微服务-Sentinel流控降级
1. Sentinel简介
1.1 Sentinel是什么?
随着分布式系统变得越来越流行,服务之间的可靠性变得比以往任何时候都更加重要。
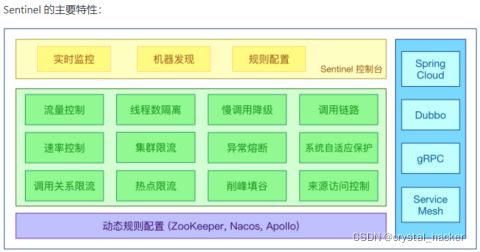
Sentinel, 是一个强大的流控组件,以“流”为切入点,涵盖流控、并发限制、熔断、自适应系统保护等多个领域,保障微服务的可靠性, 简单理解就是流量哨兵, 类似SpringCloud里的熔断器Hystrix, 且比Hystrix更加强大.
轻量级的流量控制、熔断降级的Java库
→Sentinel的GitHub开源
→Sentinel官方介绍
→Sentinel官方下载
1.2 Sentinel能干什么?
1.3 如何使用?
官方使用手册
解决微服务中的服务雪崩 , 服务降级 , 服务熔断 , 服务限流等问题.
1.4 安装Sentinel控制台
Sentinel分为两个部分:
- 核心库(Java客户端), 不依赖任何框架/库, 能够运行于所有Java运行时环境, 同时对Dubbo/SpringCloud等框架提供较好的支持.
- 控制台(Dashboard), 基于SpringBoot开发, 打包后可以直接运行, 不需要额外的Tomcat等应用容器. 也称
哨兵仪表盘.
Sentinel Dashboard 是一个轻量级的控制台,提供机器发现、单服务器资源监控、集群资源数据概览以及规则管理等功能。要使用这些功能,您只需完成几个步骤:
-
或者下载源代码来构建 Sentinel 仪表板,
mvn clean package构建打包即可. -
启动仪表盘, Sentinel 仪表板是标准的 SpringBoot 应用程序,您可以在 Spring Boot 模式下运行 JAR 文件。要求Jdk8环境, 且8080端口不能被占用. 因为Sentinel仪表盘默认使用的8080端口访问.
java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.7.0.jar -
如果与 8080 端口有冲突,可以使用-Dserver.port=new port定义一个新的端口。
java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.7.0.jar -Dserver.port=8081

-
访问Sentinel控制台, 用户名密码默认sentinel/sentinel.
http://localhost:8080

输入用户密码后, 进入Sentinel控制台, 发现是控制台是空的, 因为Sentinel是懒加载的, 需要发一个请求才会有监听的服务.

2. Sentinel入门使用
2.1 创建演示工程
创建演示工程cloudalibaba-sentinel-service-8401
2.1.1 pom依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>atguigu-cloud-2020artifactId>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloudalibaba-sentinel-service-8401artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId>
<version>${project.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discoveryartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cspgroupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacosartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinelartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeignartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutoolgroupId>
<artifactId>hutool-allartifactId>
<version>4.6.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
2.1.2 yml配置
server:
port: 8401
spring:
application:
name: cloudalibaba-sentinel-service
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
#Nacos服务注册中心地址
server-addr: localhost:8848
sentinel:
transport:
#配置Sentinel dashboard地址
dashboard: localhost:8080
#默认8719端口,假如被占用会自动从8719开始依次+1扫描,直至找到未被占用的端口
port: 8719
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: '*'
2.1.3 主启动类
创建主启动类, 并添加注解@EnableDiscoveryClient 开启服务注册和发现配置.
package com.atguigu.springcloud;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class MainApp8401 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApp8401.class);
}
}
2.1.4 编写controller
package com.atguigu.springcloud.controller;
import com.atguigu.springcloud.alibaba.service.OrderService;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
public class FlowLimitController{
@Resource
private FlowLimitService flowLimitService;
@GetMapping("/testA")
public String testA(){
return flowLimitService.common() + "----testA";
}
@GetMapping("/testB")
public String testB(){
return flowLimitService.common() + "----testB";
}
}
package com.atguigu.springcloud.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class FlowLimitService {
// @SentinelResource(value = "common")
public String common() {
return "common";
}
}
2.2 测试
首先, 启动 Nacos注册中心; 再启动Sentinel.
java -jar sentinel-dashboard-1.7.0.jar
启动微服务cloudalibaba-sentinel-service, 访问 http://localhost:8401/testA, http://localhost:8401/testB , 再查看Sentinel控制台.
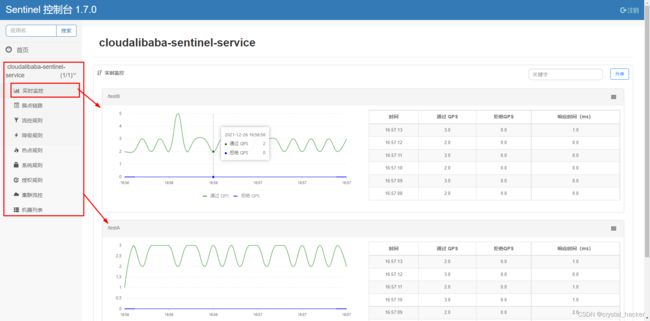
通过上图可以看到Sentinel正在监听微服务cloudalibaba-sentinel-service. 图中可以看到, 除了实时监控外, Sentinel还提供了流控规则, 降级规则, 热点规则, 系统规则 , 授权规则等. 下面将逐个进行介绍.
3. 簇点链路
访问过的资源, 都会被sentinel监控并显示在簇点链路标签页, 每个资源后面提供了为当前资源配置流控, 降级, 热点, 授权规则的入口. 也可以在左侧导航栏分别进行配置.

4. 流控规则
4.1 流控规则介绍
[流控规则]->[+新增流控规则]进行流控规则的创建, 如下图所示:

流控规则的配置项介绍:
- 资源名: 唯一名称, 默认请求路径.
- 针对来源: Sentinel可以针对调用者进行限流, 填写微服务名, 默认default(不区分来源).
- 阈值类型/单机阈值:
QPS: 每秒钟的请求数量, 当调用该api的QPS达到阈值的时候, 进行限流.
线程数: 当调用该api的线程数达到阈值时, 进行限流. - 是否集群: 默认不需要集群.
- 流控模式:
直接: api达到限流条件时, 直接限流.
关联: 当关联的资源达到阈值时, 就限流自己.
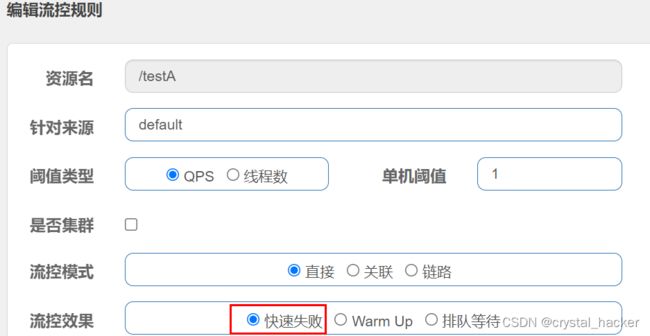
链路: 只记录指定链路上的流量(指定资源从入口资源进来的流量, 如果达到阈值, 就进行限流), 属于api级别的针对来源. - 流控效果:
快速失败: 直接失败, 抛异常.
Warm Up: 根据codeFactor(冷加载因子,默认3)的值, QPS从阈值/codeFactor值开始, 经过预热时长后, 才到达设置的QPS阈值.
排队等待: 匀速排队, 让请求以均速通过, 阈值类型必须设置为QPS, 否则无效.

4.2 流控模式
4.2.1 直接(默认)
系统默认流控模式为直接, 下图表示1秒内/testA资源的访问次数超过设置的阈值1次, 就会直接-快速失败, 转发到系统默认异常界面.

/testA流控规则添加完成, 在流控规则列表可以查看.

快速点击访问 http://localhost:8401/testA, 因为QPS超过阈值被限流了: Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)
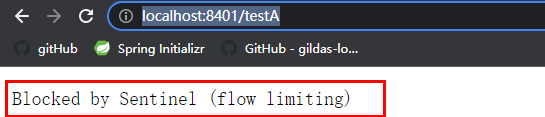
思考: 直接调用默认报错信息, 技术方面是没有问题, 但是客户体验就难说了, 是否应该有类似fallback的后续兜底方法处理. 后面会有解决方案.
4.2.2 关联
当关联的资源达到阈值时, 就限流自己. 比如下图所示:
当与/testA关联的资源/testB达到设置阈值1后, 就限流/testA自己. /testB惹事导致 /testA挂掉.

使用postman密集访问/testB.

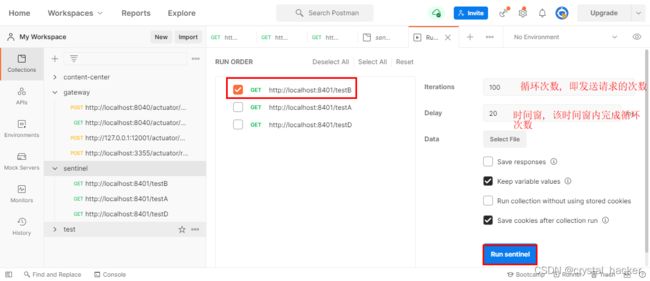
此时再访问http://localhost:8401/testA, 发现/testA资源被流控了.

4.2.3 链路
只记录指定链路上的流量。指定资源从入口资源进来的流量, 如果达到设置阈值, 就进行限流.
FlowLimitController的/testA和/testB都调用FlowLimitService#common()方法,
在FlowLimitService#common()方法上使用注解@SentinelResource添加资源名称, 这样可以被Sentinel监控.
@Service
public class FlowLimitService {
// 添加资源名称common, 会被sentinel监控.
@SentinelResource(value = "common")
public String common() {
return "common";
}
}
然后给资源common设置链路流控规则, 当/testA超过设置阈值时, 会被流控.
这里common是指定资源, /testA是入口资源.

频繁访问/testA, 发现链路的流控规则生效。只为指定链路/testA的资源common限流, /testB的访问不受影响。

频繁访问/testB正常.
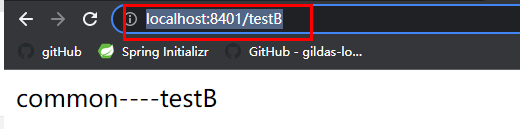
链路的流控规则, 只为/testA的common设置流控规则, /testB的common不受影响.
4.3 流控效果
官方手册→QPS流量控制
当 QPS 超过某个阈值的时候,则采取措施进行流量控制。流量控制的效果包括以下几种:快速失败、Warm Up、匀速排队。对应 FlowRule 中的controlBehavior 字段。
4.3.1 快速失败
默认的流控处理, 直接失败, 抛出异常. Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)
相关源码 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller.DefaultController
4.3.2 Warm Up(预热)
即预热/冷启动方式。当系统长期处于低水位的情况下,当流量突然增加时,直接把系统拉升到高水位可能瞬间把系统压垮。通过"冷启动",让通过的流量缓慢增加,在一定时间内逐渐增加到阈值上限,给冷系统一个预热的时间,避免冷系统被压垮。详细文档可以参考 流量控制 - Warm Up 文档.
通常冷启动的过程系统允许通过的 QPS 曲线如下图所示:

相关源码 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller.WarmUpController
public WarmUpController(double count, int warmUpPeriodInSec) {
construct(count, warmUpPeriodInSec, 3);
}
根据codeFactor(默认3)的值,请求QPS从阈值threshold/codeFactor,经过预热时长,才逐渐达到设置的QPS阈值。
应用场景:秒杀活动,开始瞬间流量会激增,很有可能把系统打死, 使用Warm Up可以使访问流量缓慢的增加, 达到保护系统的效果。
下图为资源/testA设置排队等待的流控规则,根据codeFactor为3,首次阈值为10/3,经过预热时长3s,才会慢慢到达设置的QPS阈值10.

使用Jmeter压测, 前3s放行的QPS差不多10/3左右, 经过预热时长3s后, QPS慢慢恢复到设置的阈值10.

4.3.3 排队等待
匀速排队(RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_RATE_LIMITER)方式会严格控制请求通过的间隔时间,即是让请求以均匀的速度通过,对应的是漏桶算法。详细文档可以参考流量控制-匀速排队模式. 阈值类型必须设置为QPS, 否则无效.
该方式的作用如下图所示:

相关源码: com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.flow.controller.RateLimiterController
应用场景:
主要用于处理间隔性突发的流量,例如消息队列。想象一下这样的场景,在某一秒有大量的请求到来,而接下来的几秒则处于空闲状态,我们希望系统能够在接下来的空闲期间逐渐处理这些请求,而不是在第一秒直接拒绝多余的请求。
给资源/testA设置排队等待规则, 每秒1次请求,超过的话就排队等待,等待的超时时间为20000毫秒。

使用Jmeter压测, 通过控制台日志可以发现系统每秒放行1个请求.

5. 降级规则
Sentinel 熔断降级会在调用链路中某个资源出现不稳定状态时(例如调用超时或异常比例升高),对这个资源的调用进行限制,让请求快速失败,避免影响到其它的资源而导致级联错误。
复习Hystrix
半开状态的系统自动去检测是否请求有异常, 没有异常就关闭断路器,恢复使用,
有异常则继续打开断路器, 系统不可用.
当资源被降级后,在接下来的降级时间窗口之内,对该资源的调用都自动熔断(默认行为是抛出 DegradeException)。
降级-相关源码 com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.slots.block.degrade.DegradeRule#passCheck
官方文档→熔断降级
降级策略介绍:
-
RT(平均响应时间,秒级)
平均响应时间超出阈值且在时间窗口内通过的请求>=5,两个条件同时满足后触发降级; 窗口期过后关闭断路器; RT最大4900(更大的需要通过-Dcsp.sentinel.statistic.max.rt=XXXX才能生效) -
异常比列(秒级)
QPS >= 5 且异常比例(秒级统计)超过阈值时,触发降级;时间窗口结束后,关闭降级.
5.1 RT
平均响应时间(秒级统计) , 当1s内持续进入5个请求, 对应时刻的平均响应时间(秒级)超过阈值(以ms为单位), 那么在接下来的时间窗口内, 对这个方法的调用都会自动熔断, 抛出DegradeException异常.
注意, Sentinel默认统计的RT上限是4900ms, 超出此阈值的都会算作4900ms, 若需要修改可以通过配置项Dcsp.sentinel.statistic.max.rt=XXXX.

添加测试代码 FlowLimitController#testD
@GetMapping("/testD")
public String testD() {
//暂停几秒钟线程
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
int a = 10 / 0; // 模拟异常
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.info("testD 测试RT");
return "------testD";
}
控制台新增RT配置, 单位时间1s内通过的QPS>=5, 且平均响应时间(秒级)超出RT阈值200ms时, 触发熔断器.

使用Jmeter压测, 高并发访问/testD资源, 来达到时间窗口内QPS>5的条件.

http://localhost:8401/testD

然后, 在浏览器访问 /testD资源, 发现服务熔断了.

结论:
永远1秒钟打进来15个线程(大于5个了)调用/testD,我们希望200毫秒处
理完本次任务,如果超过200毫秒还没处理完,在未来1秒的时间窗口内,断
路器打开(保险丝跳闸)微服务不可用.
后续我停止jmeter,没有这么大的访问量了,断路器关闭(保险丝恢复),微服务访问恢复正常.
5.2 异常比例
当单位统计时长(秒级统计)内请求数目大于设置的最小请求数5,并且异常比例大于阈值,则接下来的时间窗口内请求会自动被熔断。时间窗口后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求成功完成(没有错误)则结束熔断,否则会再次被熔断。异常比率的阈值范围是 [0.0, 1.0],代表 0% - 100%.

控制台对资源/testD添加异常比例的降级配置.

使用Jmeter压测, 高并发访问/testD资源, 来满足单位时间1s内QPS>=5的条件. 然后浏览器访问/testD. 单位时间1s内的异常比例超出设置的阈值20%, 服务被熔断降级.

5.3 异常数
当单位时长内(分钟级统计)的异常数超过阈值之后会自动进行熔断。经过时间窗口熔断时长后熔断器会进入探测恢复状态(HALF-OPEN 状态),若接下来的一个请求成功完成(没有错误)则结束熔断,否则会再次被熔断。时间窗口一定要大于等于60秒。
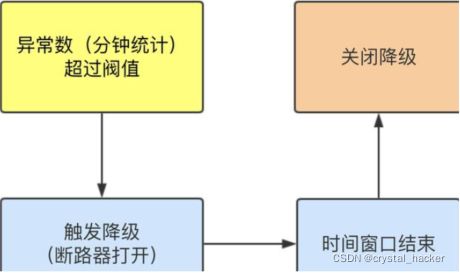
时间窗口<60秒可能会出问题. 10s内统计的异常数大于10,就会触发降级。因为异常数是分钟统计的,如果在接近1分钟时统计的异常数大于10,也会触发降级,所以建议异常数降级策略时,时间窗口的值设置大于60s.
控制台给资源/testD添加异常数的降级配置. 单位时长(1min)内的QPS异常数超出阈值5个, 接下来的时间窗口65s内服务都会被熔断降级.

使用Jmeter压测, 高并发访问/testD资源, 再到浏览器访问/testD, 服务被熔断降级.

6. 热点规则
6.1 热点参数介绍
官方手册→热点参数限流
何为热点?热点即经常访问的数据。很多时候我们希望统计某个热点数据中访问频次最高的 Top K 数据,并对其访问进行限制. 比如:
- 商品 ID 为参数,统计一段时间内最常购买的商品 ID 并进行限制.
- 用户 ID 为参数,针对一段时间内频繁访问的用户 ID 进行限制.
热点参数限流会统计传入参数中的热点参数,并根据配置的限流阈值与模式,对包含热点参数的资源调用进行限流。热点参数限流可以看做是一种特殊的流量控制,仅对包含热点参数的资源调用生效。
Sentinel 利用 LRU 策略统计最近最常访问的热点参数,结合令牌桶算法来进行参数级别的流控。热点参数限流支持集群模式。
6.2 承上启下
之前的案例中, 服务访问异常后被限流,降级或熔断时, 都是给出的系统默认提示:
Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting) .
我们能不能自定义提示, 类似hystrix, 某个api异常后, 就找到对应的兜底方法呢?
答案是有的, hystrix给我们提供的是@HystrixCommand , Sentinel也提供了@SentinelResource注解解决方案.
添加测试代码, @SentinelResource指定资源名称, 以及兜底方法.
@GetMapping(value = "/testHotKey")
@SentinelResource(value = "testHotKey", blockHandler = "dealHandler_testHotKey")
public String testHotKey(@RequestParam(value = "p1", required = false) String p1,
@RequestParam(value = "p2", required = false) String p2) {
int a = 10 / 0; // 模拟异常
return "------testHotKey";
}
public String dealHandler_testHotKey(String p1, String p2, BlockException exception) {
// sentinel系统默认的提示:Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)
return "-----dealHandler_testHotKey";
}
sentinel控制台添加热点参数规则, 下图表示第一个参数有值的话,1秒的QPS为1,超过就限流,限流后调用dealHandler_testHotKey支持方法。

限流模式只支持QPS模式,固定写死了。(这才叫热点)
@SentinelResource注解的方法参数索引,0代表第一个参数,1代表第二个参数,以此类推, 单机阀值以及统计窗口时长表示在此窗口时间超过阀值就限流。
频繁访问 http://localhost:8401/testHotKey?p1=ad, 方法testHotkey里面第一个参数只要QPS超过1, 马上被限流处理. 如果是传入第二个参数p2则访问正常.

6.3 热点参数指定值
上面的热点参数限流仅是普通的做法, 我们期望p1参数为某个特殊值时, 它的限流和平时不一样. 假如: 当p1=5时, 它的阈值可以达到200.
按照特例参数值添加配置

频繁访问http://localhost:8401/testHotKey?p1=3 , 发现时间窗口内QPS超过1, 就被限流.

当频繁访问http://localhost:8401/testHotKey?p1=5, 阈值变为200, 服务正常返回模拟的异常.

上图服务正常返回模拟的异常, 而没有被兜底方法处理. 说明 @SentinelResource注解的blockHandler属性只对Sentinel控制台的配置规则有效, 对程序本身的异常无法处理. 后面可以通过fallback属性进行兜底.
7. 系统规则
官方手册→系统自适应规则
系统保护规则是从应用级别的入口流量进行控制,从单台机器的 load、CPU 使用率、平均 RT、入口 QPS 和并发线程数等几个维度监控应用指标,让系统尽可能跑在最大吞吐量的同时保证系统整体的稳定性。
系统保护规则是应用整体维度的,而不是资源维度的,并且仅对入口流量生效。入口流量指的是进入应用的流量(EntryType.IN),比如 Web 服务或 Dubbo 服务端接收的请求,都属于入口流量。
系统规则支持以下的模式:
- Load 自适应(仅对 Linux/Unix-like 机器生效):系统的 load1 作为启发指标,进行自适应系统保护。当系统 load1 超过设定的启发值,且系统当前的并发线程数超过估算的系统容量时才会触发系统保护(BBR 阶段)。系统容量由系统的 maxQps * minRt 估算得出。设定参考值一般是 CPU cores * 2.5。
- CPU usage(1.5.0+ 版本):当系统 CPU 使用率超过阈值即触发系统保护(取值范围 0.0-1.0),比较灵敏。
- 平均 RT:当单台机器上所有入口流量的平均 RT 达到阈值即触发系统保护,单位是毫秒。
- 并发线程数:当单台机器上所有入口流量的并发线程数达到阈值即触发系统保护。
- 入口 QPS:当单台机器上所有入口流量的 QPS 达到阈值即触发系统保护。

我们把系统处理请求的过程想象为一个水管,到来的请求是往这个水管灌水,当系统处理顺畅的时候,请求不需要排队,直接从水管中穿过,这个请求的RT是最短的;反之,当请求堆积的时候,那么处理请求的时间则会变为:排队时间 + 最短处理时间。
系统规则不是针对资源维度, 而是面向整个系统的入口流量. 有点儿一刀切的感觉. 毕竟有些api的请求并发量可能很大, 有的api请求又很小, 根据业务场景和生产实际情况进行配置使用.
控制台添加入口QPS的系统规则.

频繁访问/testA, /testB或/testD, 都被限流.
![]()


8. 授权规则
官方手册→黑白名单控制
很多时候,我们需要根据调用来源来判断该次请求是否允许放行,这时候可以使用 Sentinel 的来源访问控制(黑白名单控制)的功能。来源访问控制根据资源的请求来源(origin)限制资源是否通过,若配置白名单则只有请求来源位于白名单内时才可通过;若配置黑名单则请求来源位于黑名单时不通过,其余的请求通过。
流控应用 这个位置要填写的是来源标识,Sentinel提供了 RequestOriginParser 接口来处理来源。只要Sentinel保护的接口资源被访问,Sentinel就会调用 RequestOriginParser 的实现类去解析访问来源。
新增一个类交给容器管理:
@Component
public class RequestOriginParserDefinition implements RequestOriginParser {
@Override
public String parseOrigin(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest) {
// 当前 流控应用 放在了请求参数里面,可以放到的地方有很多,比如 参数/请求头/session/等等
return httpServletRequest.getParameter("sourceName");
}
}
为资源/testA设置黑名单.
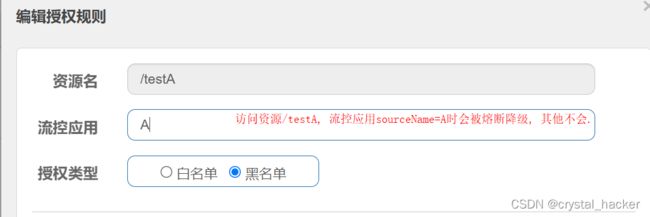
访问 http://localhost:8401/testA?sourceName=A, 服务被熔断降级.

访问http://localhost:8401/testA?sourceName=B正常.

9. @SentinelResource
9.1 按资源名称限流
pom依赖引入自定义的api通用包,可以使用Payment支付Entity
<dependency>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId>
<version>${project.version}version>
dependency>
添加测试代码, 通过@SentinelResource注解指定资源名称 byResource, 自定义限流兜底方法 handleException
@RestController
@Slf4j
public class FlowLimitController {
// ......此处省略部分代码
@GetMapping("/byResource")
@SentinelResource(value = "byResource", blockHandler = "handleException")
public CommonResult byResource() {
return new CommonResult(200, "按资源名称限流测试OK", new Payment(2020L, "serial001"));
}
public CommonResult handleException(BlockException exception) {
return new CommonResult(444, exception.getClass().getCanonicalName() + " 服务不可用");
}
}
在Sentinel控制台对资源 byResource 新增流控规则.
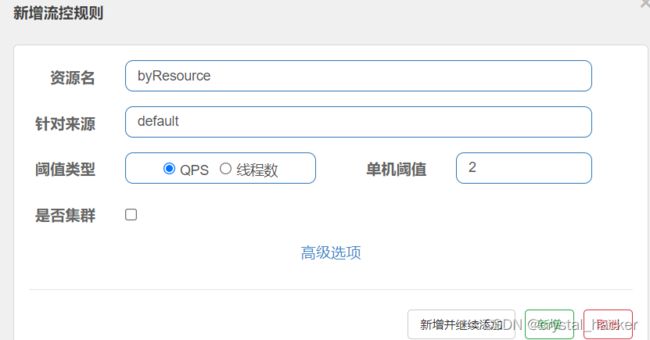
代码和配置对应关系

首先访问一次http://localhost:8401/byResource, 能够正常返回.

当频繁点击访问http://localhost:8401/byResource时, 就会被限流处理, 并返回自定义的兜底处理.
![]()
9.2 按URL地址限流
通过访问的URL来限流, 会返回Sentinel默认的限流处理信息.
添加测试代码, 没有指定自定义兜底方法. 先访问一次该URL, 触发Sentinel监控.
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/byUrl")
@SentinelResource(value = "byUrl")
public CommonResult byUrl() {
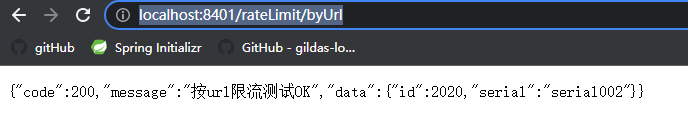
return new CommonResult(200, "按url限流测试OK", new Payment(2020L, "serial002"));
}
Sentinel控制台对URL资源/rateLimit/byUrl添加流控规则.

![]()
先访问一次http://localhost:8401/rateLimit/byUrl , 正常返回.
然后频繁点击, QPS>2时, 触发限流, 返回Sentinel默认的异常信息.
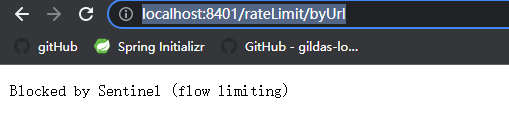
上面的兜底方案面临的问题:
- 系统默认的,没有体现我们自己的业务要求。
- 依照现有条件,我们自定义的处理方法又和业务代码耦合在一块,不直观。
- 每个业务方法都添加一个兜底的,造成代码膨胀加剧。
- 没有全局统一的处理方法。
9.3 自定义限流
创建CustomerBlockHandler类用于自定义限流处理.
public class CustomerBlockHandler {
public static CommonResult handleException(BlockException exception) {
return new CommonResult(2020, "自定义的限流处理信息......CustomerBlockHandler");
}
}
在FlowLimitController类中添加测试代码, 使用@SentinelResource注解的blockHandlerClass属性指定自定义处理类, blockHandler 指定自定义处理方法.
/**
* 自定义通用的限流处理逻辑,
* blockHandlerClass = CustomerBlockHandler.class
* blockHandler = handleException
* 上述配置:找CustomerBlockHandler类里的handleException方法进行兜底处理
*/
/**
* 自定义通用的限流处理逻辑
*/
@GetMapping("/rateLimit/customerBlockHandler")
@SentinelResource(value = "customerBlockHandler", blockHandlerClass = CustomerBlockHandler.class, blockHandler = "handleException")
public CommonResult customerBlockHandler() {
return new CommonResult(200, "按客户自定义限流处理逻辑");
}
启动微服务后先调用一次 http://localhost:8401/rateLimit/customerBlockHandler , 触发Sentinel对该资源的监控.

然后在Sentinel控制台查看customerBlockHandler资源并添加流控规则.

配置规则与代码对应关系

配置流控规则后, 再多次点击访问http://localhost:8401/rateLimit/customerBlockHandler, 就会触发customerBlockHandler资源的流控规则, 被限流处理.

10. 服务熔断
Sentinel整合Ribbon + OpenFeign + fallback, 先启动Nacos和Sentinel的jar包.
10.1 Sentinel整合Ribbon
10.1.1 创建服务提供者
新建服务提供者模块cloudalibaba-provider-payment-9003和cloudalibaba-provider-payment-9004 , 两台做集群部署.
pom依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>atguigu-cloud-2020artifactId>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloudalibaba-provider-payment-9003artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discoveryartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId>
<version>${project.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
yml配置
server:
port: 9003 # 9004
spring:
application:
name: nacos-payment-provider
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848 #配置Nacos地址
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
exclude: '*'
主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class PaymentMain9003 { // PaymentMain9004
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(PaymentMain9003.class);
}
}
controller
这里用写死的数据模拟db查询的数据.
@RestController
public class PaymentController {
@Value("${server.port}")
private String serverPort;
public static HashMap<Long, Payment> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
static {
hashMap.put(1L, new Payment(1L, "28a8c1e3bc2742d8848569891fb42181"));
hashMap.put(2L, new Payment(2L, "bba8c1e3bc2742d8848569891ac32182"));
hashMap.put(3L, new Payment(3L, "6ua8c1e3bc2742d8848569891xt92183"));
}
@GetMapping(value = "/paymentSQL/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> paymentSQL(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
Payment payment = hashMap.get(id);
CommonResult<Payment> result = new CommonResult(200, "from mysql,serverPort: " + serverPort, payment);
return result;
}
}
测试服务提供方
访问9003 , http://localhost:9003/paymentSQL/1, 测试通过.
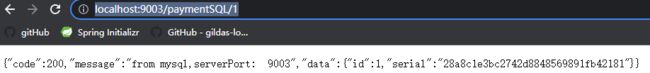
访问9004, http://localhost:9004/paymentSQL/1 , 测试通过.

10.1.2 创建消费者
新建消费者微服务 cloudalibaba-consumer-nacos-order-84.
pom依赖
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>atguigu-cloud-2020artifactId>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<artifactId>cloudalibaba-consumer-nacos-order-84artifactId>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeignartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discoveryartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinelartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.atguigu.springcloudgroupId>
<artifactId>cloud-api-commonsartifactId>
<version>${project.version}version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuatorartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtoolsartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
yml配置
server:
port: 84
spring:
application:
name: nacos-order-consumer
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: localhost:8848 #配置Nacos地址
sentinel:
transport:
dashboard: localhost:8080 #配置Sentinel dashboard地址
port: 8719 #默认8719端口,假如被占用会自动从8719开始依次+1扫描,直至找到未被占用的端口
#消费者将要去访问的微服务名称(注册成功进nacos的微服务提供者)
service-url:
nacos-user-service: http://nacos-payment-provider
# 激活Sentinel对Feign的支持
#feign:
# sentinel:
# enabled: true
主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@EnableFeignClients
public class OrderNacosMain84 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(OrderNacosMain84.class);
}
}
RestTemplate配置
@Configuration
public class ApplicationContextConfig {
@Bean
@LoadBalanced
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
return new RestTemplate();
}
}
controller
@RestController
public class CircleBreakerController {
@Value("${service-url.nacos-user-service}")
private String SERVICE_URL;
@Resource
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
}
10.1.3 业务方法裸测
上面controller中的业务方法不加任何配置.
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback") // 什么兜底方法都没有指定
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
启动微服务应用 , 访问 http://localhost:84//consumer/fallback/4
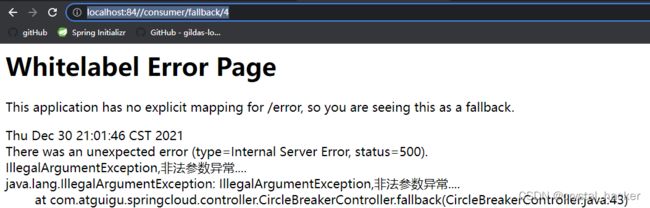
访问http://localhost:84//consumer/fallback/5

上面测试效果是直接给出异常信息界面, 对客户端来说不是很友好. 下面给出友好方案.
10.1.4 业务方法添加fallback
上面controller中的业务方法中使用注解@SentinelResource只添加fallback属性配置, 没有Sentinel配置.
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback") //fallback负责业务异常
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
// 异常兜底方法
public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable Long id, Throwable e) {
Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null");
return new CommonResult<>(444, "兜底异常handlerFallback,exception内容 " + e.getMessage(), payment);
}
重启微服务应用,访问http://localhost:84/consumer/fallback/4
![]()
访问http://localhost:84//consumer/fallback/5

10.1.5 业务方法添加blockHandler
上面controller中的业务方法中使用@SentinelResource注解只添加blockHandler属性配置, 并添加Sentinel配置.
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler") //blockHandler负责在sentinel里面配置的降级限流
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
// 服务限流降级方法
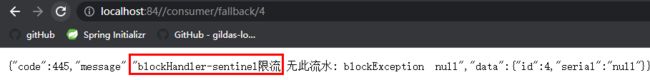
public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable Long id, BlockException blockException) {
Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null");
return new CommonResult<>(445, "blockHandler-sentinel限流,无此流水: blockException " + blockException.getMessage(), payment);
}
在Sentinel控制台给资源fallback添加降级规则配置. 异常数是分钟级统计, 时间窗口>60s.

重启微服务应用, 频繁访问/consumer/fallback/4或/consumer/fallback/5, 异常数超过阈值2时, 被限流降级处理.


10.1.6 同时配置fallback和blockHandler
在上面controller的业务方法上使用@SentinelResource注解同时配置fallback和blockHandler.
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
// fallback和blockHandler都配置, 如果触发sentinel控制台配置的限流或降级规则,blockHandler优先进行降级处理,即blockHandler是针对sentinel配置规则生效的; 如果没有触发sentinel控制台配置的限流或降级规则, 遇到异常由fallback进行兜底.
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler")
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
// 异常兜底方法
public CommonResult handlerFallback(@PathVariable Long id, Throwable e) {
Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null");
return new CommonResult<>(444, "兜底异常handlerFallback,exception内容 " + e.getMessage(), payment);
}
// 服务限流降级方法
public CommonResult blockHandler(@PathVariable Long id, BlockException blockException) {
Payment payment = new Payment(id, "null");
return new CommonResult<>(445, "blockHandler-sentinel限流,无此流水: blockException " + blockException.getMessage(), payment);
}

在sentinel控制台给fallback资源添加流控规则配置.

重启微服务应用, 访问 http://localhost:84//consumer/fallback/1, 正常返回数据.

频繁访问, 当QPS超过阈值2时, 被限流处理.

我们来访问异常数据试试 , http://localhost:84//consumer/fallback/4, 被fallback兜底方法处理.

频繁访问, 当QPS超过阈值2时, 被blockHandler限流处理.
总结:
- fallback负责业务异常
- blockHandler负责在sentinel里面配置的限流降级
- fallback和blockHandler都配置, 如果触发sentinel控制台配置的限流或降级规则,blockHandler优先进行降级处理,即blockHandler是针对sentinel配置规则生效的; 如果没有触发sentinel控制台配置的限流或降级规则, 遇到异常由fallback进行兜底.
10.1.7 忽略属性配置
在上面controller的业务方法中,可以使用@SentinelResource注解的属性exceptionsToIgnore指定不被监控的异常类型. 例如: 我要忽略非法参数异常IllegalArgumentException.
@RequestMapping("/consumer/fallback/{id}")
@SentinelResource(value = "fallback", fallback = "handlerFallback", blockHandler = "blockHandler", exceptionsToIgnore = {IllegalArgumentException.class})
public CommonResult<Payment> fallback(@PathVariable Long id) {
CommonResult<Payment> result = restTemplate.getForObject(SERVICE_URL + "/paymentSQL/" + id, CommonResult.class, id);
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("IllegalArgumentException,非法参数异常....");
} else if (result.getData() == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("NullPointerException,该ID没有对应记录,空指针异常");
}
return result;
}
重启微服务应用, 访问 /consumer/fallback/4, 无论QPS是否超过阈值, 始终都是返回的原生异常界面. 并没有被Sentinel监控并进行限流控制.

10.2 Sentinel整合OpenFeign
10.2.1 添加OpenFeign依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloudgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeignartifactId>
dependency>
10.2.2 配置Feign
激活Sentinel对Feign的支持配置
# 激活Sentinel对Feign的支持
feign:
sentinel:
enabled: true
编写FeignClient接口, 使用@FeignClient注解的value属性声明远程调用的服务实例名称, fallback或fallbackFactory属性指定Feign接口的具体兜底实现.
//@FeignClient(value = "nacos-payment-provider", fallback = PaymentFeignFallback.class)
@FeignClient(value = "nacos-payment-provider", fallbackFactory = PaymentFeignFallbackFactory.class)
public interface PaymentFeignService {
@GetMapping(value = "/paymentSQL/{id}")
CommonResult<Payment> paymentSQL(@PathVariable("id") Long id);
}
10.2.3 编写FeignClient接口实现
@Component
@Slf4j
public class PaymentFeignFallback implements PaymentFeignService {
@Override
public CommonResult<Payment> paymentSQL(Long id) {
log.info(">>>Feign fallback 处理....");
return new CommonResult<>(444, "服务降级返回,没有该流水信息", new Payment(id, "errorSerial......"));
}
}
或者
@Component
@Slf4j
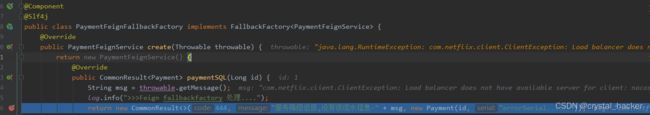
public class PaymentFeignFallbackFactory implements FallbackFactory<PaymentFeignService> {
@Override
public PaymentFeignService create(Throwable throwable) {
return new PaymentFeignService() {
@Override
public CommonResult<Payment> paymentSQL(Long id) {
String msg = throwable.getMessage();
log.info(">>>Feign fallbackfactory 处理....");
return new CommonResult<>(444, "服务降级返回,没有该流水信息-" + msg, new Payment(id, "errorSerial......"));
}
};
}
}
10.2.4 编写controller
controller中添加Feign调用的业务方法.
//--------OpenFeign
@Resource
private PaymentFeignService paymentFeignService;
@RequestMapping("/consumer/openfeign/{id}")
public CommonResult<Payment> paymentSQL(@PathVariable("id") Long id) {
if (id == 4) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法参数,没有该id");
}
return paymentFeignService.paymentSQL(id);
}
主启动类添加@EnableFeignClients注解开启Feign客户端配置.
10.2.5 测试Feign
测试消费者84调用服务提供方9003, http://localhost:84/consumer/openfeign/1, 此时正常返回数据, 说明Feign客户端远程调用服务提供方成功.

此时故意关闭服务提供方 9003 , 再次访问/consumer/openfeign/1, 看消费者84是否会自动降级处理.
通过断点调试可以看到, 调用走到了Feign接口的兜底实现方法中. 对服务调用进行了主动熔断降级处理, 防止消费者84被拖死.

10.3 熔断框架比较
11. 规则持久化
Sentinel控制台的流控规则, 一旦遇到Sentinel重启后就会丢失, 生产环境需要将配置进行持久化.
将限流规则持久化到Nacos配置中心, 只需要刷新微服务实例的某个rest地址, sentinel控制台对其的流控规则就能看到, 只要Nacos里面的持久化配置不删除, Sentinel对微服务实例监控的流控规则就持续有效.
为了Sentinel的规则持久化,下面对微服务cloudalibaba-sentinel-service-8401进行改造. 添加持久化相关的依赖.
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cspgroupId>
<artifactId>sentinel-datasource-nacosartifactId>
dependency>
添加持久化的配置支持
spring:
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
#Nacos服务注册中心地址
server-addr: localhost:8848
sentinel:
transport:
#配置Sentinel dashboard地址
dashboard: localhost:8080
#默认8719端口,假如被占用会自动从8719开始依次+1扫描,直至找到未被占用的端口
port: 8719
# 持久化配置
datasource:
ds1:
nacos:
server-addr: localhost:8848
dataId: cloudalibaba-sentinel-service
groupId: DEFAULT_GROUP
data-type: json
rule-type: flow
nacos配置中心添加sentinel流控规则的配置内容
cloudalibaba-sentinel-service
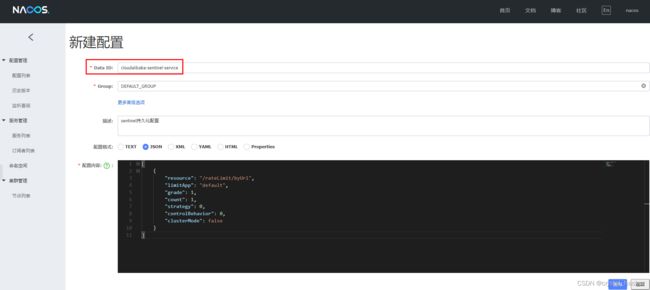
resource:资源名称;
limitApp:来源应用;
grade:阈值类型,0表示线程数,1表示QPS;
count:单机阈值;
strategy:流控模式,0表示直接,1表示关联,2表示链路;
controlBehavior:流控效果,0表示快速失败,1表示Warm Up,2表示排队等待;
clusterMode:是否集群。
重启Sentinel, 启动cloudalibaba-sentinel-service-8401微服务, 访问一次/rateLimit/byUrl, 触发Sentinel对资源/rateLimit/byUrl的监控, 查看Sentinel控制台. 已经从Nacos配置中心拉取了资源/rateLimit/byUrl的流控规则配置内容.

频繁访问 http://localhost:8401//rateLimit/byUrl, 当QPS>1时,会被限流处理.

现在我将Nacos配置中心的流控规则的QPS阈值改为3.

然后刷新Sentinel控制台, 查看到资源/rateLimit/byUrl的流控规则的QPS也更新为3了. 说明应用端从Nacos配置中心拉取了最新的配置同步到Sentinel.

- 上面的持久化是在Nacos配置中心配置的流控规则内容, 然后微服务应用端从Nacos配置中心拉取流控配置内容同步到Sentinel.
- 存在的问题:
上面方案只有拉模式, 从Nacos配置中心拉取最新配置; 没有推模式, 如果Sentinel控制台修改流控规则, 并不会同步到Nacos配置中心.- 推模式的实现需要修改Sentinel源码实现, 可参考 Sentinel规则持久化-推模式-基于Nacos
个人博客
欢迎访问个人博客: https://www.crystalblog.xyz/
备用地址: https://wang-qz.gitee.io/crystal-blog/