【Pytorch】由torch.nn.MaxPool2d和torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d理解类模块与函数之间的差别
引言
torch.nn.MaxPool2d和torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d,在pytorch构建模型中,都可以作为最大池化层的引入,但前者为类模块,后者为函数,在使用上存在不同。
1. torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d
pytorch中的函数,可以直接调用,源码如下:
def max_pool2d_with_indices(
input: Tensor, kernel_size: BroadcastingList2[int],
stride: Optional[BroadcastingList2[int]] = None,
padding: BroadcastingList2[int] = 0,
dilation: BroadcastingList2[int] = 1,
ceil_mode: bool = False,
return_indices: bool = False
) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]:
r"""Applies a 2D max pooling over an input signal composed of several input
planes.
See :class:`~torch.nn.MaxPool2d` for details.
"""
if has_torch_function_unary(input):
return handle_torch_function(
max_pool2d_with_indices,
(input,),
input,
kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
dilation=dilation,
ceil_mode=ceil_mode,
return_indices=return_indices,
)
if stride is None:
stride = torch.jit.annotate(List[int], [])
return torch._C._nn.max_pool2d_with_indices(input, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, ceil_mode)
def _max_pool2d(
input: Tensor, kernel_size: BroadcastingList2[int],
stride: Optional[BroadcastingList2[int]] = None,
padding: BroadcastingList2[int] = 0,
dilation: BroadcastingList2[int] = 1,
ceil_mode: bool = False,
return_indices: bool = False
) -> Tensor:
if has_torch_function_unary(input):
return handle_torch_function(
max_pool2d,
(input,),
input,
kernel_size,
stride=stride,
padding=padding,
dilation=dilation,
ceil_mode=ceil_mode,
return_indices=return_indices,
)
if stride is None:
stride = torch.jit.annotate(List[int], [])
return torch.max_pool2d(input, kernel_size, stride, padding, dilation, ceil_mode)
max_pool2d = boolean_dispatch(
arg_name="return_indices",
arg_index=6,
default=False,
if_true=max_pool2d_with_indices,
if_false=_max_pool2d,
module_name=__name__,
func_name="max_pool2d",
)
使用如下:
import torch.nn.functional as F
input = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 32) # 输入张量
F.max_pool2d(input, kernel_size=2, stride=1,padding=0)
"""
其中:
Shape:
- Input: :math:`(N, C, H_{in}, W_{in})`
- Output: :math:`(N, C, H_{out}, W_{out})`, where
"""
2. torch.nn.MaxPool2d
pytorch中的类模块,先实例化,再调用其函数,源码如下(笔者已将源码中的注释简化):
class MaxPool2d(_MaxPoolNd):
kernel_size: _size_2_t
stride: _size_2_t
padding: _size_2_t
dilation: _size_2_t
def forward(self, input: Tensor) -> Tensor:
return F.max_pool2d(input, self.kernel_size, self.stride,
self.padding, self.dilation, self.ceil_mode,
self.return_indices)
使用如下:
import torch
m = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2) # 实例化
# 或者
m = torch.nn.MaxPool2d((3, 2), stride=(2, 1)) # 实例化
input = torch.randn(20, 16, 50, 32) # 输入张量
output = m(input) # 使用该类
"""
Shape:
- Input: :math:`(N, C, H_{in}, W_{in})`
- Output: :math:`(N, C, H_{out}, W_{out})`, where
"""
3. 对比类和函数的使用
通过上述比较,torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d作为函数可以直接调用,传入参数(input(四个维度的输入张量), kernel_size(卷积核尺寸), stride(步幅),padding(填充), dilation, ceil_mode,return_indices)即可。
torch.nn.MaxPool2d,要先实例化,并在forward调用了torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d函数。
综上:torch.nn.functional.max_pool2d函数包含于torch.nn.MaxPool2d类模块中,可以单独使用,也可以实例化类再使用。
在模型构建下的使用:
(1)使用类模块
import torch
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
self.pooling = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(2) # kernel_size = 2,实例化
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(320, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# Flatten data from(n,1,28,28) to (n,784)
batch_size = x.s(0)
x = F.relu(self.pooling(self.conv1(x)))
x = F.relu(self.pooling(self.conv2(x)))
x = x.view(batch_size, -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
说明:kernel_size 是必须要指定的参数,否则会报错
笔者修改了torch.nn.MaxPool2d的源码,说明传入参数要求(记得改回来!):
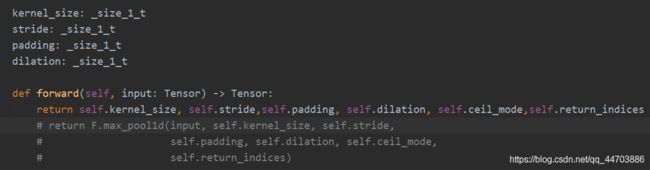
import torch
pooling1 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(1,2,3,4)
print(pooling1)
pooling2 = torch.nn.MaxPool2d(1)
print(pooling2)
输出为
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=1, stride=2, padding=3, dilation=4, ceil_mode=False)
MaxPool2d(kernel_size=1, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, ceil_mode=False)
(2)直接调用函数
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
class Net(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(Net, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size=5)
self.conv2 = torch.nn.Conv2d(10, 20, kernel_size=5)
# 最大池化层无需实例化,直接在forward中调用
self.fc = torch.nn.Linear(320, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# Flatten data from(n,1,28,28) to (n,784)
batch_size = x.s(0)
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv1(x), kernel_size=2)) # 一定要指定kernel_size
x = F.relu(F.max_pool2d(self.conv2(x), kernel_size=2))
x = x.view(batch_size, -1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x