MySQL中的索引和查询(进阶)
目录
索引
索引分类
索引的优缺点
优点
缺点
适用场景
查询
聚合查询
聚合函数
聚合字段
联合查询
内连接
外连接
子查询
单行子查询
多行子查询
字符串函数upper,substr,concat
索引
索引分类
| index |
普通索引 |
| unique | 唯一索引 |
| fulltext | 全文索引 |
| spatial | 时空索引 |
| primary | 主键 |
索引的优缺点
优点
- 索引可以提高查询的速度;
- 通过索引的唯一性,保证了数据库表中的每一行数据都是唯一的
缺点
- 空间的使用会增加
- 造成修改的性能下降,包括增、删、改。没有索引的情况下,直接修改数据,有索引的情况下,需要修改索引和数据
适用场景
- 当数据量达到一定的规模,可以使用索引
- 尽量针对需要查询多次,而且修改比较少的表建立索引
- 只针对频繁被查询的字段建立索引
查询
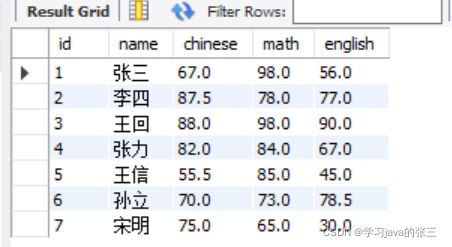
- 先建表
CREATE TABLE exam_result (
id INT,
name VARCHAR(20),
chinese DECIMAL(3,1),
math DECIMAL(3,1),
english DECIMAL(3,1)
);
-- 插入测试数据
INSERT INTO exam_result (id,name, chinese, math, english) VALUES
(1,'张三', 67, 98, 56),
(2,'李四', 87.5, 78, 77),
(3,'王回', 88, 98, 90),
(4,'张力', 82, 84, 67),
(5,'王信', 55.5, 85, 45),
(6,'孙立', 70, 73, 78.5),
(7,'宋明', 75, 65, 30);聚合查询
聚合函数
count-----返回查询到数据的数量
-- 如果有 null,不算
select count(*) FROM exam_result;
select count(1) from exam_result;sum-----返回查询到数据的总和
-- 聚合的意思是竖着计算的
-- 要计算某个人的语文 + 数学 + 英语,作为对比,这种不叫聚合
select sum(math) from exam_result;avg-----返回查询到数据的平均值
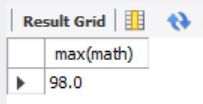
select avg(math) from exam_result;max-----返回查询到数据的最大值
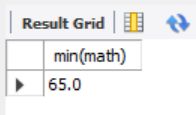
select max(math) from exam_result;min-----返回查询到数据的最小值
select min(math) from exam_result;聚合字段
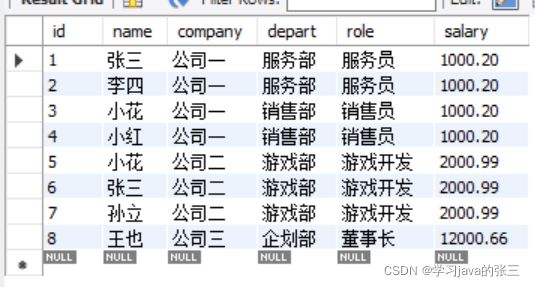
- 先建表
create table emp(
id int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(20) not null,
company varchar(20) not null,
depart varchar(20) not null,
role varchar(20) not null,
salary numeric(11,2)
);
insert into emp(name, company, depart, role, salary) values
('张三', '公司一', '服务部', '服务员', 1000.20),
('李四', '公司一', '服务部', '服务员', 1000.20),
('小花', '公司一', '销售部', '销售员', 1000.20),
('小红', '公司一', '销售部', '销售员', 1000.20),
('小花', '公司二', '游戏部', '游戏开发', 2000.99),
('张三', '公司二', '游戏部', '游戏开发', 2000.99),
('孙立', '公司二', '游戏部', '游戏开发', 2000.99),
('王也', '公司三', '企划部', '董事长', 12000.66);group by子句
-- group : 分组进行聚合;
-- by 以哪个字段作为依据进行分组
-- 每种角色都是一个独立的聚合单位
- 根据公司名查询公司数目
select company, count(*) from emp group by company;- 根据公司不同的部门角色员工的升序查询
select company, depart, role, count(*) sum
from emp
group by depart, role, company
order by sum;having
group by 子句进行分组以后,需要对分组结果再进行条件过滤时,不能使用 WHERE 语句,而需要用 having,having在聚合之后,where在聚合之前
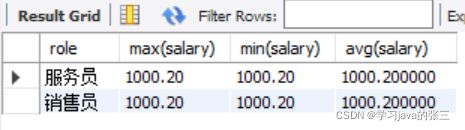
- 查询平均工资低于1500的角色和他的平均工资
select role,max(salary),min(salary),avg(salary)
from emp
group by role
having avg(salary)<1500;联合查询
- 先建表
create table users (
uid int primary key auto_increment,
name varchar(45) not null
);
create table articles (
aid int primary key auto_increment,
author_id int not null,
title varchar(45) not null
);
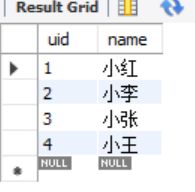
insert into users (name) values ('小红'), ('小李'), ('小张'), ('小王');
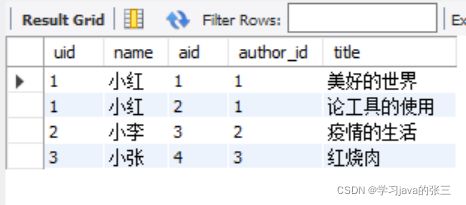
insert into articles (author_id, title) values
(1, '美好的世界'),
(1, '论工具的使用'),
(2, '疫情的生活'),
(3, '红烧肉'),
(5, '没有作者的一篇文章');内连接
内连接只保留连接的表的有交集的部分
- 从两张表查询数据
-- 在 from 后边直接跟 2 张表(/2 张以上)
-- 同时从 2 张表中查询数据
-- 一共 20 条数据 = 4 * 5
select * from users, articles;
select * from users join articles;- 但是这种情况查询到的数据是无意义的,需要添加连表条件才有意义
-- inner 可以省略
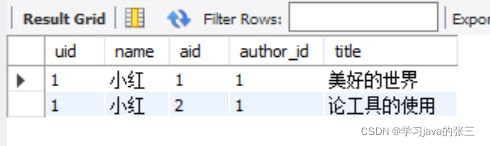
select * from users inner join articles on uid = author_id; - 查询作者是小红的书籍
select * from users, articles
where users.uid = articles.author_id and users.name = '小红';
select * from users, articles
where uid = author_id and users.name = '小红';
select * from users
join articles on uid = author_id where users.name = '小红';外连接
左外连接
左表的所有数据都要体现
-- 左外联
-- outer可以省略
select * from users left outer join articles on uid = author_id;
select * from users left join articles on uid = author_id; 右外连接
左表的所有数据都要体现
-- 右外联
select * from users right outer join articles on uid = author_id;
select * from users right join articles on uid = author_id;子查询
子查询是指嵌入在其他sql语句中的select语句,也叫嵌套查询。把查询出来的信息逻辑上看作一张表,在这个表的基础上继续查询
单行子查询
返回一行记录的子查询
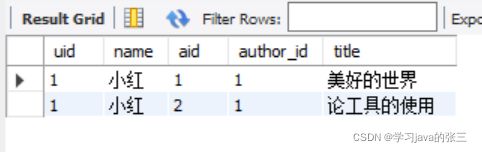
- 查询作者是小红的书籍
select *
from (select * from users join articles on uid = author_id) c
where uid = 1;多行子查询
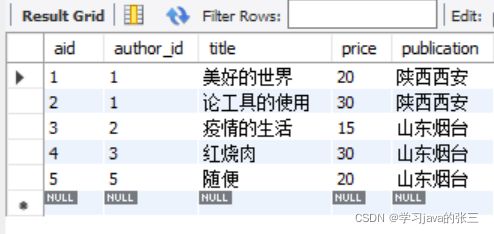
返回多行记录的子查询
- 新建表
create table articles2 (
aid int primary key auto_increment,
author_id int not null,
title varchar(45) not null,
price int not null,
publication varchar(45) not null
);
insert into articles2 (author_id, title,price,publication) values
(1, '美好的世界',20,'陕西西安'),
(1, '论工具的使用',30,'陕西西安'),
(2, '疫情的生活',15,'山东烟台'),
(3, '红烧肉',30,'山东烟台'),
(5, '随便',20,'山东烟台');IN关键字
select * from articles2
where author_id in (select uid from users where name = '小红');
NOT IN关键字
select * from articles2
where author_id not in (select uid from users where name = '小红');EXISTS关键字
select * from articles2 where exists(select name from users
where (name = '小红' or name = '小李') and author_id = uid);NOT EXISTS关键字
select * from articles2 where not exists(select name from users
where (name = '小红' or name = '小李') and author_id = uid);字符串函数upper,substr,concat
1.upper(s);-----小写转大写
select upper('aa');2.substr(s,start,length);-----截取字符串,从start位置截取到length位置
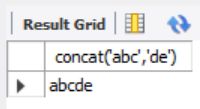
select substr('Andy',1,2);3.concat(s1,s2);-----合并s1,s2两个字符串
select concat('abc','de');