Pytorch 学习率衰减 之 余弦退火与余弦warmup 自定义学习率衰减scheduler
学习率衰减,通常我们英文也叫做scheduler。本文学习率衰减自定义,通过2种方法实现自定义,一是利用lambda,另外一个是继承pytorch的lr_scheduler
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from torch.optim import *
from torchvision import models
class Net(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net,self).__init__()
self.fc = nn.Linear(1, 10)
def forward(self,x):
return self.fc(x)
余弦退火
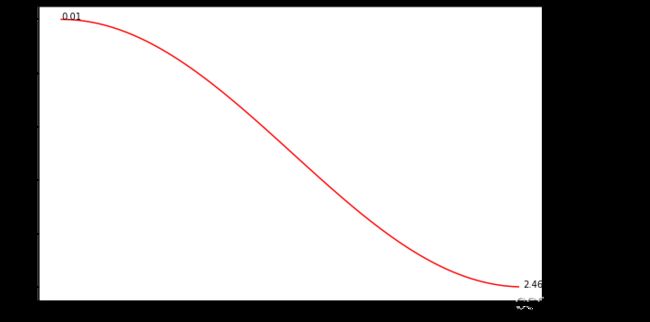
- 当T_max=20
lrs = []
model = Net()
LR = 0.01
epochs = 100
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(),lr = LR)
scheduler = lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=20, eta_min=1e-9)
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer.step()
lrs.append(optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr'])
scheduler.step()
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(lrs, color='r')
plt.text(0, lrs[0], str(lrs[0]))
plt.text(epochs, lrs[-1], str(lrs[-1]))
plt.show()
- 当T_max = epochs,这就是我们经常用到的弦退火的 scheduler,下面再来看看带Warm-up的
lrs = []
model = Net()
LR = 0.01
epochs = 100
optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(),lr = LR)
scheduler = lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=epochs, eta_min=1e-9)
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer.step()
lrs.append(optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr'])
scheduler.step()
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(lrs, color='r')
plt.text(0, lrs[0], str(lrs[0]))
plt.text(epochs, lrs[-1], str(lrs[-1]))
plt.show()
WarmUp
下面来看看 Pytorch定义的余弦退货的公式如下
η t = η m i n + 1 2 ( η m a x − η m i n ) ( 1 + cos ( T c u r T m a x π ) ) , T c u r ≠ ( 2 k + 1 ) T m a x ; η t + 1 = η t + 1 2 ( η m a x − η m i n ) ( 1 − cos ( 1 T m a x π ) ) , T c u r = ( 2 k + 1 ) T m a x . \begin{aligned} \eta_t & = \eta_{min} + \frac{1}{2}(\eta_{max} - \eta_{min})\left(1 + \cos\left(\frac{T_{cur}}{T_{max}}\pi\right)\right), & T_{cur} \neq (2k+1)T_{max}; \\ \eta_{t+1} & = \eta_{t} + \frac{1}{2}(\eta_{max} - \eta_{min}) \left(1 - \cos\left(\frac{1}{T_{max}}\pi\right)\right), & T_{cur} = (2k+1)T_{max}. \end{aligned} ηtηt+1=ηmin+21(ηmax−ηmin)(1+cos(TmaxTcurπ)),=ηt+21(ηmax−ηmin)(1−cos(Tmax1π)),Tcur=(2k+1)Tmax;Tcur=(2k+1)Tmax.
实际上是用下面的公式做为更新的, 当 T c u r = T m a x T_{cur} = T_{max} Tcur=Tmax是, c o s cos cos部分为0,所以就等于 η m i n \eta_{min} ηmin
η t = η m i n + 1 2 ( η m a x − η m i n ) ( 1 + cos ( T c u r T m a x π ) ) \eta_t = \eta_{min} + \frac{1}{2}(\eta_{max} - \eta_{min})\left(1 + \cos\left(\frac{T_{cur}}{T_{max}}\pi\right)\right) ηt=ηmin+21(ηmax−ηmin)(1+cos(TmaxTcurπ))
这里直接根据公式的定义来画个图看看
etas = []
epochs = 100
eta_max = 1e-4
eta_min = 1e-9
t_max = epochs / 1
for i in range(epoch):
t_cur = i
eta = eta_min + 0.5 * (eta_max - eta_min) * (1 + np.cos(np.pi * t_cur / t_max))
etas.append(eta)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(range(len(etas)), etas, color='r')
plt.text(epochs, lrs[-1], str(lrs[-1]))
plt.show()

从图上来看,跟上面的余弦退化是一样的,眼尖的都会发现lr_min 不等于eta_min=1e-9
利用Lambda来定义的
有个较小的bug(也不算,在description里有指出)
def warm_up_cosine_lr_scheduler(optimizer, epochs=100, warm_up_epochs=5, eta_min=1e-9):
"""
Description:
- Warm up cosin learning rate scheduler, first epoch lr is too small
Arguments:
- optimizer: input optimizer for the training
- epochs: int, total epochs for your training, default is 100. NOTE: you should pass correct epochs for your training
- warm_up_epochs: int, default is 5, which mean the lr will be warm up for 5 epochs. if warm_up_epochs=0, means no need
to warn up, will be as cosine lr scheduler
- eta_min: float, setup ConsinAnnealingLR eta_min while warm_up_epochs = 0
Returns:
- scheduler
"""
if warm_up_epochs <= 0:
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, T_max=epochs, eta_min=eta_min)
else:
warm_up_with_cosine_lr = lambda epoch: eta_min + (epoch / warm_up_epochs) if epoch <= warm_up_epochs else 0.5 * (
np.cos((epoch - warm_up_epochs) / (epochs - warm_up_epochs) * np.pi) + 1)
scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.LambdaLR(optimizer, lr_lambda=warm_up_with_cosine_lr)
return scheduler
# warm up consin lr scheduler
lrs = []
model = Net()
LR = 1e-4
warm_up_epochs = 30
epochs = 100
optimizer = SGD(model.parameters(), lr=LR)
scheduler = warm_up_cosine_lr_scheduler(optimizer, warm_up_epochs=warm_up_epochs, eta_min=1e-9)
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer.step()
lrs.append(optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr'])
scheduler.step()
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6)) 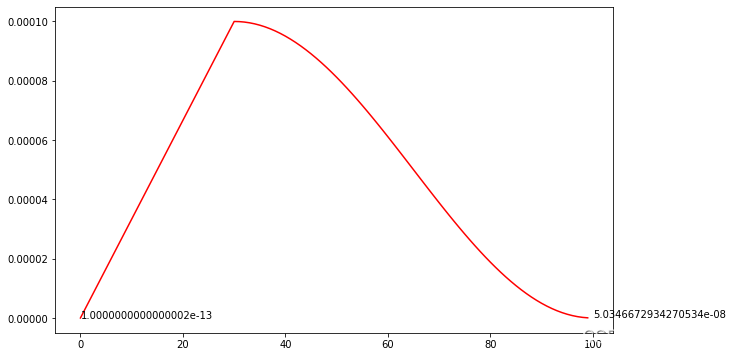
plt.plot(lrs, color='r')
plt.text(0, lrs[0], str(lrs[0]))
plt.text(epochs, lrs[-1], str(lrs[-1]))
plt.show()

从图上看,第一个lr非常非常小,导致训练时的,第一个epoch基本上不更新
继承lr_scheduler的类
class WarmupCosineLR(lr_scheduler._LRScheduler):
def __init__(self, optimizer, lr_min, lr_max, warm_up=0, T_max=10, start_ratio=0.1):
"""
Description:
- get warmup consine lr scheduler
Arguments:
- optimizer: (torch.optim.*), torch optimizer
- lr_min: (float), minimum learning rate
- lr_max: (float), maximum learning rate
- warm_up: (int), warm_up epoch or iteration
- T_max: (int), maximum epoch or iteration
- start_ratio: (float), to control epoch 0 lr, if ratio=0, then epoch 0 lr is lr_min
Example:
<<< epochs = 100
<<< warm_up = 5
<<< cosine_lr = WarmupCosineLR(optimizer, 1e-9, 1e-3, warm_up, epochs)
<<< lrs = []
<<< for epoch in range(epochs):
<<< optimizer.step()
<<< lrs.append(optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr'])
<<< cosine_lr.step()
<<< plt.plot(lrs, color='r')
<<< plt.show()
"""
self.lr_min = lr_min
self.lr_max = lr_max
self.warm_up = warm_up
self.T_max = T_max
self.start_ratio = start_ratio
self.cur = 0 # current epoch or iteration
super().__init__(optimizer, -1)
def get_lr(self):
if (self.warm_up == 0) & (self.cur == 0):
lr = self.lr_max
elif (self.warm_up != 0) & (self.cur <= self.warm_up):
if self.cur == 0:
lr = self.lr_min + (self.lr_max - self.lr_min) * (self.cur + self.start_ratio) / self.warm_up
else:
lr = self.lr_min + (self.lr_max - self.lr_min) * (self.cur) / self.warm_up
# print(f'{self.cur} -> {lr}')
else:
# this works fine
lr = self.lr_min + (self.lr_max - self.lr_min) * 0.5 *\
(np.cos((self.cur - self.warm_up) / (self.T_max - self.warm_up) * np.pi) + 1)
self.cur += 1
return [lr for base_lr in self.base_lrs]
# class
epochs = 100
warm_up = 5
cosine_lr = WarmupCosineLR(optimizer, 1e-9, 1e-3, warm_up, epochs, 0.1)
lrs = []
for epoch in range(epochs):
optimizer.step()
lrs.append(optimizer.state_dict()['param_groups'][0]['lr'])
cosine_lr.step()
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(lrs, color='r')
plt.text(0, lrs[0], str(lrs[0]))
plt.text(epochs, lrs[-1], str(lrs[-1]))
plt.show()
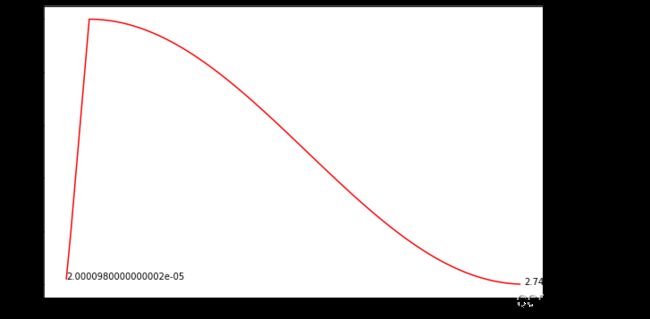
从图上看出,第一个epoch的lr也不至于非常非常小了,达到了所需预期,当然,如果你说first epoch的lr,你也需要非常非常小(<1e-8),你也可以自己尝试其它值。