reportlab是Python的一个标准库,可以画图、画表格、编辑文字,最后可以输出PDF格式。它的逻辑和编辑一个word文档或者PPT很像。有两种方法:
1)建立一个空白文档,然后在上面写文字、画图等;
2)建立一个空白list,以填充表格的形式插入各种文本框、图片等,最后生成PDF文档。因为需要产生一份给用户看的报告,里面需要插入图片、表格等,所以采用的是第二种方法。
安装第三方库
reportlab输入Python的第三方库,使用前需要先安装:pip install reportlab
模块导入提前导入相关内容,并且注册字体。(注册字体前需要先准备好字体文件)
from reportlab.pdfbase import pdfmetrics # 注册字体
from reportlab.pdfbase.ttfonts import TTFont # 字体类
from reportlab.platypus import Table, SimpleDocTemplate, Paragraph, Image # 报告内容相关类
from reportlab.lib.pagesizes import letter # 页面的标志尺寸(8.5*inch, 11*inch)
from reportlab.lib.styles import getSampleStyleSheet # 文本样式
from reportlab.lib import colors # 颜色模块
from reportlab.graphics.charts.barcharts import VerticalBarChart # 图表类
from reportlab.graphics.charts.legends import Legend # 图例类
from reportlab.graphics.shapes import Drawing # 绘图工具
from reportlab.lib.units import cm # 单位:cm
# 注册字体(提前准备好字体文件, 如果同一个文件需要多种字体可以注册多个)
pdfmetrics.registerFont(TTFont('SimSun', 'SimSun.ttf'))封装不同内容对应的函数
创建一个Graphs类,通过不同的静态方法提供不同的报告内容,包括:标题、普通段落、图片、表格和图表。函数中的相关数据目前绝大多数都是固定值,可以根据情况自行设置成相关参数。
class Graphs:
# 绘制标题
@staticmethod
def draw_title(title: str):
# 获取所有样式表
style = getSampleStyleSheet()
# 拿到标题样式
ct = style['Heading1']
# 单独设置样式相关属性
ct.fontName = 'SimSun' # 字体名
ct.fontSize = 18 # 字体大小
ct.leading = 50 # 行间距
ct.textColor = colors.green # 字体颜色
ct.alignment = 1 # 居中
ct.bold = True
# 创建标题对应的段落,并且返回
return Paragraph(title, ct)
# 绘制小标题
@staticmethod
def draw_little_title(title: str):
# 获取所有样式表
style = getSampleStyleSheet()
# 拿到标题样式
ct = style['Normal']
# 单独设置样式相关属性
ct.fontName = 'SimSun' # 字体名
ct.fontSize = 15 # 字体大小
ct.leading = 30 # 行间距
ct.textColor = colors.red # 字体颜色
# 创建标题对应的段落,并且返回
return Paragraph(title, ct)
# 绘制普通段落内容
@staticmethod
def draw_text(text: str):
# 获取所有样式表
style = getSampleStyleSheet()
# 获取普通样式
ct = style['Normal']
ct.fontName = 'SimSun'
ct.fontSize = 12
ct.wordWrap = 'CJK' # 设置自动换行
ct.alignment = 0 # 左对齐
ct.firstLineIndent = 32 # 第一行开头空格
ct.leading = 25
return Paragraph(text, ct)
# 绘制表格
@staticmethod
def draw_table(*args):
# 列宽度
col_width = 120
style = [
('FONTNAME', (0, 0), (-1, -1), 'SimSun'), # 字体
('FONTSIZE', (0, 0), (-1, 0), 12), # 第一行的字体大小
('FONTSIZE', (0, 1), (-1, -1), 10), # 第二行到最后一行的字体大小
('BACKGROUND', (0, 0), (-1, 0), '#d5dae6'), # 设置第一行背景颜色
('ALIGN', (0, 0), (-1, -1), 'CENTER'), # 第一行水平居中
('ALIGN', (0, 1), (-1, -1), 'LEFT'), # 第二行到最后一行左右左对齐
('VALIGN', (0, 0), (-1, -1), 'MIDDLE'), # 所有表格上下居中对齐
('TEXTCOLOR', (0, 0), (-1, -1), colors.darkslategray), # 设置表格内文字颜色
('GRID', (0, 0), (-1, -1), 0.5, colors.grey), # 设置表格框线为grey色,线宽为0.5
# ('SPAN', (0, 1), (0, 2)), # 合并第一列二三行
# ('SPAN', (0, 3), (0, 4)), # 合并第一列三四行
# ('SPAN', (0, 5), (0, 6)), # 合并第一列五六行
# ('SPAN', (0, 7), (0, 8)), # 合并第一列五六行
]
table = Table(args, colWidths=col_width, style=style)
return table
# 创建图表
@staticmethod
def draw_bar(bar_data: list, ax: list, items: list):
drawing = Drawing(500, 250)
bc = VerticalBarChart()
bc.x = 45 # 整个图表的x坐标
bc.y = 45 # 整个图表的y坐标
bc.height = 200 # 图表的高度
bc.width = 350 # 图表的宽度
bc.data = bar_data
bc.strokeColor = colors.black # 顶部和右边轴线的颜色
bc.valueAxis.valueMin = 5000 # 设置y坐标的最小值
bc.valueAxis.valueMax = 26000 # 设置y坐标的最大值
bc.valueAxis.valueStep = 2000 # 设置y坐标的步长
bc.categoryAxis.labels.dx = 2
bc.categoryAxis.labels.dy = -8
bc.categoryAxis.labels.angle = 20
bc.categoryAxis.categoryNames = ax
# 图示
leg = Legend()
leg.fontName = 'SimSun'
leg.alignment = 'right'
leg.boxAnchor = 'ne'
leg.x = 475 # 图例的x坐标
leg.y = 240
leg.dxTextSpace = 10
leg.columnMaximum = 3
leg.colorNamePairs = items
drawing.add(leg)
drawing.add(bc)
return drawing
# 绘制图片
@staticmethod
def draw_img(path):
img = Image(path) # 读取指定路径下的图片
img.drawWidth = 5*cm # 设置图片的宽度
img.drawHeight = 8*cm # 设置图片的高度
return img生成报告
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建内容对应的空列表
content = list()
# 添加标题
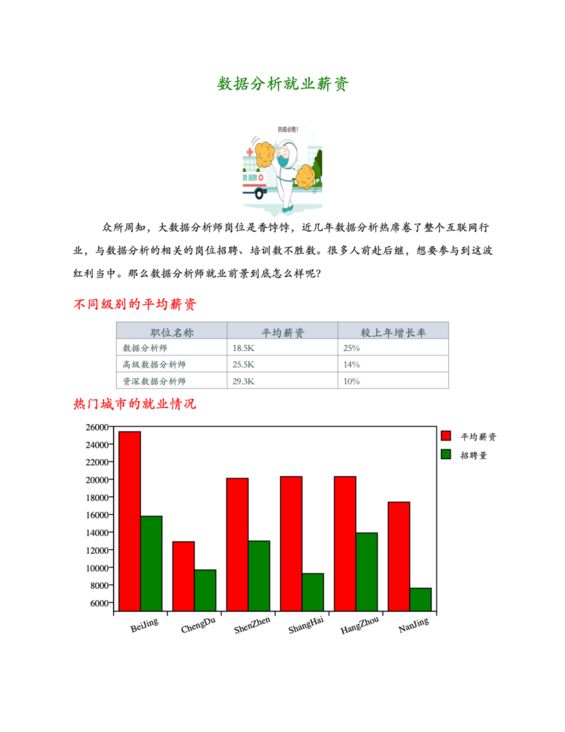
content.append(Graphs.draw_title('数据分析就业薪资'))
# 添加图片
content.append(Graphs.draw_img('抗疫必胜.png'))
# 添加段落文字
content.append(Graphs.draw_text('众所周知,大数据分析师岗位是香饽饽,近几年数据分析热席卷了整个互联网行业,与数据分析的相关的岗位招聘、培训数不胜数。很多人前赴后继,想要参与到这波红利当中。那么数据分析师就业前景到底怎么样呢?'))
# 添加小标题
content.append(Graphs.draw_title(''))
content.append(Graphs.draw_little_title('不同级别的平均薪资'))
# 添加表格
data = [
('职位名称', '平均薪资', '较上年增长率'),
('数据分析师', '18.5K', '25%'),
('高级数据分析师', '25.5K', '14%'),
('资深数据分析师', '29.3K', '10%')
]
content.append(Graphs.draw_table(*data))
# 生成图表
content.append(Graphs.draw_title(''))
content.append(Graphs.draw_little_title('热门城市的就业情况'))
b_data = [(25400, 12900, 20100, 20300, 20300, 17400), (15800, 9700, 12982, 9283, 13900, 7623)]
ax_data = ['BeiJing', 'ChengDu', 'ShenZhen', 'ShangHai', 'HangZhou', 'NanJing']
leg_items = [(colors.red, '平均薪资'), (colors.green, '招聘量')]
content.append(Graphs.draw_bar(b_data, ax_data, leg_items))
# 生成pdf文件
doc = SimpleDocTemplate('report.pdf', pagesize=letter)
doc.build(content)以上就是本次分享的所有内容,如果你觉得文章还不错,欢迎关注公众号:Python编程学习圈,每日干货分享,内容覆盖Python电子书、教程、数据库编程、Django,爬虫,云计算等等。或是前往编程学习网,了解更多编程技术知识。