Java-IO流(常用类)
Java-IO流
文章目录
- Java-IO流
-
- 1.文件
-
- 1.1什么是文件
- 1.2文件流
- 1.3常用的文件操作
- 2. IO 流原理及流的分类
-
- 2.1Java IO 流原理
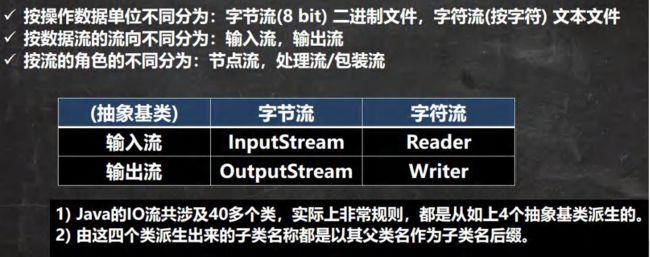
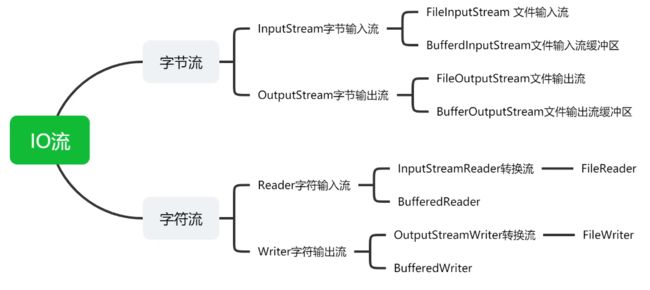
- 2.2流的分类
- 2.3字节流
- 2.3.1OutputStream
- 2.3.2InputStream
- 2.4字符流
-
- 2.4.1字符输出流Writer
- 2.4.2字符输入流Reader
- 2.4.3字节流与字符流的区别
- 2.5打印流
-
- 2.5.1printStream类的常用方法
1.文件
1.1什么是文件
文件其实就是保存数据的地方,比如常用的world文档,txt文件,excel文件都是文件。
1.2文件流
1.3常用的文件操作
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("d:\\hello.txt");
try{
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("success!");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
File类的对象实例化完成之后,就可以使用createNewFile()创建一个文件了,但是次方法使用了throws关键字声明,所以得进行异常处理。
继续修改程序!
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String PAHT = "d:" + File.separator + "hello1000.txt";
File file = new File(PAHT);
try{
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("success!");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
可以使用File.separator拼凑出\\
删除一个指定的文件
可以使用delete()方法
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String PAHT = "d:" + File.separator + "hello1000.txt";
File file = new File(PAHT);
try{
file.delete();
System.out.println("success!");
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
删除文件的前提是保证文件存在,所以上面最好先判断文件是否存在,可以使用File类提供的exists()方法
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String PAHT = "d:" + File.separator + "hello1000.txt";
File file = new File(PAHT);
if(file.exists()){
file.delete();
}
}
}
同样File可以创建文件也可以创建一个文件夹,可以使用mkdir()方法创建一个文件夹,另外还有些方法不一一列出,读者自己尝试。
2. IO 流原理及流的分类
2.1Java IO 流原理
输入input:读取外部数据(磁盘、光盘灯存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)中。
输出output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘灯存储设备中。
2.2流的分类
2.3字节流
字节流只要操作byte类型数据,以byte数组为例,主要操作类是OutputStream类和InputStream类。
2.3.1OutputStream
| 序号 | 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | close() | 关闭输出流 |
| 2 | flush() | 刷新缓冲区 |
| 3 | write(byte []) | 将一个byte数组写入数据流 |
| 4 | write(byte []int off.int len) | 将一个指定范围的byte数据写入数据流 |
| 5 | write(int b) | 将一个字节数据写入数据流 |
向文件写入字符串
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest.txt");
//第二步通过子类实例化对象
OutputStream out=null;
out = new FileOutputStream(f);
//第三步,进行写的操作
String str = "hellojava";
byte b[] = str.getBytes();
out.write(b);
//关闭输出流
out.close();
}
}
文件不存在则会自动拆功能键,在操作之前文件本身是不存在的,但是操作之后程序会为用户自动拆功能键新的文件,将内容写入到文件中去。
同样也可以循环写入,两者并没有什么不同之处,都可以使用。
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest.txt");
//第二步通过子类实例化对象
OutputStream out=null;
out = new FileOutputStream(f);
//第三步,进行写的操作
String str = "hellojava111";
byte b[] = str.getBytes();
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
out.write(b[i]);
}
//关闭输出流
out.close();
}
}
追加新内容
只需要将上面程序修改这一行即可
out = new FileOutputStream(f,true);
可以发现,每次执行后,都会向文件末尾追加内容。
2.3.2InputStream
既然程序可以向文件写入内容,也可以通过Inputstream从文件把内容读取出来。
Inputstream类常用的方法
| 序号 | 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | available() | 可以取得输入文件的大小 |
| 2 | close() | 关闭输入流 |
| 3 | read() | 读取内容,以数字的方式读取 |
| 4 | read(byte[] b) | 将内容读取到byte数组中,同时返回读入的个数 |
从文件中读取内容
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest.txt");
//通过子类实例化父类对象
InputStream input=null;
input = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
input.read(b);
input.close();
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
}
 内容已经被读取出来, 但是发现后面有很多空格,因为是开辟了byte数组大小为1024的空间,而实际内容没有那么多。其他的空间就浪费了。
内容已经被读取出来, 但是发现后面有很多空格,因为是开辟了byte数组大小为1024的空间,而实际内容没有那么多。其他的空间就浪费了。
调整程序
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest.txt");
//通过子类实例化父类对象
InputStream input=null;
input = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[1024];
int len = input.read(b);
input.close();
System.out.println(len);
System.out.println(new String(b,0,len));
}
}
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest.txt");
InputStream input=null;
input = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[(int)f.length()];
input.read(b);
input.close();
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
}
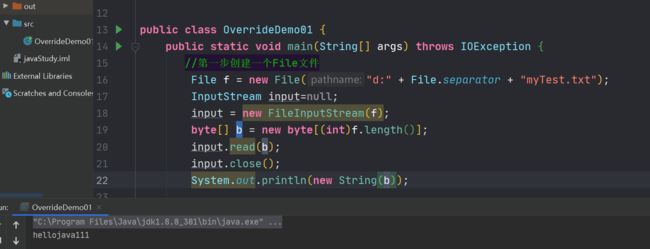
使用read()通过循环读取
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest.txt");
InputStream input=null;
input = new FileInputStream(f);
byte[] b = new byte[(int)f.length()];
for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) {
b[i] = (byte) input.read();
}
input.close();
System.out.println(new String(b));
}
}
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest.txt");
InputStream input=null;
input = new FileInputStream(f);
int len = 0;
byte b[] = new byte[1024];
int temp=0;
while((temp=input.read())!=-1){
b[len]=(byte)temp;
len++;
}
input.close();
System.out.println(new String(b,0,len));
}
}
文件读到末尾了,则返回的内容为-1
以上程序代码中要判断temp接受到的内容是否为-1,正常情况下是不会返回-1的。只要当输入流的内容读到底,才会返回这个数字
2.4字符流
2.4.1字符输出流Writer
Writer常用方法
| 序号 | 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | close() | 关闭输出流 |
| 2 | writer(String str) | 将字符串输出 |
| 3 | writer(char[] cbuf) | 将字符数组输出 |
| 4 | flush() | 强制性清空缓存 |
向文件中写入数据
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest1.txt");
Writer out=null;
out = new FileWriter(f);
String str = "hello world!";
out.write(str);
out.close();
}
}
向文件追加内容
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest1.txt");
Writer out=null;
out = new FileWriter(f,true);
String str = "hello world!";
out.write(str);
out.close();
}
}
2.4.2字符输入流Reader
Reader是使用字符的方式从文件中读取数据
Reader类常用的方法
| 序号 | 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | close() | 关闭输出流 |
| 2 | read() | 读取单个字符 |
| 3 | read(char[] cbuf) | 将内容读到字符数组中,返回读取的长度 |
从文件中读取内容
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest1.txt");
Reader reader=null;
reader = new FileReader(f);
char[] c = new char[1024];
int len = reader.read(c);
reader.close();
System.out.println(new String(c,0,len));
}
}
如果此时不知道数据的长度,可以像操作字节流那样,使用循环的方式进行内容的读取。
使用循环的方式读取内容
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//第一步创建一个File文件
File f = new File("d:" + File.separator + "myTest1.txt");
Reader reader=null;
reader = new FileReader(f);
char[] c = new char[1024];
int temp=0;
int len = 0;
while((temp=reader.read())!=-1){
c[len]=(char) temp;
len++;
}
reader.close();
System.out.println(new String(c,0,len));
}
}
2.4.3字节流与字符流的区别
字节流与字符流的使用非常相似,两者除了操作代码上有不同之外,两者有什么不同吗?
实际上字节流在操作时本身不会用到缓冲区(内存),是文件本身的操作,而字符流在操作时也使用了缓冲区,通过缓冲区在操作文件。
总结:字符流使用了缓冲区,而字节流没有使用缓冲区。
缓冲区可以简单理解成一段内存区域
2.5打印流
在整个Iowa包中,打印流是输出信息最方便的累。主要包含字节打印流和字符打印流,打印流提供了非常方便的打印功能。
2.5.1printStream类的常用方法
| 序号 | 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | printStream(File file) | 通过应该File对象实例化PrintStream类 |
| 2 | printStream(OutprintStream out) | 接收OutputStream对象,实例化PrintStream |
| 3 | printStream print(Locale,1,String frmat,Object…args) | 根据指定的Locale进行格式化输出 |
| 4 | printStream print(String format,Object…argc) | 根据本地环境格式化输出 |
| 5 | print(boolean b) | 此方法被重载很多次,输出任意数据 |
| 6 | println(boolean b) | 此方法被重载很多次,输出任意数据后换行 |
使用PrintStream输出
public class OverrideDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
PrintStream ps =null;
ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("d:\\mytest110.txt")));
ps.print("hello");
ps.print("1+1="+2);
ps.close();
}
}