MybatisPlus学习总结
MybatisPlus学习总结
一、MybatisPlus环境的搭建
SpringBoot整合mybatisPlus的一个简单应用,
第一步、我们先数据库建表
#创建用户表
CREATE TABLE user (
id BIGINT(20) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL COMMENT '主键',
name VARCHAR(30) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '姓名',
age INT(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '年龄',
email VARCHAR(50) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '邮箱',
manager_id BIGINT(20) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '直属上级id',
create_time DATETIME DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
CONSTRAINT manager_fk FOREIGN KEY (manager_id)
REFERENCES user (id)
) ENGINE=INNODB CHARSET=UTF8;
#初始化数据:
INSERT INTO user (id, name, age, email, manager_id
, create_time)
VALUES (1087982257332887553, '大boss', 40, '[email protected]', NULL
, '2019-01-11 14:20:20'),
(1088248166370832385, '王天风', 25, '[email protected]', 1087982257332887553
, '2019-02-05 11:12:22'),
(1088250446457389058, '李艺伟', 28, '[email protected]', 1088248166370832385
, '2019-02-14 08:31:16'),
(1094590409767661570, '张雨琪', 31, '[email protected]', 1088248166370832385
, '2019-01-14 09:15:15'),
(1094592041087729666, '刘红雨', 32, '[email protected]', 1088248166370832385
, '2019-01-14 09:48:16');
第二步、导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbcartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processorartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<optional>trueoptional>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidougroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>3.1.2version>
dependency>
第三步、Springboot配置文件
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
username: root
password: root
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=CTT&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&allowMultiQueries=true
logging:
level:
root: warn
org.ywb.demo.dao: trace
pattern:
console: '%p%m%n'
第四步、创建相关包,如图:
第五步:在pojo包中新建和数据库user表映射的类
@Data //这个注解帮我们自动生成下面字段的get set 方法
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
private String managerId;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
}
第六步、在dao包中创建mapper接口,并集成mybatisPlus的BaseMapper
(解释:这里的BaseMapper类里面已经帮我们封装了很多增删改查,条件搜索的方法。这就是mybatisPlus在原有mybatis上的加强的地方)
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> { //UserMapper继承了BaseMapper以后,UserMapper里面就会继承BaseMapper里面的很多关于User类的增删改查,条件搜索等等方法
}
第七步、在springboot启动类添加@MapperScan扫描dao层接口
@MapperScan("org.ywb.demo.dao")
@SpringBootApplication
public class MybatisPlusDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MybatisPlusDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
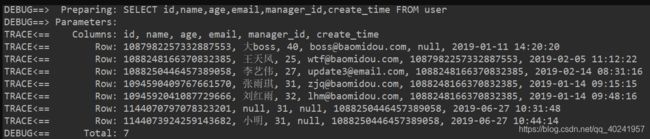
第八步、编写测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class MybatisPlusDemoApplicationTests {
@Resource
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void select(){
List<User> users = userMapper.selectList(null); //这里的selectList()方法是userMapper从BaseMapper里继承过来的方法
users.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
二、mybatisPlus常用注解
MyBatisPlus提供了一些注解供我们在实体类和表信息出现不对应的时候使用。通过使用注解完成逻辑上匹配。
@Data
@TableName("t_user")
public class User {
@TableId("user_id")
private Long id;
@TableField("real_name")
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
private Long managerId;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
}
排除实体类中非表字段
- 使用
transient关键字修饰非表字段,但是被transient修饰后,无法进行序列化。 - 使用
static关键字,因为我们使用的是lombok框架生成的get/set方法,所以对于静态变量,我们需要手动生成get/set方法。 - 使用
@TableField(exist = false)注解(说明:@TableField(exist = false) 注解加在bean属性上,表示当前属性不是数据库的字段,但在项目中必须使用,这样在新增等使用bean的时候,mybatis-plus就会忽略这个,不会报错)
三、利用CURD进行增删改查
BaseMapper(说明:BaseMapper是mybatisPlus里面的自带的)中封装了很多关于增删该查的方法,后期自动生成,我们直接调用接口中的相关方法即可完成相应的操作。
我们可以看一下BaseMapper部分源码
public interface BaseMapper<T> extends Mapper<T> {
int insert(T entity);
int deleteById(Serializable id);
int deleteByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap);
int delete(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> wrapper);
int deleteBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable> idList);
int updateById(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity);
...
}
接下来我们插入一条记录测试:
@Test
public void insert(){
User user = new User();
user.setAge(31);
user.setManagerId(1088250446457389058L);
user.setCreateTime(LocalDateTime.now());
int insert = userMapper.insert(user); //这个insert()是userMapper从BaseMapper里面继承过来的方法
System.out.println("影像记录数:"+insert);
}
四、条件构造器查询
BaseMapper中提供简单的增删改查方法之外,还提供了很多关于区间查询,多表连接查询,分组等等查询功能,实现的类图如下所示:

通过观察类图可知,我们需要这些功能时,只需要创建QueryWrapper对象即可。
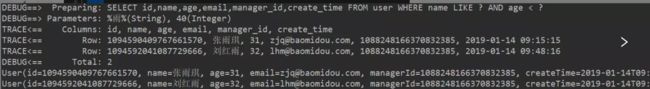
1.模糊查询
/**
* 查询名字中包含'雨'并且年龄小于40
* where name like '%雨%' and age < 40
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapper(){
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.like("name","雨").lt("age",40); //下面有代码讲解
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);//这里的selectList是userMapper从BaseMapper里面继承过来的
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
讲解:like()是对某个字段进行模糊匹配,lt()是指定某个字段的值小于多少
2.嵌套查询
/**
* 创建日期为2019年2月14日并且直属上级姓名为王姓
* date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d') and manager_id in (select id from user where name like '王%')
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapper2(){
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.apply("date_format(create_time,'%Y-%m-%d')={0}","2019-02-14")
.inSql("manager_id","select id from user where name like '王%'");//下面有代码讲解
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
讲解:inSql("manager_id","select id from user where name like '王%'")理解: 先调用select id from user where name like '王%'查出id的值,然后把id的值赋值给manager_id。
注意:上面的日期查询使用的是占位符的形式(说明:在本例中是{0})进行查询,目的就是为了防止SQL注入的风险,有兴趣的可以更深入地去。
3.and & or
/**
* 名字为王姓,(年龄小于40或者邮箱不为空)
*/
@Test
public void selectByWrapper3(){
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); //下面有代码讲解
queryWrapper.likeRight("name","王").and(wq-> wq.lt("age",40).or().isNotNull("email"));
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
讲解:
likeRight("name", "王")的作用就是name like '王%'- 后面的and()函数理解:
and()里的wq是queryWrapper.likeRight("name","王")执行完返回的结果
and()的用法如下 (提示:下面的<>是不等于的意思)
例:and(i -> i.eq("name", "李白").ne("status", "活着"))—>and (name = '李白' and status <> '活着')
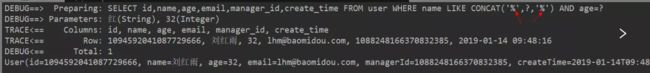
4.between & and
/**
* 名字为王姓,(年龄小于40,并且年龄大于20,并且邮箱不为空)
*/
@Test
public void selectWrapper4(){ //queryWrapper是用于查询的查询对象
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(); //下面会有代码讲解
queryWrapper.likeRight("name", "王").and(wq -> wq.between("age", 20, 40).and(wqq -> wqq.isNotNull("email")));
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);//这里的selectList()是userMapper从mybatisPlus系统自带的BaseMapper里面继承过来的
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
讲解:and()里的wq是queryWrapper.likeRight("name", "王")执行后返回的结果

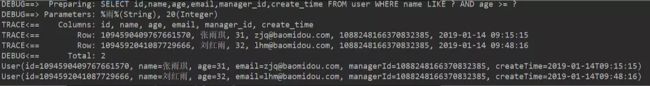
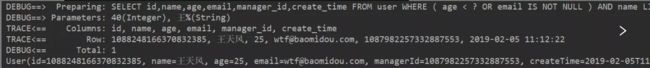
5.nested
/**
* (年龄小于40或者邮箱不为空)并且名字为王姓
* (age<40 or email is not null)and name like '王%'
*/
@Test
public void selectWrapper5(){
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//下面会有代码讲解
queryWrapper.nested(wq- >wq.lt("age",40).or().isNotNull("email")).likeRight("name","王");
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);//这里的selectList()是userMapper从mybatisPlus系统自带的BaseMapper里面继承过来的
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
讲解:
queryWrapper.nested(wq- >wq.lt("age",40).or().isNotNull("email")).likeRight("name","王");可以这样理解,先执行 queryWrapper.nested(wq- >wq.lt("age",40).or().isNotNull("email"))得到返回结果,然后拿返回结果继续执行likeRight("name","王");从而得到最终的结果
6.in
in就是“在什么之中”
/**
* 年龄为30,31,35,34的员工
*/
@Test
public void selectWrapper6(){
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//Arrays.asList()的作用就是将数组或一些元素转为集合,
queryWrapper.in("age", Arrays.asList(30,31,34,35));
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
7.last 有SQL注入的风险!!!
/**
* 无视优化规则直接拼接到 sql 的最后(有sql注入的风险,请谨慎使用)
* 例: last("limit 1")
* 注意只能调用一次,多次调用以最后一次为准
*
* @param condition 执行条件
* @param lastSql sql语句
* @return children
*/
Children last(boolean condition, String lastSql);
last使用示例如下:
/**
* 只返回满足条件的一条语句即可
* limit 1
*/
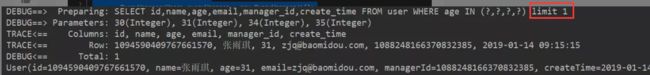
@Test
public void selectWrapper7(){
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.in("age", Arrays.asList(30,31,34,35)).last("limit 1");
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
我们看运行结果里红框框部分,就是通过last(“limit 1”)得到的,很显然last()容易引起sql注入(sql注入举例:在sql语句最后加上or 1=1,那么整个sql语句就成了“永真式”)
8.查询指定部分列
/**
* 查找为王姓的员工的姓名和年龄
*/
@Test
public void selectWrapper8(){ //下面会有代码讲解部分
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//下面的select("name","age")代表查询出员工的姓名和年龄
queryWrapper.select("name","age").likeRight("name","王");
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
讲解:likeRight("name", "王")的作用就是name like '王%'

9.使用过滤器查询指定列
/**
* 查询所有员工信息除了创建时间和员工ID列
*/
@Test
public void selectWrapper9(){ //下面会有代码讲解
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
queryWrapper.select(User.class,info->!info.getColumn().equals("create_time")
&&!info.getColumn().equals("manager_id"));
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
讲解:
queryWrapper.select(User.class,info->!info.getColumn().equals("create_time") &&!info.getColumn().equals("manager_id"));
部分可以这样理解: 查询的信息最后都映射到User.class中,后面的info->!info.etColumn()…是一个lambda表达式,也就是相当于一个函数,info就当成是执行完 queryWrapper.select(User.class之后返回的结果。
五、实体作为条件构造方法的参数
在web开发中,controller层常常会传递给我们一个用户的对象,比如通过用户姓名和用户年龄查询用户列表。
我们可以将传递过来的对象直接以构造参数的形式传递给QueryWrapper,MyBatisPlus会自动根据实体对象中的属性自动构建相应查询的SQL语句。
@Test
public void selectWrapper10(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("刘红雨");
user.setAge(32);
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(user);
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
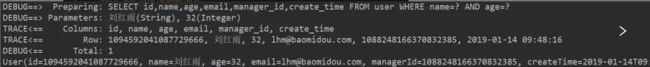
如果想通过对象中某些属性进行模糊查询,我们可以在跟数据库表对应的实体类中相应的属性标注注解即可。
比如我们想通过姓名进行模糊查询用户列表。
//在对应的实体内里面加上如下注解,SqlCondition.LIKE就是模糊查询的意思
@TableField(condition = SqlCondition.LIKE)
private String name;
@Test
public void selectWrapper10(){
User user = new User();
user.setName("红");
user.setAge(32);
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(user);
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(queryWrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
六、Lambda条件构造器
MybatisPlus提供了4种方式创建lambda条件构造器,前三种分别是这样的
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<User>().lambda();
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper1 = new LambdaQueryWrapper<>();
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper2 = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
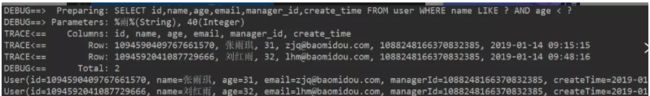
例一、查询名字中包含‘雨’并且年龄小于40的员工信息
@Test
public void lambdaSelect(){
LambdaQueryWrapper<User> lambdaQueryWrapper = Wrappers.lambdaQuery();
//User::getName是对User的name字段进行控制,lt()是“小于”的意思
lambdaQueryWrapper.like(User::getName,"雨").lt(User::getAge,40);
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(lambdaQueryWrapper);
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
问题:QueryWrapper类已经提供了很强大的功能,而lambda条件构造器做的和QueryWrapper的事也是相同的为什么要冗余的存在lambda条件构造器呢?
答:QueryWrapper是通过自己写表中相应的属性进行构造where条件的,容易发生拼写错误,在编译时不会报错,只有运行时才会报错,而lambda条件构造器是通过调用实体类中的方法,如果方法名称写错,直接进行报错,所以lambda的纠错功能比QueryWrapper要提前很多。
举个例子来说明这个问题吧!
查找姓名中包含“雨”字的员工信息。
使用QueryWrapper的方式如下:
queryWrapper.like("name","雨");
使用lambda的方式如下:
lambdaQueryWrapper.like(User::getName,"雨");
如果在拼写name的时候不小心,写成了naem,程序并不会报错,但是如果把方法名写成了getNaem程序立即报错。
七、第四种lambda构造器
细心的人都会发现无论是之前的lambda构造器还是queryWrapper,每次编写完条件构造语句后都要将对象传递给mapper 的selectList方法,比较麻烦,MyBatisPlus提供了第四种函数式编程方式,不用每次都传。
1.查询名字中包含“雨”字的,并且年龄大于20的员工信息
@Test
public void lambdaSelect(){
List<User> userList = new LambdaQueryChainWrapper<>(userMapper).like(User::getName, "雨").ge(User::getAge, 20).list();
//直接用userList调用forEach()即可
userList.forEach(System.out::println);
}
八、自定义SQL
(解释:除了mybatisPlus自带的一些增删改查,条件查询方法之外,我们还可以自定义我们需要的sql)
1.在resources资源文件夹下新建mapper文件夹,并将mapper文件夹的路径配置到配置文件中
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: mapper/*.xml
2.在mapper 文件夹中新建UserMapper.xml。
3.像mybatis那样在UseMapper接口中写接口,在UserMapper接口中写SQL即可。
UserMapper.java
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
/**
* 查询所有用户信息
* @return list
*/
List<User> selectAll();
}
UserMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="org.ywb.demo.dao.UserMapper">
<select id="selectAll" resultType="org.ywb.demo.pojo.User">
select * from user
select>
mapper>
九、分页查询
MyBatis分页提供的是逻辑分页,每次将所有数据查询出来,存储到内存中,然后根据页容量,逐页返回。如果表很大,无疑是一种灾难!
MyBatisPlus物理分页插件
1.新建config类,在config类中创建PaginationInterceptor对象
@Configuration
public class MybatisPlusConfig {
@Bean
public PaginationInterceptor paginationInterceptor(){
return new PaginationInterceptor();
}
}
2.测试:查询年龄大于20 的用户信息,并以每页容量为两条分页的形式返回。
@Test
public void selectPage(){
//构建查询条件对象
QueryWrapper<User> queryWrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
//ge()是“大于”的意思
queryWrapper.ge("age",20);
//设置当前页和页容量
Page<User> page = new Page<>(1, 2);
//下面的selectPage()是userMapper从BaseMapper中继承过来的方法
IPage<User> userIPage = userMapper.selectPage(page, queryWrapper);
System.out.println("总页数:"+userIPage.getPages());
System.out.println("总记录数:"+userIPage.getTotal());
userIPage.getRecords().forEach(System.out::println);
}
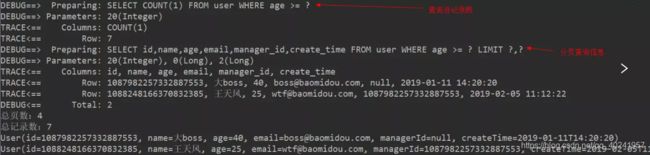
扩展知识:分页查询的时候:不查询总记录数,分页查询Page类的构造参数提供了参数的重载,第三个参数为false时,不会查询总记录数。
public Page(long current, long size, boolean isSearchCount) {
this(current, size, 0, isSearchCount);
}
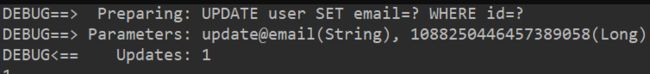
十、更新数据
1. 通过userMapper提供的方法更新用户信息
@Test
public void updateTest1(){
User user = new User();
user.setId(1088250446457389058L);
user.setEmail("update@email");
int rows = userMapper.updateById(user); //根据id进行更新,没有传值的属性就不会更新
System.out.println(rows);
}
2.使用UpdateWrapper更新数据(相当于使用联合主键)
@Test
public void testEntityWrapperUpdate(){
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setLastName("苍老师");
employee.setEmail("[email protected]");
employee.setGender(0);
emplopyeeDao.update(employee, //下面有代码讲解
new EntityWrapper<Employee>()
.eq("last_name","tom")
.eq("age",25)
);
}
讲解:该案例表示把last_name为tom,age为25的所有用户的信息更新为employee对象中设置的信息。
3.当我们更新少量用户信息的时候,可以不用创建对象,直接通过调用set方法更新属性即可。
@Test
public void updateTest3(){
//下面会有代码讲解
UpdateWrapper<User> updateWrapper = new UpdateWrapper<>();
updateWrapper.eq("name","李艺伟").eq("age",26).set("email","[email protected]");
//下面的null,其实没有什么实际意义
userMapper.update(null,updateWrapper);
}
讲解: 上面代码的作用:把数据库中name字段等于李艺伟且age字段等于26的记录里面的email字段更新成[email protected],可以结合下面的sql日志来理解
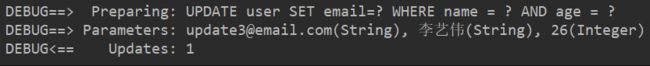
4.使用lambda更新数据
(说明:跟上面的第3点原理一样)
@Test
public void updateByLambda(){
LambdaUpdateWrapper<User> lambdaUpdateWrapper = Wrappers.lambdaUpdate();
lambdaUpdateWrapper.eq(User::getName,"李艺伟").eq(User::getAge,26).set(User::getAge,27);
//下面的null,其实没有什么实际意义
userMapper.update(null,lambdaUpdateWrapper);
}
十一、删除
(1)、根据id删除:
emplopyeeDao.deleteById(1);
(2)、根据条件删除:
Map<String,Object> columnMap = new HashMap<>();
columnMap.put("gender",0);
columnMap.put("age",18);
//将条件封装在columnMap中,然后调用deleteByMap方法,传入columnMap即可,返回值是Integer类型,表示影响的行数。
emplopyeeDao.deleteByMap(columnMap);
(3)、根据id批量删除:
List<Integer> idList = new ArrayList<>();
idList.add(1);
idList.add(2);
//把需要删除的记录的id装进idList,然后调用deleteBatchIds,传入idList即可。
emplopyeeDao.deleteBatchIds(idList);
十二、AR模式(Active Record)
直接通过实体类完成对数据的增删改查。(说明:之前上面讲的十一个内容,都是不需要让实体类继承Model类 的,因为我们上面讲的十一个内容都是让Mapper来对数据进行增删改查(当然了,Mapper需要继承BaseMapper类),而不是直接让实体类进行数据增删改查)
1.实体类继承Model类
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = false)
public class User extends Model<User> {
private Long id;
@TableField(condition = SqlCondition.LIKE)
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String email;
private Long managerId;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
}
Model类中封装了很多增删改查方法,不用使用UserMapper即可完成对数据的增删改查。
示例:查询所有用户信息
@Test
public void test(){
User user = new User();
user.selectAll().forEach(System.out::println);
}
十三、主键策略
MyBatisPlus的主键策略封装在IdType枚举类中。
@Getter
public enum IdType {
/**
* 数据库ID自增
*/
AUTO(0),
/**
* 该类型为未设置主键类型(将跟随全局)
*/
NONE(1),
/**
* 用户输入ID
* 该类型可以通过自己注册自动填充插件进行填充
*/
INPUT(2),
/* 以下3种类型、只有当插入对象ID 为空,才自动填充。 */
/**
* 全局唯一ID (idWorker)
*/
ID_WORKER(3),
/**
* 全局唯一ID (UUID)
*/
UUID(4),
/**
* 字符串全局唯一ID (idWorker 的字符串表示)
*/
ID_WORKER_STR(5);
private final int key;
IdType(int key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
在实体类中对应数据库中的主键id属性上标注注解TableId(type='xxx')即可完成主键配置。例如下面,@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)表示主键自增
@TableId(type = IdType.AUTO)
private Long id;
这种配置方式的主键策略只能在该表中生效(说明:上面的就是局部配置,而下面的就是全局配置),但是其他表还需要进行配置,为了避免冗余,麻烦,MybatisPlus提供了全局配置,在配置文件中配置主键策略即可实现。
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: mapper/*.xml
global-config:
db-config:
id-type: auto
如果全局策略和局部策略全都设置,局部策略优先。
十四、基本配置
mybatis-plus:
mapper-locations: mapper/*.xml
global-config:
db-config:
# 主键策略
id-type: auto
# 表名前缀
table-prefix: t
# 表名是否使用下划线间隔,默认:是
table-underline: true
# 添加mybatis配置文件路径
config-location: mybatis-config.xml
# 配置实体类包地址
type-aliases-package: org.ywb.demo.pojo
# 驼峰转下划线
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
本文转载参考自;https://www.jianshu.com/p/12ec123d20e8