Redis 的 Java 客户端
文章目录
- Jedis 客户端
-
- 普通连接方式
- 连接池的方式
- SpringDataRedis 客户端
-
- 搭建一个 SpringDataRedis 项目
- 自定义序列化
- 手动序列化
- 对 Hash 等数据的存储和获取
Redis 在官网中提供了各种语言的客户端,地址:
https://redis.io/docs/clients/
在这我就主要介绍的是 Jedis 和 SpringDataReids 的客户端
Jedis 客户端
普通连接方式
创建一个 maven 工程。
首先在 maven 中引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clientsgroupId>
<artifactId>jedisartifactId>
<version>3.7.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupitergroupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiterartifactId>
<version>5.7.0version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
先新建一个单元的测试类:
测试前的初始化:
private Jedis jedis;
// 这个注解为测试情啊的初始化
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
// 1.建立连接
// jedis = new Jedis("192.168.150.101", 6379);
jedis = JedisConnectionFactory.getJedis();
// 2.设置密码
jedis.auth("123321");
// 3.选择库
jedis.select(0);
}
测设内容:
@Test
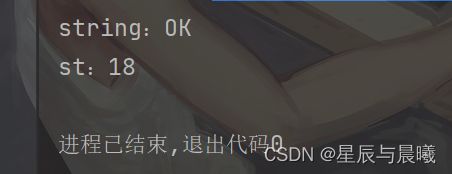
void testString() {
// 存入数据
String string = jedis.set("com:one:age", "18");
System.out.println("string:" + string);
//读取数据
String st = jedis.get("com:one:age");
System.out.println("st:" + st);
}
测试内容结束后的一些操作(释放资源):
@AfterEach
void afterAll() {
if (jedis != null) {
jedis.close();
}
}
用 Hash 类型的数据再测试一下:
@Test
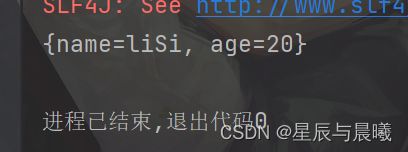
void testHash() {
// 存入哈希的值
jedis.hset("com:two", "name", "liSi");
jedis.hset("com:two", "age", "20");
//读取哈希值
Map<String, String> map = jedis.hgetAll("com:two");
System.out.println(map);
}
也都是没有问题的。
但在这里我们就要考虑一个问题了:
Jedis 本身是线程不安全的,并且频繁的创建和销毁连接会有性能损耗,因此我们推荐大家使用 Jedis连接池代替 Jedis 的直连方式。
连接池的方式
创建一个 Jedis 自带的连接池,我们只需把参数传进去即可。
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPool;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
public class JedisPoolDemo {
//jedis 自身提供的一个连接池
private static final JedisPool jedispool;
static {
//配置连接池
JedisPoolConfig jedisPoolConfig = new JedisPoolConfig();
//最大连接数
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxTotal(8);
//最大空闲连接数
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxIdle(8);
//最小空闲连接数
jedisPoolConfig.setMinIdle(0);
// 最大等待时间,默认为-1,无限等。时间单位毫秒
jedisPoolConfig.setMaxWaitMillis(1000);
// 创建连接池对象
jedispool = new JedisPool(jedisPoolConfig, "192.168.71.128", 6379,
1000, "wasd");
}
public static Jedis getJedis() {
return jedispool.getResource();
}
}
然后在需要用的时候,直接调用这个类里的 getJedis 方法,就可以获得线程进行操作。
SpringDataRedis 客户端
SpringData 是 Spring 中数据操作的模块,包含对各种数据库的集成,其中对Redis的集成模块就叫做 SpringDataRedis。
官网地址:https://spring.io/projects/spring-data-redis
特性:
- 提供了对不同 Redis 客户端的整合(Lettuce和Jedis)
- 提供了 RedisTemplate 统一 API 来操作 Redis
- 支持 Redis 的发布订阅模型
- 支持 Redis 哨兵和 Redis 集群
- 支持基于 Lettuce 的响应式编程
- 支持基于JDK、JSON、字符串、Spring对象的数据序列化及反序列化
- 支持基于 Redis 的 JDKCollection 实现
SpringDataRedis 中提供了 RedisTemplate 工具类,其中封装了各种对 Redis 的操作。并且将不同数据类型的操作 API 封装到了不同的类型中:
| API | 返回数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| redisTemplate.opsForValue() | ValueOperations | 操作 String 类型的数据 |
| redisTemplate.opsForHash() | HashOperations | 操作 Hash 类型的数据 |
| redisTemplate.opsForList() | ListOperations | 操作 List 类型的数据 |
| redisTemplate.opsForSet() | SetOperations | 操作 Set 类型的数据 |
| redisTemplate.opsForZSet() | ZSetOperations | 操作SortedSet 类型的数据 |
| redisTemplate | 通用命令 |
搭建一个 SpringDataRedis 项目
先引入依赖
在创建项目的时候,会自动打包一些 jar包
主要还是要包含这些 jar 包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commonsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2artifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.coregroupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databindartifactId>
dependency>
在配置文件当中配置一些东西:
spring:
redis:
host: 192.168.150.101
port: 6379
password: 123321
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 8
max-idle: 8
min-idle: 0
max-wait: 100ms
注入 RedisTemplate
因为有了SpringBoot的自动装配,我们可以拿来就用:
@SpringBootTest
class RedisStringTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
}
编写代码进行测试:
@Test
void testString() {
// 写入一条 String 数据
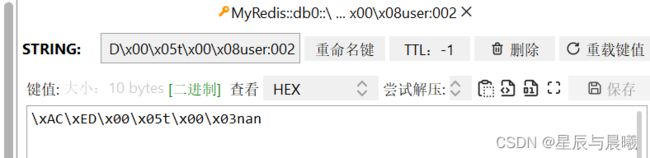
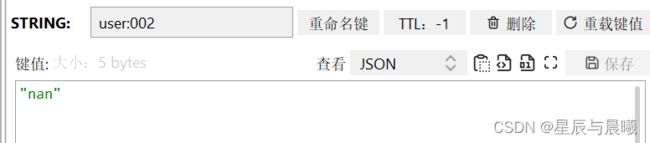
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user:002", "nan");
//获取得到一条数据
Object o = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user:002");
System.out.println(o);
}
结果也完美的得到了我们存储进去的数据。
发现它实际在 Redis 保存的并不是我们在 java 当中人为起的名字。
这是因为 Reids 会在保存的时候会调用的是 jdk 里面的序列化,然后在读取的时候,进行反序列化。
在 Java 当中,对我们正常的使用来说,是不会有什么影响的。但是对 Redis 来说它就可读性差,并且占用空间大。
所以在这我们就可以自定义 RedisTemplate 来对其进行序列化。
自定义序列化
自己定义的 conf 序列化的代码如下:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
// 创建 RedisTemplate 对象
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
// 设置连接工厂
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
// 创建 JSON 序列化
GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer();
// 设置 key 序列化
template.setKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
template.setHashKeySerializer(RedisSerializer.string());
// 设置 value 序列化
template.setValueSerializer(serializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);
// 返回
return template;
}
}
这里采用了 JSON 序列化来代替默认的 JDK 序列化方式。
我们再对 Redis 进行操作后,然后再查看桌面客户端的页面:
发现它就没有什么太大的问题。
那么我们现在对一个对象,给 Redis 里面进行保存。
先简简单单创建一个对象:
package com.example.redistest.redis.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
public class User {
private String name;
private Integer sex;
}
然后对这个类的对象进行保存。
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
@SpringBootTest
class RedisTestApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void testSaveUser() {
//写入数据
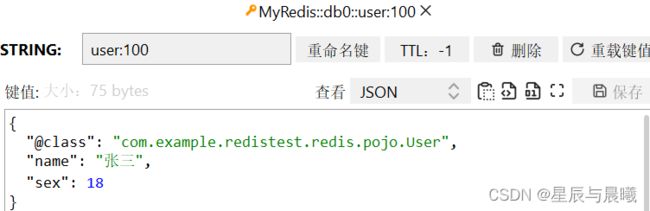
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user:100", new User("张三", 18));
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user:200", new User("李四", 20));
//读取数据
User user1 = (User) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user:100");
User user2 = (User) redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user:200");
System.out.println("user1:" + user1);
System.out.println("user2:" + user2);
}
}
也成功的在 Reids 中对其进行了保存。
在 Redis 里面进行保存的时候,也对其正确的进行了保存,但是我们可以查看到第一条,有一个 @class 的数据,因为我们自定义的序列化,是批量默认进行的,所以也必须保存这个信息,不然在反序列化的时候,压根不知道反序列化给谁的格式。(这个就是不能再继续消除的)
但是这个也可以消除掉,那就是我们手动的具体进行序列化
手动序列化
代码演示:
import com.example.redistest.redis.pojo.User;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import java.util.Map;
@SpringBootTest
public class RedisStringDemo {
@Autowired
private StringRedisTemplate redisTemplate;
private static final ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
@Test
void testUser() throws JsonProcessingException {
// 写入数据
// 创建对象
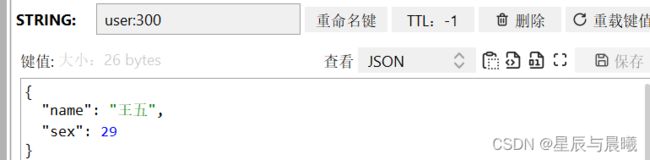
User user = new User("王五", 29);
// 手动序列化
String s = mapper.writeValueAsString(user);
// 最终发送给 redis
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user:300", s);
// 获取数据
String s1 = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user:300");
// 手动反序列化
User user1 = mapper.readValue(s1, User.class);
System.out.println(user1);
}
}
得到了它保存的数据是没有任何问题的。
对 Hash 等数据的存储和获取
简单用代码演示一下,主要指明要使用的方法。
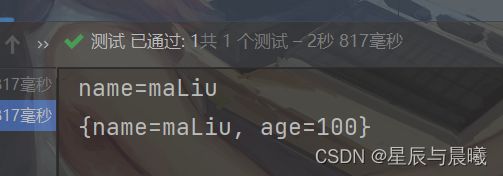
@Test
void testHash() {
// 存数据
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user:400", "name", "maLiu");
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put("user:400", "age", "100");
// 取数据
Object name = redisTemplate.opsForHash().get("user:400", "name");
System.out.println("name=" + name);
// 获取全部数据
Map<Object, Object> entries = redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries("user:400");
System.out.println(entries);
}