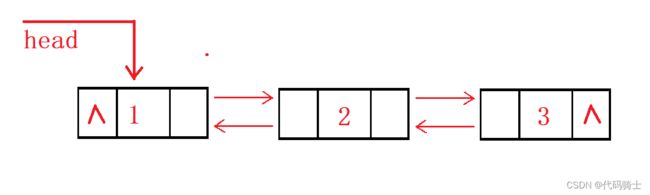
数据结构-双向链表操作
先创建好一个双向链表:
代码:
#include
#include
//定义结点信息
typedef struct Line{
struct Line*prior;
int data;
struct Line*next;
}line;
//函数声明
line*initLine(line*head);//初始化
void display(line*head);//打印链表
int main()
{
line*p=NULL;
p=initLine(p);
display(p);
return 0;
}
line*initLine(line*head){
//创建首元结点
head=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
head->prior=NULL;
head->data=1;
head->next=NULL;
line*temp=head;
for(int i=2;i<4;i++)
{
line*body=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
body->prior=NULL;
body->data=i;
body->next=NULL;
temp->next=body;
body->prior=temp;
temp=body;
}
return head;
}
void display(line*head){
line*t=head;
while(t){
if(t->next==NULL){
printf("%d\n",t->data);
}else{
printf("%d <-> ",t->data);
}
t=t->next;
}
} 结果:
1、双向链表增加节点
(1)加表头
假设新元素节点为 temp,表头节点为 head,则需要做以下 2 步操作即可:
- temp->next=head; head->prior=temp;
- 将 head 移至 temp,重新指向新的表头;
//新建数据域为data的结点
line * temp=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
temp->data=data;
temp->prior=NULL;
temp->next=NULL;
//插入到链表头,要特殊考虑
if (add==1) {
temp->next=head;
head->prior=temp;
head=temp;(2)加表中
- 新节点先与其直接后继节点建立双层逻辑关系;
- 新节点的直接前驱节点与之建立双层逻辑关系;
line * body=head;
//找到要插入位置的前一个结点
for (int i=1; inext;
}
body->next->prior=temp;
temp->next=body->next;
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body; (3)加表尾
- 找到双链表中最后一个节点;
- 让新节点与最后一个节点进行双层逻辑关系;
//判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾
if (body->next==NULL) {
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}2、双向链表删除节点
只需遍历链表找到要删除的结点,然后将该节点从表中摘除即可
//删除结点的函数,data为要删除结点的数据域的值
line * delLine(line * head,int data){
line * temp=head;
//遍历链表
while (temp) {
//判断当前结点中数据域和data是否相等,若相等,摘除该结点
if (temp->data==data) {
temp->prior->next=temp->next;
temp->next->prior=temp->prior;
free(temp);
return head;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("链表中无该数据元素");
return head;
}3、双向链表查找节点
双向链表同单链表一样,都仅有一个头指针。因此,双链表查找指定元素的实现同单链表类似,都是从表头依次遍历表中元素。
//head为原双链表,elem表示被查找元素
int selectElem(line * head,int elem){
//新建一个指针t,初始化为头指针 head
line * t=head;
int i=1;
while (t) {
if (t->data==elem) {
return i;
}
i++;
t=t->next;
}
//程序执行至此处,表示查找失败
return -1;
}4、双向链表修改节点
通过遍历找到存储有该数据元素的结点,直接更改其数据域即可。
//更新函数,其中,add 表示更改结点在双链表中的位置,newElem 为新数据的值
line *amendElem(line * p,int add,int newElem){
line * temp=p;
//遍历到被删除结点
for (int i=1; inext;
}
temp->data=newElem;
return p;
} 完整代码:
#include
#include
typedef struct line{
struct line * prior;
int data;
struct line * next;
}line;
//双链表的创建
line* initLine(line * head);
//双链表插入元素,add表示插入位置
line * insertLine(line * head,int data,int add);
//双链表删除指定元素
line * delLine(line * head,int data);
//双链表中查找指定元素
int selectElem(line * head,int elem);
//双链表中更改指定位置节点中存储的数据,add表示更改位置
line *amendElem(line * p,int add,int newElem);
//输出双链表的实现函数
void display(line * head);
int main() {
line * head=NULL;
//创建双链表
head=initLine(head);
display(head);
//在表中第 3 的位置插入元素 7
head=insertLine(head, 7, 3);
display(head);
//表中删除元素 2
head=delLine(head, 2);
display(head);
printf("元素 3 的位置是:%d\n",selectElem(head,3));
//表中第 3 个节点中的数据改为存储 6
head = amendElem(head,3,6);
display(head);
return 0;
}
line* initLine(line * head){
head=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
head->prior=NULL;
head->next=NULL;
head->data=1;
line * list=head;
for (int i=2; i<=5; i++) {
line * body=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
body->prior=NULL;
body->next=NULL;
body->data=i;
list->next=body;
body->prior=list;
list=list->next;
}
return head;
}
line * insertLine(line * head,int data,int add){
//新建数据域为data的结点
line * temp=(line*)malloc(sizeof(line));
temp->data=data;
temp->prior=NULL;
temp->next=NULL;
//插入到链表头,要特殊考虑
if (add==1) {
temp->next=head;
head->prior=temp;
head=temp;
}else{
line * body=head;
//找到要插入位置的前一个结点
for (int i=1; inext;
}
//判断条件为真,说明插入位置为链表尾
if (body->next==NULL) {
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}else{
body->next->prior=temp;
temp->next=body->next;
body->next=temp;
temp->prior=body;
}
}
return head;
}
line * delLine(line * head,int data){
line * temp=head;
//遍历链表
while (temp) {
//判断当前结点中数据域和data是否相等,若相等,摘除该结点
if (temp->data==data) {
temp->prior->next=temp->next;
temp->next->prior=temp->prior;
free(temp);
return head;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
printf("链表中无该数据元素");
return head;
}
//head为原双链表,elem表示被查找元素
int selectElem(line * head,int elem){
//新建一个指针t,初始化为头指针 head
line * t=head;
int i=1;
while (t) {
if (t->data==elem) {
return i;
}
i++;
t=t->next;
}
//程序执行至此处,表示查找失败
return -1;
}
//更新函数,其中,add 表示更改结点在双链表中的位置,newElem 为新数据的值
line *amendElem(line * p,int add,int newElem){
line * temp=p;
//遍历到被删除结点
for (int i=1; inext;
}
temp->data=newElem;
return p;
}
//输出链表的功能函数
void display(line * head){
line * temp=head;
while (temp) {
if (temp->next==NULL) {
printf("%d\n",temp->data);
}else{
printf("%d->",temp->data);
}
temp=temp->next;
}
} 输出结果: