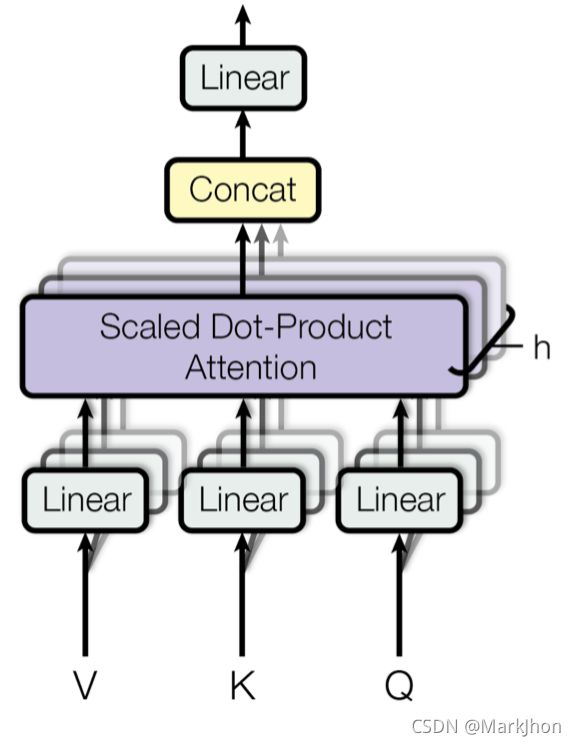
注意力机制学习:Multi-Head Attention
多头注意力机制(Mutil-head Attention):多头注意( Multihead Attention )是注意机制模块。
实现:通过一个注意力机制的多次并行运行,将独立的注意力输出串联起来,线性地转化为预期维度。直观看来,多个注意头允许对序列的不同部分进行注意力运算。
![]()
其中,![]() 都是可学习的参数矩阵。
都是可学习的参数矩阵。
注:缩放点积注意力(Scaled dot-product attention)在这个模块中很常用的,同时也可以将其换为其他类型的注意力机制。
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class ScaledDotProductAttention(nn.Module):
''' Scaled Dot-Product Attention '''
def __init__(self, temperature, attn_dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.temperature = temperature
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(attn_dropout)
def forward(self, q, k, v, mask=None):
attn = torch.matmul(q / self.temperature, k.transpose(2, 3))
if mask is not None:
attn = attn.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
attn = self.dropout(F.softmax(attn, dim=-1))
output = torch.matmul(attn, v)
return output, attn
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
''' Multi-Head Attention module '''
def __init__(self, n_head, d_model, d_k, d_v, dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.n_head = n_head
self.d_k = d_k
self.d_v = d_v
self.w_qs = nn.Linear(d_model, n_head * d_k, bias=False)
self.w_ks = nn.Linear(d_model, n_head * d_k, bias=False)
self.w_vs = nn.Linear(d_model, n_head * d_v, bias=False)
self.fc = nn.Linear(n_head * d_v, d_model, bias=False)
self.attention = ScaledDotProductAttention(temperature=d_k ** 0.5)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(d_model, eps=1e-6)
def forward(self, q, k, v, mask=None):
d_k, d_v, n_head = self.d_k, self.d_v, self.n_head
sz_b, len_q, len_k, len_v = q.size(0), q.size(1), k.size(1), v.size(1)
residual = q
# Pass through the pre-attention projection: b x lq x (n*dv)
# Separate different heads: b x lq x n x dv
q = self.w_qs(q).view(sz_b, len_q, n_head, d_k)
k = self.w_ks(k).view(sz_b, len_k, n_head, d_k)
v = self.w_vs(v).view(sz_b, len_v, n_head, d_v)
# Transpose for attention dot product: b x n x lq x dv
q, k, v = q.transpose(1, 2), k.transpose(1, 2), v.transpose(1, 2)
if mask is not None:
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1) # For head axis broadcasting.
q, attn = self.attention(q, k, v, mask=mask)
# Transpose to move the head dimension back: b x lq x n x dv
# Combine the last two dimensions to concatenate all the heads together: b x lq x (n*dv)
q = q.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(sz_b, len_q, -1)
q = self.dropout(self.fc(q))
q += residual
q = self.layer_norm(q)
return q, attn
class PositionwiseFeedForward(nn.Module):
''' A two-feed-forward-layer module '''
def __init__(self, d_in, d_hid, dropout=0.1):
super().__init__()
self.w_1 = nn.Linear(d_in, d_hid) # position-wise
self.w_2 = nn.Linear(d_hid, d_in) # position-wise
self.layer_norm = nn.LayerNorm(d_in, eps=1e-6)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, x):
residual = x
x = self.w_2(F.relu(self.w_1(x)))
x = self.dropout(x)
x += residual
x = self.layer_norm(x)
return x