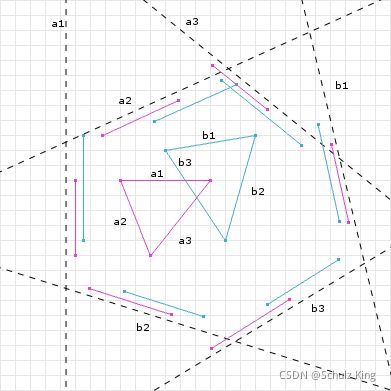
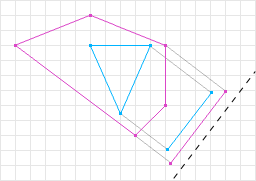
- Django REST framework - 序列器关系
djangopython
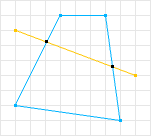
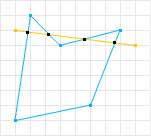
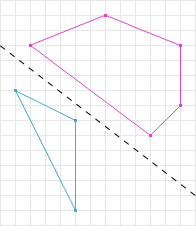
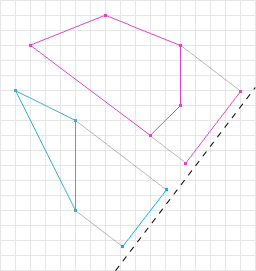
简介数据结构而非算法是编程的核心。—RobPike关系字段用于表示模型间的关系。它们可以应用于ForeignKey、ManyToManyField和OneToOneField关系,以及反向关系和自定义关系(如GenericForeignKey)。注意:关系字段在relations.py中声明,但按照惯例,应从serializers模块导入,使用fromrest_frameworkimportser
- 后端Spring Data Elasticsearch的集群故障恢复
AI大模型应用实战
springelasticsearchjavaai
后端SpringDataElasticsearch的集群故障恢复关键词:SpringDataElasticsearch、集群故障恢复、分布式系统、故障处理、数据一致性摘要:本文围绕后端SpringDataElasticsearch的集群故障恢复展开深入探讨。首先介绍了相关背景,包括目的范围、预期读者等。接着阐述了核心概念与联系,详细讲解了核心算法原理及具体操作步骤,并结合数学模型和公式进行说明。通
- LeetCode第300题_最长递增子序列
@蓝莓果粒茶
算法leetcode算法职场和发展学习c#游戏python
LeetCode第300题:最长递增子序列文章摘要本文详细解析LeetCode第300题"最长递增子序列",这是一道考察动态规划和二分查找的中等难度题目。文章提供了动态规划和贪心+二分查找两种实现方案,包含C#、Python、C++三种语言实现,配有详细的算法分析和性能对比。适合学习动态规划和二分查找的读者。核心知识点:动态规划、二分查找、贪心算法难度等级:中等推荐人群:具备基础算法知识,想要提升
- LeetCode第301题_删除无效括号
@蓝莓果粒茶
算法leetcode算法职场和发展c#学习pythonc++
LeetCode第301题:删除无效括号文章摘要本文详细解析LeetCode第301题"删除无效括号",这是一道考察DFS和括号匹配的困难难度题目。文章提供了DFS和BFS两种实现方案,包含C#、Python、C++三种语言实现,配有详细的算法分析和性能对比。适合学习深度优先搜索和字符串处理的读者。核心知识点:DFS、BFS、括号匹配、字符串处理难度等级:困难推荐人群:具备基础算法知识,想要提升搜
- Java 访问HTTP,信任所有证书,解决SSL报错问题
qq_492448446
javahttpssl
packagecom.welab.automation.framework.utils.api;importcom.welab.automation.framework.GlobalVar;importcom.welab.automation.framework.utils.entity.api.SignatureUtil;importorg.apache.http.HttpEntity;impo
- Python binary search二分查找算法详解及源码
猿来如此yyy
Python算法详解及源码算法python排序算法开发语言数据库人工智能数据结构
二分查找算法是一种在有序数组中查找特定元素的常用算法。它的基本思想是将要查找的元素与数组的中间元素进行比较,如果相等,则返回该元素的索引;如果要查找的元素比中间元素小,则在数组的左半部分继续查找;如果要查找的元素比中间元素大,则在数组的右半部分继续查找。通过不断缩小查找范围,最终可以找到要查找的元素或确定该元素不存在于数组中。二分查找算法的优点是时间复杂度为O(logn),效率较高。这是因为每一次
- 华为OD 机试 2025 B卷 - 最大报酬 (C++&Python&JAVA&JS&GO)
无限码力
华为OD机试真题刷题笔记华为od算法华为OD2025B卷华为OD机试2025B卷华为OD机考2025B卷
最大报酬2025B卷目录点击查看:华为OD机试2025B卷真题题库目录|机考题库+算法考点详解2025B卷100分题型题目描述小明每周上班都会拿到自己的工作清单,工作清单内包含n项工作,每项工作都有对应的耗时时间(单位h)和报酬,工作的总报酬为所有已完成工作的报酬之和,那么请你帮小明安排一下工作,保证小明在指定的工作时间内工作收入最大化。输入描述T代表工作时长(单位h,00),w代表该项工作的报酬
- 华为OD机试2025B卷 - 比赛 (C++ & Python & JAVA & JS & GO)
无限码力
华为OD机试真题刷题笔记华为od华为OD2025B卷华为OD机考2025B卷华为OD机试华为OD机试2025B卷
比赛2025B卷目录点击查看:华为OD机试2025B卷真题题库目录|机考题库+算法考点详解华为OD2025B卷100分题型题目描述一个有N个选手参加比赛,选手编号为1~N(3<=N<=100),有M(3<=M<=10)个评委对选手进行打分。打分规则为每个评委对选手打分,最高分10分,最低分1分。请计算得分最多的3位选手的编号。如果得分相同,则得分高分值最多的选手排名靠前(10分数量相同,则比较9分
- 基于OpenCv的运动物体检测算法
Liu_LongPo
计算机视觉OpenCv运动物体检测
基于一个实现的基于OpenCv的运动物体检测算法,可以用于检测行人或者其他运动物体。#include#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char**argv){//声明IplImage指针IplImage*pFrame=NULL;IplImage*pFrImg=NULL;IplImage*pBkImg=NULL;CvMat*pFrameMat=NULL;
- 免费小学口算出题器:自动生成语数英题目 支持打印导出
小龙软件库
开源软件电脑windows
各位家有小学生的宝爸宝妈们,还有辛勤的老师们,快来听我说!你们有没有过这样的经历,想给孩子找点合适的练习题,结果翻遍资料也找不到,累得头晕眼花?别急,小学生出题软件这一神器闪亮登场啦!软件下载地址这软件就是专门给小学阶段孩子量身打造的智能教育小帮手。它能帮家长和老师轻松地弄出符合孩子学习进度的练习题。软件有个预设算法,能自动生成数学、语文、英语这些科目的题目。数学题那是应有尽有,加减乘除、分数运算
- 关联规则算法学习—Apriori
Did然
数据挖掘算法学习python数据挖掘
关联规则算法学习—Apriori一、实验项目:关联规则算法学习项目性质:设计型二、实验目的:理解并掌握关联规则经典算法Apriori算法,理解算法的原理,能够实现算法,并对给定的数据集进行关联规则挖掘三、实验内容:1、实现Apriori算法,验证算法的正确性,并将算法应用于给定的数据集Groceries,根据设定的支持度和置信度,挖掘出符合条件的频繁项集及关联规则。2、挑选几个有代表性的频繁项集和
- 关联规则挖掘--Apriori算法
别团等shy哥发育
数据挖掘与机器学习算法数据挖掘机器学习Apriori
关联规则挖掘--Apriori算法1、关联规则概述2、置信度、支持度、提升度的概念3、关联规则挖掘问题4、Apriori算法4.1算法步骤4.2先验原理4.3寻找最大频繁项的过程4.4注意问题:项的连接5、代码实战1、关联规则概述 关联规则(AssociationRules)反映一个事物与其他事物之间的相互依存性和关联性。如果两个或者多个事物之间存在一定的关联关系,那么,其中一个事物就能够通过其
- 数据挖掘 关联规则挖掘 Apriori算法 C++实现
王者灵梦
数据挖掘c++机器学习
提示:文章写完后,目录可以自动生成,如何生成可参考右边的帮助文档文章目录前言一、Apriori是什么,大致步骤?二、全部代码全部代码总结前言本文只是基于课程作业的相关理解,请谨慎参考,如有不妥,欢迎各位批评指正。一、Apriori是什么,大致步骤?示例:Apriori算法是一种最有影响的布尔关联规则频繁项集的算法,Apriori使用一乘坐逐层扫描的迭代方法,“K-1”项集用于搜索“K”项集。大致步
- FP16、BF16、INT8、INT4精度模型加载所需显存以及硬件适配的分析
herosunly
大模型精度BF16硬件适配
大家好,我是herosunly。985院校硕士毕业,现担任算法研究员一职,热衷于机器学习算法研究与应用。曾获得阿里云天池比赛第一名,CCF比赛第二名,科大讯飞比赛第三名。拥有多项发明专利。对机器学习和深度学习拥有自己独到的见解。曾经辅导过若干个非计算机专业的学生进入到算法行业就业。希望和大家一起成长进步。 本文主要介绍了FP16、INT8、INT4精度模型加载占用显存大小的分析,希望对学习大
- educoder机器学习 --- 神经网络
木右加木
educoder机器学习神经网络
第1关:神经网络基本概念1、C第2关:激活函数#encoding=utf8defrelu(x):'''x:负无穷到正无穷的实数'''#*********Begin*********#ifx<=0:return0else:returnx#*********End*********#第3关:反向传播算法#encoding=utf8importosimportpandasaspdfromsklearn.
- 回归预测 | MATLAB实现LSTM-SVR(长短期记忆神经网络-支持向量机)多输入单输出
matlab科研社
神经网络回归matlab
✅作者简介:热爱数据处理、数学建模、仿真设计、论文复现、算法创新的Matlab仿真开发者。更多Matlab代码及仿真咨询内容点击主页:Matlab科研工作室个人信条:格物致知,期刊达人。内容介绍长短期记忆神经网络(LSTM)作为一种循环神经网络(RNN)的变体,擅长处理序列数据并捕捉长期依赖关系,而支持向量机(SVR)则是一种强大的回归算法,能够有效地处理高维数据并防止过拟合。将两者结合的LSTM
- SSVEP Next:现代化的 SSVEP 可视化 Web 快速实现
框架主义者
web脑机接口
SSVEPNext:现代化的SSVEP可视化Web快速实现在线使用|GithubSSVEP-Next是一个基于React、TypeScript和Vite构建的单页面应用(SPA),用于快速设计和运行稳态视觉诱发电位(SSVEP)实验的视觉刺激界面。该项目继承自quick-ssvep的核心科学算法,并在架构和交互体验上进行了全面升级。主要特性包括:拖拽式可视化设计:用户可通过拖拽和属性面板,直观地在
- C++贪心算法
kobe_zlx
c++贪心算法开发语言
目录一,定义二,特点三,使用四,步骤:1.将问题分解为若干个问题2.找出适合该题目的贪心策略3.求解每个子问题的最优解4.组合局部最优解五,例题:1,最优装载题目分析(个人想法):详见代码:2,删数问题题目分析:ACcode一,定义贪心算法(greedyalgorithm)是指,在对问题求解时,总是做出在当前看来是最好的选择。也就是说,不从整体最优上加以考虑,得到的是在某种意义上的局部最优解二,特
- C++算法——贪心算法的讲解与实践
不東工作室
算法c++贪心算法
目录引言贪心算法概述贪心算法的适用条件贪心算法的实现步骤C++实现贪心算法问题:硬币找零问题C++代码实现总结参考文献引言在算法的世界中,贪心算法是一种在每一步选择中都采取在当前状态下最好或最优的选择,从而希望导致结果是全局最好或最优的算法策略。这种算法简单易懂,且在某些问题上能够快速得到近似最优解。本文将通过C++语言对贪心算法进行讲解,并结合实际例子来展示其应用。贪心算法概述贪心算法在解决问题
- Java 里 Hibernate 的多租户架构实现
AI大模型应用实战
javahibernate架构ai
Java里Hibernate的多租户架构实现关键词:Java、Hibernate、多租户架构、多租户实现、数据隔离摘要:本文深入探讨了在Java中利用Hibernate实现多租户架构的相关技术。首先介绍了多租户架构的背景和意义,包括目的、预期读者、文档结构以及相关术语。接着阐述了Hibernate多租户的核心概念,给出了原理和架构的文本示意图与Mermaid流程图。详细讲解了核心算法原理,通过Py
- Lynda.com软件教程英文字幕集锦
mater lai
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:Lynda.com平台上的英文字幕文件汇集了从基础到高级的各类软件教程,涵盖AutodeskMaya、AdobeIllustrator、MicrosoftPowerPoint、AdobePhotoshop、Windows7操作系统、3dsMax、AutoCAD以及AdobeAfterEffects的使用和技巧。这些字幕文件为学习者提供了精准理解软件操作和技术术
- 深度学习 vs 传统机器学习:哪个更适合你的项目?
AI大模型应用之禅
深度学习机器学习人工智能ai
深度学习vs传统机器学习:哪个更适合你的项目?关键词:深度学习、传统机器学习、特征工程、数据量、计算资源、项目选择、算法对比摘要:本文将用"炒菜"和"拼图"等生活案例,从核心原理、适用场景、资源需求等维度对比深度学习与传统机器学习。通过具体代码示例和真实项目场景分析,帮助开发者和企业决策者快速判断:你的项目该选深度学习还是传统机器学习?背景介绍目的和范围随着AI技术普及,"该用深度学习还是传统机器
- colour-demosaicing:实现多款CFA去马赛克算法的Python开源包
常琚蕙
colour-demosaicing:实现多款CFA去马赛克算法的Python开源包colour-demosaicingCFA(ColourFilterArray)DemosaicingAlgorithmsforPython项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/co/colour-demosaicing项目介绍在数字图像处理领域,马赛克效应(Mosaicing)是
- 【python数据分析】数据建模之Kmeans聚类
斑点鱼 SpotFish
python数据建模聚类python数据分析
K-means聚类:最常用的机器学习聚类算法,且为典型的基于距离的聚类算法。K均值:基于原型的、划分的距离技术,它试图发现用户指定个数(K)的簇以欧式距离作为相似度测度Kmeans聚类案例分析:make_blobs聚类数据生成器#导入模块from sklearn.cluster import KMeansfromsklearn.datasetsimportmake_blobs#创建数据x,y_tr
- Golang领域GOROOT的配置与使用技巧
Golang编程笔记
golang爬虫开发语言ai
Golang领域GOROOT的配置与使用技巧关键词:Golang,GOROOT,配置,使用技巧,环境变量摘要:本文详细介绍了Golang领域中GOROOT的相关知识。首先阐述了GOROOT的背景,包括其目的、适用读者、文档结构和相关术语。接着深入解析了GOROOT的核心概念及与其他关键元素的联系,并通过Mermaid流程图展示其架构。之后详细讲解了GOROOT配置的核心算法原理及具体操作步骤,配以
- 常见机器学习算法与应用场景
计算机软件程序设计
知识科普机器学习算法人工智能
当然可以。下面是对常见机器学习算法的全面详细阐述,包括每种算法的基本原理、特点以及典型应用场景。1.监督学习(SupervisedLearning)1.1线性回归(LinearRegression)原理:通过拟合一条直线来表示输入和输出之间的关系,适用于预测连续值输出。特点:简单易懂,计算速度快,但只能捕捉线性关系。应用场景:房价预测股票价格预测销售额预测1.2逻辑回归(LogisticRegre
- python安装apk到手机_Python3 UI 自动化通过线程解决安装 apk 时的权限弹窗 (一)
张云雷宝宝
python安装apk到手机
#-*-coding:utf-8-*-#@author:xiaoxiao#@date:2019/4/6importthreadingimportosimportuiautomator2asu2driver=u2.connect("882QADT9UWT")classusb_install_thread(threading.Thread):#安装确认def__init__(self):threadi
- 自动化时候的坑:adb install时如何处理可恶的风险管控弹窗或者未知来源应用弹窗!
dialogtwb
ui自动化多线程adbpython软件测试
各位在自动化通过adbinstall或者pminstall的时候,有没有遇到过华为或者小米或者一加手机的各种安装弹窗呢,除了手动设置,该如何解决呢?目前自动化主流框架,pythonuiautomator2或者appuim等在执行测试的时候会自动给手机安装atx或者appuim引擎,但是如果不手动的点击允许,那么会导致测试失败,这种情况改如果处理呢?下面提供一种多线程的解决方案,亲测可行1个线程执行
- LeetCode 70:爬楼梯|递归到动态规划全路径解析
kiki_2411
算法设计与分析leetcode动态规划算法
本篇博客将通过LeetCode第70题“ClimbingStairs”为例,系统讲解从递归暴力解法到记忆化搜索、再到动态规划及空间优化的四种典型思路,适合算法初学者深入掌握递归与DP基础。文章目录LeetCode70|爬楼梯一、题目描述二、思路分析三、方法一:递归(不带记忆)思路C++代码四、方法二:递归+记忆化搜索(Top-DownDP)思路五、方法三:动态规划(Bottom-Up)思路六、方法
- 深入理解HashMap:从数据结构到高并发战场
达利源
java面试题哈希算法散列表算法
以下是我在财税业务中的自我体会:一、核心矛盾与设计哲学想象一个存放千万级纳税人信息的仓库(Map)。你需要:极速存取:输入ID,瞬间定位到对象。动态扩容:纳税人数量激增时,仓库能自动变大。空间高效:避免仓库大部分区域空置。线程安全(可选):多窗口(线程)同时办理业务不混乱。HashMap的答卷:核心武器:数组+链表/红黑树灵魂算法:哈希函数(HashFunction)扩容策略:负载因子(LoadF
- rust的指针作为函数返回值是直接传递,还是先销毁后创建?
wudixiaotie
返回值
这是我自己想到的问题,结果去知呼提问,还没等别人回答, 我自己就想到方法实验了。。
fn main() {
let mut a = 34;
println!("a's addr:{:p}", &a);
let p = &mut a;
println!("p's addr:{:p}", &a
- java编程思想 -- 数据的初始化
百合不是茶
java数据的初始化
1.使用构造器确保数据初始化
/*
*在ReckInitDemo类中创建Reck的对象
*/
public class ReckInitDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建Reck对象
new Reck();
}
}
- [航天与宇宙]为什么发射和回收航天器有档期
comsci
地球的大气层中有一个时空屏蔽层,这个层次会不定时的出现,如果该时空屏蔽层出现,那么将导致外层空间进入的任何物体被摧毁,而从地面发射到太空的飞船也将被摧毁...
所以,航天发射和飞船回收都需要等待这个时空屏蔽层消失之后,再进行
&
- linux下批量替换文件内容
商人shang
linux替换
1、网络上现成的资料
格式: sed -i "s/查找字段/替换字段/g" `grep 查找字段 -rl 路径`
linux sed 批量替换多个文件中的字符串
sed -i "s/oldstring/newstring/g" `grep oldstring -rl yourdir`
例如:替换/home下所有文件中的www.admi
- 网页在线天气预报
oloz
天气预报
网页在线调用天气预报
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8"
pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transit
- SpringMVC和Struts2比较
杨白白
springMVC
1. 入口
spring mvc的入口是servlet,而struts2是filter(这里要指出,filter和servlet是不同的。以前认为filter是servlet的一种特殊),这样就导致了二者的机制不同,这里就牵涉到servlet和filter的区别了。
参见:http://blog.csdn.net/zs15932616453/article/details/8832343
2
- refuse copy, lazy girl!
小桔子
copy
妹妹坐船头啊啊啊啊!都打算一点点琢磨呢。文字编辑也写了基本功能了。。今天查资料,结果查到了人家写得完完整整的。我清楚的认识到:
1.那是我自己觉得写不出的高度
2.如果直接拿来用,很快就能解决问题
3.然后就是抄咩~~
4.肿么可以这样子,都不想写了今儿个,留着作参考吧!拒绝大抄特抄,慢慢一点点写!
- apache与php整合
aichenglong
php apache web
一 apache web服务器
1 apeche web服务器的安装
1)下载Apache web服务器
2)配置域名(如果需要使用要在DNS上注册)
3)测试安装访问http://localhost/验证是否安装成功
2 apache管理
1)service.msc进行图形化管理
2)命令管理,配
- Maven常用内置变量
AILIKES
maven
Built-in properties
${basedir} represents the directory containing pom.xml
${version} equivalent to ${project.version} (deprecated: ${pom.version})
Pom/Project properties
Al
- java的类和对象
百合不是茶
JAVA面向对象 类 对象
java中的类:
java是面向对象的语言,解决问题的核心就是将问题看成是一个类,使用类来解决
java使用 class 类名 来创建类 ,在Java中类名要求和构造方法,Java的文件名是一样的
创建一个A类:
class A{
}
java中的类:将某两个事物有联系的属性包装在一个类中,再通
- JS控制页面输入框为只读
bijian1013
JavaScript
在WEB应用开发当中,增、删除、改、查功能必不可少,为了减少以后维护的工作量,我们一般都只做一份页面,通过传入的参数控制其是新增、修改或者查看。而修改时需将待修改的信息从后台取到并显示出来,实际上就是查看的过程,唯一的区别是修改时,页面上所有的信息能修改,而查看页面上的信息不能修改。因此完全可以将其合并,但通过前端JS将查看页面的所有信息控制为只读,在信息量非常大时,就比较麻烦。
- AngularJS与服务器交互
bijian1013
JavaScriptAngularJS$http
对于AJAX应用(使用XMLHttpRequests)来说,向服务器发起请求的传统方式是:获取一个XMLHttpRequest对象的引用、发起请求、读取响应、检查状态码,最后处理服务端的响应。整个过程示例如下:
var xmlhttp = new XMLHttpRequest();
xmlhttp.onreadystatechange
- [Maven学习笔记八]Maven常用插件应用
bit1129
maven
常用插件及其用法位于:http://maven.apache.org/plugins/
1. Jetty server plugin
2. Dependency copy plugin
3. Surefire Test plugin
4. Uber jar plugin
1. Jetty Pl
- 【Hive六】Hive用户自定义函数(UDF)
bit1129
自定义函数
1. 什么是Hive UDF
Hive是基于Hadoop中的MapReduce,提供HQL查询的数据仓库。Hive是一个很开放的系统,很多内容都支持用户定制,包括:
文件格式:Text File,Sequence File
内存中的数据格式: Java Integer/String, Hadoop IntWritable/Text
用户提供的 map/reduce 脚本:不管什么
- 杀掉nginx进程后丢失nginx.pid,如何重新启动nginx
ronin47
nginx 重启 pid丢失
nginx进程被意外关闭,使用nginx -s reload重启时报如下错误:nginx: [error] open() “/var/run/nginx.pid” failed (2: No such file or directory)这是因为nginx进程被杀死后pid丢失了,下一次再开启nginx -s reload时无法启动解决办法:nginx -s reload 只是用来告诉运行中的ng
- UI设计中我们为什么需要设计动效
brotherlamp
UIui教程ui视频ui资料ui自学
随着国际大品牌苹果和谷歌的引领,最近越来越多的国内公司开始关注动效设计了,越来越多的团队已经意识到动效在产品用户体验中的重要性了,更多的UI设计师们也开始投身动效设计领域。
但是说到底,我们到底为什么需要动效设计?或者说我们到底需要什么样的动效?做动效设计也有段时间了,于是尝试用一些案例,从产品本身出发来说说我所思考的动效设计。
一、加强体验舒适度
嗯,就是让用户更加爽更加爽的用你的产品。
- Spring中JdbcDaoSupport的DataSource注入问题
bylijinnan
javaspring
参考以下两篇文章:
http://www.mkyong.com/spring/spring-jdbctemplate-jdbcdaosupport-examples/
http://stackoverflow.com/questions/4762229/spring-ldap-invoking-setter-methods-in-beans-configuration
Sprin
- 数据库连接池的工作原理
chicony
数据库连接池
随着信息技术的高速发展与广泛应用,数据库技术在信息技术领域中的位置越来越重要,尤其是网络应用和电子商务的迅速发展,都需要数据库技术支持动 态Web站点的运行,而传统的开发模式是:首先在主程序(如Servlet、Beans)中建立数据库连接;然后进行SQL操作,对数据库中的对象进行查 询、修改和删除等操作;最后断开数据库连接。使用这种开发模式,对
- java 关键字
CrazyMizzz
java
关键字是事先定义的,有特别意义的标识符,有时又叫保留字。对于保留字,用户只能按照系统规定的方式使用,不能自行定义。
Java中的关键字按功能主要可以分为以下几类:
(1)访问修饰符
public,private,protected
p
- Hive中的排序语法
daizj
排序hiveorder byDISTRIBUTE BYsort by
Hive中的排序语法 2014.06.22 ORDER BY
hive中的ORDER BY语句和关系数据库中的sql语法相似。他会对查询结果做全局排序,这意味着所有的数据会传送到一个Reduce任务上,这样会导致在大数量的情况下,花费大量时间。
与数据库中 ORDER BY 的区别在于在hive.mapred.mode = strict模式下,必须指定 limit 否则执行会报错。
- 单态设计模式
dcj3sjt126com
设计模式
单例模式(Singleton)用于为一个类生成一个唯一的对象。最常用的地方是数据库连接。 使用单例模式生成一个对象后,该对象可以被其它众多对象所使用。
<?phpclass Example{ // 保存类实例在此属性中 private static&
- svn locked
dcj3sjt126com
Lock
post-commit hook failed (exit code 1) with output:
svn: E155004: Working copy 'D:\xx\xxx' locked
svn: E200031: sqlite: attempt to write a readonly database
svn: E200031: sqlite: attempt to write a
- ARM寄存器学习
e200702084
数据结构C++cC#F#
无论是学习哪一种处理器,首先需要明确的就是这种处理器的寄存器以及工作模式。
ARM有37个寄存器,其中31个通用寄存器,6个状态寄存器。
1、不分组寄存器(R0-R7)
不分组也就是说说,在所有的处理器模式下指的都时同一物理寄存器。在异常中断造成处理器模式切换时,由于不同的处理器模式使用一个名字相同的物理寄存器,就是
- 常用编码资料
gengzg
编码
List<UserInfo> list=GetUserS.GetUserList(11);
String json=JSON.toJSONString(list);
HashMap<Object,Object> hs=new HashMap<Object, Object>();
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
- 进程 vs. 线程
hongtoushizi
线程linux进程
我们介绍了多进程和多线程,这是实现多任务最常用的两种方式。现在,我们来讨论一下这两种方式的优缺点。
首先,要实现多任务,通常我们会设计Master-Worker模式,Master负责分配任务,Worker负责执行任务,因此,多任务环境下,通常是一个Master,多个Worker。
如果用多进程实现Master-Worker,主进程就是Master,其他进程就是Worker。
如果用多线程实现
- Linux定时Job:crontab -e 与 /etc/crontab 的区别
Josh_Persistence
linuxcrontab
一、linux中的crotab中的指定的时间只有5个部分:* * * * *
分别表示:分钟,小时,日,月,星期,具体说来:
第一段 代表分钟 0—59
第二段 代表小时 0—23
第三段 代表日期 1—31
第四段 代表月份 1—12
第五段 代表星期几,0代表星期日 0—6
如:
*/1 * * * * 每分钟执行一次。
*
- KMP算法详解
hm4123660
数据结构C++算法字符串KMP
字符串模式匹配我们相信大家都有遇过,然而我们也习惯用简单匹配法(即Brute-Force算法),其基本思路就是一个个逐一对比下去,这也是我们大家熟知的方法,然而这种算法的效率并不高,但利于理解。
假设主串s="ababcabcacbab",模式串为t="
- 枚举类型的单例模式
zhb8015
单例模式
E.编写一个包含单个元素的枚举类型[极推荐]。代码如下:
public enum MaYun {himself; //定义一个枚举的元素,就代表MaYun的一个实例private String anotherField;MaYun() {//MaYun诞生要做的事情//这个方法也可以去掉。将构造时候需要做的事情放在instance赋值的时候:/** himself = MaYun() {*
- Kafka+Storm+HDFS
ssydxa219
storm
cd /myhome/usr/stormbin/storm nimbus &bin/storm supervisor &bin/storm ui &Kafka+Storm+HDFS整合实践kafka_2.9.2-0.8.1.1.tgzapache-storm-0.9.2-incubating.tar.gzKafka安装配置我们使用3台机器搭建Kafk
- Java获取本地服务器的IP
中华好儿孙
javaWeb获取服务器ip地址
System.out.println("getRequestURL:"+request.getRequestURL());
System.out.println("getLocalAddr:"+request.getLocalAddr());
System.out.println("getLocalPort:&quo