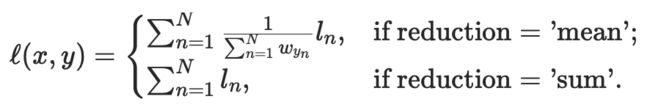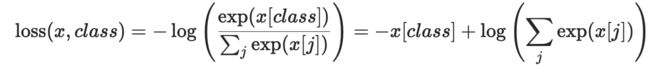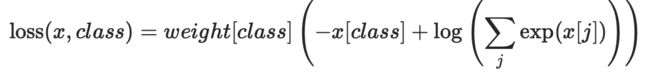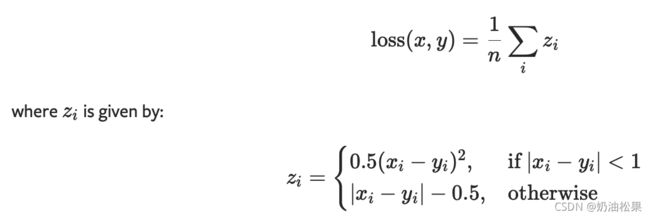Pytorch学习 - Task6 PyTorch常见的损失函数和优化器使用
Pytorch学习 - Task6 PyTorch常见的损失函数和优化器使用
- 官方参考链接
- 1. 损失函数
-
-
- (1)BCELoss 二分类
-
- 计算公式
- 小例子:
- (2) BCEWithLogitsLoss 将Sigmoid函数和BCELoss方法结合到一个类中
-
- 计算公式
- 多出参数:
- 小例子
- (3)NLLLoss(多分类问题) - 多分类的负对数似然损失函数(negative log likelihood loss)
-
- 计算公式
- 多出参数
- 小例子
- (4)CrossEntropyLoss 多分类问题 - 将nn.LogSoftmax()和nn.NLLLoss()方法结合到一个类中
-
- 计算公式
- 小例子
- (5)L1Loss(L1 norm) 计算平均绝对误差
-
- 计算公式
- 小例子
- (6)MSELoss(L2 norm) 计算均方误差
-
- 计算公式
- 小例子
- (7)SmoothL1Loss - 绝对元素误差小于1,则使用平方项。否则使用L1项。
-
- 计算公式
- 小例子
- 总结
- 常见错误
-
- 2. 优化器 - 主要使用四个
-
-
-
- 使用示例
- 具体讲解
- (1) SGD
-
- 功能
- 参数
- 小例子 - 不推荐
- (1.1)带动量Momentum的SGD - 可以一试
- (1.2)使用牛顿加速法NAG的SGD - 不如不用
- (2) RMSprop - 均方根传递 - 推荐
-
- 参数
- (3) Adam(AMSGrad) - 将Momentum算法和RMSProp算法结合起来使用的一种算法
-
- 参数
-
-
- 3. 小练习
-
-
- 题目
-
- (1)损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.1
- (2)损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.5
- (3)损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.01
-
官方参考链接
参考文档链接:损失函数
参考文档链接:【英文】优化器的使用
参考文档链接:【中文】优化器的使用
1. 损失函数
损失函数的基本用法
criterion = LossCriterion() # 构造函数有自己的参数
loss = criterion(x,y) # 调用标准时也有参数
!!! 得到的loss结果已经对mini-batch进行取平均操作
(1)BCELoss 二分类
使用
CLASS torch.nn.BCELoss(weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
'''
# BCELoss二分类
# 创建一个衡量目标和输出之间二进制交叉熵的criterion
参数:
weight(Tensor,可选) 每批元素损失的手工重标权重。如果给定,必须是一个大小为nbatch大小的张量
size_average(bool,可选)
弃用(见reduction参数)。默认情况下,设置为True,即对批处理中的每个损失元素进行平均。注意,对于某些损失,每个样本有多个元素。如果字段size_average设置为False,则对每个小批的损失求和。当reduce为False时,该参数被忽略。默认值:True
reduce(bool,可选)
弃用(见reduction参数)。默认情况下,设置为True,即根据size_average参数的值决定对每个小批的观察值是进行平均或求和。如果reduce为False,则返回每个批处理元素的损失,不进行平均和求和操作,即忽略size_average参数。默认值:True
reduction(string,可选)
指定要应用于输出的reduction,操作'none|mean|sum'。 默认值mean
'none':表示不进行任何reduction操作
'mean':求平均值,输出的和 除以输出中的元素数
'sum':输出求和
!!!指定任何size_average和reduce参数都将使reduction参数失效
形状:
输入:(N,*)
目标: (N,*) 与输入相同维度
输出:标量scalar。如果reduce为false,不做任何处理则为(N,*)
'''
计算公式
![]()
其中N代表batch size,xn为输出,yn为目标。
当reduction不同设置时,如mean和sum,返回值的变化:

小例子:
进行二分类问题时 即激活函数采用sigmoid时,常使用交叉熵作为损失函数。能够解决因sigmoid函数导致的梯度消失问题
如果使用MSELoss作为损失函数,会产生梯度消失问题。
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
m = nn.Sigmoid()
loss = nn.BCELoss()
input = torch.randn(3,requires_grad=True)
print("input: ",input)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2) # torch.empty()创建一个使用未初始化值填满的tensor
print("target: ",target)
output = loss(m(input),target)
print("m(input): ",m(input))
print("output: ",output)
output.backward()
print("output after backward: ",output)
结果:
input: tensor([-0.7129, 1.3618, 0.6582], requires_grad=True)
target: tensor([1., 0., 1.])
m(input): tensor([0.3289, 0.7961, 0.6588], grad_fn=<SigmoidBackward0>) 通过激活函数sigmoid后输出的值
output: tensor(1.0397, grad_fn=<BinaryCrossEntropyBackward0>)
output的计算 = (-1)[1*math.log(0.3289)+ 0*math.log(1-0.3289)
0*math.log(0.7961)+1*math.log(1-0.7961)+
1*math.log(0.6588)+0*math.log(1-0.6588)]/3 = 1.0397
(2) BCEWithLogitsLoss 将Sigmoid函数和BCELoss方法结合到一个类中
CLASS torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean', pos_weight=None)
计算公式
多出参数:
- pos_weight (Tensor,可选) –正值例子的权重,必须是有着与分类数目相同的长度的向量
- 参数作用:可以通过增加正值示例的权重来权衡召回率和准确性。在多标签分类的情况下,损失可以描述为:

c表示类的数量(c>1表明是多标签二进制分类,c=1表明是单标签二进制分类),n为一批中的例子数量,pc为类别c的正值的权重,解决正负例样本不均衡的情况
pc>1增加召回率,pc<1增加准确性
小例子
上一个损失函数的例子等价于
loss = nn.BCEWithLogicLoss()
input = nn.randn(3,requires_grad=True)
target = torch.empty(3).random_(2)
output = loss(input,target)
'''
区别 无需自定义m函数对input进行操作(nn.sigmoid())
'''
(3)NLLLoss(多分类问题) - 多分类的负对数似然损失函数(negative log likelihood loss)
使用:
CLASS torch.nn.NLLLoss(weight=None, size_average=None, ignore_index=-100, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
计算公式
通过转发调用给出的输入 (即nn.LogSoftmax()后的输出) 应该包含每个类的log-probability。输入要么是大小为(minibatch,C)或大小(minibatch,C,d1,d2,…,dK)的Tensor,k>=1表示k维的输入
通过在网络的最后一层添加LogSoftmax层,可以很容易地获得神经网络中的log-probability。如果不喜欢添加额外的层,可以使用CrossEntropyLoss损失函数来替代。
损失预期的目标应该是[0,c - 1]范围内的类索引,其中C =类的数量;如果指定ignore_index参数,该损失函数也接受这个类索引(这个索引不一定在类范围内)。
多出参数
- ignore_index(int,optional) - 指定一个被忽略的目标值,该目标值不影响输入梯度。当size_average为真时,对非忽略目标的损失进行平均。
小例子
# 多分类问题 低维举例
m = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
loss = nn.NLLLoss()
# input is of size N*c = 3*5
input = torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print("input : ",input)
print("m(input): ",m(input)) # 对input先进行softmax计算(转化成0-1之间的数值) 再取log 得到的都是负数
target = torch.tensor([1,0,4])
print("target: ",target)
output = loss(m(input),target)
print("output: ",output)
结果:
input : tensor([[ 0.1047, -0.5505, -0.3458, -0.1031, -0.7769],
[-0.3304, -0.7051, 0.5704, 1.2910, -0.1523],
[ 0.5005, 1.4218, 0.9723, 0.4399, -2.0973]], requires_grad=True)
m(input): tensor([[-1.2188, -1.8741, -1.6693, -1.4266, -2.1004],
[-2.3422, -2.7169, -1.4414, -0.7208, -2.1641],
[-1.8133, -0.8921, -1.3416, -1.8739, -4.4112]],
grad_fn=<LogSoftmaxBackward0>)
target: tensor([1, 0, 4])
output: tensor(2.8758, grad_fn=<NllLossBackward0>)
# 多分类问题 高维举例
N,C = 5,4
loss = nn.NLLLoss()
data = torch.randn(N,16,10,10)
print("data: ",data)
conv = nn.Conv2d(16,C,(3,3)) # 输出为5*8*8
print("conv: ",conv)
m = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
# each element in target has to in 0<=value<=C
target = torch.empty(N,8,8,dtype=torch.long).random_(0,C)
print("target:",target)
print("conv(data):",conv(data))
print("m(conv(data)):",m(conv(data)))
print("data shape : ",data.shape)
print("target shape",target.shape)
print("conv(data).shape:",conv(data).shape)
print("m(conv(data)).shape:",m(conv(data)).shape)
output = loss(m(conv(data)),target)
print("output : ",output)
print("output shape : ",output.shape)
结果:
conv: Conv2d(16, 4, kernel_size=(3, 3), stride=(1, 1))
data shape : torch.Size([5, 16, 10, 10])
conv(data).shape: torch.Size([5, 4, 8, 8])
m(conv(data)).shape: torch.Size([5, 4, 8, 8])
(4)CrossEntropyLoss 多分类问题 - 将nn.LogSoftmax()和nn.NLLLoss()方法结合到一个类中
使用:
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
当用C类训练分类问题时,它是有用的。如果提供了,可选的参数weight权重应该是一个一维张量,为每个类分配权重。当你有一个不平衡的训练集时,这是特别有用的。
每个类的输入应该包含原始的、未标准化的分数。
输入应该是大小为(minibatch,C)或大小(minibatch,C,d1,d2,…,dK)的Tensor,k>=1表示k维的输入
该criterion期望在[0,c - 1]范围内的一个类指标作为小batch大小的一维张量的每个值的目标值;如果指定ignore_index,该criterion也接受这个类索引值(这个索引不一定在类范围内)。
计算公式
小例子
上面先使用nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1),再使用nn.NLLLoss()的等价于下面这段代码
!!注意事项:nn.CrossEntropyLoss() 是一个类,应该先行进行实例化。否则会报错“RuntimeError: Boolean value of Tensor with more than one value is ambiguous”
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
input = torch.randn(3,5,requires_grad=True)
print("input:",input)
target = torch.empty(3,dtype=torch.long).random_(5)
print("target:",target)
output = loss(input,target)
print("output:",output)
(5)L1Loss(L1 norm) 计算平均绝对误差
使用:计算input x和target y中每个元素的平均绝对误差MAE
CLASS torch.nn.L1Loss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
计算公式
reduction=none
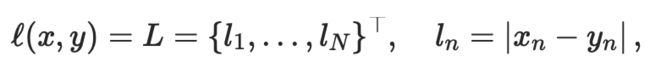
reduction = mean/sum
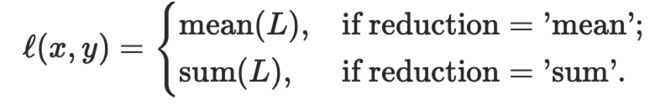
小例子
loss = nn.L1Loss()
input = torch.randn(1,2,requires_grad=True)
print("input:",input)
target = torch.randn(1,2)
print("target:",target)
output = loss(input,target)
print("output:",output)
结果:
input: tensor([[-0.3543, -0.8127]], requires_grad=True)
target: tensor([[-1.0530, -1.4032]])
output: tensor(0.6446, grad_fn=<L1LossBackward0>)
output = (abs(-0.3543+1.0530) + abs(-0.8127+1.4032))/2
(6)MSELoss(L2 norm) 计算均方误差
使用:计算input x和target y中每个元素的均方误差MAE
CLASS torch.nn.MSELoss()
loss = nn.MSELoss()
计算公式
reduction = none

reduction = mean/sum
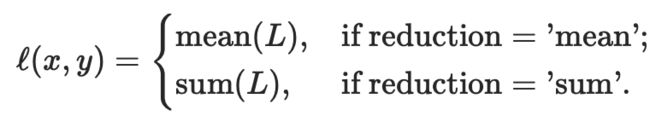
小例子
loss = nn.MSELoss()
input = torch.randn(1,2,requires_grad=True)
print("input: ",input)
target = torch.rand(1,2)
print("target: ",target)
output = loss(input,target)
print("output: ",output)
结果:
input: tensor([[-0.5910, 0.0345]], requires_grad=True)
target: tensor([[0.9664, 0.4840]])
output: tensor(1.3138, grad_fn=<MseLossBackward0>)
output = (pow((-0.5910-0.9664),2) + pow((0.0345-0.4840),2))/2 = 1.313772505
(7)SmoothL1Loss - 绝对元素误差小于1,则使用平方项。否则使用L1项。
使用:对异常值敏感度较低
CLASS torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss(size_average=None, reduce=None, reduction='mean')
计算公式
小例子
loss = nn.SmoothL1Loss()
input = torch.randn(3,2,requires_grad=True)
print("input: ",input)
target = torch.rand(3,2)
print("target: ",target)
output = loss(input,target)
print("output: ",output)
结果:
input: tensor([[ 1.2615, -0.8428],
[-1.0714, -0.4162],
[-0.4159, -1.0941]], requires_grad=True)
target: tensor([[0.0581, 0.2579],
[0.1083, 0.9786],
[0.5719, 0.9244]])
output: tensor(0.8142, grad_fn=<SmoothL1LossBackward0>)
output计算验证函数
l = input
t = target
>>> s = 0
>>> for i in range(len(l)):
... for j in range(len(l[0])):
... if abs(l[i][j] - t[i][j]) < 1:
... s+=0.5*pow((l[i][j] - t[i][j]),2)
... else:
... s += abs(l[i][j] - t[i][j]) - 0.5
... print(abs(l[i][j] - t[i][j]))
>>> output = s/6
>>> output
> 0.8141624033333335
总结
| 损失函数 | 名称 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|
| torch.nn.BCELoss() | 二分类交叉损失函数 | 二分类问题(激活函数sigmoid) |
| torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss() | 多分类交叉损失函数 | 多分类问题(sigmoid和BCELoss结合) |
| torch.nn.NLLLoss() | 多分类的负对数似然损失函数 | 多分类问题 |
| torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss() | 交叉熵损失函数 | 多分类问题 |
| torch.nn.L1Loss() | 平均绝对误差 L1 norm | 回归 |
| torch.nn.MSELoss() | 均方误差L2 norm | 回归 |
| torch.nn.SmoothL1Loss() | 平滑的L1损失 | 回归 |
常见错误
1、loss.backward()使用前不要忘记设置loss保存梯度
- 报错:“RuntimeError: element 0 of tensors does not require grad and does not have a grad_fn”
- 修改:在 backward()使用前增加 loss.requires_grad_(True)
2、在使用CrossEntropyLoss()交叉熵损失函数中遇到的问题
- 报错:IndexError: Dimension out of range (expected to be in range of [-1, 0], but got 1)
- 原因分析:参考链接: 感谢!!!!
'''
关于使用torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss()函数出现IndexError的问题详细了解
'''
# 正确的示例
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
func = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
a = torch.Tensor([[ 0.0606,0.1610,0.2990,0.2101, 0.5104],
[0.6388,0.4053, 0.4196, 0.7060, 0.2793],
[ 0.3973,0.6114, 0.1127, 0.7732, 0.0592]])
b = torch.Tensor([3,1,0])
loss = func(a,b.long())
print(loss)
结果:
loss = tensor(1.6690)
a.shape torch.Size([3, 5])
错误代码
a1 = torch.Tensor([ 0.0606,0.1610,0.2990,0.2101, 0.5104])
a2 = torch.Tensor([0.6388,0.4053, 0.4196, 0.7060, 0.2793])
a3 = torch.Tensor([ 0.3973,0.6114, 0.1127, 0.7732, 0.0592])
b1 = torch.Tensor([3])
b2 = torch.Tensor([1])
b3 = torch.Tensor([0])
loss_1 = func(a1,b1.long())
print(loss_1)
loss_2 = func(a2,b2.long())
print(loss_2)
loss_3 = func(a3,b3.long())
print(loss_3)
报错了!!
检查一下a1.shape torch.Size([5]) 维度不对了 因此需要升维
a1.unsqueeze(0) tensor([[0.0606, 0.1610, 0.2990, 0.2101, 0.5104]])
a1.unsqueeze(0).shape torch.Size([1, 5])
正确代码
a1 = torch.Tensor([ 0.0606,0.1610,0.2990,0.2101, 0.5104])
a2 = torch.Tensor([0.6388,0.4053, 0.4196, 0.7060, 0.2793])
a3 = torch.Tensor([ 0.3973,0.6114, 0.1127, 0.7732, 0.0592])
b1 = torch.Tensor([3])
b2 = torch.Tensor([1])
b3 = torch.Tensor([0])
loss_1 = func(a1.unsqueeze(0),b1.long())
print(loss_1)
loss_2 = func(a2.unsqueeze(0),b2.long())
print(loss_2)
loss_3 = func(a3.unsqueeze(0),b3.long())
print(loss_3)
结果:
tensor(1.6595)
tensor(1.7065)
tensor(1.6410)
2. 优化器 - 主要使用四个
参考博文1:
参考博文2:
torch.optim包是一个实现了各种优化算法的库。构建一个optimizer对象
常用优化器SGD/Adam/RMSprop
使用示例
import torch.optim as optim
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.01,momentum=0.9)
optimizer = optim.Adam([var1,var2],lr=0.00001)
具体讲解
(1) SGD
class torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=, momentum=0, dampening=0, weight_decay=0, nesterov=False)
功能
参数
- params 参数组,优化器需要管理的那部分参数
- lr 学习率,可随着训练过程不断调整
- momentum 动量,常设置为0.8,0.9
- dampening 暂时用不了
- weight_decay 权值衰减系数,L2正则项的系数
- nesterov bool选项,是否使用NAG??
注意事项:
pytroch中使用SGD十分需要注意的是,更新公式与其他框架略有不同!
- pytorch中是这样的:
v=ρ∗v+g
p=p−lr∗v = p - lr∗ρ∗v - lr∗g - 其他框架:
v=ρ∗v+lr∗g
p=p−v = p - ρ∗v - lr∗g - ρ是动量,v是速率,g是梯度,p是参数,其实差别就是在ρ∗v这一项,pytorch中将此项也乘了一个学习率。
小例子 - 不推荐
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.01,momentum=0.9)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss_fn(model(input),target).backward()
optimizer.step()
(1.1)带动量Momentum的SGD - 可以一试
(1.2)使用牛顿加速法NAG的SGD - 不如不用
可以理解为往标准动量中添加了一个校正因子
(2) RMSprop - 均方根传递 - 推荐
**思想:**梯度震动较大的项,在下降时,减小其下降速度;对于震动幅度小的项,在下降时,加速其下降速度
对于RNN有很好的效果
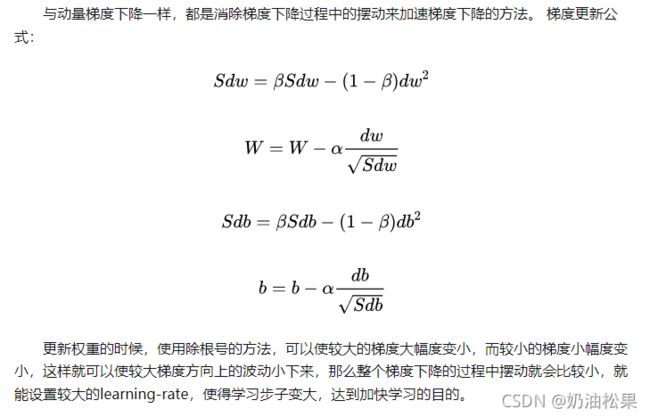
torch.optim.RMSprop(params, lr=0.01, alpha=0.99, eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0, momentum=0, centered=False)
参数
- params(iterable) 待优化参数组
- lr(float,可选) 学习率
- **alpha(float,可选) 平滑常数,默认0.99
- eps(float,可选) 为了增加数值计算的稳定性而加到分母里的项,默认:1e-8
- weight_decay(float,可选) 权重衰减L2惩罚,默认:0
- momentum(float,可选) 动量因子,默认:0
- centered(bool,可选) 如果为True,计算中心化的RMSProp,并且用它的方差预测值对梯度进行归一化**
(3) Adam(AMSGrad) - 将Momentum算法和RMSProp算法结合起来使用的一种算法
torch.optim.Adam(params, lr=0.001, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-08, weight_decay=0)
参数
- params
- lr 默认1e-3
- betas (Tuple[float,float], 可选) – 用于计算梯度以及梯度平方的运行平均值的系数(默认:0.9,0.999)
- eps 为了增加数值计算的稳定性而加到分母里的项,默认:1e-8
- weight_decay 权重衰减系数
3. 小练习
题目
设置不同的优化器和学习率,重复任务2的回归过程
1. 损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.1
2. 损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.5
3. 损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.01
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net,self).__init__()
self.w = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.tensor([7.]))
self.b = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.tensor([6.]))
def forward(self,x):
return self.w * x+self.b
(1)损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.1
net = Net()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr=0.1)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
for step in range(1000):
output = net(x)
loss = loss_func(output,y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if step%10 == 0:
print(loss)
(2)损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.5
net = Net()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr=0.5)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
for step in range(1000):
output = net(x)
loss = loss_func(output,y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if step%10 == 0:
print(loss)
(3)损失函数MSE、优化器SGD、学习率0.01
net = Net()
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(),lr=0.01)
loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss()
for step in range(1000):
output = net(x)
loss = loss_func(output,y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
if step%10 == 0:
print(loss)