Pytorch搭建DeepLabv3
Pytorch搭建DeepLabv3
- 前言
-
- 原理
-
- 带空洞卷积的backbone
- ASPP
- 输出层
- 代码实现
前言
学习一下经典语义分割网络DeepLabv3
DeepLabv3相比于v1和v2网络的改进在于:
①重新讨论了空洞卷积的使用,在级联模块和空间金字塔池化的框架下,能够获取更大的感受野从而获取多尺度信息。
②改进了ASPP模块:加入了BN层,以级联或并行的方式布局模块。
③讨论了一个重要问题:使用大采样率的3×3的空洞卷积,因为图像边界响应无法捕捉远距离信息,会退化为1×1的卷积,所以将图像级特征融合到ASPP模块中。
原理
DeepLabv3提出了串行和并行两种网络结构,如下面两张图所示。其中并行结构的精度更高,下面着重讨论下并行结构:

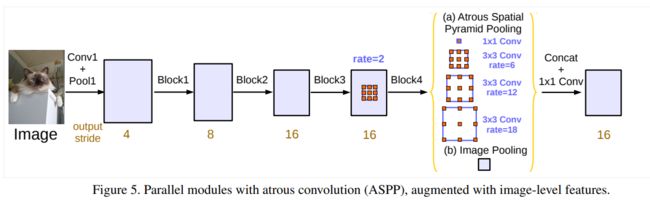
并行结构的DeepLabv3主要由特征提取骨干网络、ASPP模块以及最后的输出层组成。
带空洞卷积的backbone
DeepLabv3的backbone采用ResNet101。通常的CNN分类网络,由于多次下采样,特征图尺寸不断减小,会降低语义分割的准确度。因此DeepLab将空洞卷积引入backbone,修改了ResNet101后面的block,用空洞卷积来替换stride=2的下采样层,在不降低特征图大小的同时保持感受野与原网络一致。
在DeepLab中,将输入图片与输出特征图的尺度之比记为output_stride。一般output_stride为16或8精度比较高。但是通常的CNN分类网络的output_stride为32,以ResNet101为例,block4的output_stride原本为32。此时如果希望output_stride=16,则将最后一个下采样层的stride设置为1,并且将3×3卷积层的dilation_rate设置为2;如果希望output_stride=8,则将最后两个下采样层的stride改为1,并且将对应的3×3卷积层的dilation_rate分别设为2和4,从而达到不减小特征图尺寸而增大感受野的效果。上图所示就是output_stride=16的情况。
ASPP
ASPP(Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling),空洞空间金字塔池化,用来提取多尺度信息。改进的ASPP模块包括以下几个部分:
- 一个1×1卷积和三个3×3的空洞卷积,对于ouput_stride=16,其rate为(6,12,18);对于output_stride=8,其rate为(12,24,36)。每个卷积层的输出通道数都是256且都加入了BN层;
- 一个全局平均池化层得到图像级特征,接着经过1×1卷积层(输出通道数为256,加入了BN层),再双线性插值到原来尺寸;
- 所有分支得到的结果按照通道维度进行concat融合,并通过1×1卷积(输出通道数为256,加入了BN层)得到特征图。
输出层
最后是输出层,简单地通过1×1卷积将通道数映射为类别数,再通过双线性插值上采样到原始图片分辨率,得到最终分割结果。
代码实现
下面实现DeepLabv3。第一部分是特征提取backbone,采用ResNet101。先定义ResNet101的bottleneck残差块,conv3×3、conv1×1函数是常用的3×3卷积和1×1卷积。在通常的分类网络的卷积层基础上,这里加入了一个参数dilation,表示空洞卷积的采样率。注意到,对于3×3空洞卷积,将padding设为dilation可以使卷积前后特征图大小一致。
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo
def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1, dilation=1):
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride,
padding=dilation, bias=False, dilation=dilation)
def conv1x1(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1):
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, dilation=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = conv1x1(inplanes, planes)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes, stride, dilation)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(planes, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
residual = self.downsample(x)
out += residual
out = self.relu(out)
return out
接着是ResNet网络的主体。对于output_stride=16的特征提取方式,将最后一个下采样层的stride设置为1,并且将3×3卷积层的dilation_rate设置为2;
对于output_stride=8的特征提取方式,将最后两个下采样层的stride改为1,并且将对应的3×3卷积层的dilation_rate分别设为2和4。
if output_stride == 16:
strides = [2, 2, 1]
dilations = [1, 1, 2]
elif output_stride == 8:
strides = [2, 1, 1]
dilations = [1, 2, 4]
else:
raise NotImplementedError
参数block表示残差块,参数layers是一个列表,指定了每个模块中包含残差块的数量。_make_layer函数将一定数量的残差块组合成一个模块,共组成四个模块layer1-layer4。_load_pretrained_model()函数用于加载预训练权重。
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block, layers, output_stride, pretrained=True):
self.inplanes = 64
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
if output_stride == 16:
strides = [2, 2, 1]
dilations = [1, 1, 2]
elif output_stride == 8:
strides = [2, 1, 1]
dilations = [1, 2, 4]
else:
raise NotImplementedError
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.inplanes, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3,
bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.inplanes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=strides[0], dilation=dilations[0])
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=strides[1], dilation=dilations[1])
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=strides[2], dilation=dilations[2])
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm2d, nn.GroupNorm)):
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
if pretrained:
self._load_pretrained_model()
def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1, dilation=1):
downsample = None
if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion:
downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion),
)
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, dilation, downsample))
self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion
for i in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, dilation=dilation))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
return x
def _load_pretrained_model(self):
pretrain_dict = model_zoo.load_url('https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth')
model_dict = {}
state_dict = self.state_dict()
for k, v in pretrain_dict.items():
if k in state_dict:
model_dict[k] = v
state_dict.update(model_dict)
self.load_state_dict(state_dict)
对于ResNet101,四个模块对应的bottleneck数量为[3, 4, 23, 3]。
def ResNet101(output_stride=16, pretrained=False):
"""Constructs a ResNet-101 model.
Args:
pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet
"""
model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], output_stride, pretrained=pretrained)
return model
然后就是DeepLabv3了。DeepLabv3的主体由backbone、ASPP模块、输出层三部分组成。
backbone是ResNet101;
ASPP模块由一个1×1卷积、三个3×3的空洞卷积、一个图像池化层组成。对于三个3×3的空洞卷积,若ouput_stride=16,其rate为(6,12,18);若output_stride=8,其rate为(12,24,36)。
输出层是简单地通过一个3×3卷积和一个1×1卷积将通道数映射为类别数,最后通过双线性插值上采样到原始图片分辨率。
class DeepLabV3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_classes=21, output_stride=16, pretrained=False):
super(DeepLabV3, self).__init__()
if output_stride == 16:
atrous_rates = [6, 12, 18]
elif output_stride == 8:
atrous_rates = [12, 24, 36]
else:
raise NotImplementedError
self.backbone = ResNet101(output_stride, pretrained)
self.aspp = ASPP(2048, atrous_rates)
self.out = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(256, 256, 3, padding=1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(256, num_classes, 1)
)
def forward(self, x):
input_shape = x.size()[-2:]
x = self.backbone(x)
x = self.aspp(x)
x = self.out(x)
x = F.interpolate(x, size=input_shape, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
return x
再仔细看一下ASPP模块,每个卷积层的输出通道数都是256,且都加入了BN层。
对于图像池化层,先用平均池化得到图像级特征,接着经过1×1卷积映射通道数,再双线性插值到原来尺寸。
最后,将一个1×1卷积、三个3×3的空洞卷积以及图像池化这5个分支得到的结果按照通道维度进行concat融合,并通过1×1卷积得到特征图。
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
from ResNet_features import ResNet101
class ASPPConv(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, dilation):
modules = [
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 3, padding=dilation, dilation=dilation, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
]
super(ASPPConv, self).__init__(*modules)
class ASPPPooling(nn.Sequential):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
super(ASPPPooling, self).__init__(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU())
def forward(self, x):
size = x.shape[-2:]
for mod in self:
x = mod(x)
return F.interpolate(x, size=size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
class ASPP(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, atrous_rates, out_channels=256):
super(ASPP, self).__init__()
modules = []
modules.append(nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()))
rates = tuple(atrous_rates)
for rate in rates:
modules.append(ASPPConv(in_channels, out_channels, rate))
modules.append(ASPPPooling(in_channels, out_channels))
self.convs = nn.ModuleList(modules)
self.project = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(len(self.convs) * out_channels, out_channels, 1, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.5))
def forward(self, x):
res = []
for conv in self.convs:
res.append(conv(x))
res = torch.cat(res, dim=1)
return self.project(res)
Reference
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/bFe4F1QGIWm-yCAx9YvWDQ