~treated] = -99999
except (TypeError, AttributeError):
endog_nomissing = [endog[i] if treated[i] else -99999 for i in range(len(treated))]
# create 1-D array that will be np.nan for every row of exog_select that has any missing
# values and a finite value otherwise for the call to super().__init__ so that it can
# strip out rows where exog_select has missing data if missing option is set
if np.asarray(exog_select).ndim==2:
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder = \
[np.nan if any(np.isnan(row)) else 1 for row in np.asarray(exog_select)]
else: # assume ==1
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder = [np.nan if np.isnan(row) else 1 for row in np.asarray(exog_select)]
if pd.__name__ in type(endog).__module__:
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder = pd.Series(exog_select_1dnan_placeholder, index=endog.index)
else:
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder = np.array(exog_select_1dnan_placeholder)
# create array of sequential row positions so that rows of exog_select that have missing
# data can be identified after call to super().__init__
obsno = np.array(list(range(len(endog))))
# call super().__init__
super(Heckman, self).__init__(
endog_nomissing, exog=exog,
exog_select_1dnan_placeholder=exog_select_1dnan_placeholder, obsno=obsno,
treated=treated,
**kwargs)
# put np.nan back into endog for treated rows
self.endog = self.data.endog = \
np.asarray(
[self.endog[i] if self.treated[i] else np.nan for i in range(len(self.treated))]
)
# strip out rows stripped out by call to super().__init__ in Z variable
self.exog_select = np.asarray([np.asarray(exog_select)[obs] for obs in self.obsno])
# store variable names of exog_select
try:
self.exog_select_names = exog_select.columns.tolist()
except AttributeError:
self.exog_select_names = None
# delete attributes created by the call to super().__init__ that are no longer needed
del self.exog_select_1dnan_placeholder
del self.obsno
# store observation counts
self.nobs_total = len(endog)
self.nobs_uncensored = self.nobs = np.sum(self.treated)
self.nobs_censored = self.nobs_total - self.nobs_uncensored
def initialize(self):
self.wendog = self.endog
self.wexog = self.exog
def whiten(self, data):
"""
Model whitener for Heckman correction model does nothing.
"""
return data
def get_datamats(self):
Y = np.asarray(self.endog)
Y = Y[self.treated]
X = np.asarray(self.exog)
X = X[self.treated,:]
if X.ndim==1:
X = np.atleast_2d(X).T
Z = np.asarray(self.exog_select)
if Z.ndim==1:
Z = np.atleast_2d(Z).T
return Y, X, Z
def fit(self, method='twostep', start_params_mle=None, method_mle=None, maxiter_mle=None, **kwargs_mle):
"""
Fit the Heckman selection model.
Parameters
----------
method : str
Can only be "2step", which uses Heckman's two-step method.
start_params_mle: 1darray
If using MLE, starting parameters.
method_mle: str
If using MLE, the MLE estimation method.
maxiter_mle: scalar
If using MLE, the maximum number of iterations for MLE estimation.
**kwargs_mle:
Other arguments to pass to optimizer for MLE estimation.
Returns
-------
A HeckmanResults class instance.
See Also
---------
HeckmanResults
"""
## Show warning to user if estimation is by two-step but MLE arguments were also provided
if method=='twostep':
if start_params_mle is not None or method_mle is not None or maxiter_mle is not None or \
len(kwargs_mle.keys())>0:
warnings.warn('The user chose to estimate the Heckman model by Two-Step,' + \
' but MLE arguments were provided. Extraneous MLE arguments will be ignored.')
## fit
if method=='twostep':
results = self._fit_twostep()
elif method=='mle':
results = self._fit_mle(
start_params_mle=start_params_mle, method_mle=method_mle, maxiter_mle=maxiter_mle,
**kwargs_mle)
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid choice for estimation method.")
## return fitted Heckman model
return results
def _fit_twostep(self):
########################################################################
# PRIVATE METHOD
# Fits using Heckman two-step from Heckman (1979).
########################################################################
## prep data
Y, X, Z = self.get_datamats()
## Step 1
step1model = sm.Probit(self.treated, Z)
step1res = step1model.fit(disp=False)
step1_fitted = np.atleast_2d(step1res.fittedvalues).T
step1_varcov = step1res.cov_params()
inverse_mills = norm.pdf(step1_fitted)/norm.cdf(step1_fitted)
## Step 2
W = np.hstack((X, inverse_mills[self.treated] ) )
step2model = sm.OLS(Y, W)
step2res = step2model.fit()
params = step2res.params[:-1]
betaHat_inverse_mills = step2res.params[-1]
## Compute standard errors
# Compute estimated error variance of censored regression
delta = np.multiply(inverse_mills, inverse_mills + step1_fitted)[self.treated]
sigma2Hat = step2res.resid.dot(step2res.resid) / self.nobs_uncensored + \
(betaHat_inverse_mills**2 * sum(delta)) / self.nobs_uncensored
sigma2Hat = sigma2Hat[0]
sigmaHat = np.sqrt(sigma2Hat)
rhoHat = betaHat_inverse_mills / sigmaHat
# compute standard errors of beta estimates of censored regression
delta_1d = delta.T[0]
Q = rhoHat**2 * ((W.T*delta_1d).dot(Z[self.treated])).dot(step1_varcov).dot((Z[self.treated].T*delta_1d).dot(W))
WT_W_inv = np.linalg.inv(W.T.dot(W))
WT_R = W.T*(1 - rhoHat**2 * delta_1d)
normalized_varcov_all = WT_W_inv.dot(WT_R.dot(W)+Q).dot(WT_W_inv)
del WT_W_inv
del WT_R
del delta_1d
normalized_varcov = normalized_varcov_all[:-1,:-1]
varcov_all = sigma2Hat * normalized_varcov_all
varcov = varcov_all[:-1,:-1]
stderr_all = np.sqrt(np.diag(varcov_all))
stderr = stderr_all[:-1]
stderr_betaHat_inverse_mills = stderr_all[-1]
## store results
results = HeckmanResults(self, params, normalized_varcov, sigma2Hat,
select_res=step1res,
params_inverse_mills=betaHat_inverse_mills, stderr_inverse_mills=stderr_betaHat_inverse_mills,
var_reg_error=sigma2Hat, corr_eqnerrors=rhoHat,
method='twostep')
return results
def _fit_mle(self, start_params_mle=None, method_mle=None, maxiter_mle=None, **kwargs_mle):
# get number of X parameters and number of Z parameters
Y, X, Z = self.get_datamats()
num_xvars = X.shape[1]
num_zvars = Z.shape[1]
# let the Heckman two-step parameter estimates be the starting values
# of the the optimizer of the Heckman MLE estimate if not specified by user
if start_params_mle is None:
twostep_res = self._fit_twostep()
xparams = np.asarray(twostep_res.params)
zparams = np.asarray(twostep_res.select_res.params)
params_all = np.append(xparams, zparams)
params_all = np.append(params_all,
np.log(np.sqrt(twostep_res.var_reg_error)))
params_all = np.append(params_all,
(1./2.)*np.log((1+twostep_res.corr_eqnerrors)/(1-twostep_res.corr_eqnerrors)))
start_params_mle = params_all
# fit Heckman parameters by MLE
results_mle = super(Heckman, self).fit(
start_params=start_params_mle, method=method_mle, maxiter=maxiter_mle,
**kwargs_mle
)
xbeta_hat = np.asarray(results_mle.params[:num_xvars]) # reg eqn coefs
zbeta_hat = np.asarray(results_mle.params[num_xvars:num_xvars+num_zvars]) # selection eqn coefs
log_sigma_hat = results_mle.params[-2]
atanh_rho_hat = results_mle.params[-1]
sigma_hat = np.exp(log_sigma_hat)
rho_hat = np.tanh(atanh_rho_hat)
scale = results_mle.scale
xbeta_ncov_hat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[:num_xvars,:num_xvars]
zbeta_ncov_hat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[
num_xvars:(num_xvars+num_zvars),num_xvars:(num_xvars+num_zvars)
]
imr_hat = rho_hat*sigma_hat
# use the Delta method to compute the variance of lambda (the inverse Mills ratio)
log_sigma_var_hat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[-2,-2] * scale
atanh_rho_var_hat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[-1,-1] * scale
def grad_lambda(log_sigma, atanh_rho):
return np.array([atanh_rho, log_sigma])
grad_lambda_hat = np.atleast_2d(grad_lambda(sigma_hat, rho_hat))
covmat = results_mle.normalized_cov_params[-2:,-2:] * scale
imr_stderr_hat = np.sqrt(
grad_lambda_hat.dot(covmat).dot(grad_lambda_hat.T)[0,0]
)
del grad_lambda_hat
del covmat
# fill in results for this fit, and return
DUMMY_COEF_STDERR_IMR = 0.
results = HeckmanResults(self, xbeta_hat,
xbeta_ncov_hat, scale,
select_res=base.LikelihoodModelResults(None, zbeta_hat, zbeta_ncov_hat, scale),
params_inverse_mills=imr_hat, stderr_inverse_mills=imr_stderr_hat,
var_reg_error=sigma_hat**2, corr_eqnerrors=rho_hat,
method='mle')
return results
def loglike(self, params):
return self.loglikeobs(params).sum(axis=0)
def nloglike(self, params):
return -self.loglikeobs(params).sum(axis=0)
def loglikeobs(self, params_all):
"""
Log-likelihood of model.
Parameters
----------
params_all : array-like
Parameter estimates, with the parameters for the regression
equation coming first, then the parameters for the
selection equation, then log sigma, then atanh rho.
Returns
-------
loglike : float
The value of the log-likelihood function for a Heckman correction model.
"""
# set up data and parameters needed to compute log likelihood
Y, X, Z = self.get_datamats()
D = self.treated
num_xvars = X.shape[1]
num_zvars = Z.shape[1]
xbeta = np.asarray(params_all[:num_xvars]) # reg eqn coefs
zbeta = np.asarray(params_all[num_xvars:num_xvars+num_zvars]) # selection eqn coefs
log_sigma = params_all[-2]
atanh_rho = params_all[-1]
sigma = np.exp(log_sigma)
rho = np.tanh(atanh_rho)
# line the data vectors up
Z_zbeta_aligned = Z.dot(zbeta)
X_xbeta = X.dot(xbeta)
X_xbeta_aligned = np.empty(self.nobs_total)
X_xbeta_aligned[:] = np.nan
X_xbeta_aligned[D] = X_xbeta
del X_xbeta
Y_aligned = np.empty(self.nobs_total)
Y_aligned[:] = np.nan
Y_aligned[D] = Y
# create an array where each row is the log likelihood for the corresponding observation
norm_cdf_input = (Z_zbeta_aligned+(Y_aligned-X_xbeta_aligned)*rho/sigma) / np.sqrt(1-rho**2)
norm_cdf_input[~D] = 0 # dummy value
ll_obs_observed = \
np.multiply(D,
norm.logcdf(norm_cdf_input) - \
(1./2.)*((Y_aligned-X_xbeta_aligned)/sigma)**2 - \
np.log(np.sqrt(2*np.pi)*sigma))
ll_obs_observed[~D] = 0
ll_obs_notobserved = \
np.multiply(1-D,
norm.logcdf(-Z_zbeta_aligned))
ll_obs = ll_obs_observed + ll_obs_notobserved
# return log likelihood by observation vector
return ll_obs
def score(self, params):
'''
Gradient of log-likelihood evaluated at params
'''
#this is the numerical approx func taken from
# base.model.GenericLikelihoodModel
kwds = {}
kwds.setdefault('centered', True)
return approx_fprime(params, self.loglike, **kwds).ravel()
def jac(self, params, **kwds):
'''
Jacobian/Gradient of log-likelihood evaluated at params for each
observation.
'''
#this is the numerical approx func taken from
# base.model.GenericLikelihoodModel
#kwds.setdefault('epsilon', 1e-4)
kwds.setdefault('centered', True)
return approx_fprime(params, self.loglikeobs, **kwds)
def hessian(self, params):
'''
Hessian of log-likelihood evaluated at params
'''
#this is the numerical approx func taken from
# base.model.GenericLikelihoodModel
from statsmodels.tools.numdiff import approx_hess
# need options for hess (epsilon)
return approx_hess(params, self.loglike)
def predict(self, params, exog=None):
"""
Return linear predicted values from a design matrix.
Parameters
----------
exog : array-like
Design / exogenous data
params : array-like, optional after fit has been called
Parameters of a linear model
Returns
-------
An array of fitted values
Notes
-----
If the model has not yet been fit, params is not optional.
"""
if exog is None:
exog = self.exog
return np.dot(exog, params)
if self._results is None and params is None:
raise ValueError("If the model has not been fit, then you must specify the params argument.")
if self._results is not None:
return np.dot(exog, self._results.params)
else:
return np.dot(exog, params)
class HeckmanResults(base.LikelihoodModelResults):
"""
Class to represent results/fits for Heckman model.
Attributes
----------
select_res : ProbitResult object
The ProbitResult object created when estimating the selection equation.
params_inverse_mills : scalar
Parameter estimate of the coef on the inverse Mills term in the second step.
stderr_inverse_mills : scalar
Standard error of the parameter estimate of the coef on the inverse Mills
term in the second step.
var_reg_error : scalar
Estimate of the "sigma" term, i.e. the error variance estimate of the
regression (response) equation
corr_eqnerrors : scalar
Estimate of the "rho" term, i.e. the correlation estimate of the errors between the
regression (response) equation and the selection equation
method : string
The method used to produce the estimates, i.e. 'twostep', 'mle'
"""
def __init__(self, model, params, normalized_cov_params=None, scale=1.,
select_res=None,
params_inverse_mills=None, stderr_inverse_mills=None,
var_reg_error=None, corr_eqnerrors=None,
method=None):
super(HeckmanResults, self).__init__(model, params,
normalized_cov_params,
scale)
self.select_res = select_res
self.params_inverse_mills = params_inverse_mills
self.stderr_inverse_mills = stderr_inverse_mills
self.var_reg_error = var_reg_error
self.corr_eqnerrors = corr_eqnerrors
self.method = method
if not hasattr(self, 'use_t'):
self.use_t = False
if not hasattr(self.select_res, 'use_t'):
self.select_res.use_t = False
def summary(self, yname=None, xname=None, zname=None, title=None, alpha=.05):
"""Summarize the Heckman model Results
Parameters
-----------
yname : string, optional
Default is `y`
xname : list of strings, optional
Default is `x_##` for ## in p the number of regressors
in the regression (response) equation.
zname : list of strings, optional
Default is `z_##` for ## in p the number of regressors
in the selection equation.
title : string, optional
Title for the top table. If not None, then this replaces the
default title
alpha : float
significance level for the confidence intervals
Returns
-------
smry : Summary instance
this holds the summary tables and text, which can be printed or
converted to various output formats.
See Also
--------
statsmodels.iolib.summary.Summary : class to hold summary
results
"""
## Put in Z name detected from data if none supplied, unless that too could not be
## inferred from data, then put in generic names
if zname is None and self.model.exog_select_names is not None:
zname=self.model.exog_select_names
elif zname is None and self.model.exog_select_names is None:
try:
zname = ['z' + str(i) for i in range(len(self.model.exog_select[0]))]
zname[0] = 'z0_or_zconst'
except TypeError:
zname = 'z0_or_zconst'
if isinstance(zname, str):
zname = [zname]
## create summary object
# instantiate the object
smry = summary.Summary()
# add top info
if self.method=='twostep':
methodstr = 'Heckman Two-Step'
elif self.method=='mle':
methodstr = 'Heckman MLE'
else:
raise ValueError("Invalid method set")
top_left = [('Dep. Variable:', None),
('Model:', None),
('Method:', [methodstr]),
('Date:', None),
('Time:', None),
('No. Total Obs.:', ["%#i" % self.model.nobs_total]),
('No. Censored Obs.:', ["%#i" % self.model.nobs_censored]),
('No. Uncensored Obs.:', ["%#i" % self.model.nobs_uncensored]),
]
if hasattr(self, 'cov_type'):
top_left.append(('Covariance Type:', [self.cov_type]))
top_right = [
]
if title is None:
title = self.model.__class__.__name__ + ' ' + "Regression Results"
smry.add_table_2cols(self, gleft=top_left, gright=top_right,
yname=yname, xname=xname, title=title)
# add the Heckman-corrected regression table
smry.add_table_params(self, yname=yname, xname=xname, alpha=alpha,
use_t=self.use_t)
# add the selection equation estimates table
smry.add_table_params(self.select_res, yname=yname, xname=zname, alpha=alpha,
use_t=self.select_res.use_t)
# add the estimate to the inverse Mills estimate (z-score)
smry.add_table_params(
base.LikelihoodModelResults(None, np.atleast_1d(self.params_inverse_mills),
normalized_cov_params=np.atleast_1d(self.stderr_inverse_mills**2), scale=1.),
yname=None, xname=['IMR (Lambda)'], alpha=alpha,
use_t=False)
# add point estimates for rho and sigma
diagn_left = [('rho:', ["%#6.3f" % self.corr_eqnerrors]),
('sigma:', ["%#6.3f" % np.sqrt(self.var_reg_error)]),
]
diagn_right = [
]
smry.add_table_2cols(self, gleft=diagn_left, gright=diagn_right,
yname=yname, xname=xname,
title="")
# add text at end
smry.add_extra_txt(['First table are the estimates for the regression (response) equation.',
'Second table are the estimates for the selection equation.',
'Third table is the estimate for the coef of the inverse Mills ratio (Heckman\'s Lambda).'])
## return
return smry
参考文献:
Heckman两阶段法介绍