Linux内核4.14版本——alsa框架分析(2)-sound.c分析(应用层如何调用到内核层的)
1. alsa_sound_init
1.1 snd_minors
1.2 snd_register_device
2 以pcm和clt的调用关系来分析如何注册snd_minors
2.1 pcm注册snd_minors
2.1.1 snd_pcm_new
2.1.2 _snd_pcm_new
2.1.3 snd_pcm_dev_register
2.2 clt注册snd_minors
2.2.1 snd_ctl_create
2.2.2 snd_ctl_dev_register
3. sound成功编入内核后的现象
3.1 查看cat /proc/devices
3.2 ls /dev/snd/ -l
1. alsa_sound_init
alsa的核心入口函数是sound\core\sound.c中的alsa_sound_init
static int major = CONFIG_SND_MAJOR;
static int __init alsa_sound_init(void)
{
snd_major = major;
snd_ecards_limit = cards_limit;
if (register_chrdev(major, "alsa", &snd_fops)) {
pr_err("ALSA core: unable to register native major device number %d\n", major);
return -EIO;
}
if (snd_info_init() < 0) {
unregister_chrdev(major, "alsa");
return -ENOMEM;
}
#ifndef MODULE
pr_info("Advanced Linux Sound Architecture Driver Initialized.\n");
#endif
return 0;
}
static void __exit alsa_sound_exit(void)
{
snd_info_done();
unregister_chrdev(major, "alsa");
}
subsys_initcall(alsa_sound_init);
module_exit(alsa_sound_exit);注册了一个主设备号为CONFIG_SND_MAJOR(116),名字为“alsa”的字符设备,其操作函数为snd_fops。
static const struct file_operations snd_fops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = snd_open,
.llseek = noop_llseek,
};在应用程序中调用open,最终在内核中会调用snd_open。
static struct snd_minor *snd_minors[SNDRV_OS_MINORS];
static int snd_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
unsigned int minor = iminor(inode);
struct snd_minor *mptr = NULL;
const struct file_operations *new_fops;
int err = 0;
if (minor >= ARRAY_SIZE(snd_minors))
return -ENODEV;
mutex_lock(&sound_mutex);
mptr = snd_minors[minor];
.......
new_fops = fops_get(mptr->f_ops);
.....
if (file->f_op->open)
err = file->f_op->open(inode, file);
return err;
}1.1 snd_minors
最终会通过次设备号来匹配snd_minors,并且调用它的open函数。我们看看全局变量snd_minors在哪注册的,它是静态变量,所以在sound.c文件中搜索,发现其注册为snd_register_device。
/**
* snd_register_device - Register the ALSA device file for the card
* @type: the device type, SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_XXX
* @card: the card instance
* @dev: the device index
* @f_ops: the file operations
* @private_data: user pointer for f_ops->open()
* @device: the device to register
*
* Registers an ALSA device file for the given card.
* The operators have to be set in reg parameter.
*
* Return: Zero if successful, or a negative error code on failure.
*/
int snd_register_device(int type, struct snd_card *card, int dev,
const struct file_operations *f_ops,
void *private_data, struct device *device)
{
int minor;
int err = 0;
struct snd_minor *preg;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!device))
return -EINVAL;
preg = kmalloc(sizeof *preg, GFP_KERNEL);
if (preg == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
preg->type = type;
preg->card = card ? card->number : -1;
preg->device = dev;
preg->f_ops = f_ops;
preg->private_data = private_data;
preg->card_ptr = card;
mutex_lock(&sound_mutex);
minor = snd_find_free_minor(type, card, dev);
if (minor < 0) {
err = minor;
goto error;
}
preg->dev = device;
device->devt = MKDEV(major, minor);
err = device_add(device);
if (err < 0)
goto error;
snd_minors[minor] = preg;
error:
mutex_unlock(&sound_mutex);
if (err < 0)
kfree(preg);
return err;
}1.2 snd_register_device
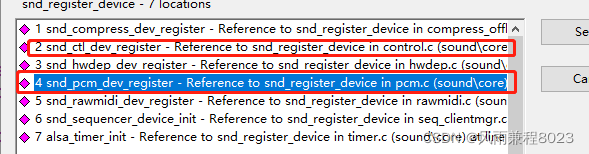
搜索snd_register_device,看谁调用了该函数,发现有如下函数调用了。
我们以红框中的两个函数分析他。
2 以pcm和clt的调用关系来分析如何注册snd_minors
2.1 pcm注册snd_minors
snd_pcm_new->_snd_pcm_new->snd_pcm_dev_register->snd_register_device
2.1.1 snd_pcm_new
/**
* snd_pcm_new - create a new PCM instance
* @card: the card instance
* @id: the id string
* @device: the device index (zero based)
* @playback_count: the number of substreams for playback
* @capture_count: the number of substreams for capture
* @rpcm: the pointer to store the new pcm instance
*
* Creates a new PCM instance.
*
* The pcm operators have to be set afterwards to the new instance
* via snd_pcm_set_ops().
*
* Return: Zero if successful, or a negative error code on failure.
*/
int snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device,
int playback_count, int capture_count, struct snd_pcm **rpcm)
{
return _snd_pcm_new(card, id, device, playback_count, capture_count,
false, rpcm);
}2.1.2 _snd_pcm_new
static int _snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device,
int playback_count, int capture_count, bool internal,
struct snd_pcm **rpcm)
{
struct snd_pcm *pcm;
int err;
static struct snd_device_ops ops = {
.dev_free = snd_pcm_dev_free,
.dev_register = snd_pcm_dev_register,
.dev_disconnect = snd_pcm_dev_disconnect,
};
........
if (id)
strlcpy(pcm->id, id, sizeof(pcm->id));
err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK,
playback_count);
if (err < 0)
goto free_pcm;
err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, capture_count);
if (err < 0)
goto free_pcm;
err = snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_PCM, pcm, &ops);
if (err < 0)
goto free_pcm;
if (rpcm)
*rpcm = pcm;
return 0;
free_pcm:
snd_pcm_free(pcm);
return err;
}
先创建playback和capture两个substream,最终创建pcm设备,ops最终为pcm的ops。
2.1.3 snd_pcm_dev_register
static int snd_pcm_dev_register(struct snd_device *device)
{
..............
err = snd_pcm_add(pcm);
if (err)
goto unlock;
for (cidx = 0; cidx < 2; cidx++) {
int devtype = -1;
if (pcm->streams[cidx].substream == NULL)
continue;
switch (cidx) {
case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK:
devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK;
break;
case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE:
devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_CAPTURE;
break;
}
/* register pcm */
err = snd_register_device(devtype, pcm->card, pcm->device,
&snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx], pcm,
.............
}
pcm_call_notify(pcm, n_register);
unlock:
mutex_unlock(®ister_mutex);
return err;
}这里注意snd_pcm_f_ops结构体,如下所示。sound\core\pcm_native.c
/*
* Register section
*/
const struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = {
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.write = snd_pcm_write,
.write_iter = snd_pcm_writev,
.open = snd_pcm_playback_open,
.release = snd_pcm_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_pcm_playback_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,
.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,
.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,
.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,
},
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = snd_pcm_read,
.read_iter = snd_pcm_readv,
.open = snd_pcm_capture_open,
.release = snd_pcm_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_pcm_capture_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat,
.mmap = snd_pcm_mmap,
.fasync = snd_pcm_fasync,
.get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area,
}
};该操作函数集被注册在snd_minors结构体的操作函数集中,所以上层应用最终的open,compat_ioctl等函数,最终都会调用到这里。
int snd_register_device(int type, struct snd_card *card, int dev,
const struct file_operations *f_ops,
void *private_data, struct device *device)
{
..........
preg->f_ops = f_ops;
preg->private_data = private_data;
preg->card_ptr = card;
mutex_lock(&sound_mutex);
minor = snd_find_free_minor(type, card, dev);
if (minor < 0) {
err = minor;
goto error;
}
.............
snd_minors[minor] = preg;
error:
mutex_unlock(&sound_mutex);
if (err < 0)
kfree(preg);
return err;
}2.2 clt注册snd_minors
snd_card_new->snd_ctl_create->snd_ctl_dev_register->snd_register_device
2.2.1 snd_ctl_create
int snd_ctl_create(struct snd_card *card)
{
static struct snd_device_ops ops = {
.dev_free = snd_ctl_dev_free,
.dev_register = snd_ctl_dev_register,
.dev_disconnect = snd_ctl_dev_disconnect,
};
int err;
if (snd_BUG_ON(!card))
return -ENXIO;
if (snd_BUG_ON(card->number < 0 || card->number >= SNDRV_CARDS))
return -ENXIO;
snd_device_initialize(&card->ctl_dev, card);
dev_set_name(&card->ctl_dev, "controlC%d", card->number);
err = snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_CONTROL, card, &ops);
if (err < 0)
put_device(&card->ctl_dev);
return err;
}最终会调用snd_device_new把control设备加入到snd_device链表里面,ops也为control设备的ops。
2.2.2 snd_ctl_dev_register
/*
* registration of the control device
*/
static int snd_ctl_dev_register(struct snd_device *device)
{
struct snd_card *card = device->device_data;
return snd_register_device(SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_CONTROL, card, -1,
&snd_ctl_f_ops, card, &card->ctl_dev);
}注册control设备,snd_ctl_f_ops为改设备的操作函数集。
static const struct file_operations snd_ctl_f_ops =
{
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.read = snd_ctl_read,
.open = snd_ctl_open,
.release = snd_ctl_release,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.poll = snd_ctl_poll,
.unlocked_ioctl = snd_ctl_ioctl,
.compat_ioctl = snd_ctl_ioctl_compat,
.fasync = snd_ctl_fasync,
};3. sound成功编入内核后的现象
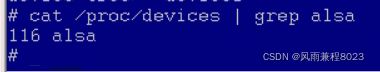
3.1 查看cat /proc/devices
主设备号为116的,名称为alsa的设备。
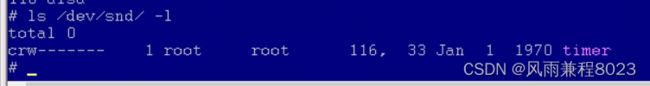
3.2 ls /dev/snd/ -l
主设备号为116,次设备号为33,名称为timer的字符设备。