【数学建模】-聚类模型学习笔记之基于密度的聚类算法DBSCAN算法
学习来源:
清风老师
机器学习聚类算法之DBSCAN
DBSCAN聚类算法——机器学习(理论+图解+python代码
DBSCAN 算法
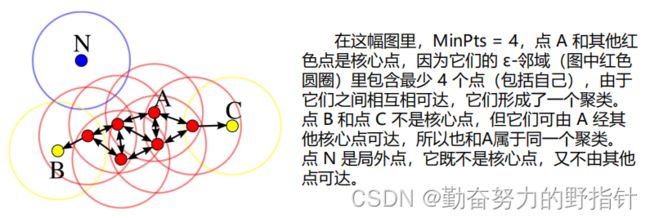
基本概念
DBSCAN算法迭代可视化展示
DBSCAN是一种基于密度的聚类方法,聚类前不需要预先指定聚类的个数,生成的簇的个数不定(和数据有关)。该算法利用基于密度的聚类的概念,即要求聚类空间中的一定区域内所包含对象(点或其他空间对象)的数目不小于某一给定阈值。该方法能在具有噪声的空间数据库中发现任意形状的簇,可将密度足够大的相邻区域连接,能有效处理异常数据。
DBSCAN算法将数据点分为三类:
• 核心点:在半径Eps内含有不少于MinPts数目的点
• 边界点:在半径Eps内点的数量小于MinPts,但是落在核心
点的邻域内
• 噪音点:既不是核心点也不是边界点的点
Matlab代码
clc;
clear;
close all;
%% Load Data
load mydata;
%% Run DBSCAN Clustering Algorithm
epsilon=0.5;
MinPts=10;
IDX=DBSCAN(X,epsilon,MinPts);
%% Plot Results
% 如果只要两个指标的话就可以画图啦
PlotClusterinResult(X, IDX);
title(['DBSCAN Clustering (\epsilon = ' num2str(epsilon) ', MinPts = ' num2str(MinPts) ')']);
function [IDX, isnoise]=DBSCAN(X,epsilon,MinPts)
C=0;
n=size(X,1);
IDX=zeros(n,1); % 初始化全部为0,即全部为噪音点
D=pdist2(X,X);
visited=false(n,1);
isnoise=false(n,1);
for i=1:n
if ~visited(i)
visited(i)=true;
Neighbors=RegionQuery(i);
if numel(Neighbors)<MinPts
% X(i,:) is NOISE
isnoise(i)=true;
else
C=C+1;
ExpandCluster(i,Neighbors,C);
end
end
end
function ExpandCluster(i,Neighbors,C)
IDX(i)=C;
k = 1;
while true
j = Neighbors(k);
if ~visited(j)
visited(j)=true;
Neighbors2=RegionQuery(j);
if numel(Neighbors2)>=MinPts
Neighbors=[Neighbors Neighbors2]; %#ok
end
end
if IDX(j)==0
IDX(j)=C;
end
k = k + 1;
if k > numel(Neighbors)
break;
end
end
end
function Neighbors=RegionQuery(i)
Neighbors=find(D(i,:)<=epsilon);
end
end
function PlotClusterinResult(X, IDX)
k=max(IDX);
Colors=hsv(k);
Legends = {};
for i=0:k
Xi=X(IDX==i,:);
if i~=0
Style = 'x';
MarkerSize = 8;
Color = Colors(i,:);
Legends{end+1} = ['Cluster #' num2str(i)];
else
Style = 'o';
MarkerSize = 6;
Color = [0 0 0];
if ~isempty(Xi)
Legends{end+1} = 'Noise';
end
end
if ~isempty(Xi)
plot(Xi(:,1),Xi(:,2),Style,'MarkerSize',MarkerSize,'Color',Color);
end
hold on;
end
hold off;
axis equal;
grid on;
legend(Legends);
legend('Location', 'NorthEastOutside');
end
优缺点
优点
- 基于密度定义,能处理任意形状和大小的簇;
- 可在聚类的同时发现异常点;
- 与K-means比较起来,不需要输入要划分的聚类个数。
缺点
- 对输入参数ε和Minpts敏感,确定参数困难;
- 由于DBSCAN算法中,变量ε和Minpts是全局唯一的,当聚类的密度不均匀时,聚 类距离相差很大时,聚类质量差;
- 当数据量大时,计算密度单元的计算复杂度大。
建议
只有两个指标,且你做出散点图后发现数据表现得很“DBSCAN”,这时候你再用DBSCAN进行聚类。 其他情况下,全部使用系统聚类吧。
K‐means也可以用,不过用了的话你论文上可写的东西比较少。
python代码
from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
from sklearn.datasets import make_blobs
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import mglearn
X, y = make_blobs(random_state=0, n_samples=12)
dbscan = DBSCAN()
clusters = dbscan.fit_predict(X)
# 都被标记为噪声
print('Cluster memberships:\n{}'.format(clusters))
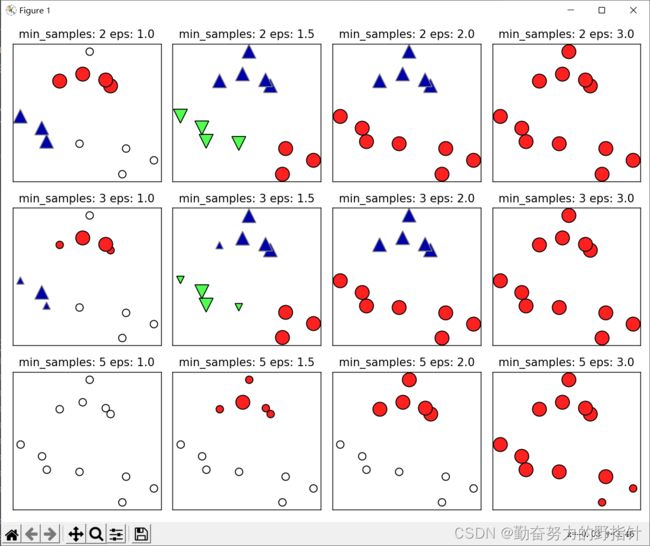
mglearn.plots.plot_dbscan()
plt.show()
# eps: float,ϵ-邻域的距离阈值
# min_samples :int,样本点要成为核心对象所需要的 ϵ-邻域的样本数阈值
# core_sample_indices_ : 核心点的索引,因为labels_不能区分核心点还是边界点,所以需要用这个索引确定核心点
# components_:训练样本的核心点
# labels_:每个点所属集群的标签,-1代表噪声点
Cluster memberships:
[-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1]
min_samples: 2 eps: 1.000000 cluster: [-1 0 0 -1 0 -1 1 1 0 1 -1 -1]
min_samples: 2 eps: 1.500000 cluster: [0 1 1 1 1 0 2 2 1 2 2 0]
min_samples: 2 eps: 2.000000 cluster: [0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
min_samples: 2 eps: 3.000000 cluster: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
min_samples: 3 eps: 1.000000 cluster: [-1 0 0 -1 0 -1 1 1 0 1 -1 -1]
min_samples: 3 eps: 1.500000 cluster: [0 1 1 1 1 0 2 2 1 2 2 0]
min_samples: 3 eps: 2.000000 cluster: [0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0]
min_samples: 3 eps: 3.000000 cluster: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]
min_samples: 5 eps: 1.000000 cluster: [-1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1]
min_samples: 5 eps: 1.500000 cluster: [-1 0 0 0 0 -1 -1 -1 0 -1 -1 -1]
min_samples: 5 eps: 2.000000 cluster: [-1 0 0 0 0 -1 -1 -1 0 -1 -1 -1]
min_samples: 5 eps: 3.000000 cluster: [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]