c++学习笔记1(实验1)_封装CMatrix类
文章目录
- 为何要数据抽象和封装
- 一、类
-
- 1. 类的定义和声明
-
- 1.1 概念
- 1.2 类声明
-
- 1.2.1 访问控制
- 1. 2. #ifndef:
- 1.3 实现类成员函数
- 1.4 const成员函数
- 2. this指针
- 3. 构造函数与析构函数
-
- 3.1 构造函数
- 3.2 析构函数
- 4. 对象数组
- 5. 类作用域
- 6. 抽象数据类型
- 二、使用类
-
- 1. 运算符重载
-
- 1. 1 赋值操作符
- 1. 2 输入和输出运输符
- 1. 3 算术运算符重载
- 1. 4 关系运算符重载
- 1. 5 下标操作符
- 1. 6 调用操作符
- 2. 友元
- 3. 转换
- 4. static 类成员
- 实验部分(封装CMatrix类)
-
- 1. 类声明——cmatrix.h
- 2. 实现类成员函数——cmatrix.cpp
- 3.使用类——mian.cpp
- 结果
为何要数据抽象和封装
- 避免类内部出现无意的、可能破坏对象状态的用户级错误
- 随时间推移可以根据需求改变货缺陷报告来完善类实现,而无需改变用户级代码
一、类
1. 类的定义和声明
1.1 概念
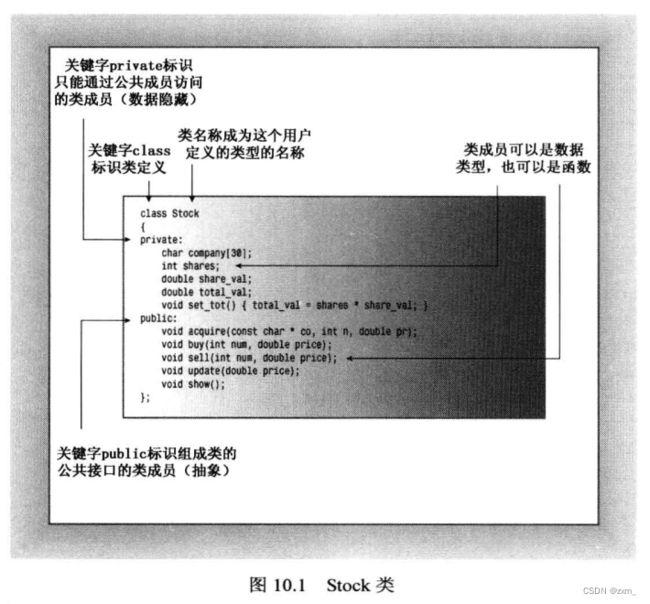
类:
类是一种将抽象转化为用户定义类型(用户定义类型:实现抽象接口的类设计)的C++工具。
接口:
接口是一个共享框架是一个共享框架,共两个系统(eg:我与计算机)交互时使用。比如我们使用计算机时,程序接口将我们的意图转化为存储在计算机中的具体信息。
通常,将接口(类定义)放在头文件(类声明)中,将实现(类方法的代码)放在源代码文件中。
一般,我们将类名首字母大写(常见但不通用的约定)
类设计:
类设计应尽可能将公有接口与实现细节分开。例如,将类函数定义和类声明放在不同的文件中。
公有接口表示设计的抽象组件————————————类声明
将实现细节放在一起并将细节与抽象分开(封装)——类函数定义
1.2 类声明
1.2.1 访问控制
防止程序直接访问数据-》数据隐藏
public (都可以访问)
private(数据隐藏:数据部分的访问状态时私有的,这意味这程序不能直接访问数据成员,只能通过成员函数来访问数据成员)
protected(与private类似,区别只有在基类派生的类中才会表现出来)
由于隐藏数据时OOP的主要目标之一,通常将数据项放在私有部分,组成类接口的成员函数放在公有部分。
1. 2. #ifndef:
#ifndef 来访问多次包含包含同一个文件
#ifndef <标识>
...
#endif
#ifndef起到的效果是防止一个源文件两次包含同一个头文件,而不是防止两个源文件包含同一个头文件。事实上,防止同一头文件被两个不同的源文件包含这种要求本身就是不合理的,头文件存在的价值就是被不同的源文件包含。
假如你有一个C源文件,它包含了多个头文件,比如头文件A和头文件B,而头文件B又包含了头文件A,则最终的效果是,该源文件包含了两次头文件A。如果你在头文件A里定义了结构体或者类类型(这是最常见的情况),那么问题来了,编译时会报大量的重复定义错误。
1.3 实现类成员函数
基本与常规函数定义类似,有两个特征:
- 定义成员函数时,使用作用域解析运算符(::)来标识函数所属的类
- 类方法可以访问类的private组件(非成员函数禁止这样做,友元函数除外)
1.4 const成员函数
![]()
像这种方式声明和定义的类函数——>const成员函数
只要类方法不修改调用对象,就应该声明为const
- 在C++中,只有被声明为const的成员函数才能被一个const类对象调用。
值得注意的是,如果类中存在指针类型的数据成员即便是const函数只能保证不修改该指针的值,并不能保证不修改指针指向的对象。 - const成员函数可以被对应的具有相同形参列表的非const成员函数重载
2. this指针
this为对象的地址,*this为对象本身
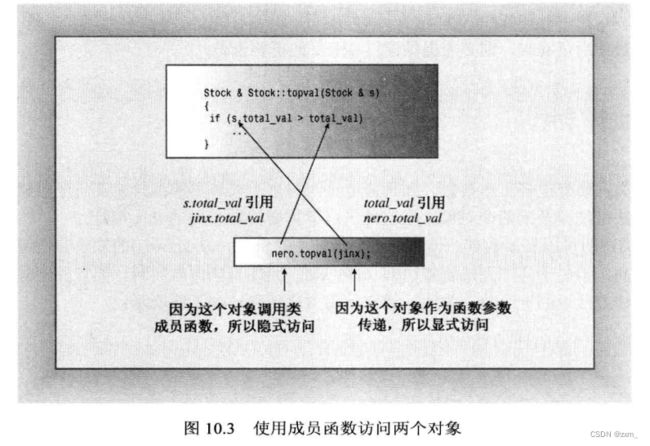
当类成员函数涉及到两个对象时,需要使用this指针
每个成员函数(包括构造函数和析构函数)都有一个this指针,this指针指向调用对象。
如果在函数后面加上const(const成员函数),将this限定为从const,则不能使用this来修改对象的值。
返回类型为引用(* this 专门用于表示当前对象的地址)——返回的时调用对象本身而不是副本
3. 构造函数与析构函数
3.1 构造函数
最好在创建对象时对它进行初始化,C++提供了一个特殊的成员函数——类构造函数,专门用于构造新对象、将值赋给它们的数据成员(在创建类对象时被调用)。
通过函数重载,可以创建多个同名的构造函数,条件是他们的 参数列表 不同
默认构造函数 (如果没有提供任何构造函数,c++将自动提供默认构造函数,但是为类定义了构造函数之后,程序员就必须为其提供默认构造函数)

构造函数是特殊的成员函数,只要创建类类型的新对象,都要执行构造函数,其目的是保证每个对象的数据成员具有合适的初始值。
3.2 析构函数
在构造函数创建对象后,程序负责跟踪该对象,直到其过期为止。对象过期时,程序将自动调用析构函数。析构函数将完成清理工作,如果构造函数中使用new来分配内存,那么析构函数将使用delete来释放这些内存。
构造函数和析构函数都可以没有返回值和声明类型。
![]()
此外,析构函数还可以没有参数。
4. 对象数组
5. 类作用域
6. 抽象数据类型
二、使用类
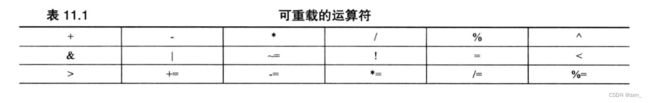
1. 运算符重载
函数多态(函数重载)指的是可以有多个同名的函数,因此对函数的名称进行了重载。
特征标——函数的参数列表(特征标相同==参数数目和类型相同+参数的排列顺序相同(与变量名无关))
注意点:
- C++进行检查时,为了避免混乱,将类型引用 &x 和类型本身 x 是为同一特征标
- const指针和常规指针要注意:将非const值赋给const是合法的,但反之是非法的
- 如果函数调用没有和任何原型匹配,C++将尝试使用标准类型转换 强制进行匹配
运算符重载是一种形式的C++多态。
重载限制:
1. 1 赋值操作符
// 重载=运算符
CMatrix & CMatrix::operator=(const CMatrix & mIn)
{
Release();
m_nRow=mIn.m_nRow;
m_nCol=mIn.m_nCol;
m_pData=new double[m_nRow*m_nCol];
memcpy(m_pData,mIn.m_pData,sizeof(double)*m_nRow*m_nCol);
return *this;
}
// 重载+=运算符 写法一(使用时只能写一种写法)
CMatrix & CMatrix:: operator+=(const CMatrix &b)
{ // 该函数隐式地访问一个对象,显式地访问另一个对象,并返回其中一个对象的引用
if(m_nRow==b.m_nRow&&m_nCol==b.m_nCol)
{
for(int i=0;i<m_nRow*m_nCol;i++)
{
m_pData[i]=m_pData[i]+b.m_pData[i];
}
}
return *this;
}
// 重载+=运算符 写法二(使用时只能写一种写法)
CMatrix & CMatrix::operator+=(const CMatrix &a,const CMatrix &b)
{
CMatrix c;
if(a.m_nRow==b.m_nRow&&a.m_nCol==b.m_nCol)
{
c.Create(a.m_nRow,a.m_nCol);
for(int i=0;i<a.m_nRow*a.m_nCol;i++)
{
c.m_pData[i]=a.m_pData[i]+b.m_pData[i];
}
}
return c;
}
1. 2 输入和输出运输符
// 重载<<运算符
ostream & operator<<(ostream &out, const CMatrix & s)
{
out<<s.m_nRow<<"\t"<<s.m_nCol<<"\t";
for(int i=0;i<s.m_nRow*s.m_nCol;i++)
out<<s.m_pData[i]<<"\t";
return out;
}
// 重载>>运算符
istream & operator>>(istream &in, CMatrix & s)
{
if(s.m_pData)
{
delete[] s.m_pData;
s.m_nRow=0;
s.m_nCol=0;
}
in>>s.m_nRow>>s.m_nCol;
s.m_pData = new double[s.m_nRow*s.m_nCol];
for(int i=0;i<s.m_nRow*s.m_nCol;i++)
{
in>>s.m_pData[i];
}
return in;
}
1. 3 算术运算符重载
CMatrix & CMatrix::operator+(const CMatrix &a,const CMatrix &b)
{
CMatrix c;
if(a.m_nRow==b.m_nRow&&a.m_nCol==b.m_nCol)
{
c.Create(a.m_nRow,a.m_nCol);
for(int i=0;i<a.m_nRow*a.m_nCol;i++)
{
c.m_pData[i]=a.m_pData[i]+b.m_pData[i];
}
}
return c;
}
1. 4 关系运算符重载
bool & CMatrix::operator==(const CMatrix &b)
{
bool flag=true;
if(m_nRow==b.m_nRow&&m_nCol==b.m_nCol)
{
for(int i=0;i<m_nRow*m_nCol;i++)
{
if(m_pData[i]!=b.m_pData[i])
flag=false;
}
}
return flag;
}
1. 5 下标操作符
double & CMatrix::operator[](int nIndex){
return m_pData[nIndex];
}
1. 6 调用操作符
double & CMatrix::operator()(int i,int j){
return m_pData[i*m_nRow+j];
}
2. 友元
 通过让函数成为类的友元,可以赋予该函数与类的成员函数相同的访问权限。
通过让函数成为类的友元,可以赋予该函数与类的成员函数相同的访问权限。
3. 转换
C++是如何处理内置类型转换:
将一个标准类型变量的值赋给另一种标准类型的变量时,如果这两种类型兼容,则C++自动将这个值转换为接收变量的类型。
// 自动转换
int side = 3.33; // double value 3.33 converted to type int 3
// 强制转换
int * p =(int *) 10; // ok, p and (int *) 10 both pointers
CMatrix::operator double() const
{
// 不需要返回值,这个是隐式类型转换
// 虽然没有声明返回类型,但是这个函数也将返回所需的值。
double sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<m_nRow*m_nCol;i++)
{
sum+=m_pData[i];
}
return sum;
}
4. static 类成员
注意:不要将静态成员的定义放在头文件中,除非保证该头文件不会被两个不同的源文件包含,不然会报重复定义错误,相当于是在两个源文件中都定义了同一个变量。对于这种同一头文件被不同源文件包含的情况,使用#ifndef或者#pragma once是没用的。这种预编译宏是为了解决一个源文件两次包含同一个头文件的问题。
同时,对静态数据成员的定义也不能放在main()函数里,否则编译报错:error C2655: “Box::height”: 当前范围内的定义或重新声明非法。正确的做法,就如上面所说,把它放在定义类的成员函数的源文件中。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/fb_941219/article/details/101024110
// 声明cpp
static int GetDim();
// 实现cpp
int CMatrix::GetDim()
{
cout<<"GetDim()" <<endl;
return m_nDim;
}
实验部分(封装CMatrix类)
1. 类声明——cmatrix.h
#ifndef CMATRIX_R
#define CMATRIX_R
#include
double * m_pData;
int m_nCol;//列数
int m_nRow;//行数
static const int m_nDim=2;//const 修饰成员变量
};
// 内联函数 需要先声明
inline double CMatrix::Get(int nIndex) const
{
cout<<"Get(int)" <<endl;
return m_pData[nIndex];
}
inline double CMatrix::Get(int nRow,int nCol) const
{
cout<<"Get(int,int)" <<endl;
return m_pData[nRow*nCol+nCol];
}
#endif //CMATRIX_H
2. 实现类成员函数——cmatrix.cpp
#include "cmatrix.h"
#include
double & CMatrix::operator[](int nIndex){
cout<<"重载下标操作符([]" <<endl;
return m_pData[nIndex];
}
double & CMatrix::operator()(int i,int j){
cout<<"重载调用操作符()" <<endl;
return m_pData[i*m_nRow+j];
}
CMatrix::operator double() const
{
//不需要返回值,这个是隐式类型转换
cout<<"重载double()" <<endl;
double sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<m_nRow*m_nCol;i++)
{
sum+=m_pData[i];
}
return sum;
}
3.使用类——mian.cpp
#include 结果
CMatrix(int,int,double)
Create(int,int)
Release()
Write(string) const
Read(string)
m_nRow=3 m_nCol=3
m_nRow*m_nCol=9
i=0
i=1
i=2
i=3
i=4
i=5
i=6
i=7
i=8
Write(string) const
重载<<
3 3 1 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 3
Set(int,int,double)
Get(int,int)
getint=3
Write(string) const
重载<<
3 3 3 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 3
Read(string)
m_nRow=3 m_nCol=3
m_nRow*m_nCol=9
i=0
i=1
i=2
i=3
i=4
i=5
i=6
i=7
i=8
重载=
Release()
重载==
flag(a==b)=1
重载==
flag(m2==b)=0
m2 重载<<
3 3 3 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 3
b 重载<<
3 3 1 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 3
重载+
Create(int,int)
Release()
重载=
Release()
~CMatrix()
a 重载<<
3 3 1 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 3
b 重载<<
3 3 1 2 3 2 2 2 3 3 3
重载+=
a+=b 重载<<
3 3 2 4 6 4 4 4 6 6 6
c=a+b 重载<<
3 3 2 4 6 4 4 4 6 6 6
重载下标操作符([]
c[0]2
重载调用操作符()
c(1,1)4
重载double()
sum=42
~CMatrix()
~CMatrix()
~CMatrix()
~CMatrix()
~CMatrix()
~CMatrix()