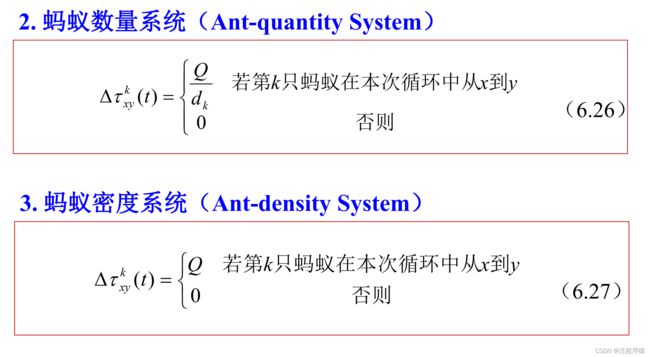
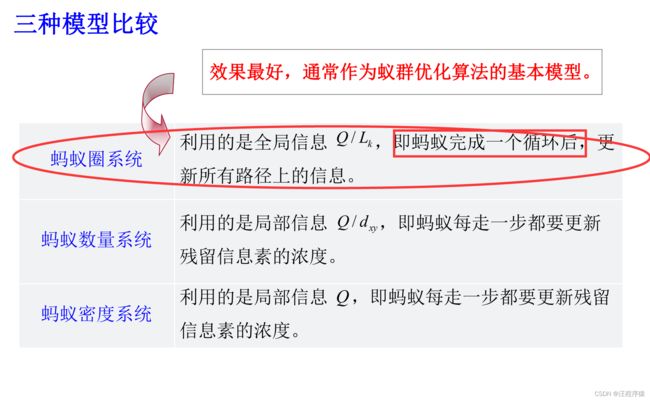
群智能算法及其应用(蚁群算法和粒子群算法)
粒子群算法
粒子群优化算法及其应用
粒子群优化算法流程图
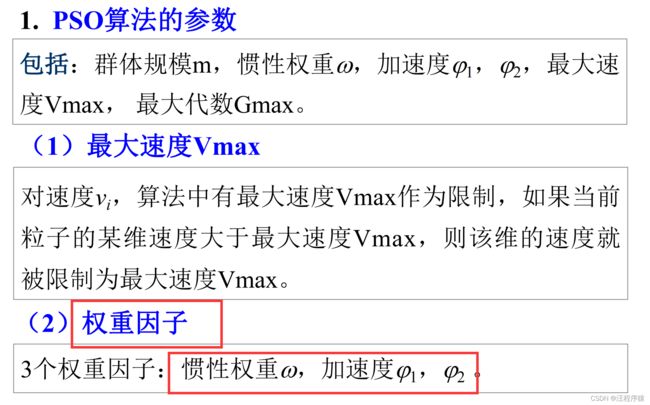
粒子群优化算法的参数分析
粒子群算法解决TSP问题
项目结构
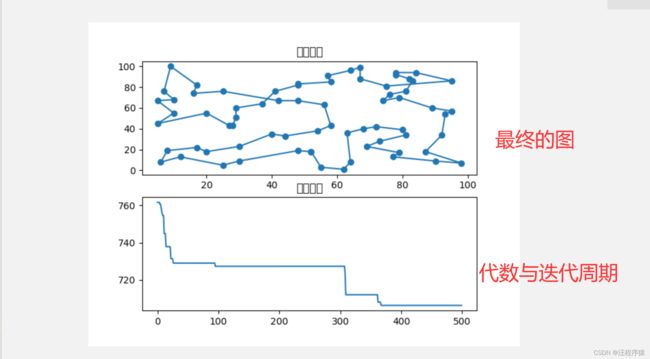
运行截图
数据集
NAME: st70
TYPE: TSP
COMMENT: 70-city problem (Smith/Thompson)
DIMENSION: 70
EDGE_WEIGHT_TYPE : EUC_2D
NODE_COORD_SECTION
1 64 96
2 80 39
3 69 23
4 72 42
5 48 67
6 58 43
7 81 34
8 79 17
9 30 23
10 42 67
11 7 76
12 29 51
13 78 92
14 64 8
15 95 57
16 57 91
17 40 35
18 68 40
19 92 34
20 62 1
21 28 43
22 76 73
23 67 88
24 93 54
25 6 8
26 87 18
27 30 9
28 77 13
29 78 94
30 55 3
31 82 88
32 73 28
33 20 55
34 27 43
35 95 86
36 67 99
37 48 83
38 75 81
39 8 19
40 20 18
41 54 38
42 63 36
43 44 33
44 52 18
45 12 13
46 25 5
47 58 85
48 5 67
49 90 9
50 41 76
51 25 76
52 37 64
53 56 63
54 10 55
55 98 7
56 16 74
57 89 60
58 48 82
59 81 76
60 29 60
61 17 22
62 5 45
63 79 70
64 9 100
65 17 82
66 74 67
67 10 68
68 48 19
69 83 86
70 84 94
EOF
代码
import random
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 作者:WWS(山东工商学院)
class PSO(object):
def __init__(self, num_city, data):
# 初始化参数
self.iter_max = 500 # 迭代数目
self.num = 200 # 粒子数目
self.num_city = num_city # 城市数
self.location = data # 城市的位置坐标
# 计算距离矩阵
self.dis_mat = self.compute_dis_mat(num_city, self.location) # 计算城市之间的距离矩阵
# 初始化所有粒子
self.particals = self.greedy_init(self.dis_mat,num_total=self.num,num_city =num_city)
self.lenths = self.compute_paths(self.particals)
# 得到初始化群体的最优解
init_l = min(self.lenths)
init_index = self.lenths.index(init_l)
init_path = self.particals[init_index]
# 画出初始的路径图
init_show = self.location[init_path]
# 记录每个个体的当前最优解
self.local_best = self.particals
self.local_best_len = self.lenths
# 记录当前的全局最优解,长度是iteration
self.global_best = init_path
self.global_best_len = init_l
# 输出解
self.best_l = self.global_best_len
self.best_path = self.global_best
# 存储每次迭代的结果,画出收敛图
self.iter_x = [0]
self.iter_y = [init_l]
def greedy_init(self, dis_mat, num_total, num_city):
start_index = 0
result = []
for i in range(num_total):
rest = [x for x in range(0, num_city)]
# 所有起始点都已经生成了
if start_index >= num_city:
start_index = np.random.randint(0, num_city)
result.append(result[start_index].copy())
continue
current = start_index
rest.remove(current)
# 找到一条最近邻路径
result_one = [current]
while len(rest) != 0:
tmp_min = math.inf
tmp_choose = -1
for x in rest:
if dis_mat[current][x] < tmp_min:
tmp_min = dis_mat[current][x]
tmp_choose = x
current = tmp_choose
result_one.append(tmp_choose)
rest.remove(tmp_choose)
result.append(result_one)
start_index += 1
return result
# 随机初始化
def random_init(self, num_total, num_city):
tmp = [x for x in range(num_city)]
result = []
for i in range(num_total):
random.shuffle(tmp)
result.append(tmp.copy())
return result
# 计算不同城市之间的距离
def compute_dis_mat(self, num_city, location):
dis_mat = np.zeros((num_city, num_city))
for i in range(num_city):
for j in range(num_city):
if i == j:
dis_mat[i][j] = np.inf
continue
a = location[i]
b = location[j]
tmp = np.sqrt(sum([(x[0] - x[1]) ** 2 for x in zip(a, b)]))
dis_mat[i][j] = tmp
return dis_mat
# 计算一条路径的长度
def compute_pathlen(self, path, dis_mat):
a = path[0]
b = path[-1]
result = dis_mat[a][b]
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
a = path[i]
b = path[i + 1]
result += dis_mat[a][b]
return result
# 计算一个群体的长度
def compute_paths(self, paths):
result = []
for one in paths:
length = self.compute_pathlen(one, self.dis_mat)
result.append(length)
return result
# 评估当前的群体
def eval_particals(self):
min_lenth = min(self.lenths)
min_index = self.lenths.index(min_lenth)
cur_path = self.particals[min_index]
# 更新当前的全局最优
if min_lenth < self.global_best_len:
self.global_best_len = min_lenth
self.global_best = cur_path
# 更新当前的个体最优
for i, l in enumerate(self.lenths):
if l < self.local_best_len[i]:
self.local_best_len[i] = l
self.local_best[i] = self.particals[i]
# 粒子交叉
def cross(self, cur, best):
one = cur.copy()
l = [t for t in range(self.num_city)]
t = np.random.choice(l,2)
x = min(t)
y = max(t)
cross_part = best[x:y]
tmp = []
for t in one:
if t in cross_part:
continue
tmp.append(t)
# 两种交叉方法
one = tmp + cross_part
l1 = self.compute_pathlen(one, self.dis_mat)
one2 = cross_part + tmp
l2 = self.compute_pathlen(one2, self.dis_mat)
if l1<l2:
return one, l1
else:
return one, l2
# 粒子变异
def mutate(self, one):
one = one.copy()
l = [t for t in range(self.num_city)]
t = np.random.choice(l, 2)
x, y = min(t), max(t)
one[x], one[y] = one[y], one[x]
l2 = self.compute_pathlen(one,self.dis_mat)
return one, l2
# 迭代操作
def pso(self):
for cnt in range(1, self.iter_max):
# 更新粒子群
for i, one in enumerate(self.particals):
tmp_l = self.lenths[i]
# 与当前个体局部最优解进行交叉
new_one, new_l = self.cross(one, self.local_best[i])
if new_l < self.best_l:
self.best_l = tmp_l
self.best_path = one
if new_l < tmp_l or np.random.rand()<0.1:
one = new_one
tmp_l = new_l
# 与当前全局最优解进行交叉
new_one, new_l = self.cross(one, self.global_best)
if new_l < self.best_l:
self.best_l = tmp_l
self.best_path = one
if new_l < tmp_l or np.random.rand()<0.1:
one = new_one
tmp_l = new_l
# 变异
one, tmp_l = self.mutate(one)
if new_l < self.best_l:
self.best_l = tmp_l
self.best_path = one
if new_l < tmp_l or np.random.rand()<0.1:
one = new_one
tmp_l = new_l
# 更新该粒子
self.particals[i] = one
self.lenths[i] = tmp_l
# 评估粒子群,更新个体局部最优和个体当前全局最优
self.eval_particals()
# 更新输出解
if self.global_best_len < self.best_l:
self.best_l = self.global_best_len
self.best_path = self.global_best
print(cnt, self.best_l)
self.iter_x.append(cnt)
self.iter_y.append(self.best_l)
return self.best_l, self.best_path
def run(self):
best_length, best_path = self.pso()
# 画出最终路径
return self.location[best_path], best_length
# 读取数据
def read_tsp(path):
lines = open(path, 'r').readlines()
assert 'NODE_COORD_SECTION\n' in lines
index = lines.index('NODE_COORD_SECTION\n')
data = lines[index + 1:-1]
tmp = []
for line in data:
line = line.strip().split(' ')
# EOF为结束
if line[0] == 'EOF':
continue
tmpline = []
for x in line:
if x == '':
continue
else:
tmpline.append(float(x))
if tmpline == []:
continue
tmp.append(tmpline)
data = tmp
return data
# 读取数据
data = read_tsp('data/st70.tsp')
data = np.array(data)
data = data[:, 1:]
# 加上一行因为会回到起点
show_data = np.vstack([data, data[0]])
model = PSO(num_city=data.shape[0], data=data.copy())
Best_path, Best = model.run()
Best_path = np.vstack([Best_path, Best_path[0]])
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=False, sharey=False)
axs[0].scatter(Best_path[:, 0], Best_path[:,1])
Best_path = np.vstack([Best_path, Best_path[0]])
axs[0].plot(Best_path[:, 0], Best_path[:, 1])
axs[0].set_title('规划结果')
iterations = model.iter_x
best_record = model.iter_y
axs[1].plot(iterations, best_record)
axs[1].set_title('收敛曲线')
plt.show()
蚁群算法
蚁群算法及其应用
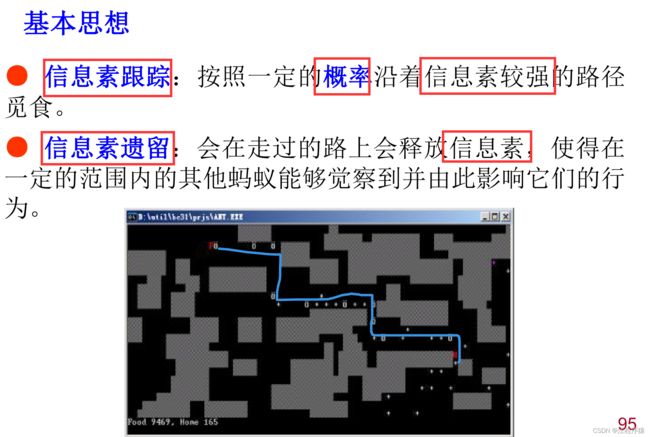
基本蚁群算法模型
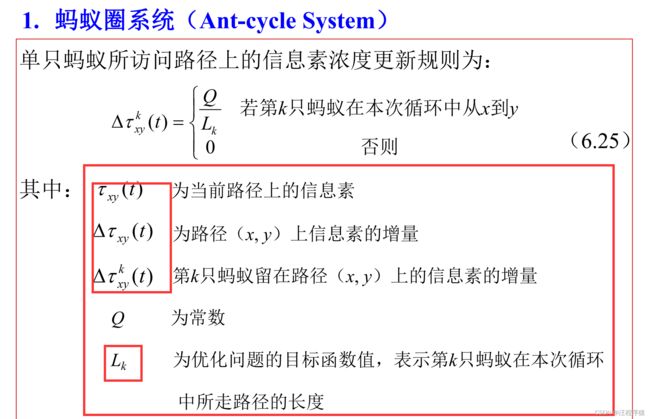
蚁群算法的解决TSP问题
项目结构
运行截图


这个图看样子是乱七八糟,但是距离为705,和粒子群算法结果几乎一直。
代码
这里使用的数据集和粒子群里面的数据集是同一个。
import random
import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 作者:WWS(山东工商学院)
class ACO(object):
def __init__(self, num_city, data):
self.m = 50 # 蚂蚁数量
self.alpha = 1 # 信息素重要程度因子
self.beta = 5 # 启发函数重要因子
self.rho = 0.1 # 信息素挥发因子
self.Q = 1 # 常量系数
self.num_city = num_city # 城市规模
self.location = data # 城市坐标
self.Tau = np.zeros([num_city, num_city]) # 信息素矩阵
self.Table = [[0 for _ in range(num_city)] for _ in range(self.m)] # 生成的蚁群
self.iter = 1
self.iter_max = 500
self.dis_mat = self.compute_dis_mat(num_city, self.location) # 计算城市之间的距离矩阵
self.Eta = 10. / self.dis_mat # 启发式函数
self.paths = None # 蚁群中每个个体的长度
# 存储存储每个温度下的最终路径,画出收敛图
self.iter_x = []
self.iter_y = []
# self.greedy_init(self.dis_mat,100,num_city)
def greedy_init(self, dis_mat, num_total, num_city):
start_index = 0
result = []
for i in range(num_total):
rest = [x for x in range(0, num_city)]
# 所有起始点都已经生成了
if start_index >= num_city:
start_index = np.random.randint(0, num_city)
result.append(result[start_index].copy())
continue
current = start_index
rest.remove(current)
# 找到一条最近邻路径
result_one = [current]
while len(rest) != 0:
tmp_min = math.inf
tmp_choose = -1
for x in rest:
if dis_mat[current][x] < tmp_min:
tmp_min = dis_mat[current][x]
tmp_choose = x
current = tmp_choose
result_one.append(tmp_choose)
rest.remove(tmp_choose)
result.append(result_one)
start_index += 1
pathlens = self.compute_paths(result)
sortindex = np.argsort(pathlens)
index = sortindex[0]
result = result[index]
for i in range(len(result)-1):
s = result[i]
s2 = result[i+1]
self.Tau[s][s2]=1
self.Tau[result[-1]][result[0]] = 1
# for i in range(num_city):
# for j in range(num_city):
# return result
# 轮盘赌选择
def rand_choose(self, p):
x = np.random.rand()
for i, t in enumerate(p):
x -= t
if x <= 0:
break
return i
# 生成蚁群
def get_ants(self, num_city):
for i in range(self.m):
start = np.random.randint(num_city - 1)
self.Table[i][0] = start
unvisit = list([x for x in range(num_city) if x != start])
current = start
j = 1
while len(unvisit) != 0:
P = []
# 通过信息素计算城市之间的转移概率
for v in unvisit:
P.append(self.Tau[current][v] ** self.alpha * self.Eta[current][v] ** self.beta)
P_sum = sum(P)
P = [x / P_sum for x in P]
# 轮盘赌选择一个一个城市
index = self.rand_choose(P)
current = unvisit[index]
self.Table[i][j] = current
unvisit.remove(current)
j += 1
# 计算不同城市之间的距离
def compute_dis_mat(self, num_city, location):
dis_mat = np.zeros((num_city, num_city))
for i in range(num_city):
for j in range(num_city):
if i == j:
dis_mat[i][j] = np.inf
continue
a = location[i]
b = location[j]
tmp = np.sqrt(sum([(x[0] - x[1]) ** 2 for x in zip(a, b)]))
dis_mat[i][j] = tmp
return dis_mat
# 计算一条路径的长度
def compute_pathlen(self, path, dis_mat):
a = path[0]
b = path[-1]
result = dis_mat[a][b]
for i in range(len(path) - 1):
a = path[i]
b = path[i + 1]
result += dis_mat[a][b]
return result
# 计算一个群体的长度
def compute_paths(self, paths):
result = []
for one in paths:
length = self.compute_pathlen(one, self.dis_mat)
result.append(length)
return result
# 更新信息素
def update_Tau(self):
delta_tau = np.zeros([self.num_city, self.num_city])
paths = self.compute_paths(self.Table)
for i in range(self.m):
for j in range(self.num_city - 1):
a = self.Table[i][j]
b = self.Table[i][j + 1]
delta_tau[a][b] = delta_tau[a][b] + self.Q / paths[i]
a = self.Table[i][0]
b = self.Table[i][-1]
delta_tau[a][b] = delta_tau[a][b] + self.Q / paths[i]
self.Tau = (1 - self.rho) * self.Tau + delta_tau
def aco(self):
best_lenth = math.inf
best_path = None
for cnt in range(self.iter_max):
# 生成新的蚁群
self.get_ants(self.num_city) # out>>self.Table
self.paths = self.compute_paths(self.Table)
# 取该蚁群的最优解
tmp_lenth = min(self.paths)
tmp_path = self.Table[self.paths.index(tmp_lenth)]
# 可视化初始的路径
if cnt == 0:
init_show = self.location[tmp_path]
init_show = np.vstack([init_show, init_show[0]])
# 更新最优解
if tmp_lenth < best_lenth:
best_lenth = tmp_lenth
best_path = tmp_path
# 更新信息素
self.update_Tau()
# 保存结果
self.iter_x.append(cnt)
self.iter_y.append(best_lenth)
print(cnt,best_lenth)
return best_lenth, best_path
def run(self):
best_length, best_path = self.aco()
return self.location[best_path], best_length
# 读取数据
def read_tsp(path):
lines = open(path, 'r').readlines()
assert 'NODE_COORD_SECTION\n' in lines
index = lines.index('NODE_COORD_SECTION\n')
data = lines[index + 1:-1]
tmp = []
for line in data:
line = line.strip().split(' ')
if line[0] == 'EOF':
continue
tmpline = []
for x in line:
if x == '':
continue
else:
tmpline.append(float(x))
if tmpline == []:
continue
tmp.append(tmpline)
data = tmp
return data
data = read_tsp('data/st70.tsp')
data = np.array(data)
data = data[:, 1:]
# 加上一行因为会回到起点
show_data = np.vstack([data, data[0]])
aco = ACO(num_city=data.shape[0], data=data.copy())
Best_path, Best = aco.run()
print(Best)
Best_path = np.vstack([Best_path, Best_path[0]])
plt.plot(Best_path[:, 0], Best_path[:, 1])
plt.title('st70:蚁群算法规划结果')
plt.show()
资料参考:
人工智能导论浙江工业大学