【学习笔记】PyTorch(1)神经网络入门
神经网络
利用torch.nn包来构建神经网络,其训练过程大致包括以下几点:
- 定义一个包含可训练参数的神经网络;
- 迭代整个输入;
- 通过神经网络前向传播处理输入;
- 利用优化器计算损失(loss);
- 反向传播梯度到神经网络的参数;
- 更新训练的参数;
1 神经网络各层
神经网络通常包含有:
- 卷积层 Convolution Layer;
- 池化层 Pooling Layer;
- 非线性激活层 Non-linear Activation Layer;
- 线性激活层 Linear Layer;
很多层和函数都可以在torch.nn.functional 和nn.Module中直接调用,什么时候使用nn.Module,什么时候使用nn.functional呢?
一般情况下,如果模型有可学习的参数(如卷积层、全连接层),最好用nn.Module;其他情况(激活函数,损失函数)nn.functional相对更简单一些。
1.1 卷积层
在输入矩阵外填充padding圈0,卷积核在输入矩阵上以stride为步长移动,对应位置元素相乘再相加,得到新的特征图。
- conv
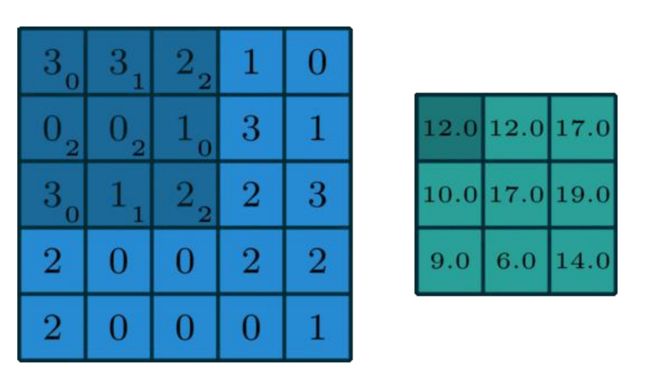
卷积的手动实现
import torch
from torch import nn
def corr2d(X,K):
"""二维卷积"""
xh,xw = X.shape
kh,kw = K.shape
Y = torch.zeros((xh - kh + 1,xw - kw + 1))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]):
for j in range(Y.shape[1]):
Y[i][j] = (X[i:i+kh,j:j+kw] * K).sum()
return Y
class Conv2D(nn.Module):
"""加入可调参数"""
def __init__(self, kernel_size):
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(kernel_size))
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1))
def forward(self, x):
return corr2d(x, self.weight) + self.bias
- padding
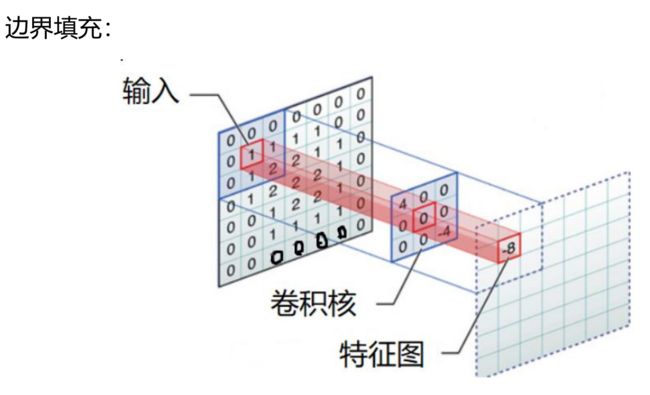
- stride
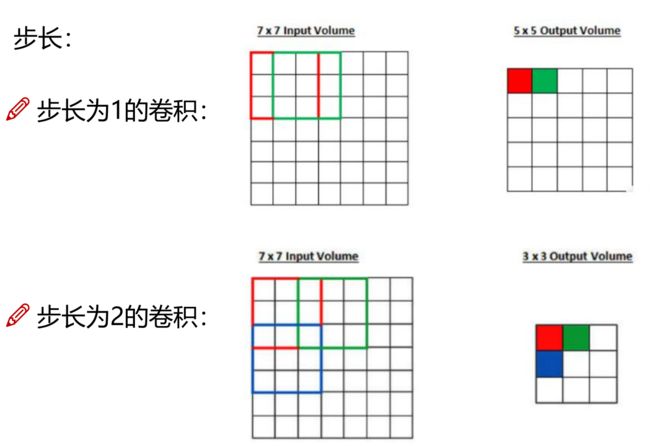
设输入图像的宽度和长度分别为W1、H1,F为卷积核长和宽、P为边界填充(加几圈0),S为滑动窗口步长。输出特征图的宽度和长度分别为W2、H2,其计算公式如下:

eg:
卷积层用torch.nn.functional实现
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
# convolution layer
input = torch.Tensor([[[1,1,2,2,1],
[1,1,1,2,1],
[2,1,1,0,2],
[2,1,0,1,2],
[2,1,2,2,2]],
[[0,1,2,0,1],
[2,2,1,1,0],
[2,1,0,0,2],
[1,0,0,0,2],
[0,1,0,1,2]],
[[2,2,0,1,2],
[0,0,2,1,2],
[2,1,0,2,1],
[1,1,0,0,0],
[0,0,1,1,1]]])
print(input.shape)
kernel = torch.Tensor([[[1,1,1],
[-1,-1,0],
[-1,1,0]],
[[-1,-1,-1],
[-1,1,0],
[-1,1,0]],
[[1,0,-1],
[0,0,0],
[1,-1,-1]]])
# 变换尺寸
input = torch.reshape(input,(1,3,5,5))
kernel = torch.reshape(kernel,(1,3,3,3))
# conv2d二维卷积
output = F.conv2d(input,kernel)
print('stride=1;padding=0时的卷积结果:')
print(output)
# 卷积步长为2
print('stride=2;padding=0时的卷积结果:')
output2 = F.conv2d(input,kernel,stride=2)
print(output2)
# 卷积步长为2;边界填充1圈0;偏置为1
bias = torch.tensor([1])
print('stride=2;padding=1;bias=1时的卷积结果:')
output3 = F.conv2d(input,kernel,bias,stride=2,padding=1)
print(output3)
结果:
stride=1;padding=0时的卷积结果:
tensor([[[[ 0., -2., -7.],
[-10., -4., 2.],
[ -2., -3., -1.]]]])
stride=2;padding=0时的卷积结果:
tensor([[[[ 0., -7.],
[-2., -1.]]]])
stride=2;padding=1;bias=1时的卷积结果:
tensor([[[[ 3., -5., -4.],
[ 0., -3., 7.],
[ 0., 0., -1.]]]])
1.2 池化层
池化层进行下采样,可以减小计算量,防止过拟合。有最大池化(MaxPool)和平均池化(AvgPool),一般采用最大池化。
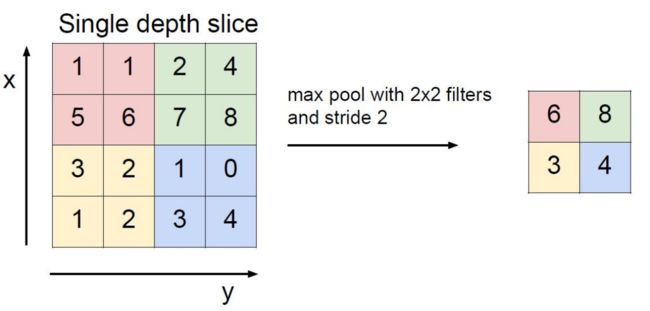
池化手动实现
def pool2d(X, pool_size, mode='max'):
'''池化:mode='max';mode='avg' '''
p_h, p_w = pool_size
Y = torch.zeros((X.shape[0] - p_h + 1, X.shape[1] - p_w + 1))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]):
for j in range(Y.shape[1]):
if mode == 'max':
Y[i, j] = X[i: i + p_h, j: j + p_w].max()
elif mode == 'avg':
Y[i, j] = X[i: i + p_h, j: j + p_w].mean()
return Y
池化层用torch.nn.functional实现
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
# convolution layer
input = torch.Tensor([[1,1,2,4],
[5,6,7,8],
[3,2,1,0],
[1,2,3,4]])
# 变换尺寸
input = torch.reshape(input,(1,1,4,4))
output = F.max_pool2d(input,2)#默认stride=kernel_size;此处默认stride=2
print(output)
结果:
tensor([[[[6., 8.],
[3., 4.]]]])
- 池化层和卷积层类似,都有stride和padding,但没有可以学习的参数;
- 输入通道数=输出通道数。
1.3 非线性激活层
没有激活函数的每层都相当于矩阵相乘,都是线性变换。非线性激活层给神经网络引入了非线性,常用的非线性激活函数有Sigmoid、Tanh、ReLU、Softmax等。
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
input = torch.tensor([[1,-0.5],
[-1, 3]])
print(input)
output = F.relu(input)
print('经过relu后:')
print(output)
结果:
tensor([[ 1.0000, -0.5000],
[-1.0000, 3.0000]])
经过relu后:
tensor([[1., 0.],
[0., 3.]])
1.4 线性层
线性层又称全连接层,每个神经元实现与上一层所有神经元链接,实现对前一层的线性组合。
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
input = torch.tensor([[1,2,3]])
print(input.shape)
weight = torch.tensor([[1,2,3,4],
[1,2,3,4],
[1,2,3,4]])
print(weight.shape)
output = F.linear(input,weight.T)
print('经过linear后:')
print(output)
结果:
torch.Size([1, 3])
torch.Size([3, 4])
经过linear后:
tensor([[ 6, 12, 18, 24]])
2 定义简单的神经网络
定义网络时需要继承nn.Module类,在 __init__函数里定义网络的各层,在forward函数中进行前向传播。
# 导入模块
import torch
from torch.nn import ReLU
input = torch.tensor([[1,-0.5],
[-1, 3]])
input = torch.reshape(input,(-1,1,2,2))
class Model(nn.Module):#继承Module类
def __init__(self) -> None:
super(Model,self).__init__()
#定义网络各层
self.relu1 = ReLU()
# 前向传播函数
def forward(self,input):
output = self.relu1(input)#调用定义的网络层
return output
model = Model()#实例化模型
print('模型:')
print(model)
print('输入:')
print(input)
output = model(input)#用模型迭代输入
print('输出:')
print(output)
结果:
模型:
Model(
(relu1): ReLU()
)
输入:
tensor([[[[ 1.0000, -0.5000],
[-1.0000, 3.0000]]]])
输出:
tensor([[[[1., 0.],
[0., 3.]]]])
- 可以用
Sequential()简化模型定义
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import Conv2d,MaxPool2d,Flatten,Linear,Sequential,L1Loss
import torch
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super(Model,self).__init__()
# self.conv1 = Conv2d(3,32,5,padding=2)#64*32*32*32
# self.maxpool1 = MaxPool2d(2)#64*32*16*16
# self.conv2 = Conv2d(32,32,5,padding=2)#64*32*16*16
# self.maxpool2 = MaxPool2d(2)#64*32*8*8
# self.conv3 = Conv2d(32,64,5,padding=2)#64*64*8*8
# self.maxpool3 = MaxPool2d(2)#64*64*4*4
# self.flatten = Flatten()#64*1024
# self.linear1 = Linear(1024,64)#64*64
# self.linear2 = Linear(64,10)#64*10
self.model1 = Sequential(
Conv2d(3,32,5,padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32,32,5,padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32,64,5,padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Flatten(),
Linear(1024,64),
Linear(64,10)
)
def forward(self,x):
# x = self.conv1(x)
# x = self.maxpool1(x)
# x = self.conv2(x)
# x = self.maxpool2(x)
# x = self.conv3(x)
# x = self.maxpool3(x)
# x = self.flatten(x)
# x = self.linear1(x)
# x = self.linear2(x)
x = self.model1(x)
return x
model = Model()
print(model)
input = torch.ones((64,3,32,32))
print(input.shape)
output = model(input)
print(output.shape)
结果:
Model(
(model1): Sequential(
(0): Conv2d(3, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(1): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(2): Conv2d(32, 32, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(3): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(4): Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=(5, 5), stride=(1, 1), padding=(2, 2))
(5): MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(6): Flatten(start_dim=1, end_dim=-1)
(7): Linear(in_features=1024, out_features=64, bias=True)
(8): Linear(in_features=64, out_features=10, bias=True)
)
)
torch.Size([64, 3, 32, 32])
torch.Size([64, 10])
3 反向传播
3.1 损失函数
损失函数用于计算实际输出和目标之间的差距、为反向传播更新输出提供一定的依据。回归问题中常用损失函数为均方误差MSE、MAE等,分类问题中常用交叉熵Cross-Entropy。
import torch
from torch.nn import L1Loss,MSELoss
inputs = torch.tensor([1,2,3],dtype=torch.float32)
targets =torch.tensor([1,2,5],dtype=torch.float32)
loss = L1Loss()#2/3
result = loss(inputs,targets)
loss_mse = MSELoss()#4/3
result_mse = loss_mse(inputs,targets)
print(result)
print(result_mse)
结果:
tensor(0.6667)
tensor(1.3333)
3.2 优化器
优化器可以对模型参数进行优化,使得的损失最小化,通常是对于梯度进行优化。常见的优化器有BGD、SGD、MBGD、Adam。
from torch import nn
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
import torchvision
from torch.nn import Conv2d,MaxPool2d,Flatten,Linear,Sequential,L1Loss
import torch
# 加载数据集CIFAR10
dataset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10("./dataset",train=False, transform=torchvision.transforms.ToTensor(),download=True)
#构建数据集
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset,batch_size=1)
#定义模型
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super(Model,self).__init__()
#定义网络各层
self.model1 = Sequential(
Conv2d(3,32,5,padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32,32,5,padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Conv2d(32,64,5,padding=2),
MaxPool2d(2),
Flatten(),
Linear(1024,64),
Linear(64,10)
)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.model1(x)
return x
# 损失函数
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
#模型实例化
model = Model()
#设置优化器
optim = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(),lr=0.01)
开始训练
for epoch in range(20):
running_loss = 0.0
for data in dataloader:
imgs,targets = data#获取数据
outputs = model(imgs)#用模型遍历数据
result_loss = loss(outputs,targets)#计算损失
optim.zero_grad()#梯度清零
result_loss.backward()#反向传播
optim.step()#更新参数
# print(result_loss)
running_loss += result_loss
print(running_loss)
参考:
视频教程1
视频教程2
视频教程3