Cucumber高阶用法 —— 活用Cucumber测试服务端开放API
Abstract
本文首先介绍了服务端开放API的交互参数和返回格式,引出测试这样风格的API所需要注意的点,进而介绍如何使用Cucumber结合开源的Rest-Assured来测试开放API。对JSON格式的返回数据,本文介绍了如何使用JSON Schema来做数据结构和数据有效性验证,从而保证即使在复杂、大量返回数据的情况下也能够轻松地验证数据结构是否符合期望,同时不放过任何一个不合法的字段值。
服务端开放API
服务端开放API简介
所谓的开放API(OpenAPI)是服务型网站常见的一种应用,网站的服务商将自己的网站服务封装成一系列API(Application Programming Interface,应用编程接口)开放出去,供第三方开发者使用,所开放的API就被称作OpenAPI(开放API)
介绍本例中所使用的API功能,参数和返回结构
本文中所涉及到的开放API主要实现了对数据的查询:根据卡号查询银行卡信息、分页获取满足条件的银行卡记录、查询银行卡对应的账单地址信息等。读者可以通过类io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.AppController所提供的各个方法去逐个查看。后续行文中主要使用了一个开放API:/card/query
Sample app 的实现和启动方式
本文中所述被测试应用是基于Spring boot实现,采用Spring boot可以加快开发和部署速度,加上Spring boot的快速启动方式,能够在开发环境中迅速启动并验证功能的实现是否符合预期设计。
功能实现
被测应用在功能上主要模拟现实的银行业务场景,简单实现了银行卡及其持卡人的信息管理。为了切合当前我们所介绍的测试方法,在实现业务的过程中主要关注了银行卡、持卡人信息的查询。对于行文中所采用的被测Open API,下文会给出详细的解释。
系统略图
在实现开放API功能的过程中,本文主要采用了如图 1 所示的架构,并使用主流的工具加以实现。
应用启动
AppStarter类是整个应用的启动点,启动过程中主要做了:
1, 初始化Spring;
2, 启动Spring boot 及其内嵌的Web Container以接收HTTP请求;
3, 为了便于读者搭建环境,减少不必要的数据库配置过程,同时也为了保证每次运行的时候都是一个干净的环境,数据库采用的是Derby的Memory模式,这样,在Sample app每次启动时都需要重新初始化数据库,并写入测试数据。
当应用成功启动之后,可以从控制台看到类似如下的输出信息
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v1.3.2.RELEASE)
…… …… ……
/*** Database initialization ***/
CREATE TABLE CARD
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY ( START WITH 1, INCREMENT BY 1),
CARD_NUM CHAR(8) NOT NULL UNIQUE,
IS_PRIMARY_CARD SMALLINT DEFAULT 0 NOT NULL,
CARD_OWNER_NAME VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
CARD_TYPE SMALLINT DEFAULT 0 NOT NULL,
STAR_POINTS DECIMAL(10) DEFAULT 0.00 NOT NULL
)
INSERT INTO CARD (CARD_NUM, IS_PRIMARY_CARD, CARD_OWNER_NAME, CARD_TYPE, STAR_POINTS)
VALUES ('C0000001', 1, 'CENT LUI', 0, 1024.64)
INSERT INTO CARD (CARD_NUM, IS_PRIMARY_CARD, CARD_OWNER_NAME, CARD_TYPE, STAR_POINTS)
VALUES ('C0000002', 1, 'ROD JOHN', 0, 1048576.16)
INSERT INTO CARD (CARD_NUM, IS_PRIMARY_CARD, CARD_OWNER_NAME, CARD_TYPE, STAR_POINTS)
VALUES ('C0000003', 1, 'STEVE JOBS', 0, 1048576.16)
INSERT INTO CARD (CARD_NUM, IS_PRIMARY_CARD, CARD_OWNER_NAME, CARD_TYPE, STAR_POINTS)
VALUES ('S0000001', 0, 'CENT LUI', 1, 0.00)
INSERT INTO CARD (CARD_NUM, IS_PRIMARY_CARD, CARD_OWNER_NAME, CARD_TYPE, STAR_POINTS)
VALUES ('S0000002', 0, 'ROD JOHN', 1, 512.64)
INSERT INTO CARD (CARD_NUM, IS_PRIMARY_CARD, CARD_OWNER_NAME, CARD_TYPE, STAR_POINTS)
VALUES ('S0000003', 0, 'STEVE JOBS', 1, 1024.64)
CREATE TABLE ADDRESS
(
ID INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY ( START WITH 1, INCREMENT BY 1),
CARD_NUM CHAR(8) NOT NULL,
REGION VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
COUNTRY VARCHAR(6) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'CHN',
STATE VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
CITY VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
STREET VARCHAR(64) NOT NULL,
EXT_DETAIL VARCHAR(128) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (CARD_NUM) REFERENCES CARD (CARD_NUM)
)
INSERT INTO ADDRESS (CARD_NUM, REGION, COUNTRY, STATE, CITY, STREET, EXT_DETAIL)
SELECT
CARD_NUM,
'AP',
'CN',
'HeNan',
'LuoYang',
'Peking Rd',
'Apartment 1-13-01 No.777'
FROM CARD
INSERT INTO ADDRESS (CARD_NUM, REGION, COUNTRY, STATE, CITY, STREET, EXT_DETAIL)
SELECT
CARD_NUM,
'EU',
'ES',
'Madrid',
'Sol',
'Century Rd',
'Apartment 1-13-01 No.777'
FROM CARD
…… …… ……
/*** Open API URI mappings ***/
Mapped "{[/address/count],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.AppController.countAddress(java.lang.String)
Mapped "{[/card/count],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.AppController.countCards(java.lang.String)
Mapped "{[/address/query],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.AppController.getAddressByCardNum(java.lang.String)
Mapped "{[/address/all],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.AppController.getAllAddress()
Mapped "{[/address/paged],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.AppController.getPagedAddress(java.lang.Integer,java.lang.Integer)
Mapped "{[/card/query],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.AppController.getCardByCardNum(java.lang.String)
Mapped "{[/card/all],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.AppController.getAllCards()
Mapped "{[/card/paged],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.AppController.getPagedCards(java.lang.Integer,java.lang.Integer)
Mapped "{[/database/test],methods=[GET],produces=[application/json]}" onto org.springframework.http.ResponseEntityInteger >> io.cucumber.samples.dw.controller.DatabaseController.filterAddressByCardNum()
…… …… ……
Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http)应用启动验证
当应用启动之后,可以通过应用提供的Open API/database/test来验证系统是否正确启动。若系统正确启动了所有的模块,那么当以GET方法访问Open API/database/test时,能够看到如下的输出内容:
[
{
"cardCount": 6
},
{
"addressCount": 12
}
]开放API “/card/query”
在本例中,这个开放API提供了根据卡号查询银行卡信息以及对应账单地址信息的功能,通过查看它的实现代码,可以发现它接收一个String类型的参数“cardNum”;其返回值是一个银行卡列表所序列化之后的JSON数据。
@RequestMapping(value = "/card/query", method = RequestMethod.GET, produces = "application/json")
@ResponseBody
ResponseEntity getCardByCardNum(@RequestParam("cardNum") String cardNum) {
StandardJsonResponse> response = new StandardJsonResponse<>();
List cardList = cardService.queryCardsByCardNum(cardNum);
response.setData(cardList);
ResponseEntity entity = new ResponseEntity(response, HttpStatus.OK);
return entity;
} 在一次测试调用中,该Open API返回了如下的测试内容:
{
"errName": null,
"errMsg": "SUCCESS",
"errCode": 0,
"data": [
{
"id": 5,
"cardNum": "S0000002",
"cardOwnerName": "ROD JOHN",
"cardType": "1",
"cardSeqNum": 0,
"starPoints": 512,
"cardBillingAddressList": [
{
"id": 5,
"cardNum": "S0000002",
"region": "AP",
"country": "CN",
"state": "HeNan",
"city": "LuoYang",
"street": "Peking Rd",
"extDetail": "Apartment 1-13-01 No.777"
},
{
"id": 11,
"cardNum": "S0000002",
"region": "EU",
"country": "ES",
"state": "Madrid",
"city": "Sol",
"street": "Century Rd",
"extDetail": "Apartment 1-13-01 No.777"
}
],
"primaryCard": false
}
]
}测试面临的问题和测试方法
通过以上对Open API的简介和本例中所主要使用的API/card/query的介绍,相信读者对于被测试的应用及其功能有了较为清晰的理解。如果一个测试人员拿到了这样的Open API的测试需求,他会如何验证这个API是否正如它声称的那样来提供卡片信息查询功能呢?
测试面对的问题
作为测试人员,在面对这个Open API测试需求时,通常需要弄明白以下的问题:
1,该API的主要功能是什么?
2,调用该API的参数是什么?
3,调用该API的HTTP Method方法是什么?
4,该API的返回内容和结构如何?
5,调用该API所产生的影响是否符合期望?
诚然,对于真实情况下的Open API,除去正向的功能性验证之外还有很多需要验证的点,这里暂时先不考虑这些非功能性验证内容和异常验证相关的部分。
其实,上述5个问题的答案已经在前述行文中给出了,手动验证该API,获取上述问题的答案也不是什么不能完成的任务,但是手动验证却也有其局限性,尤其是有大量待验证的API的情形下。通常,在解决了API能否被被验证的问题之后,所面临的是如何能以一种简单而且行之有效的方式自动化的验证这些API。
现实工作中,由于开发迭代速度快,产品代码变更速度快、幅度大,更会出现API文档更新不及时甚至没有文档的情况。基于解决这些问题的考虑,我们首先想到了Live documentation,想到了基于Cucumber来实现自动化验证Open API。
搭建基于Cucumber的测试工程
之所以选择基于Cucumber来测试Open API主要是因为:
1,基于Cucumber的功能描述可以作为Live documentation:既能保持明确清晰的功能描述,又能做到保持最新版本;
2,基于Cucumber-JVM能够轻松实现自动化验证,并且有类似Rest-Assured这样的开源工具,对于时下盛行的返回JSON数据的Open API的验证会非常有效、非常方便。
以下本文以step-by-step的方式讲述如何实现基于Cucumber测试Open API。行文中涉及到的功能实现要求实验机器必须预装Java7和Maven3.2,对于如何安装Java7和Maven3.2以及对应的环境设置,已经超出了本文范畴,如感兴趣,可以参考Oracle JDK和Apache Maven的相关文档。
创建测试Maven项目并启用Cucumber
首先,从创建Maven项目(Intellij IDEA下称作模块)开始,
创建Maven项目可以采用可视化的方式来做:Eclipse和Intellij IDEA都已经充分支持,且有详细的创建过程描述。本文采用命令行方式来创建Maven项目,待配置好JDK和Maven环境之后,在命令行下执行如下命令,既可以创建一个Maven项目:
mvn -B archetype:generate -DgroupId=io.cucumber.samples.dw -DartifactId=open-api-test -Dversion=1.0.0-SNAPSHOT其次,添加project denpendencies:
待上述命令执行完成之后,在命令执行的目录下,会发现有一个新建的项目“open-api-test”。进入该项目,打开pom.xml,添加所需要的dependencies,此处将测试所需要的所有dependencies都添加进来,后续行文中涉及到工具或功能本身时,会对对应的dependencies加以介绍。
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>io.cucumber.samples.dwgroupId>
<artifactId>open-api-testartifactId>
<packaging>jarpackaging>
<version>1.0.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<name>open-api-testname>
<url>http://maven.apache.orgurl>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.7java.version>
<maven.compiler.version>3.3maven.compiler.version>
<junit.version>4.12junit.version>
<cucumber.version>1.2.4cucumber.version>
<spring.version>4.1.7.RELEASEspring.version>
<restassured.version>2.9.0restassured.version>
<jodaTime.version>2.9.3jodaTime.version>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>info.cukesgroupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-javaartifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>info.cukesgroupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-junitartifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>info.cukesgroupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-springartifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-testartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>${junit.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.restassuredgroupId>
<artifactId>rest-assuredartifactId>
<version>${restassured.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.restassuredgroupId>
<artifactId>json-schema-validatorartifactId>
<version>${restassured.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-pluginartifactId>
<version>${maven.compiler.version}version>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF-8encoding>
<source>${java.version}source>
<target>${java.version}target>
<compilerArgument>-WerrorcompilerArgument>
configuration>
plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-resources-pluginartifactId>
<version>2.7version>
<configuration>
<encoding>UTF-8encoding>
configuration>
plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.pluginsgroupId>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-pluginartifactId>
<version>2.19version>
<configuration>
<argLine>-Dfile.encoding=UTF-8argLine>
configuration>
plugin>
plugins>
build>
project>做完上述工作之后,可以通过Maven命令下载对应dependencies到本地,并验证配置的正确性:
mvn clean compile最后,启用Cucumber
使用Cucumber可以有很多层次,上述步骤中添加了Cucumber-JVM到Maven的项目依赖中,也是一种启用,Gherkin feature文件已经可以被正确识别和解析,也可以在测试代码编写中使用Cucumber-JVM所提供的各种功能了。
使用Cucumber DI 容器简化设计
对于致力于以Cucumber实现Live Documentation的读者来说,本文建议是用Cucumber高阶的功能:DI(Dependency Injection)容器。是的,这里所说的Dependency Injection就是大家在使用Spring Framework入门所学习的那个DI。
Cucumber DI容器简介
DI容器可以帮我们管理类实例的创建和维护,使得我们在使用类的时候不需要再使用new关键字去创建它,并且,DI容器可以按照指定的生命周期去管理类的实例,这样,我们在设计和实现测试用例时,能够更加关注架构和业务。
Cucumber几乎支持所有主流的DI容器:
PicoContainer:这是Cucumber-JVM作者Aslak Hellesøy所贡献的一个开源DI容器,其最大的特点是轻量且易于使用。如果读者在此之前尚未接触过DI容器,建议以此DI容器入门;
Guice:Google提供的轻量级DI容器,如果读者已经使用过诸如Spring的DI容器,不建议再采用Guice作为DI容器,原因是:
有一定的学习成本;
在设计上与Spring不太一致,易于混淆。
Spring:一系列非常流行的Java框架,不仅包括DI容器,而且包含了其他非常多的功能;
CDI/Weld:Context and Dependency Injection规范在J2EE平台的实现版本;
OpenEJB:Apache的一款stand-alone EJB Server实现,其中包含了Context and Dependency Injection的实现。
本文采用Spring作为DI容器,原因是Spring Framework在Java开发者中使用极其广泛,对于Spring DI的用法,有比较大的群众基础。
使用Spring作为Cucumber DI容器
将Spring与Cucumber集成的过程其实相当简单,Cucumber-JVM提供了一个cucumber-spring模块工具,管理Cucumber steps、helper utilities的创建,并注入到对应的测试场景中。上述Maven项目的dependencies中的如下部分,是用于Cucumber和Spring集成的:
<dependency>
<groupId>info.cukesgroupId>
<artifactId>cucumber-springartifactId>
<version>${cucumber.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-contextartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframeworkgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-testartifactId>
<version>${spring.version}version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>其中spring-context部分可以有不同的表现形式,可以以上述dependency的形式出现,也可以用Spring annotation配置的形式出现,例如,如下java snippet中的 ContextConfiguration annotation:
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:cucumber.xml")
public class AppStarterTest {
}以Spring作为DI容器,还需要给出Spring beans/context的配置文件,cucumber-spring将其定义为cucumber.xml,关于cucumber.xml中的内容,其符合Spring定义规范,其中你可以定义各种bean,引用各种properties,也可以定义需要scan的packages,也可以定义是否用采用annotation…
下面是本文中所采用的一个样例,由于本文采用了annotation config方式,因此在cucumber.xml中所需要的定义非常简单。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
">
<context:annotation-config/>
<context:component-scan base-package="io.cucumber.samples.dw.helpers"/>
beans>何时初始化DI容器
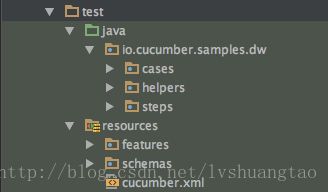
既然DI容器中包含了测试用例运行所需要的各种要素,那么何时初始化各种资源是至关重要的。在解释容器初始化之前,本文为您推荐一个较为实用的测试用例组织结构:
1,resources/features:定义各种功能specifications;
2,resources/schemas:定义JSON Schema validation相关文件;
3,steps:feature文件对应的Java Steps;
4,helpers:用于定义测试用例所共用的工具类、方法等;
5:cases:测试用例入口点。
之所以采用这样的组织结构在于能够:
- 1,能够清晰的组织测试用例;
2,对于同一类artifact,通过命名规范,能够快速定位;
3,统一的测试入口点便于设置Cucumber options,对于用例开发过程中的debug、error analysis有统一的起点。
那么DI容器应该在什么时候初始化呢?
首先,使用helpers初始化DI容器肯定是不合适的,因为helper类和方法自身不能够描述场景,他们只是场景中的一个部分;
其次,如果采用steps类来初始化DI容器,会造成一个问题:对于有多个steps类的情况,会造成DI容器初始化多次!
最后,也是最合适的地方:cases package下的测试用例入口点,其中使用了@ContextConfiguration("classpath:cucumber.xml")出使初始化了DI容器。 请看如下的一个sample:
package io.cucumber.samples.dw.cases;
import cucumber.api.CucumberOptions;
import cucumber.api.junit.Cucumber;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
/**
* Created by stlv for developerworks article
*/
@RunWith(Cucumber.class)
@CucumberOptions(
format = {
"pretty",
"html:target/html-report/",
"json:target/json-report/dw.json"
}
, features = {
"classpath:features"
}
, glue = {
"io.cucumber.samples.dw.steps"
}
, tags = {
"@api",
"~@ui"
}
)
@ContextConfiguration("classpath:cucumber.xml")
public class AppStarterTest {
}对于CucumberOptions,请参考Cucumber使用进阶文章中的介绍,此处不再赘述。
CucumberOptions的override
为什么要override已经定义好的CucumberOptions?最常见的情况可能是这样的:
1,有一个(些)测试用例失败了,在不改变任何文件的前提下,通过override CucumberOptions就能重新运行失败的测试用例,这个是实际场景中最常见的情况;
2,对于不同的测试环境,可以通过override CucumberOptions来实现在不同的环境下运行不同的测试用例;
因此,能够掌握override CucumberOptions,对于熟练掌握Cucumber是非常有益处的。Override CucumberOptions的常用方法有如下两种:
1,通过override Java系统属性
cucumber.options来实现。将
cucumber.options直接传递给Java命令,例如:
java -Dcucumber.options="-g step_definitions features" cucumber.api.cli.Main将
cucumber.options传递给Maven命令,例如:
mvn test -Dcucumber.options="-g step_definitions features"
2,通过定义环境变量
CUCUMBER_OPTIONS来实现:export CUCUMBER_OPTIONS="-g step_definitions features"
以上两种方式的效果是等价的,读者可以依据实际情况采用不同的实现方式。
截止到这里,读者应该已经能够成功搭建出基于Spring DI容器的自动化用例测试工程了;能够以Live documentation方式来做测试。
但是,对于本文中待测的Open API,它返回的是JSON数据,因此,并不建议读者止步于此,建议读者继续阅读下文,了解Rest-Assured工具,将其集成到测试环境,以便实现JSON Schema验证。
集成Rest-Assured和JSON Schema验证
JSON Schema是一个非常强大的JSON结构验证工具,它通过定义JSON的结构、数据取值范围等方式验证JSON数据。
常用类型
JSON Schema将JSON数据类型划分为6中类型:
1,string:文本类型,可以包含Unicode字符;
2,number/integer:数字型或整数型;
3,object:类似于Java中map的概念,包含key机器对应的value,key在JSON中对应与properties,因此object在JSON中对应的是包含零个或多个的properties的复杂结构;
4,array:对应于数组或Java中list的概念。
5,boolean:布尔数据类型。
6,null:null通常用来表示一个不存在的值,当Schema中定义某一个property是null,那么这个property的取值只有一个:null。
另外,加之JSON Schema也支持“引用”的概念,实现Schema定义的复用,因此,使用上述常用类型通过各种组合,就可以定义出各种复杂的数据类型。
定义Schema验证Card这一数据模型
本文所述的Open API的返回值也是JSON数据,样例如下snippet所示。从中可以看出,返回的JSON数据最外层是一个通用的结构,用于表示本次API调用结果;然后,data property是API调用所返回的业务数据。在本例中,它是一个卡片信息描述数据,包括了id,cardNum等诸多properties。同时,还包含了一个cardBillingAddressList用于标识持卡人的账单地址信息列表。
{
"errName": null,
"errMsg": "SUCCESS",
"errCode": 0,
"data": [
{
"id": 1,
"cardNum": "C0000001",
"cardOwnerName": "CENT LUI",
"cardType": "0",
"cardSeqNum": 0,
"starPoints": 1024,
"cardBillingAddressList": [
{
"id": 1,
"cardNum": "C0000001",
"region": "AP",
"country": "CN",
"state": "HeNan",
"city": "LuoYang",
"street": "Peking Rd",
"extDetail": "Apartment 1-13-01 No.777"
},
{
"id": 7,
"cardNum": "C0000001",
"region": "EU",
"country": "ES",
"state": "Madrid",
"city": "Sol",
"street": "Century Rd",
"extDetail": "Apartment 1-13-01 No.777"
}
],
"primaryCard": true
}
]
}对于这样的返回值,根据上面所述的JSON Schema知识,定义出的Schema信息可以如下:
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema#",
"title": "银行卡数据格式验证Schema",
"definitions": {
"eleInnerData": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 1 },
"cardNum": {
"$ref":"common-schema.json#/definitions/cardNum" },
"cardOwnerName": {
"type": "string",
"minLength": 2,
"maxLength": 128 },
"cardType": {
"type": "string",
"minLength": 1,
"maxLength": 1,
"enum": [ "0", "1" ] },
"cardSeqNum": {
"type": "integer",
"minimum": 0,
"maximum": 127 },
"starPoints": {
"type": "number",
"minimum": 0.00 },
"cardBillingAddressList": {
"$ref": "address-schema.json" },
"primaryCard": {
"type": "boolean",
"enum": [ true, false ] }
},
"required": [
"id",
"cardNum",
"cardOwnerName",
"cardType",
"cardSeqNum",
"starPoints",
"cardBillingAddressList",
"primaryCard"
],
"additionalProperties": false
},
"eleData": {
"type": "array",
"items": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/eleInnerData"
},
"minItems": 0
}
},
"allOf": [
{
"$ref": "common-schema.json"
},
{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"data": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/eleData"
}
},
"required": [
"data"
],
"additionalProperties": true
}
]
}其中引用了common-schema的定义如下:
{
"$schema": "http://json-schema.org/draft-04/schema#",
"title": "通用交互数据格式验证Schema",
"definitions": {
"cardNum": {
"type": "string",
"minLength": 8,
"maxLength": 8,
"pattern": "[C|S](0*)\\d+"
},
"errName": {
"anyOf": [
{
"type": "string",
"minLength": 1
},
{
"type": "null"
}
]
},
"errMsg": {
"type": "string",
"minLength": 1
},
"errCode": {
"type": "integer",
"maximum": 0
}
},
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"errName": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/errName"
},
"errMsg": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/errMsg"
},
"errCode": {
"$ref": "#/definitions/errCode"
}
},
"required": ["errName","errMsg","errCode"],
"additionalProperties": true
}注意
本文对于JSON Schema的定义并未详细描述,读者可以参考Understanding JSON Schema学习如何定义一个有效的JSON Schema。
在Rest-Assured中对返回数据执行 JSON Schema Validaiton
Rest-Assured从version 2.10开始支持JSON Schema Validation,读者只需要在pom文件中添加如下的dependency就可以支持JSON Schema Validaiton了:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.restassuredgroupId>
<artifactId>json-schema-validatorartifactId>
<version>2.9.0version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>使用Rest-Assured提供的Schema Validator验证Rest-Assured Response返回数据是非常简单的,下面这个例子中,只是一行代码就能实现以schemaFile所指定的JSON Schema来验证response的body。
public void assertThatRepliedCardDataMetSchemaDefinedSpecs(String schemaFile) {
response.body(
JsonSchemaValidator.matchesJsonSchemaInClasspath("schemas/" + schemaFile));
}结束语
本文首先介绍了服务端开放API的交互参数和返回格式,引出测试这样风格的API所需要注意的点,进而介绍如何使用Cucumber结合开源的Rest-Assured来测试开放API。对JSON格式的返回数据,本文将介绍如何使用JSON Schema来做数据结构和数据合法性验证,从而保证即使在复杂、大量返回数据的情况下也能够轻松地验证数据结构,不放过一个不合法的字段值。
下载
- 示例代码
参考
- Understanding JSON Schema 通过丰富的例子介绍如何能够定义一个有效的JSON Schema。
- The Cucumber for Java Book: Behaviour-Driven Development for Testers and Developers 进阶Cucumber必读书目,Java语言描述
- Cucumber documents 了解Cucumber不同语言的实现
- Cucumber-JVM 使用Cucumber在Java中的实现