SpringBoot中使用Ehcache缓存
SpringBoot中使用Ehcache缓存
- 简介
-
- Ehcache简介
- EhCache特性
- 集成方式
- Ehcache和Redis对比
- 整合示例
简介
Ehcache简介
Ehcache 是一个纯Java的进程内缓存框架,具有快速、精干等特点,是Hibernate中默认CacheProvider。Ehcache是一种广泛使用的开源Java分布式缓存。主要面向通用缓存,Java EE和轻量级容器。它具有内存和磁盘存储,缓存加载器,缓存扩展,缓存异常处理程序,一个gzip缓存servlet过滤器,支持REST和SOAP api等特点。
Spring中提供了对缓存功能的抽象:即允许绑定不同的缓存解决方案(如Ehcache),但本身不直接提供缓存功能的实现。它支持注解方式使用缓存,非常方便。
EhCache特性
- 快速
- 简单
- 多种缓存策略
- 缓存数据有两级:内存和磁盘,因此无需担心容量问题
- 缓存数据会在虚拟机重启的过程中写入磁盘
- 可以通过RMI、可插入API等方式进行分布式缓存
- 具有缓存和缓存管理器的侦听接口
- 支持多缓存管理器实例,以及一个实例的多个缓存区域
- 提供Hibernate的缓存实现
集成方式
可以单独使用,一般在第三方库中被用到的比较多(如mybatis、shiro等)Ehcache 对分布式支持不够好,多个节点不能同步,通常和redis一块使用
Ehcache和Redis对比
Ehcache直接在jvm虚拟机中缓存,速度快,效率高;但是缓存共享麻烦,集群分布式应用不方便。
Redis是通过socket访问到缓存服务,效率比Ehcache低,比数据库要快很多,处理集群和分布式缓存方便,有成熟的方案。如果是单个应用或者对缓存访问要求很高的应用,用Ehcache。如果是大型系统,存在缓存共享、分布式部署、缓存内容很大的,建议用redis。
Ehcache也有缓存共享方案,不过是通过RMI或者Jgroup多播方式进行广播缓存通知更新,缓存共享复杂,维护不方便;简单的共享可以,但是涉及到缓存恢复,大数据缓存,则不合适。
整合示例
1、pom.xml中添加依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-cache
net.sf.ehcache
ehcache
2、创建ehcache.xml配置文件
在resources目录下创建ehcache.xml文件,可以在ehcache依赖包中找到示例文件
ehcache.xml内容及说明:
详细介绍
3、在SpringBoot配置文件中配置ehcache.xml
# .yml
spring:
cache:
ehcache:
config: ehcache.xml
# .properties
spring.cache.ehcache.config=ehcache.xml
4、在Application启动类中增加注解
@EnableCaching
5、使用缓存
注解说明
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
@Cacheable(value = "userCache")
public List findList() {
return userMapper.findList();
}
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "userCache",allEntries = true)
public Integer delete(Integer id) {
return userMapper.delete(id);
}
}
6、测试
package com.test.cache;
import com.test.cache.entity.User;
import com.test.cache.service.UserService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
@SpringBootTest
class CacheApplicationTests {
@Resource
private UserService userService;
@Test
void test1() {
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
Date start = new Date();
List list = userService.findList();
System.out.println("list.size() ------>> "+list.size());
Date end = new Date();
System.out.println("耗时:"+(end.getTime()-start.getTime())+" ms");
}
@Test
void test2(){
for (int i=0;i<4;i++){
test1();
System.out.println();
}
}
@Test
void test3(){
for (int i=0;i<4;i++){
if(i==2){
userService.delete(i);
}
test1();
System.out.println();
}
}
@Test
void test4() throws InterruptedException {
for (int i=0;i<4;i++){
if(i==2){
Thread.sleep(3000);
}
test1();
System.out.println();
}
}
}
创建了一个user表,并在里面添加了10w条记录
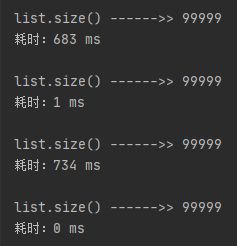
6.1、先取消findList方法的缓存注解:@Cacheable,然后运行test2()

执行成功后恢复缓存注解:@Cacheable,再次运行test2(),速度的提升一目了然

6.2、运行test3(),当执行完第二次后进入delete方法删除了一条记录,并且使用@CacheEvict注解清除了缓存数据

6.3、修改ehcache.xml中userCache的timeToLiveSeconds为2,运行test4(),由于设置了数据的总存活时间为2秒,所以当从睡眠中出来时又要去访问数据库了
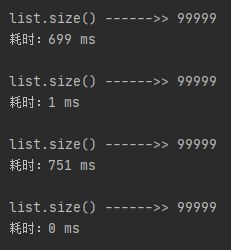
6.4、恢复上一步的改动,并将ehcache.xml中userCache的timeToIdleSeconds改为2,运行test4(),由于设置了数据的闲置时间为2秒,所以当从睡眠中出来时又要去访问数据库了