前言
适用于python2和python3
1. loads方法与load方法的异同
在Python中json是一个非常常用的模块,这个主要有4个方法:
json.dumpsjson.dumpjson.loadsjson.load
这里主要分析讲解一下json的loads和load方法。
这两个方法中都是把其他类型的对象转为Python对象,这里先说明一下Python对象,
Python对象包括:
所有Python基本数据类型,列表,元组,字典,自己定义的类,等等等等,当然不包括Python的字符串类型,把字符串或者文件鎏中的字符串转为字符串会报错的
1.1不相同点:
loads操作的是字符串load操作的是文件流
1.2 相同点
- 除了第一个参数(要转换的对象)类型不同,其他所有的参数都相同
- 最终都是转换成Python对象
1.3 例子
先来一个例子,除了要转换的对象,其他什么参数都不传:
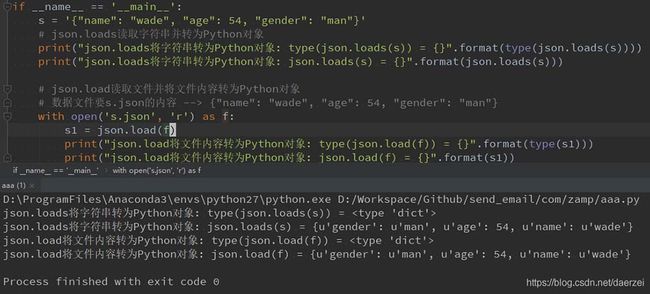
s = '{"name": "wade", "age": 54, "gender": "man"}'
# json.loads读取字符串并转为Python对象
print("json.loads将字符串转为Python对象: type(json.loads(s)) = {}".format(type(json.loads(s))))
print("json.loads将字符串转为Python对象: json.loads(s) = {}".format(json.loads(s)))
# json.load读取文件并将文件内容转为Python对象
# 数据文件要s.json的内容 --> {"name": "wade", "age": 54, "gender": "man"}
with open('s.json', 'r') as f:
s1 = json.load(f)
print("json.load将文件内容转为Python对象: type(json.load(f)) = {}".format(type(s1)))
print("json.load将文件内容转为Python对象: json.load(f) = {}".format(s1))
2. 转换成Python对象
由于loads和load两个方法只是处理的数据源不同,其他的参数都是相同的,返回的结果类型也相同,故这是loads和load方法两个只说一个,
日常工作中最常见的就是把字符串通过json.loads转为字典,其实json的loads方法不仅可以把字符串转为字典,还可以转为任何Python对象。
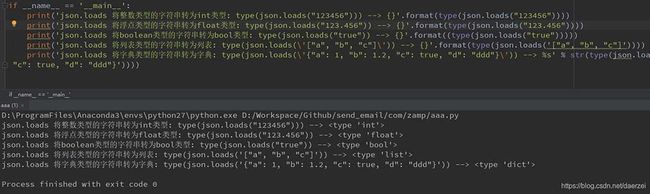
比如说,转成python基本数据类型:
print('json.loads 将整数类型的字符串转为int类型: type(json.loads("123456"))) --> {}'.format(type(json.loads("123456"))))
print('json.loads 将浮点类型的字符串转为float类型: type(json.loads("123.456")) --> {}'.format(type(json.loads("123.456"))))
print('json.loads 将boolean类型的字符串转为bool类型: type(json.loads("true")) --> {}'.format((type(json.loads("true")))))
print('json.loads 将列表类型的字符串转为列表: type(json.loads(\'["a", "b", "c"]\')) --> {}'.format(type(json.loads('["a", "b", "c"]'))))
print('json.loads 将字典类型的字符串转为字典: type(json.loads(\'{"a": 1, "b": 1.2, "c": true, "d": "ddd"}\')) --> %s' % str(type(json.loads('{"a": 1, "b": 1.2, "c": true, "d": "ddd"}'))))
json模块会根据你的字符串自动转为最符合的数据类型,但是需要注意的是不能把转为字符串,否则会报json.decoder.JSONDecodeError错误:
json.decoder.JSONDecodeError: Expecting value: line 1 column 1 (char 0)
3. json.load(s)的参数
我们先看下json.loads方法的签名:
def loads(s, encoding=None, cls=None, object_hook=None, parse_float=None,
parse_int=None, parse_constant=None, object_pairs_hook=None, **kw):
"""Deserialize ``s`` (a ``str`` or ``unicode`` instance containing a JSON # 把一个字符串反序列化为Python对象,这个字符串可以是str类型的,也可以是unicode类型的
document) to a Python object.
If ``s`` is a ``str`` instance and is encoded with an ASCII based encoding # 如果参数s是以ASCII编码的字符串,那么需要手动通过参数encoding指定编码方式,
other than utf-8 (e.g. latin-1) then an appropriate ``encoding`` name # 不是以ASCII编码的字符串,是不被允许的,你必须把它转为unicode
must be specified. Encodings that are not ASCII based (such as UCS-2)
are not allowed and should be decoded to ``unicode`` first.
``object_hook`` is an optional function that will be called with the # object_hook参数是可选的,它会将(loads的)返回结果字典替换为你所指定的类型
result of any object literal decode (a ``dict``). The return value of # 这个功能可以用来实现自定义解码器,如JSON-RPC
``object_hook`` will be used instead of the ``dict``. This feature
can be used to implement custom decoders (e.g. JSON-RPC class hinting).
``object_pairs_hook`` is an optional function that will be called with the # object_pairs_hook参数是可选的,它会将结果以key-value列表的形式返回
result of any object literal decoded with an ordered list of pairs. The # 形式如:[(k1, v1), (k2, v2), (k3, v3)]
return value of ``object_pairs_hook`` will be used instead of the ``dict``. # 如果object_hook和object_pairs_hook同时指定的话优先返回object_pairs_hook
This feature can be used to implement custom decoders that rely on the
order that the key and value pairs are decoded (for example,
collections.OrderedDict will remember the order of insertion). If
``object_hook`` is also defined, the ``object_pairs_hook`` takes priority.
``parse_float``, if specified, will be called with the string # parse_float参数是可选的,它如果被指定的话,在解码json字符串的时候,
of every JSON float to be decoded. By default this is equivalent to # 符合float类型的字符串将被转为你所指定的,比如说你可以指定为decimal.Decimal
float(num_str). This can be used to use another datatype or parser
for JSON floats (e.g. decimal.Decimal).
``parse_int``, if specified, will be called with the string # parse_int参数是可选的,它如果被指定的话,在解码json字符串的时候,
of every JSON int to be decoded. By default this is equivalent to # 符合int类型的字符串将被转为你所指定的,比如说你可以指定为float
int(num_str). This can be used to use another datatype or parser
for JSON integers (e.g. float).
``parse_constant``, if specified, will be called with one of the # parse_constant参数是可选的,它如果被指定的话,在解码json字符串的时候,
following strings: -Infinity, Infinity, NaN. # 如果出现以以下字符串: -Infinity, Infinity, NaN 那么指定的parse_constant方法将会被调用到
This can be used to raise an exception if invalid JSON numbers
are encountered.
To use a custom ``JSONDecoder`` subclass, specify it with the ``cls`` # 你也可以用cls参数通过实现一个JSONDecoder的子类,来代替JSONDecoder,通过这个功能你可以自定义上面的那些parse_xxx参数,这里就不举例了
kwarg; otherwise ``JSONDecoder`` is used.
"""
以下参数说明是根据官方文档翻译的
3.1 s参数
把一个字符串反序列化为Python对象,这个字符串可以是str类型的,也可以是unicode类型的,如果参数s是以ASCII编码的字符串,那么需要手动通过参数encoding指定编码方式,不是以ASCII编码的字符串,是不被允许的,你必须把它转为unicode
对于loads方法来说,s是一个字符串,而对于load方法来说,是一个数据流文件
3.2 object_hook参数
object_hook参数是可选的,它会将(loads的)返回结果字典替换为你所指定的类型,这个功能可以用来实现自定义解码器,如JSON-RPC
这里先定义一个Person对象:
class Person:
def __init__(self, name, age, gender):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.gender = gender
def toJSON(self):
return {
"name": self.name,
"age": self.age,
"gender": self.gender
}
@staticmethod
def parseJSON(dct):
if isinstance(dct, dict):
p = Person(dct["name"], int(dct['age']), dct['gender'])
return p
return dct
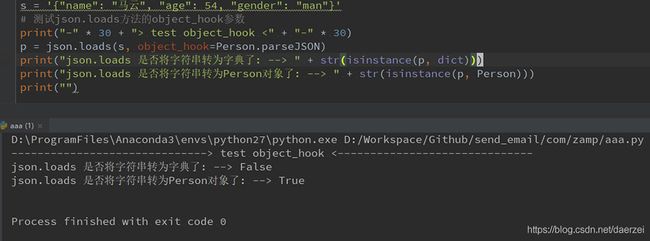
OK,试下object_hook参数吧:
s = '{"name": "马云", "age": 54, "gender": "man"}'
# 测试json.loads方法的object_hook参数
p = json.loads(s, object_hook=Person.parseJSON)
print("json.loads 是否将字符串转为字典了: --> " + str(isinstance(p, dict)))
print("json.loads 是否将字符串转为Person对象了: --> " + str(isinstance(p, Person)))
3.3 object_pairs_hook参数
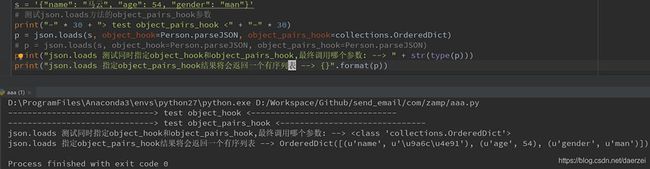
object_pairs_hook参数是可选的,它会将结果以key-value有序列表的形式返回,形式如:[(k1, v1), (k2, v2), (k3, v3)],如果object_hook和object_pairs_hook同时指定的话优先返回object_pairs_hook
s = '{"name": "马云", "age": 54, "gender": "man"}'
# 测试json.loads方法的object_pairs_hook参数
print("-" * 30 + "> test object_pairs_hook <" + "-" * 30)
p = json.loads(s, object_hook=Person.parseJSON, object_pairs_hook=collections.OrderedDict)
# p = json.loads(s, object_hook=Person.parseJSON, object_pairs_hook=Person.parseJSON)
print("json.loads 测试同时指定object_hook和object_pairs_hook,最终调用哪个参数: --> " + str(type(p)))
print("json.loads 指定object_pairs_hook结果将会返回一个有序列表 --> {}".format(p))
3.4 parse_float参数
parse_float参数是可选的,它如果被指定的话,在解码json字符串的时候,符合float类型的字符串将被转为你所指定的,比如说你可以指定为decimal.Decimal
# 测试json.loads方法的parse_float参数
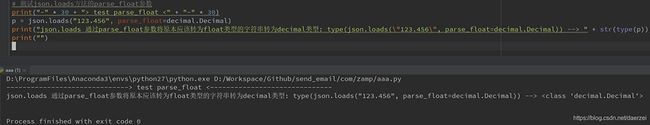
print("-" * 30 + "> test parse_float <" + "-" * 30)
p = json.loads("123.456", parse_float=decimal.Decimal)
print("json.loads 通过parse_float参数将原本应该转为float类型的字符串转为decimal类型: type(json.loads(\"123.456\", parse_float=decimal.Decimal)) --> " + str(type(p)))
print("")
3.5 parse_int参数
parse_int参数是可选的,它如果被指定的话,在解码json字符串的时候,符合int类型的字符串将被转为你所指定的,比如说你可以指定为float
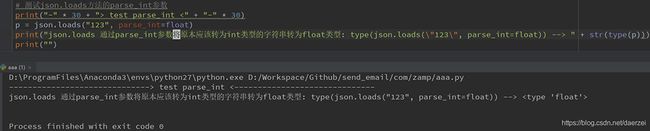
# 测试json.loads方法的parse_int参数
print("-" * 30 + "> test parse_int <" + "-" * 30)
p = json.loads("123", parse_int=float)
print("json.loads 通过parse_int参数将原本应该转为int类型的字符串转为float类型: type(json.loads(\"123\", parse_int=float)) --> " + str(type(p)))
3.6 parse_constant参数
parse_constant参数是可选的,它如果被指定的话,在解码json字符串的时候,如果出现以以下字符串:-Infinity,Infinity,NaN那么指定的parse_constant方法将会被调用到
def transform(s):
"""
此方法作为参数传给json.load(s)方法的parse_转译NAN, -Infinity,Infinity
:param s:
:return:
"""
# NaN --> not a number
if "NaN" == s:
return "Not a Number"
# 将负无穷大转为一个非常小的数
elif "-Infinity" == s:
return -999999
# 将正无穷大转为一个非常大的数
elif "Infinity" == s:
return 999999
else:
return s
# 测试json.loads方法的parse_constant参数
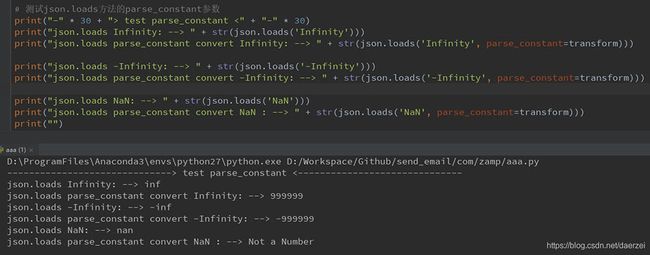
print("-" * 30 + "> test parse_constant <" + "-" * 30)
print("json.loads Infinity: --> " + str(json.loads('Infinity')))
print("json.loads parse_constant convert Infinity: --> " + str(json.loads('Infinity', parse_constant=transform_constant)))
print("json.loads -Infinity: --> " + str(json.loads('-Infinity')))
print("json.loads parse_constant convert -Infinity: --> " + str(json.loads('-Infinity', parse_constant=transform_constant)))
print("json.loads NaN: --> " + str(json.loads('NaN')))
print("json.loads parse_constant convert NaN : --> " + str(json.loads('NaN', parse_constant=transform_constant)))
print("")
3.7 cls参数
通过官方文档的注释我们可以知道json.load(s)方法具体的实现是通过JSONCoder类实现的,而cls参数是用于自定义一个JSONCoder的子类,用于替换JSONCoder类,,通过这个功能你可以自定义上面的那些parse_xxx参数,这里就不举例了
总结
到此这篇关于Python中json模块load/loads方法实战以及参数详解的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python json模块load/loads方法内容请搜索脚本之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持脚本之家!