pandas第8章-文本数据
一、str对象
1. str对象的设计意图
str 对象是定义在 Index 或 Series 上的属性,专门用于处理每个元素的文本内容,其内部定义了大量方法,因此对一个序列进行文本处理,首先需要获取其 str 对象。
字母转为大写的操作:str.upper(字符串名) 或者字符串名.str.upper()
#字母转为大写的操作:
var = 'abcd'
str.upper(var) # Python内置str模块
Out[4]: 'ABCD'
s = pd.Series(['abcd', 'efg', 'hi'])
s.str
Out[6]: <pandas.core.strings.accessor.StringMethods at 0x1fe1643fbe0>
s.str.upper() # pandas中str对象上的upper方法
Out[7]:
0 ABCD
1 EFG
2 HI
dtype: object
2. []索引器
索引,切片
3. string类型
原来所有的字符串类型都会以 object 类型的 Series 进行存储,但 object 类型只应当存储混合类型,例如同时存储浮点、字符串、字典、列表、自定义类型等,因此字符串有必要同数值型或 category 一样,具有自己的数据存储类型,从而引入了 string 类型。
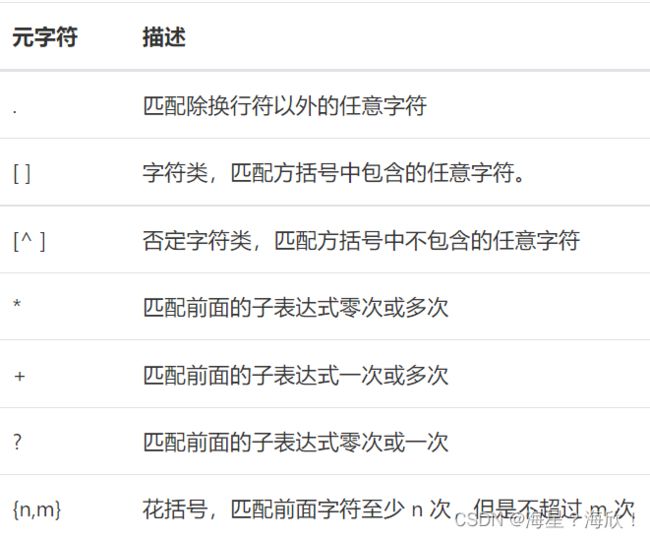
二、正则表达式基础
1. 一般字符的匹配
从左到右匹配字符串中内容的一种工具。
#在下面的字符串中找出 apple
import re
re.findall(r'Apple', 'Apple! This Is an Apple!')
Out[29]: ['Apple', 'Apple']
re.findall(r'.', 'abc')
Out[30]: ['a', 'b', 'c']
re.findall(r'[ac]', 'abc')
Out[31]: ['a', 'c']
re.findall(r'[^ac]', 'abc')
Out[32]: ['b']
re.findall(r'[ab]{2}', 'aaaabbbb') # {n}指匹配n次
Out[33]: ['aa', 'aa', 'bb', 'bb']
re.findall(r'aaa|bbb', 'aaaabbbb')
Out[34]: ['aaa', 'bbb']
re.findall(r'a\\?|a\*', 'aa?a*a')
Out[35]: ['a', 'a', 'a', 'a']
re.findall(r'a?.', 'abaacadaae')
Out[36]: ['ab', 'aa', 'c', 'ad', 'aa', 'e']
re.findall(r'.s', 'Apple! This Is an Apple!')
Out[37]: ['is', 'Is']
re.findall(r'\w{2}', '09 8? 7w c_ 9q p@')
Out[38]: ['09', '7w', 'c_', '9q']
re.findall(r'\w\W\B', '09 8? 7w c_ 9q p@')
Out[39]: ['8?', 'p@']
re.findall(r'.\s.', 'Constant dropping wears the stone.')
Out[40]: ['t d', 'g w', 's t', 'e s']
re.findall(r'上海市(.{2,3}区)(.{2,3}路)(\d+号)',
'上海市黄浦区方浜中路249号 上海市宝山区密山路5号')
Out[41]: [('黄浦区', '方浜中路', '249号'), ('宝山区', '密山路', '5号')]
三、文本处理的五类操作
1. 拆分
str.split 能够把字符串的列进行拆分,其中第一个参数为正则表达式,可选参数包括从左到右的最大拆分次数 n ,是否展开为多个列 expand 。
s.str.split(‘正则表达式’, n=)
s = pd.Series(['上海市黄浦区方浜中路249号',
'上海市宝山区密山路5号'])
s.str.split('[市区路]') #[市区路]是正则表达式
Out[43]:
0 [上海, 黄浦, 方浜中, 249号]
1 [上海, 宝山, 密山, 5号]
dtype: object
s.str.split('[市区路]', n=2, expand=True)
Out[44]:
0 1 2
0 上海 黄浦 方浜中路249号
1 上海 宝山 密山路5号
与其类似的函数是 str.rsplit ,其区别在于使用 n 参数的时候是从右到左限制最大拆分次数。
2. 合并
两个函数,分别是 str.join 和 str.cat 。
str.join 表示用某个连接符把 Series 中的字符串列表连接起来,如果列表中出现了非字符串元素则返回缺失值:
s = pd.Series([['a','b'], [1, 'a'], [['a', 'b'], 'c']])
s.str.join('-')
Out[47]:
0 a-b
1 NaN
2 NaN
dtype: object
str.cat 用于合并两个序列,主要参数为连接符 sep 、连接形式 join 以及缺失值替代符号 na_rep ,其中连接形式默认为以索引为键的左连接。
s1 = pd.Series(['a','b'])
s2 = pd.Series(['cat','dog'])
s1.str.cat(s2,sep='-')
Out[50]:
0 a-cat
1 b-dog
dtype: object
s2.index = [1, 2] #更改s2的索引序号
s1.str.cat(s2, sep='-', na_rep='?', join='outer')
Out[52]:
0 a-?
1 b-cat
2 ?-dog
dtype: object
3. 匹配
str.contains 返回了每个字符串是否包含正则模式的布尔序列:
s = pd.Series(['my cat', 'he is fat', 'railway station'])
s.str.contains('\s\wat')
Out[54]:
0 True
1 True
2 False
dtype: bool
str.startswith 和 str.endswith 返回了每个字符串以给定模式为开始和结束的布尔序列,它们都不支持正则表达式:
s.str.startswith('my')
Out[55]:
0 True
1 False
2 False
dtype: bool
s.str.endswith('t')
Out[56]:
0 True
1 True
2 False
dtype: bool
如果需要用正则表达式来检测开始或结束字符串的模式,可以使用 str.match ,其返回了每个字符串起始处是否符合给定正则模式的布尔序列:
s.str.match('m|h')
Out[57]:
0 True
1 True
2 False
dtype: bool
s.str[::-1].str.match('ta[f|g]|n') # 反转后匹配
Out[58]:
0 False
1 True
2 True
dtype: bool
还有一种返回索引的匹配函数,即 str.find 与 str.rfind ,其分别返回从左到右和从右到左第一次匹配的位置的索引,未找到则返回-1。需要注意的是这两个函数不支持正则匹配,只能用于字符子串的匹配:
s = pd.Series(['This is an apple. That is not an apple.'])
s.str.find('apple')
Out[62]:
0 11
dtype: int64
s.str.rfind('apple')
Out[63]:
0 33
dtype: int64
4. 替换
str.replace
5. 提取
用 str.extract 进行提取
四、常用字符串函数
1. 字母型函数
upper, lower, title, capitalize, swapcase 这五个函数主要用于字母的大小写转化
s = pd.Series(['lower', 'CAPITALS', 'this is a sentence', 'SwApCaSe'])
s.str.upper()
Out[87]:
0 LOWER
1 CAPITALS
2 THIS IS A SENTENCE
3 SWAPCASE
dtype: object
s.str.lower()
Out[88]:
0 lower
1 capitals
2 this is a sentence
3 swapcase
dtype: object
s.str.title()
Out[89]:
0 Lower
1 Capitals
2 This Is A Sentence
3 Swapcase
dtype: object
s.str.capitalize()
Out[90]:
0 Lower
1 Capitals
2 This is a sentence
3 Swapcase
dtype: object
s.str.swapcase()
Out[91]:
0 LOWER
1 capitals
2 THIS IS A SENTENCE
3 sWaPcAsE
dtype: object
2. 数值型函数
pd.to_numeric函数,其主要参数包括 errors 和 downcast 分别代表了非数值的处理模式和转换类型。对于不能转换为数值的有三种 errors 选项, raise, coerce, ignore 分别表示直接报错、设为缺失以及保持原来的字符串。
s = pd.Series(['1', '2.2', '2e', '??', '-2.1', '0'])
pd.to_numeric(s, errors='ignore')
Out[93]:
0 1
1 2.2
2 2e
3 ??
4 -2.1
5 0
dtype: object
pd.to_numeric(s, errors='coerce')
Out[94]:
0 1.0
1 2.2
2 NaN
3 NaN
4 -2.1
5 0.0
dtype: float64
3. 统计型函数
count 和 len 的作用分别是返回出现正则模式的次数和字符串的长度
4. 格式型函数
格式型函数主要分为两类,第一种是除空型,第二种是填充型。
除空型函数一共有三种,它们分别是 strip, rstrip, lstrip ,分别代表去除两侧空格、右侧空格和左侧空格。
对于填充型函数而言, pad 是最灵活的,它可以选定字符串长度、填充的方向和填充内容:
s.str.pad(n,‘left/right/both’,‘填充的符合’) 左/右/两边 填充,以达到n长的字符串长度。
s = pd.Series(['a','b','c'])
s.str.pad(5,'left','*')
Out[104]:
0 ****a
1 ****b
2 ****c
dtype: object
s.str.pad(5,'right','*')
Out[105]:
0 a****
1 b****
2 c****
dtype: object
s.str.pad(5,'both','*')
Out[106]:
0 **a**
1 **b**
2 **c**
dtype: object
上述的三种情况可以分别用 rjust, ljust, center 来等效完成,需要注意 ljust 是指右侧填充而不是左侧填充:
s.str.rjust(5, '*')
Out[107]:
0 ****a
1 ****b
2 ****c
dtype: object
s.str.ljust(5, '*')
Out[108]:
0 a****
1 b****
2 c****
dtype: object
s.str.center(5, '*')
Out[109]:
0 **a**
1 **b**
2 **c**
dtype: object
zfill()–在数字前补0
s = pd.Series([7, 155, 303000]).astype('string')
s.str.pad(6,'left','0')
Out[111]:
0 000007
1 000155
2 303000
dtype: string
s.str.rjust(6,'0')
Out[112]:
0 000007
1 000155
2 303000
dtype: string
s.str.zfill(6)
Out[113]:
0 000007
1 000155
2 303000
dtype: string