手把手教你cuda5.5与VS2010的编译环境搭建
目前版本的cuda是很方便的,它的一个安装里面包括了Toolkit`SDK`document`Nsight等等,而不用你自己去挨个安装,这样也避免了版本的不同步问题。
1 cuda5.5的下载地址,官方网站即可:
https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads 在里面选择你所对应的电脑版本即可。
2 VS2010这个没什么说的了,网上各种的免费资源,下载一个不需要钱的就行。
3 Cuda的安装:(win7版32bit)
安装cuda
3.1 cuda的安装文件
直接双击exe文件,弹出后,首先会监测一下你的运行环境,如果找不到Nividia对应的显卡设备,他会提示你是否要继续安装。这里面nvidia的显卡,最起码也是8800以上的,要不是无法编写CUDA的。千万不要电脑上面是intel或者AMD的显卡,却要编写cuda,除非你有钱买一个cuda-x86这个编译器。
3.2 弹出的对话框直接OK就行,这个是CUDA的一些安装文件,无所谓的:
3.3 他会监测你的电脑是否支持cuda的搭建,等待就行
3.4 系统检查
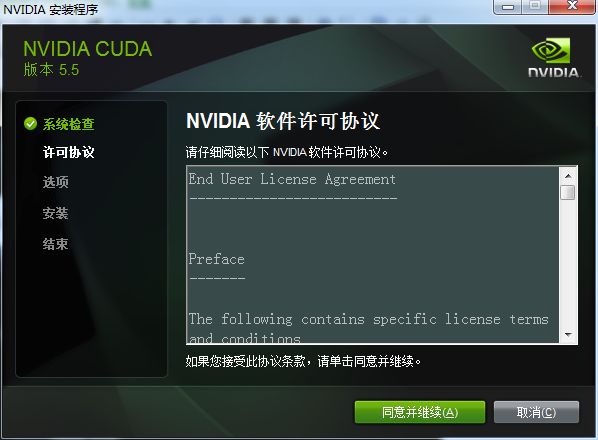
3.5 选择同意并继续
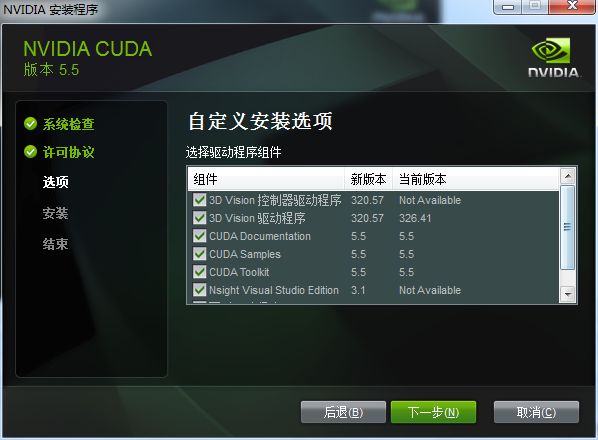
3.6 推荐先选择自定义安装
3.7 最主要的是cuda document\cuda Toolkit \cuda samples(SDK),Nsight\图形驱动程序,3D如果需要的话安装,不安装也无所谓。这里主要就是能看见都有什么,免得漏掉了,博主当初就因为选了精简安装,没安装上SDK。
3.7 安装的位置,推荐自己建三个好找的文件夹,不用他默认的路径,免得稍后配置环境变量麻烦。
博主的安装路径为:
3.8 下一步安装就行了。
至此,cuda的安装就搞定了。
4 接下来配置cuda的环境变量,默认安装好后,他会自动帮你设置好2个环境变量,但是最好还自己添加下其他的几个,方便日后配置vs使用
上面的两个环境变量是cuda默认配置的,接下来添加
CUDA_BIN_PATH %CUDA_PATH%\bin CUDA_LIB_PATH %CUDA_PATH%\lib\Win32 CUDA_SDK_BIN %CUDA_SDK_PATH%\bin\Win32 CUDA_SDK_LIB %CUDA_SDK_PATH%\common\lib\Win32 CUDA_SDK_PATH C:\cuda\cudasdk\common
添加完就行了
5 接下来是cuda的安装成功与否的监测了,这个步骤我们用到两个东西,这两个东西,都是cuda为我们准备好的。
deviceQuery.exe 和 bandwithTest.exe
首先启动cmd DOS命令窗口(博主的cuda安装到c:\cuda文件夹下)
默认进来的是c:\users\Admistrator\>路径,输入 cd .. 两次,来到c:目录下
输入dir 找到安装的cuda文件夹
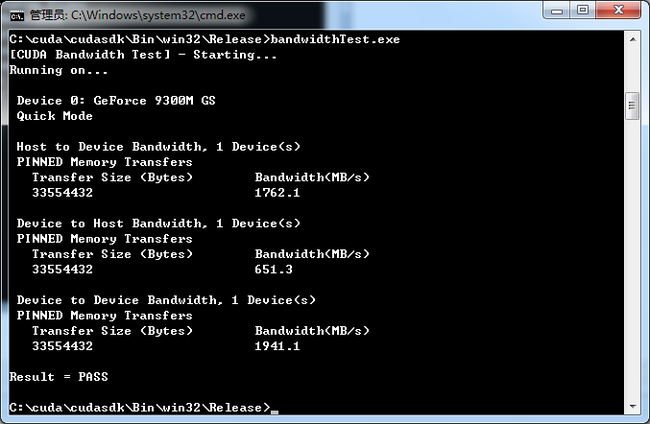
进入Release文件夹后,直接执行bandwithTest.exe
再执行deviceQuery.exe
得到以上信息,因为我的显卡比较古老9300属于第一代的cuda显卡了。Rsult=PASS及说明,都通过了。如果Rsult=Fail 那不好意思,重新安装吧(或者是您的显卡真心不给力)。
关于VS项目测试(推荐)
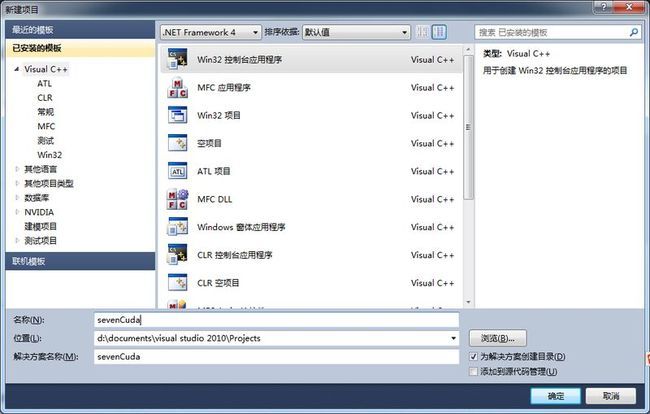
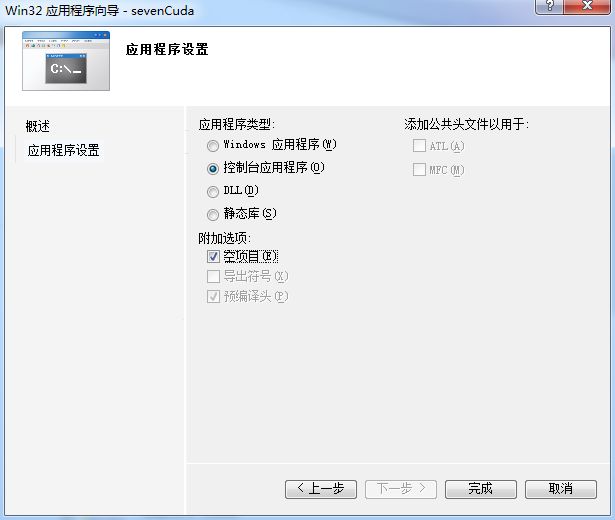
打开VS,新建项目
利用安装好的cuda向导,直接建立工程,里面会自动有一段kernel累加的代码
#include "cuda_runtime.h" #include "device_launch_parameters.h" #include <stdio.h> cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size); __global__ void addKernel(int *c, const int *a, const int *b) { int i = threadIdx.x; c[i] = a[i] + b[i]; } int main() { const int arraySize = 5; const int a[arraySize] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }; const int b[arraySize] = { 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 }; int c[arraySize] = { 0 }; // Add vectors in parallel. cudaError_t cudaStatus = addWithCuda(c, a, b, arraySize); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!"); return 1; } printf("{1,2,3,4,5} + {10,20,30,40,50} = {%d,%d,%d,%d,%d}\n", c[0], c[1], c[2], c[3], c[4]); // cudaDeviceReset must be called before exiting in order for profiling and // tracing tools such as Nsight and Visual Profiler to show complete traces. cudaStatus = cudaDeviceReset(); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceReset failed!"); return 1; } getchar(); return 0; } // Helper function for using CUDA to add vectors in parallel. cudaError_t addWithCuda(int *c, const int *a, const int *b, unsigned int size) { int *dev_a = 0; int *dev_b = 0; int *dev_c = 0; cudaError_t cudaStatus; // Choose which GPU to run on, change this on a multi-GPU system. cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?"); goto Error; } // Allocate GPU buffers for three vectors (two input, one output) . cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_c, size * sizeof(int)); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!"); goto Error; } cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_a, size * sizeof(int)); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!"); goto Error; } cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_b, size * sizeof(int)); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!"); goto Error; } // Copy input vectors from host memory to GPU buffers. cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_a, a, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!"); goto Error; } cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_b, b, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!"); goto Error; } // Launch a kernel on the GPU with one thread for each element. addKernel<<<1, size>>>(dev_c, dev_a, dev_b); // Check for any errors launching the kernel cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError(); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "addKernel launch failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus)); goto Error; } // cudaDeviceSynchronize waits for the kernel to finish, and returns // any errors encountered during the launch. cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize(); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus); goto Error; } // Copy output vector from GPU buffer to host memory. cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(c, dev_c, size * sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) { fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!"); goto Error; } Error: cudaFree(dev_c); cudaFree(dev_a); cudaFree(dev_b); return cudaStatus; }
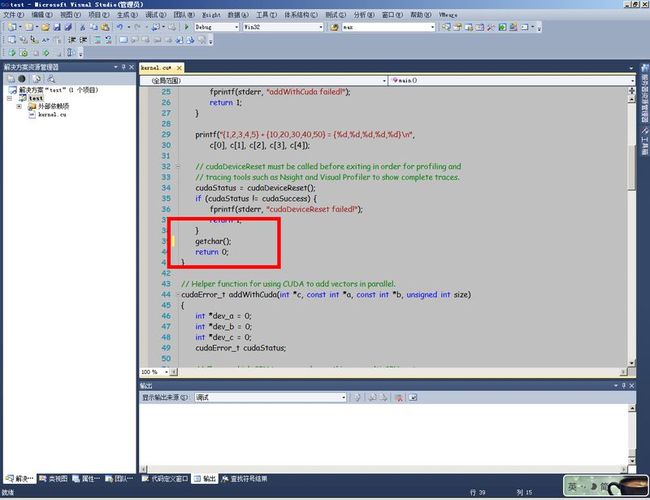
在main函数return之前加入getchar(),停止自动退出,以便观测效果
进入后,点击运行按钮,可能发生LINK错误(如果没有错误,跳过此段)
这时进入-》项目-》属性-》通用配置-》输入和输出-》嵌入清单 ---- 修改成否,原来可能为“是”
再次编译,成功运行后,会显示下面的结果
恭喜,cuda已经在您的机器上安装成功了。
如果是新手,推荐这样新建工程后,在里面修改代码成为自己的工程,配置属性不会出错。
如果想要自己手动配置也可以参考下面的例子。
手动配置VS项目(不推荐)
最后就是VS的配置了(这个是自己手动配置的,有时候容易出现问题,不是很推荐,建议用上面的方法建立项目进行测试)
5.1 启动VS2010
5.2 新建一个win32的控制台工程,空的。
5.3 右键源文件文件夹->新建项->选择cuda c/c++->新建一个以.cu结尾的文件
5.4 右键工程-》生成自定义-》选择cuda生成
5.5 右键test.cu-》属性-》选择cuda c/c++编译器
5.6 右键工程-》属性-》链接器-》常规-》附加库目录-》添加目录 $(CUDA_PATH_V5_5)\lib\$(Platform);
5.7 在链接器-》输入中添加 cudart.lib
5.8 在工具-》选项-》文本编辑器-》文件扩展名-》添加cu \cuh两个文件扩展名
至此,编译环境的相关搭建就完成了。
下面提供了一段test.cu的代码,供测试使用:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <stdlib.h> 3 #include <cuda_runtime.h> 4 5 #define DATA_SIZE 1024 6 #define checkCudaErrors(err) __checkCudaErrors (err, __FILE__, __LINE__) 7 #define getLastCudaError(msg) __getLastCudaError (msg, __FILE__, __LINE__) 8 9 int data[DATA_SIZE]; 10 11 //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// 12 // These are CUDA Helper functions 13 14 // This will output the proper CUDA error strings in the event that a CUDA host call returns an error 15 16 17 inline void __checkCudaErrors(cudaError err, const char *file, const int line ) 18 { 19 if(cudaSuccess != err) 20 { 21 fprintf(stderr, "%s(%i) : CUDA Runtime API error %d: %s.\n",file, line, (int)err, cudaGetErrorString( err ) ); 22 return ; 23 } 24 } 25 26 // This will output the proper error string when calling cudaGetLastError 27 28 29 inline void __getLastCudaError(const char *errorMessage, const char *file, const int line ) 30 { 31 cudaError_t err = cudaGetLastError(); 32 if (cudaSuccess != err) 33 { 34 fprintf(stderr, "%s(%i) : getLastCudaError() CUDA error : %s : (%d) %s.\n", 35 file, line, errorMessage, (int)err, cudaGetErrorString( err ) ); 36 return ; 37 } 38 } 39 40 // end of CUDA Helper Functions 41 42 __global__ static void sumOfSquares(int *num, int * result){ 43 int sum=0; 44 int i; 45 for(i=0;i<DATA_SIZE;i++) { 46 sum += num[i]*num[i]; 47 } 48 *result = sum; 49 } 50 void GenerateNumbers(int *number, int size){ 51 for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) { 52 number[i] = rand() % 10; 53 printf("number[%d] is %d\n",i,number[i]); 54 }} 55 56 int main(){ 57 58 cudaSetDevice(0); 59 cudaDeviceSynchronize(); 60 cudaThreadSynchronize(); 61 62 GenerateNumbers(data, DATA_SIZE); 63 64 int * gpudata, * result; 65 int sum; 66 67 checkCudaErrors( cudaMalloc((void**) &gpudata, sizeof(int)*DATA_SIZE)); 68 checkCudaErrors(cudaMalloc((void**) &result, sizeof(int))); 69 checkCudaErrors(cudaMemcpy(gpudata, data, sizeof(int)*DATA_SIZE,cudaMemcpyHostToDevice)); 70 71 sumOfSquares<<<1, 1, 0>>>(gpudata, result); 72 73 checkCudaErrors(cudaMemcpy(&sum, result, sizeof(int), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost)); 74 75 cudaFree(gpudata); 76 cudaFree(result); 77 78 printf("-----------sum: %d\n",sum); 79 80 sum = 0; 81 for(int i = 0; i < DATA_SIZE; i++) { 82 sum += data[i] * data[i]; 83 } 84 printf("sum (CPU): %d\n", sum); 85 86 getchar(); 87 return 0; 88 }