webpack如何打包资源优化你有了解吗?或者一个经常被问的面试题,首屏加载如何优化,其实无非就是从http请求、文件资源、图片加载、路由懒加载、预请求,缓存这些方向来优化,通常在使用脚手架中,成熟的脚手架已经给你做了最大的优化,比如压缩资源,代码的tree shaking等。
本文是笔者根据以往经验以及阅读官方文档总结的一篇关于webpack打包方面的长文笔记,希望在项目中有所帮助。
正文开始...
在阅读之前,本文将从以下几个点去探讨webpack的打包优化
1、webpack如何做treeShaking
2、webpack的gizp压缩
3、css如何做treeShaking,
4、入口依赖文件拆包
5、图片资源加载优化
treeShaking
在官网中有提到treeShaking,从名字上中文解释就是摇树,就是利用esModule的特性,删除上下文未引用的代码。因为webpack可以根据esModule做静态分析,本身来说它是打包编译前输出,所以webpack在编译esModule的代码时就可以做上下文未引用的删除操作。
那么如何做treeshaking?我们来分析下
快速初始化一个webpack项目
在之前我们都是手动配置搭建webpack项目,webpack官方提供了cli快速构建基本模版,无需像之前一样手动配置entry、plugins、loader等
首先安装npm i webpack webpack-cli,命令行执行`
npx webpack init一系列初始化操作后,就生成以下代码了
默认的webpack.config.js
// Generated using webpack-cli https://github.com/webpack/webpack-cli
const path = require("path");
const HtmlWebpackPlugin = require("html-webpack-plugin");
const MiniCssExtractPlugin = require("mini-css-extract-plugin");
const WorkboxWebpackPlugin = require("workbox-webpack-plugin");
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV == "production";
const stylesHandler = MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader;
const config = {
entry: "./src/index.js",
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "dist"),
},
devServer: {
open: true,
host: "localhost",
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: "index.html",
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin(),
// Add your plugins here
// Learn more about plugins from https://webpack.js.org/configuration/plugins/
],
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.(js|jsx)$/i,
loader: "babel-loader",
},
{
test: /\.less$/i,
use: [stylesHandler, "css-loader", "postcss-loader", "less-loader"],
},
{
test: /\.css$/i,
use: [stylesHandler, "css-loader", "postcss-loader"],
},
{
test: /\.(eot|svg|ttf|woff|woff2|png|jpg|gif)$/i,
type: "asset",
},
// Add your rules for custom modules here
// Learn more about loaders from https://webpack.js.org/loaders/
],
},
};
module.exports = () => {
if (isProduction) {
config.mode = "production";
config.plugins.push(new WorkboxWebpackPlugin.GenerateSW());
} else {
config.mode = "development";
}
return config;
};现在修改一下index.js,并在src中增加utils目录
// utils/index.js
export function add(a, b) {
return a + b
}
export function square(x) {
return x * x;
}index.js
import { add } from './utils'
console.log("Hello World!");
console.log(add(1, 2))在index.js中我只引入了add,相当于square这个函数在上下文中并未引用。
usedExports
不过我还需要改下webpack.config.js
...
module.exports = () => {
if (isProduction) {
config.mode = "production";
config.plugins.push(new WorkboxWebpackPlugin.GenerateSW());
} else {
config.mode = "development";
config.devtool = 'source-map'
config.optimization = {
usedExports: true
}
}
return config;
};注意我只增加了devtool:source-map与optimization.usedExports = true
我们看下package.json
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"build": "webpack --mode=production --node-env=production",
"build:dev": "webpack --mode=development",
"build:prod": "webpack --mode=production --node-env=production",
"watch": "webpack --watch",
"serve": "webpack serve"
},默认初始化已经给们预设了多个不同的打包环境,因此我只需要运行下面命令就可以选择开发环境了
npm run build:dev/* unused harmony export square */
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function square(x) {
return x * x;
}square上下文未引用,虽然给了标记,但是未真正清除。
光使用usedExports:true还不行,usedExports 依赖于 terser 去检测语句中的副作用,因此需要借助terser插件一起使用,官方webpack5提供了TerserWebpackPlugin这样一个插件
在webpack.config.js中引入
...
const TerserPlugin = require("terser-webpack-plugin");
...
module.exports = () => {
if (isProduction) {
config.mode = "production";
config.plugins.push(new WorkboxWebpackPlugin.GenerateSW());
} else {
config.mode = "development";
config.devtool = 'source-map'
config.optimization = {
usedExports: true, // 设置为true 告诉webpack会做treeshaking
minimize: true, // 开启terser
minimizer: [new TerserPlugin({
extractComments: false, // 是否将注释剥离到单独文件,默认是true
})]
}
}
return config;
};
你会发现,那个square函数就没有了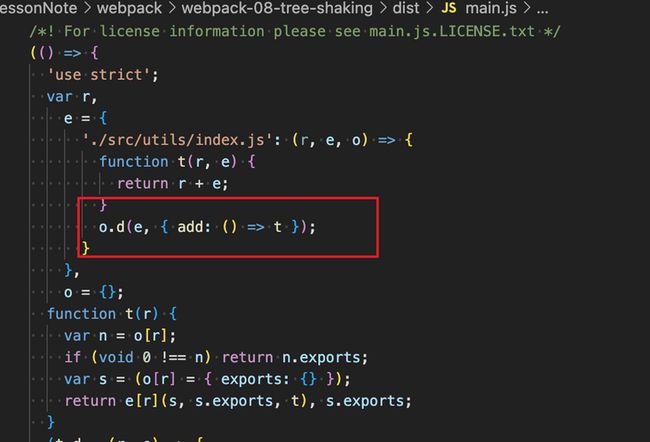
如果我将usedExports.usedExports = false,你会发现square没有被删除。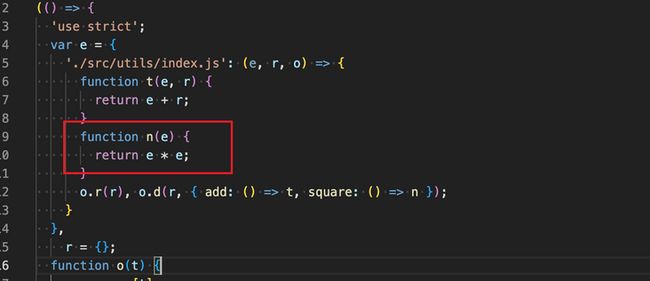
官方解释,当我们设置optimization.usedExports必须为true,当我们设置usedExports:true,且必须开起minimize: true,这样才会把上下文未使用的代码给清除掉,如果minimize: false,那么压缩插件将会失效。
当我们设置usedExports: true
此时生成打包的代码会有一个这样的魔法注释,square未使用
/* unused harmony export square */
function add(a, b) {
return a + b;
}
function square(x) {
return x * x;
}当我们设置minimize: true时,webpack5会默认开启terser压缩,然后发现有这样的unused harmony export square就会删掉对应未引入的代码。
sideEffects
这个是usedExports摇树的另一种方案,usedExports是检查上下文有没有引用,如果没有引用,就会注入魔法注释,通过terser压缩进行去除未引入的代码
而slideEffects是对没有副作用的代码进行去除
首先什么是副作用,这是一个不太好理解的词,在react中经常有听到
其实副作用就是一个纯函数中存在可变依赖的因变量,因为某个因变量会造成纯函数产生不可控的结果
举个例子
没有副作用的函数,输入输出很明确
function watchEnv(env) {
return env === 'prd' ? 'product': 'development'
}
watchEnv('prd')有副作用,函数体内有不确定性因素
export function watchEnv(env) {
const num = Math.ceil(Math.random() * 10);
if (num < 5) {
env = 'development'
}
return env === 'production' ? '生产环境' : '测试开发环境'
}
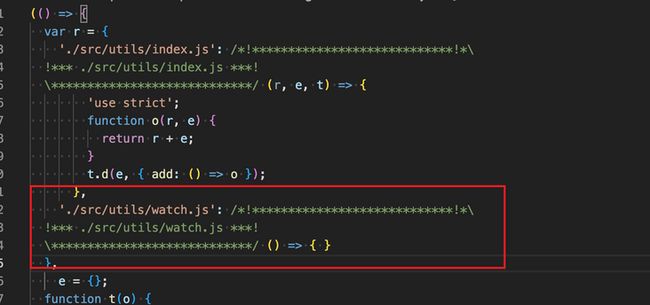
我们在index.js中引入watch.js
import { add } from './utils'
import './utils/watch.js';
console.log("Hello World!");
console.log(add(1, 2))然后运行npm run build:dev,打包后的文件有watch的引入
在index.js中引入watch.js并没有什么使用,但是我们仍然打包了进去
为了去除这引入但未被使用的代码,因此你需要在optimization.sideEffects: true,并且要在package.json中设置sideEffects: false,在optimization.sideEffects设置true,告知webpack根据package.json中的sideEffects标记的副作用或者规则,从而告知webpack跳过一些引入但未被使用的模块代码。具体参考optimization.sideEffects
module.exports = () => {
if (isProduction) {
config.mode = "production";
config.plugins.push(new WorkboxWebpackPlugin.GenerateSW());
} else {
config.mode = "development";
config.devtool = 'source-map',
config.optimization = {
sideEffects: true, // 开启sideEffects
usedExports: true,
minimize: true, // 开启terser
minimizer: [new TerserPlugin({
extractComments: false, // 是否将注释剥离到单独文件,默认是true
})]
}
}
return config;
};{
"name": "my-webpack-project",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "My webpack project",
"main": "index.js",
"sideEffects": false,
...
}此时你运行命令npm run build:dev,查看打包文件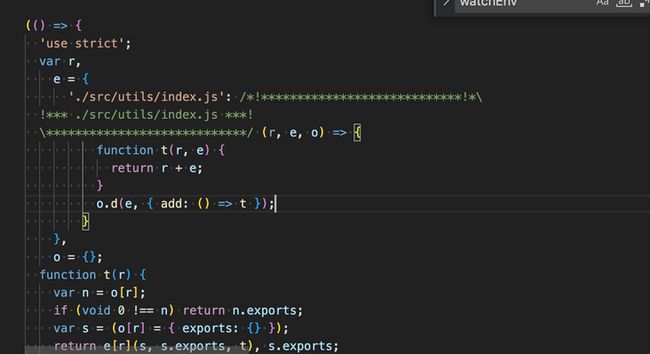
我们就会发现,引入的watch.js就没有了
在官方中有这么一段话使用 mode 为 "production" 的配置项以启用更多优化项,包括压缩代码与 tree shaking。
因此在webpack5中只要你设置mode:production那些代码压缩、tree shaking通通默认给你做了做了最大的优化,你就无需操心代码是否有被压缩,或者tree shaking了。
对于能否被tree shaking还补充几点
1、一定是esModule方式,也就是export xxx或者import xx from 'xxx'的方式
2、cjs方式不能被tree shaking
3、线上打包生产环境mode:production自动开启多项优化,可以参考生产环境的构建production
gizp压缩
首先是是在devServer下提供了一个开发环境的compress:true
{
devServer: {
open: true,
host: "localhost",
compress: true // 启用zip压缩
}
}- CompressionWebpackPlugin 插件gizp压缩
需要安装对应插件
npm i compression-webpack-plugin --save-devwebpack.config.js中引入插件
// Generated using webpack-cli https://github.com/webpack/webpack-cli
...
const CompressionWebpackPlugin = require('compression-webpack-plugin');
const config = {
...
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: "index.html",
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin(),
new CompressionWebpackPlugin(),
// Add your plugins here
// Learn more about plugins from https://webpack.js.org/configuration/plugins/
],
...
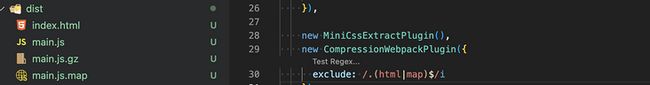
};当你运行命令后,你就会发现打包后的文件有gzip的文件了
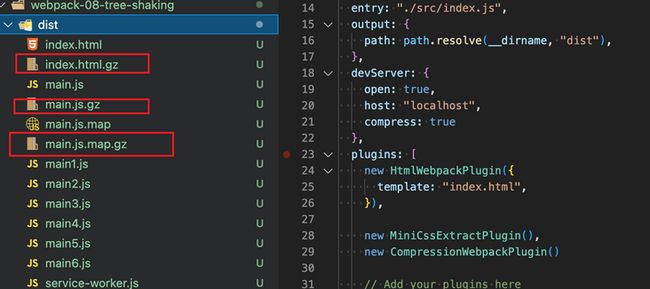
但是我们发现html以及map.js.map文件也被gizp压缩了,这是没有必要的
官方提供了一个exclude,可以排除某些文件不被gizp压缩
{
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: "index.html",
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin(),
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
exclude: /.(html|map)$/i // 排除html,map文件
})
// Add your plugins here
// Learn more about plugins from https://webpack.js.org/configuration/plugins/
],
}css tree shaking
主要删除未使用的样式,如果样式未使用,就删除掉。
现在修改下index.js
我在body中插入一个class
import { add } from './utils'
import './utils/watch';
import './css/index.css'
console.log("Hello World!");
console.log(add(1, 2))
// /*#__PURE__*/ watchEnv(process.env.NODE_ENV)
const bodyDom = document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0]
const divDom = document.createElement('div');
divDom.setAttribute('class', 'wrap-box');
bodyDom.appendChild(divDom);对应的css如下
.wrap-box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
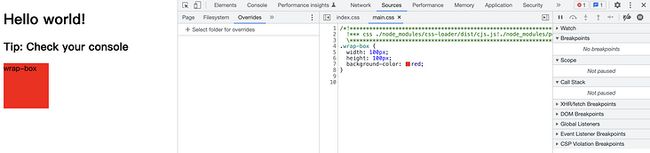
于是苦思瞑想,不得其解,于是一顿排查,当我们把sideEffects: false时,神奇的是,样式没有被删掉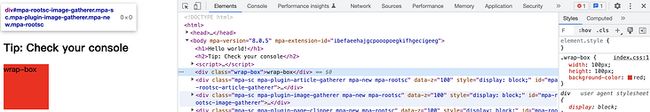
原来是sideEffects:true把引入的css当成没有副作用的代码给删除了,此时,你需要告诉webpack不要删除我的这有用的代码,不要误删了,因为import 'xxx.css'如果设置了sideEffects: true,此时引入的css会被当成无副作用的代码,就给删除了。
// package.json
{
"sideEffects": [
"**/*.css"
],
}当你设置完后,页面就可以正常显示css了
官方也提供了另外一种方案,你可以在module.rules中设置
{
module: {
rules: [
{
test: /\.css$/i,
sideEffects: true,
use: [stylesHandler, "css-loader", "postcss-loader"],
},
]
}
}以上与在package.json设置一样的效果,都是让webpack不要误删了无副作用的css的代码
但是现在有这样的css代码
.wrap-box {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
.title {
color: green;
}title页面没有被引用,但是也被打包进去了
此时需要一个插件来帮助我们来完成css的摇树purgecss-webpack-plugin
const path = require("path");
...
const glob = require('glob');
const PurgeCSSPlugin = require('purgecss-webpack-plugin');
const PATH = {
src: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src')
}
const config = {
...
plugins: [
...
new PurgeCSSPlugin({
paths: glob.sync(`${PATH.src}/**/*`, { nodir: true }),
})
// Add your plugins here
// Learn more about plugins from https://webpack.js.org/configuration/plugins/
],
...
};
分包
主要是减少入口依赖文件包的体积,如果不进行拆包,那么我们根据entry的文件打包就很大。那么也会影响首页加载的性能。
官方提供了两种方案:
- entry 分多个文件,举个栗子
引入loadsh
// index.js
import { add } from './utils';
import _ from 'loadsh';
import './utils/watch';
import './css/index.css';
console.log("Hello World!");
console.log(add(1, 2))
// /*#__PURE__*/ watchEnv(process.env.NODE_ENV)
const bodyDom = document.getElementsByTagName('body')[0]
const divDom = document.createElement('div');
divDom.setAttribute('class', 'wrap-box');
divDom.innerText = 'wrap-box';
bodyDom.appendChild(divDom);
console.log(_.last(['Maic', 'Web技术学苑']));
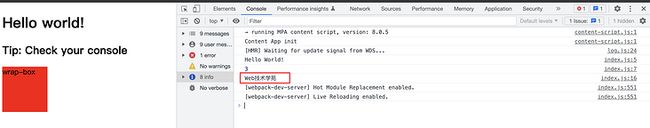
main.js中将loadsh打包进去了,体积也非常之大72kb
我们现在利用entry进行分包
const config = {
entry: {
main: { import: ['./src/index'], dependOn: 'loadsh-vendors' },
'loadsh-vendors': ['loadsh']
},
}此时我们再次运行npm run build:dev
此时main.js的大小1kb,但是loadsh已经被分离出来了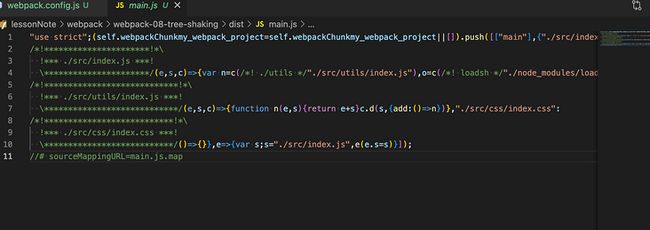

生成的loadsh-vendors.js会被单独引入
可以看下打包后的index.html
Webpack App
Hello world!
Tip: Check your console
splitChunks
主要是在optimzation.splitChunks对于动态导入模块,在webpack4+就默认采取分块策略const config = { // entry: { // main: { import: ['./src/index'], dependOn: 'loadsh-vendors' }, // 'loadsh-vendors': ['loadsh'] // }, entry: './src/index.js', ... } module.exports = () => { if (isProduction) { config.mode = "production"; config.plugins.push(new WorkboxWebpackPlugin.GenerateSW()); } else { config.mode = "development"; config.devtool = 'source-map', config.optimization = { splitChunks: { chunks: 'all' // 支持异步和非异步共享chunk }, sideEffects: true, usedExports: true, minimize: true, // 开启terser minimizer: [new TerserPlugin({ extractComments: false, // 是否将注释剥离到单独文件,默认是true })] } } return config; };
关于optimization.splitChunks的设置非常之多,有对缓存的设置,有对chunk大小的限制,最常用的还是设置chunks:all,建议SplitChunksPlugin多读几遍,一定会找到不少收获。
runtimeChunk
主要减少依赖入口文件打包体积,当我们设置optimization.runtimeChunk时,运行时依赖的代码会独立打包成一个runtime.xxx.js... config.optimization = { runtimeChunk: true, // 减少入口文件打包的体积,运行时代码会独立抽离成一个runtime的文件 splitChunks: { minChunks: 1, // 默认是1,可以不设置 chunks: 'all', // 支持异步和非异步共享chunk }, sideEffects: true, usedExports: true, minimize: true, // 开启terser minimizer: [new TerserPlugin({ extractComments: false, // 是否将注释剥离到单独文件,默认是true })] }- Externals 外部扩展
第三种方案就是,webpack提供了一个外部扩展,将输出的bundle.js排除第三方的依赖,参考Externals
const config = {
// entry: {
// main: { import: ['./src/index'], dependOn: 'loadsh-vendors' },
// 'loadsh-vendors': ['loadsh']
// },
entry: './src/index.js',
...,
externals: /^(loadsh)$/i,
/* or
externals: {
loadsh: '_'
}
*/
};
module.exports = () => {
if (isProduction) {
config.mode = "production";
config.plugins.push(new WorkboxWebpackPlugin.GenerateSW());
} else {
config.mode = "development";
config.devtool = 'source-map',
config.optimization = {
runtimeChunk: true, // 减少入口文件打包的体积,运行时代码会独立抽离成一个runtime的文件
// splitChunks: {
// minChunks: 1,
// chunks: 'all', // 支持异步和非异步共享chunk
// },
sideEffects: true,
usedExports: true,
minimize: true, // 开启terser
minimizer: [new TerserPlugin({
extractComments: false, // 是否将注释剥离到单独文件,默认是true
})]
}
}
return config;
};但是此时loash已经被我们移除了,我们还需在HtmlWebpackPlugin中加入引入的cdn地址
...
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
template: "index.html",
inject: 'body', // 插入到body中
cdn: {
basePath: 'https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs',
js: [
'/lodash.js/4.17.21/lodash.min.js'
]
}
}),
]修改模版,由于模版内容是ejs,所以我们循环取出js数组中的数据
Webpack App
Hello world!
Tip: Check your console
<% for (var i in htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn && htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.js) { %>
<% } %>
此时你运行命令npm run build:dev,然后打开html页面
但是我们发现当我们运行npm run serve启动本地服务,此时页面还是会引入loadsh,在开发环境,其实并不需要引入,本身生成的bundle.js就是在内存中加载的,很显然不是我们需要的
此时我需要做几件事
1、开发环境我不允许引入externals
2、模版html中需要根据环境判断是否需要插入cdn
const isProduction = process.env.NODE_ENV == "production";
const stylesHandler = MiniCssExtractPlugin.loader;
const PATH = {
src: path.resolve(__dirname, 'src')
}
const config = {
// entry: {
// main: { import: ['./src/index'], dependOn: 'loadsh-vendors' },
// 'loadsh-vendors': ['loadsh']
// },
entry: './src/index.js',
output: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "dist"),
},
devServer: {
open: true,
host: "localhost",
compress: true
},
plugins: [
new HtmlWebpackPlugin({
env: process.env.NODE_ENV, // 传入模版中的环境
template: "index.html",
inject: 'body', // 插入到body中
cdn: {
basePath: 'https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs',
js: [
'/lodash.js/4.17.21/lodash.min.js'
]
}
}),
new MiniCssExtractPlugin(),
new CompressionWebpackPlugin({
exclude: /.(html|map)$/i // 排除html,map文件不做gizp压缩
}),
new PurgeCSSPlugin({
paths: glob.sync(`${PATH.src}/**/*`, { nodir: true }),
})
// Add your plugins here
// Learn more about plugins from https://webpack.js.org/configuration/plugins/
],
...
// externals: /^(loadsh)$/i,
externals: isProduction ? {
loadsh: '_'
} : {}
};根据传入模版的env判断是否需要插入cdn
...
<% if (htmlWebpackPlugin.options.env === 'production') { %>
<% for (var i in htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn && htmlWebpackPlugin.options.cdn.js) { %>
<% } %>
<% } %>图片资源压缩
主要是有选择的压缩图片资源,我们可以看下module.rules.parser
module.rules.parser.dataUrlCondition
对应的资源文件可以限制图片的输出,比如静态资源模块类型module: { rules: [ { test: /\.(png|svg|jpg|jpeg|gif)$/i, type: 'asset/resource', parser: { dataUrlCondition: { maxSize: 4 * 1024 // 小于4kb将会base64输出 } } }, ], },官方提供了一个ImageMinimizerWebpackPlugin
我们需要安装npm i image-minimizer-webpack-plugin imagemin --save-dev在
webpack.config.js中引入image-minimizer-webpack-plugin,并且在plugins中引入这个插件,注意webpack5官网那份文档很旧,参考npm上npm-image-minimizer-webpack-plugin
按照官网的,就直接报错一些配置参数不存在,我估计文档没及时更新
...
const ImageMinimizerPlugin = require('image-minimizer-webpack-plugin');
const config = {
plugins: [
...
new ImageMinimizerPlugin({
minimizer: {
// Implementation
implementation: ImageMinimizerPlugin.squooshMinify,
},
})
// Add your plugins here
// Learn more about plugins from https://webpack.js.org/configuration/plugins/
],
}未压缩前
压缩后
使用压缩后,图片无损压缩体积大小压缩大小缩小一半,并且网络加载图片时间从18.87ms减少到4.81ms,时间加载上接近5倍的差距,因此可以用这个插件来优化图片加载。
这个插件可以将图片转成webp格式,具体参考官方文档效果测试一下
总结
1、webpack如何做treeShaking,主要是两种
- optimization中设置
usedExports:true,但是要配合terser压缩插件才会生效 - optimization中设置
sideEffects: true,在package.json中设置sideEffects:false去除无副作用的代码,但是注意css引入会当成无副作用的代码,此时需要在rules的css规则中标记sideEffects: true,这样就不会删除css了
2、webpack的gizp压缩
主要是利用CompressionWebpackPlugin官方提供的这个插件
3、css如何做treeShaking,
主要是利用PurgeCSSPlugin这个插件,会将没有引用css删除
4、入口依赖文件拆包
- 第一种是在入口文件
entry中分包处理,将依赖的第三方库独立打包成一个公用的bundle.js,入口文件不会把第三方包打包到里面去 - 第二种利用
optimization.splitChunks设置chunks:'all'将同步或者异步的esModule方式的代码进行分包处理,会单独打成一个公用的js - 利用外置扩展
externals将第三方包分离出去,此时第三方包不会打包到入口文件中去,不过注意要在ejs模版中进行单独引入
5、图片资源加载优化
- 主要是利用静态资源模块对文件体积小的可以进行base64
- 利用社区插件
image-minimizer-webpack-plugin做图片压缩处理
6、本文示例code-example
欢迎关注公众号:Web技术学苑
好好学习,天天向上!