python2和python3的区别
目录
1. python2 和 python3 的区别
2. 输入输出方面的差异::
2.1 输出的差异:
2.2 输入的差异:
2.3 range和xrange
2.4 异常捕获的差异:
3. 关于新式类和经典类的区别
3.1 关于使用type()函数查看实例类型的区别
1. python2 和 python3 的区别
1.整数:python2中区分整型(int)和长整型(long),python3不区分;
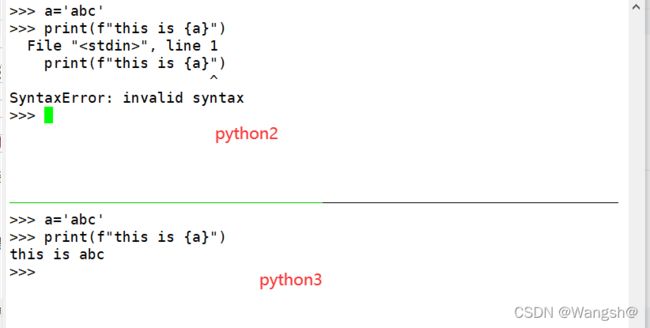
2.python2中没有f 标志位格式化,python3才有;
###########################################
3.python3里面,True和False都是关键字,python2里面不是。
###########################################
4.python2中的整数相除属于地板除,要想真除就得变成浮点数 python3中的整数相除就是真除
###########################################
5.python2的编码是ascii码,python3的默认编码是utf-8
###########################################
6.在python包结构目录里 python2 :_init_.py 是必须的 python3 :_init_.py 是可选的
###########################################
7.在导入模块运行时 python2 只会在模块同级目录下生成.pyc文件 python3 生成__pycache__目录
###########################################
2. 输入输出方面的差异::
2.1 输出的差异:
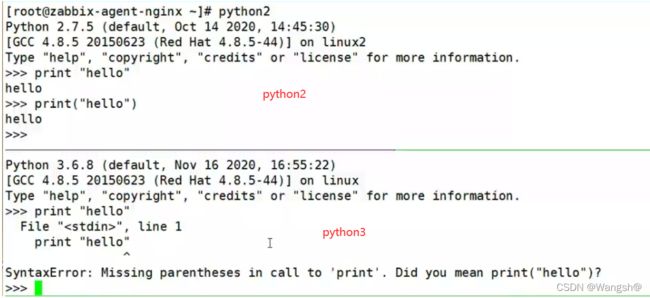
python2的print不一定要求函数形式使用
python2 可以使用 print “hello”的方式输出,(print “hello”)
python3的print强制是函数(print(“hello world”))
###########################################
2.2 输入的差异:
python3中input得到的数据都是str型
python2中input默认是int型,str要使用引号包裹,raw_input得到的都是str
###########################################
2.3 range和xrange
python2:range(0,4) -->结果:[0,1,2,3]
xrange(0,4) -->结果:是一个可迭代对象(惰性求值,使用的时候再生成)
python3:没有xrange,range函数就是python2中的xrange
得到的结果是一个可迭代对象
###########################################
2.4 异常捕获的差异:
python2:except exception,e:
python3:except exception as e:
3. 关于新式类和经典类的区别
python2里面只有继承了object的类才是新式类,其他的是经典类
python3里面默认所有类都是继承的object,所以python3都是新式类
3.1 关于使用type()函数查看实例类型的区别
[root@localhost lianxi]# python2
Python 2.7.5 (default, Oct 14 2020, 14:45:30)
[GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)] on linux2
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> class A: pass
...
>>> a = A()
>>> type(a)
>>> a.__class__
>>>
─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────
[root@localhost ~]# python3
Python 3.6.8 (default, Nov 16 2020, 16:55:22)
[GCC 4.8.5 20150623 (Red Hat 4.8.5-44)] on linux
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> class A: pass
...
>>> a = A()
>>> type(a)
>>> a.__class__
>>>