Java常用类详解笔记
Object类
基本概念
-
Object类又称超类、基类,所有类的直接或间接父类,位于继承树的最顶层
-
Object类中所定义的方法,是所有对象都具备的方法
-
Object类型可以存储任何对象
-
作为参数可以接收任何对象
-
作为返回值可以返回任何对象
-
getClass()方法
-
返回引用中存储的实际对象类型
-
通常用于判断两个引用中实际存储对象类型是否一致
-
返回的是Class类
-
目录
Object类
基本概念
getClass()方法
hashCode()方法
toString()方法
equals()方法
finalize()方法
包装类
Integer缓冲区
String类
概述
常用方法
可变字符串
BigDecimal类
Date类
Calendar类
SimpleDateFormat类
Syetem类
package com.Sucker.Object; public class TestStudent { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student("aaa",20); Student s2 = new Student("bbb",22); //判断s1和s2是不是同一个类型 Class class1 = s1.getClass(); Class class2 = s2.getClass(); if(class1==class2) System.out.println("属于同一个类型"); else System.out.println("不属于"); if(s1.getClass()==s2.getClass()) System.out.println(1); } }
hashCode()方法
-
返回值为int类型,返回该对象的哈希码值
-
哈希值是根据对象地址或字符串或数字使用hash算法计算出来的int类型的数值
-
一般情况下相同对象返回相同哈希码
-
package com.Sucker.Object; public class TestStudent { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student("aaa",20); Student s2 = new Student("bbb",22); //hashCode方法 System.out.println(s1.hashCode()); System.out.println(s2.hashCode()); Student s3 = s1; System.out.println(s3.hashCode());//与s1相同 } }
toString()方法
-
返回值是String类型,返回该对象的字符串表示(表现形式)
-
可以根据程序需求覆盖该方法(重写),如:展示对象各个属性值
-
Student s1 = new Student("aaa",20); Student s2 = new Student("bbb",22); //toString方法 System.out.println(s1.toString()); System.out.println(s2.toString());
equals()方法
-
返回值是boolean类型,有一个参数Object类型参数,boolean equals(Object obj)
-
默认实现为(this==obj),比较两个对象地址是否相同
-
public class TestStudent { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student("aaa",20); Student s2 = new Student("bbb",22); //equals方法 System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//返回false } } -
可以重写,比较两个对象的内容是否相同
-
首先比较两个引用是否指向同一个对象,是则直接返回true
-
判断obj是否为null
-
判断两个引用指向的实际对象类型是否一致
-
强制类型转换
-
依次比较各个属性值是否相同
-
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) { if (this == o) return true; //判断类型也可以用instanceof if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false; Student student = (Student) o; return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name); }
-
finalize()方法
-
当对象被判定为垃圾对象时,由JVM自动调用此方法,用以标记垃圾对象,进入回收队列
-
垃圾对象:没有有效引用指向此对象时,为垃圾对象
-
垃圾回收:由GC销毁垃圾对象,释放数据存储空间
-
自动回收机制:JVM内存耗尽,一次性回收所有垃圾对象
-
手动回收机制:使用System.gc();通知JVM进行垃圾回收
-
@Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable { System.out.println(this.name+"对象被回收了"); }public class TestStudent2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Student s1 = new Student("aaa",20); Student s2 = new Student("bbb",20); Student s3 = new Student("ccc",20); Student s4 = new Student("ddd",20); Student s5 = new Student("eee",20); //回收垃圾 new Student("eee",20); new Student("eee",20); new Student("eee",20); new Student("eee",20); System.gc(); System.out.println("回收垃圾"); } }
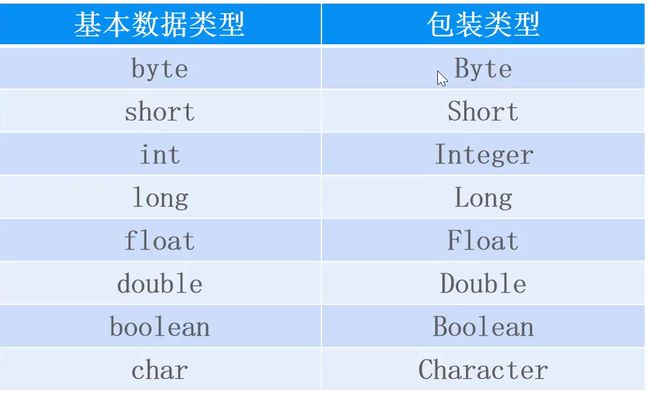
包装类
-
包装类就是基本数据类型所对应的引用数据类型
-
Object可统一所有数据,包装类的默认值是null
-
类型转换与装箱、拆箱
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //int num=10; //类型转换:装箱:基本类型转换为引用类型 int num1=18;//栈中 //使用Integer类创建对象 Integer integer1 = new Integer(num1);//放到堆中 Integer integer2 = Integer.valueOf(num1);//第二种方式 //拆箱:引用类型转成基本类型 Integer integer3 = new Integer(100);//integer3指向堆中100 int num2 = integer3.intValue();//栈中num2=100 //以上为JDK1.5前 //JDK1.5之后,提供自动装箱 int age = 30; //自动装箱 Integer integer4 = age; //自动拆箱 int age2 = integer4; } } -
基本类型与字符串之间的转换
//基本类型和字符串之间转换 //基本类型在转换成字符串 int n1=15; //1.使用+号 String s1 = n1+""; //2.使用Integer中toString方法 String s2 = Integer.toString(n1); //toString重载方法,这里表示将n1用16进制表示,输出的是f String s3 = Integer.toString(n1, 16); //字符串转换成基本类型 String str = "150"; //使用Integer.parseXXX(); int i = Integer.parseInt(str); //boolean字符串形式转换成基本类型 ”true“-->true 非"true"-->false String str2 = "tru"; boolean b = Boolean.parseBoolean(str2); System.out.println(b);//非true输出false
Integer缓冲区
-
Java预先创建了256个常用的整数包装类型对象
-
在实际应用中,对已创建的对象进行复用
-
自动装箱调用的是Integer.valueof(),此方法中初始化了数组,表示-127-128之间的数会直接是相同的地址,而下面200超过了,则使用new
public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //面试题 Integer integer1 = new Integer(100); Integer integer2 = new Integer(100); System.out.println(integer1==integer2);//对比的是地址,false Integer integer3 = 100; //自动装箱是Integer.valueof() Integer integer4 = 100; System.out.println(integer3==integer4);//这里是true Integer integer5 = 200; Integer integer6 = 200; System.out.println(integer5==integer6);//false } }
String类
概述
-
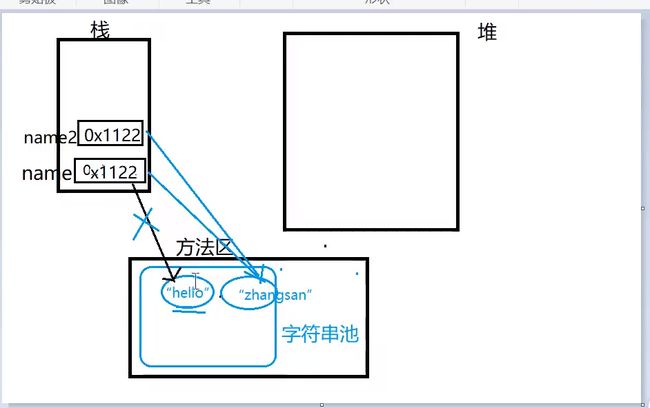
字符串是常量,创建后不可改变(指不是修改,而是重新开辟空间)
-
字符串字面值存储在字符串池中,可以共享
public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { String name = "Hello";//字符串常量存储在字符串池中 name = "zhangsan";//赋值不是修改原来的数据,而是重新开辟空间 String name2 = "zhangsan"; } } -
JDK8以前字符串池在方法区,JDK8及以后移到堆中
-
String s = "hello";产生一个对现象,字符串池中存储。String s = new String("Hello");产生两个对象,堆、池中各存储一个,此时栈中str存储的是堆中地址
//演示字符串另一种创建方式 String str = new String("Java"); String str2 = new String("Java"); System.out.println(str==str2);//false System.out.println(str.equals(str2));//这里比较了数据true
常用方法
-
public int length():返回字符串长度
-
public char charAt(int index):根据下标获取字符
-
public boolean contains(String str):判断当前字符串中是否包含str
//字符串方法的使用 //1.length() //2.charAt(int index) //3.contains(String str) String content = "java is best";//空格和中文都算一个字符 System.out.println(content.length()); System.out.println(content.charAt(content.length()-1)); System.out.println(content.contains("php")); -
public char[] toCharAray() : 将字符串转换为数组
-
public int indexOf(String str) : 查找str首次出现的下标,存在,则返回下标,否则返回-1
-
public int lastIndexOf(String str) : 查找字符串在当前字符串中最后一次出现的下标索引
String content = "java is best";//空格和中文都算一个字符 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(content.toCharArray())); System.out.println(content.indexOf("java")); System.out.println(content.indexOf("java", 4));//从第4个下标开始找 System.out.println(content.lastIndexOf("a")); -
public String trim() : 去掉字符串前后的空格
-
public String toUpperCase() : 将小写转换成大写
-
public String endWith(String str) :判断字符串是否以str结尾,startsWith判断是否以str开头
String content2 = " hello world "; System.out.println(content2.trim()); System.out.println(content2.toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT)); System.out.println(content2.toLowerCase(Locale.ROOT)); String filename = "hello.java"; System.out.println(filename.endsWith(".java"));//true System.out.println(filename.startsWith("hello"));//true -
public String replace(char oldChar,char newChar) : 将旧的字符或字符串替换成新字符或字符串,里面若填字符串就是替换字符串
-
public String[] split(String str) : 根据str做拆分
String conten3 = "java是世界上最好的语言"; System.out.println(conten3.replace("java","php")); String say = "java is the best language,java xiang"; String[] s = say.split("[ ,]+");//中括号选择,空格和逗号都可以进行拆分,加号表示可以出现一个或多个 System.out.println(s.length); for (String string : s) { System.out.println(string); } -
补充equals与compareTo(),后者比较大小,字典序
//补充equals与compareTo String s1 = "hello"; String s2 = "HELLO"; System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2));//忽略大小写的比较 String s3 = "abc";//a为97 String s4 = "xyz";//x为120 System.out.println(s3.compareTo(s4));//97-120=-23,前面相同就比后面的 String s5 = "abc"; String s6 = "abcxyz"; System.out.println(s5.compareTo(s6));//长度不同比长度,3-6=-3 -
案例实现:包含其他方法
public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { String str = "this is a text"; //1.将str中单词单独获取出来 String[] s = str.split(" "); for (String st : s) { System.out.println(st); } //2.将str中的text替换成practice String str2 = str.replace("text", "practice"); System.out.println(str2); //3.在text前插入一个easy String str3 = str.replace("text", "easy text"); System.out.println(str3); //4.将每个单词首字母变为大写 for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) { char first = s[i].charAt(0);//此时s是二维数组了 //把第一个字符转成大写 char upperfirst = Character.toUpperCase(first); String news = upperfirst+s[i].substring(1);//从s数组的1号位切分开来 System.out.println(news); } } }
可变字符串
-
StringBuffer:可变长字符串,JDK1.0提供,运行效率慢,线程安全
-
StringBuilder: 可变长字符串,JDK5.0提供,运行效率快,线程不安全
-
与String的区别
-
效率比String高
-
比String节省内存
-
-
两者基本相同,单线程情况下尽量使用StringBuilder
public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { //StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); //1. append() 追加 sb.append("java is the best"); System.out.println(sb.toString()); sb.append("java smell well"); System.out.println(sb.toString()); //2. insert() 添加 sb.insert(0,"at first"); System.out.println(sb.toString()); //3. replace() 替换 sb.replace(0,4,"hello00");//替换左闭右开,但是要是超过范围也会全部替换进去,但是不会印象到原本的第五个元素 System.out.println(sb.toString()); //4. delete() 删除 sb.delete(0,6);//左闭右开 System.out.println(sb.toString()); //清空 sb.delete(0,sb.length()); System.out.println(sb.length()); } } -
案例实现:验证效率比String高
public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { //验证StringBuilder效率高于String //开始时间 long strat = System.currentTimeMillis(); // String string=""; // for (int i = 0; i < 99999; i++) { // string+=i; // } StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(); for (int i = 0; i < 99999; i++) { sb.append(i); } //System.out.println(sb.toString()); long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("用时:"+(end-strat));//用时19127,大约19秒 //换成StringBuilder后只用13,大约0.013秒 } }
BigDecimal类
-
double存储在内存中会有误差,是近似值
-
借助BigDecimal类进行精度运算
-
位于java.math包中
-
作用:精确计算浮点数
-
创建方式:BigDecimal bd = new BigDecimal("1.0");
-
方法:
-
BigDecimal add(BigDecimal bd) 加
-
BigDecimal subtrract(BigDecimal bd) 减
-
BigDecimal multiply(BigDecimal bd) 乘
-
BigDecimal divide(BigDecimal bd) 除
-
public class Demo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { double d1 = 1.0; double d2 = 0.9; System.out.println(d1-d2);//输出为0.09999999999 //面试题 double result = (1.4-0.5)/0.9; System.out.println(result);//输出为0.99999999999 //BigDecimal。大浮点数精确计算 BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("1.0");//很多种传参方式,但是最好用字符串 BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("0.9"); //减法 BigDecimal r1 = bd1.subtract(bd2); System.out.println(r1); //加法 BigDecimal r2 = bd1.add(bd2); System.out.println(r2); //乘法 BigDecimal rr3 = bd1.multiply(bd2); //除法 BigDecimal r4 = new BigDecimal("1.4") .subtract(new BigDecimal("0.5")) .divide(new BigDecimal("0.9")); System.out.println(r4);//返回1,不是1.0 BigDecimal r5 = new BigDecimal("10") .divide(new BigDecimal("3"),2,BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP); //除不尽会报错,所以需要保留小数,此时保留2位小数,后面参数为四舍五入 System.out.println(r5); } }
-
Date类
-
Date表示特定的瞬间,精确到毫秒。Date类中的大部分方法都已经被Calendar类中的方法所取代
-
时间单位
-
1秒=1000毫秒
-
1毫秒=1000微秒
-
1微秒=1000纳秒
-
-
public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { //1.创建Date对象 Date date1 = new Date(); System.out.println(date1);//输出当前时间 //昨天,getTime返回从1970年到现在的毫秒数,以下为带参构造方法,参数为毫秒数 Date date2 = new Date(date1.getTime()-(60*60*24*1000)); System.out.println(date2); //2.方法after、before boolean b1 = date1.after(date2);//true 今天是在昨天后面 boolean b2 = date1.before(date2);//false //比较 compareTo();比较毫秒值 int i = date1.compareTo(date2);//date1减去date2的毫秒数,1表示大于,-1表示小于,0为相等 System.out.println(i); //比较是否相等equals(); boolean b = date1.equals(date2);//false } }
Calendar类
-
Calendar提供了获取或设置各种日历字段的方法
-
构造方法
-
protected Calendar() :由于修饰符是protected,所以无法直接创建该对象
-
使用静态方法Calendar getInstance获取对象
-
-
import java.util.Calendar; public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { //创建Calendar对象 Calendar calenedar = Calendar.getInstance(); System.out.println(calenedar.getTime());//返回日历时间,getTime是Date类 System.out.println(calenedar.getTimeInMillis());//从1970年到现在毫秒值 //获取时间信息 //获取年 通过源码常量 Calendar.YEAR int year = calenedar.get(Calendar.YEAR); //月 从0-11,输出可以加1 int month = calenedar.get(Calendar.MONTH); //日 int day = calenedar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH);//或者常量为DATE //小时 int hour = calenedar.get(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY);//这是24小时,HOUR是12小时 //分钟 int minute = calenedar.get(Calendar.MINUTE); //秒 int second = calenedar.get(Calendar.SECOND); System.out.println(year+"年"+(month+1)+"月"+day+"日"); //修改时间 Calendar calendar2 = Calendar.getInstance(); calendar2.set(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH, 5);//修改为日期为5号 System.out.println(calendar2.getTime()); // add方法修改时间 calendar2.add(Calendar.HOUR_OF_DAY,1);//修改小时,增加10小时,如果是负值就是减少 System.out.println(calendar2.getTime()); //补充方法 最大值和最小值 int maxmonth = calendar2.getActualMaximum(Calendar.MONTH); int maxday = calendar2.getActualMaximum(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH); int minday = calendar2.getActualMinimum(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH); } }
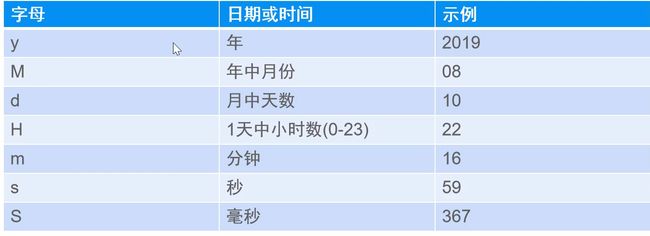
SimpleDateFormat类
-
SimpleDateFormat是一个以语言环境有关的方法来格式化和解析日期的具体类
-
进行格式化(日期 -> 文本)、解析(文本 -> 日期)
-
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat; import java.util.Date; public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{ //创建SimpleDateFormat对象 y 年 M 月 //SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");//带参构造,参数为输出的时间格式 SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd");//带参构造,参数为输出的时间格式 //创建Date Date date = new Date(); // Calendar cal = Calendar.getInstance(); // Date time = cal.getTime(); //格式化date(日期 -> 字符串) String string = simpleDateFormat.format(date);//time也是一样的 System.out.println(string); //解析(字符串 -> 日期) Date date2 = simpleDateFormat.parse("1998/05/31");//必须与上面创建对象的格式相同,同时还需要throws Exception System.out.println(date2); } }
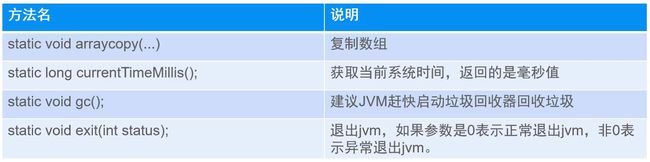
Syetem类
-
public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { //数组复制:arraycopy //src:原数组 //srcPos:从哪个位置开始复制 //dest:目标数组 //destPos:在目标数组放置位置 //length:复制的长度 int[] arr={20,18,15,8,35,26,45,90}; int[] dest=new int[8]; System.arraycopy(arr,0,dest,0,arr.length); for (int i = 0; i < dest.length; i++) { System.out.println(dest[i]); } System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());//1970-now毫秒数 //实现计时 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); for (int i = 0; i < 99999; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < 99999; j++) { int result = i+j; } } long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println(end-start); //System.gc();告诉垃圾回收器回收垃圾 //创建无人引用的垃圾对象 new Student("aaa",19); new Student("bbb",19); new Student("ccc",19); System.gc(); //退出JVM System.exit(0); System.out.println("结束了");//不会执行了 } }