- PyTorch & TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)
阿牛的药铺
算法移植部署pytorchtensorflowfpga开发
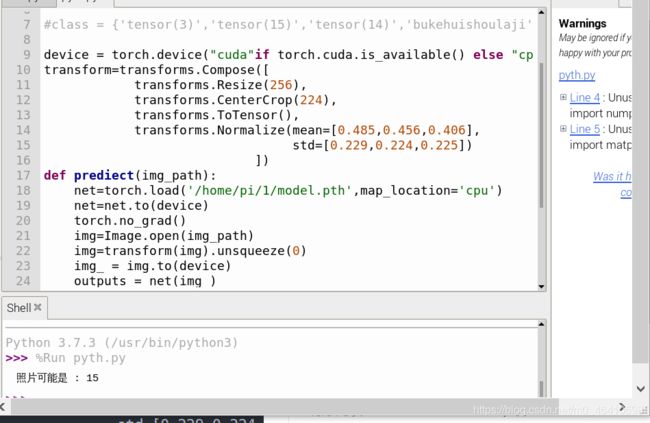
PyTorch&TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)引言:为什么算法移植工程师必须掌握框架基础?针对光学类产品算法FPGA移植岗位需求(如可见光/红外图像处理),深度学习框架是算法落地的"桥梁"——既要用PyTorch/TensorFlow验证算法可行性,又要将训练好的模型(如CNN、目标检测)转换为FPGA可部署的格式(ONNX、TFLite)。本文采用"
- 树莓派 5 - Raspberry Pi OS 新版本 Bookworm(书虫)
kuan_li_lyg
树莓派&Jetson教程机器人stm32嵌入式硬件自动驾驶ROS树莓派raspberrypi
文章目录在这里插入图片描述版本说明前言二、PipeWire三、Networking四、Firefox五、Documentation六、What’smissing? 新版本下载地址为:https://www.raspberrypi.com/software/operating-systems/版本说明 2023-10-10:基于Debianbookworm版本支持树莓派5在RaspberryPi4和
- vllm本地部署bge-reranker-v2-m3模型API服务实战教程
雷 电法王
大模型部署linuxpythonvscodelanguagemodel
文章目录一、说明二、配置环境2.1安装虚拟环境2.2安装vllm2.3对应版本的pytorch安装2.4安装flash_attn2.5下载模型三、运行代码3.1启动服务3.2调用代码验证一、说明本文主要介绍vllm本地部署BAAI/bge-reranker-v2-m3模型API服务实战教程本文是在Ubuntu24.04+CUDA12.8+Python3.12环境下复现成功的二、配置环境2.1安装虚
- 树莓派 —— 在树莓派4b板卡下编译FFmpeg源码,支持硬件编解码器(mmal或openMax硬编解码加速)
信必诺
FFmpeg树莓派FFmpeg编译源码mmalopenMax树莓派树莓派4b
FFmpeg相关音视频技术、疑难杂症文章合集(掌握后可自封大侠⓿_⓿)(记得收藏,持续更新中…) 正文 1、准备工作 (1)树莓派烧录RaspberryPi系统 (2)树莓派配置固定IP(文末) (3)xshell连接树莓派 (4)
- pycharm无法识别conda环境(已解决)
Reborker
pycharmcondaide
文章目录前言研究过程解决办法前言好久不用pycharm了,打开后提示更新,更新到了2023.1版本。安装conda后在新建了一个虚拟环境pytorch,但是无论是基础环境还是虚拟环境,pycharm都识别不出conda里的python.exe(如图)。如果不想看啰嗦直接看后面的解决办法,比较闲的话可以看看我的研究过程。研究过程看了很多博客,尝试了以下解决办法:加载conda.bat文件,虽然出现了
- jetson agx orin 刷机、cuda、pytorch配置指南【亲测有效】
jetsonagxorin刷机指南注意事项刷机具体指南cuda环境配置指南Anconda、Pytorch配置注意事项1.使用设备自带usbtoc的传输线时,注意c口插到orin左侧的口,右侧的口不支持数据传输;2.刷机时需准备ubuntu系统,可以是虚拟机,注意安装SDKManager刷机时,JetPack版本要选对,JetPack6.0的对应ubuntu22,cuda12版本,对应pytorch
- Yolov5-obb(旋转目标poly_nms_cuda.cu编译bug记录及解决方案)
关于在执行pythonsetup.pydevelop#or"pipinstall-v-e."时poly_nms_cuda.cu报错问题。前面步骤严格按照install.md环境1.pytorch版本较低时(我的是1.10):poly_nms_cuda.cu文件添加”#defineeps1e-8“,删除“constdoubleeps=1E-8;”这句2.pytorch版本较高时(我用的是1.27)h
- 深度学习实战-使用TensorFlow与Keras构建智能模型
程序员Gloria
Python超入门TensorFlowpython
深度学习实战-使用TensorFlow与Keras构建智能模型深度学习已经成为现代人工智能的重要组成部分,而Python则是实现深度学习的主要编程语言之一。本文将探讨如何使用TensorFlow和Keras构建深度学习模型,包括必要的代码实例和详细的解析。1.深度学习简介深度学习是机器学习的一个分支,使用多层神经网络来学习和表示数据中的复杂模式。其广泛应用于图像识别、自然语言处理、推荐系统等领域。
- 【深度学习实战】当前三个最佳图像分类模型的代码详解
云博士的AI课堂
大模型技术开发与实践哈佛博后带你玩转机器学习深度学习深度学习人工智能分类模型机器学习TransformerEfficientNetConvNeXt
下面给出三个在当前图像分类任务中精度表现突出的模型示例,分别基于SwinTransformer、EfficientNet与ConvNeXt。每个模型均包含:训练代码(使用PyTorch)从预训练权重开始微调(也可注释掉预训练选项,从头训练)数据集目录结构:└──dataset_root├──buy#第一类图像└──nobuy#第二类图像随机拆分:80%训练,20%验证每个Epoch输出一次loss
- python通过pyautogui库来控制鼠标和键盘
目录前言1.关于屏幕和鼠标位置2.鼠标移动、拖拽、点击、滚动和运动3.使用键盘4.消息框5.屏幕截图6.图像识别定位前言PyAutoGUI是一个纯Python的GUI自动化工具,通过它可以用程序自动控制鼠标和键盘操作。它支持Windows,MacOS和Linux。安装:pipinstallpyautogui基本用法看代码,非常简单易用。importpyautoguipyautogui.click(
- ARMv7单核CPU上SWI(软件中断)验证
liuluyang530
FPGA验证软件中断armcpu异常处理
在ARMv7单核CPU上验证SWI(软件中断)功能需结合硬件初始化、异常向量表配置、处理函数实现及调试手段,以下是详细验证方案:一、验证环境搭建1.硬件准备开发板:搭载ARMv7单核CPU(如Cortex-A7/A8/A9)的嵌入式板(如树莓派、BeagleBone或自定义板)。调试工具:JTAG/SWD调试器(如J-Link、ST-Link)用于单步调试和寄存器查看。串口工具(如UART转USB
- Text2Reward学习笔记
1.提示词请问,“glew”是一个RL工程师常用的工具库吗?请问,thiscodebase主要是做什么用的呀?1.1解释代码是否可以请您根据thiscodebase的主要功能,参考PyTorch的文档格式和文档风格,使用Markdown格式为选中的代码行编写一段相应的文档说明呢?2.项目环境配置2.1新建环境[official]2.1.1Featurizecondacreate-p~/work/d
- Embabel:下一代企业级JVM AI智能体框架的革命引言:AI时代的Java生态新机遇
DZSpace
软件开发jvm人工智能java
在生成式AI(如ChatGPT、Claude、Gemini)席卷全球的背景下,Python凭借其丰富的AI工具链(如PyTorch、LangChain)成为主流开发语言。然而,在企业级软件开发领域,Java和JVM生态(如Kotlin、Scala)长期以来占据主导地位,尤其是在金融、电信、电商等对稳定性、可扩展性、事务管理要求极高的场景。RodJohnson(Spring框架创始人)敏锐地发现了这
- 【Note】Linux Kernel 主题学习之“完整的嵌入式 Linux 环境、构建工具、编译工具链、CPU 架构”
CodeWithMe
读书笔记linuxlinux学习架构
LinuxKernel主题学习之“完整的嵌入式Linux环境、构建工具、编译工具链、CPU架构”一、完整的嵌入式Linux环境一个嵌入式Linux系统通常包括以下关键组件(以Jetson、树莓派等ARM版SBC为例):交叉编译工具链(crosstoolchain):生成目标CPU可执行代码,如aarch64-linux-gnu-gcc+glibc/musl/uClibc。Bootloader:如U
- 【第三章:神经网络原理详解与Pytorch入门】02.深度学习框架PyTorch入门-(4)Pytorch实战
IT古董
人工智能课程深度学习神经网络pytorch
第三章:神经网络原理详解与Pytorch入门第二部分:深度学习框架PyTorch入门第四节:Pytorch模型构建内容:如何搭建复杂网络以及如何修改模型与保存一、构建复杂神经网络结构在PyTorch中,构建复杂模型通常通过继承nn.Module类,分模块组织层与前向传播逻辑。示例:自定义一个卷积神经网络(CNN)importtorch.nnasnnimporttorch.nn.functional
- jetson orin nano安装GPU版本的pytorch过程
小鲈鱼-
pytorch人工智能python
一、安装jetpack组件和安装CUDA/cuDNN可以参考下面这个博客「解析」JetsonOrinNX安装CUDA/cuDNN_jetsoncuda-CSDN博客二、安装Pytorch和torchaudio可以直接看官方给的步骤https://pytorch.org/audio/main/build.jetson.html
- lstm 输入数据维度_[mcj]pytorch中LSTM的输入输出解释||LSTM输入输出详解
萬重
lstm输入数据维度
最近想了解一些关于LSTM的相关知识,在进行代码测试的时候,有个地方一直比较疑惑,关于LSTM的输入和输出问题。一直不清楚在pytorch里面该如何定义LSTM的输入和输出。首先看个pytorch官方的例子:#首先导入LSTM需要的相关模块importtorchimporttorch.nnasnn#神经网络模块#数据向量维数10,隐藏元维度20,2个LSTM层串联(如果是1,可以省略,默认为1)r
- pytorch 自动微分
this_show_time
pytorch人工智能python机器学习
自动微分1.基础概念1.1.**张量**1.2.**计算图**:1.3.**反向传播**1.4.**梯度**2.计算梯度2.1标量梯度计算2.2向量梯度计算2.3多标量梯度计算2.4多向量梯度计算3.梯度上下文控制3.1控制梯度计算(withtorch.no_grad())3.2累计梯度3.3梯度清零(torch.zero_())自动微分模块torch.autograd负责自动计算张量操作的梯度,
- PyTorch 在 Python 自然语言处理中的运用
Python编程之道
Python编程之道pythonpytorch自然语言处理ai
PyTorch在Python自然语言处理中的运用关键词:PyTorch,Python,自然语言处理,深度学习,文本分类,情感分析摘要:本文全面探讨了PyTorch在Python自然语言处理(NLP)领域的运用。首先介绍了相关背景知识,包括目的范围、预期读者等内容。接着详细阐述了核心概念,如词嵌入、循环神经网络等,并给出了相应的原理示意图和流程图。深入讲解了核心算法原理,结合Python代码进行详细
- 神经网络初步学习3——数据与损失
X Y O
神经网络学习人工智能
一、传统机器学习与神经网络前言:该部分需要一定的机器学习与数学基础(很浅的基础),如果有不理解的地方可以自行查阅。(1)区别这里不妨以图像识别为例子:(1)在传统的机器学习视角中:我们需要人工手动去设置并提取我们的特征量,例如常见的SIFT、SURF和HOG等,随后需要我们选择合适的分类器(例如:SVM、KNN等分类器),接着把我们的参数训练出来。(2)而在神经网络的视角中:我们只需要把图片喂给它
- 【AI大模型】PyTorch Lightning 简化工具
我爱一条柴ya
学习AI记录人工智能pytorchpythonaiAI编程
PyTorchLightning是一个轻量级的PyTorch封装库,它通过抽象训练循环的工程细节,让研究人员可以专注于模型设计和实验。以下是PyTorchLightning的核心概念和实战指南。核心优势基础使用:三步搭建训练流程1.定义LightningModuleimporttorchimporttorch.nnasnnimportpytorch_lightningasplfromtorchme
- 开源人工神经网络库(OpenANN)
deepdata_cn
人工智能神经网络
OpenANN(OpenANN,OpenArtificialNeuralNetworkLibrary)是一个开源的人工神经网络库,基于C++编写,依赖Eigen3库进行高效的矩阵运算,使用CMake进行项目构建,支持多种神经网络架构,包括前馈神经网络、卷积神经网络和循环神经网络等,适用于图像识别、自然语言处理、时间序列预测等多种场景。提供数据预处理、模型保存和加载、超参数优化等功能。支持GPU加速
- 人工智能怎么入门?零基础入门指南:从小白到AI实战者的第一步
OpenCV图像识别
人工智能人工智能计算机视觉自然语言处理神经网络机器学习
人工智能(AI)是当今最具前景的科技领域之一。从聊天机器人到自动驾驶,从图像识别到语音翻译,AI正在以前所未有的速度改变世界。但对于初学者来说,一个最常见的问题是:“我没有基础,也不是学数学或计算机的,人工智能还能学吗?我该怎么入门?”答案是:可以学,而且你并不孤单。越来越多的人正在以“跨专业、转行、自学”的方式进入AI领域。关键是,你需要一个清晰的入门路径,理解应该先做什么、学什么、避开什么误区
- 【零基础学AI】第30讲:生成对抗网络(GAN)实战 - 手写数字生成
1989
0基础学AI人工智能生成对抗网络神经网络python机器学习近邻算法深度学习
本节课你将学到GAN的基本原理和工作机制使用PyTorch构建生成器和判别器DCGAN架构实现技巧训练GAN模型的实用技巧开始之前环境要求Python3.8+需要安装的包:pipinstalltorchtorchvisionmatplotlibnumpyGPU推荐(可大幅加速训练)前置知识第21讲TensorFlow基础第23讲神经网络原理基本PyTorch使用经验核心概念什么是GAN?GAN就像
- 深度神经网络课程设计:从理论到实践
Vita Libre
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:深度神经网络是深度学习预测的核心技术,本课程设计项目旨在教授学生如何构建和应用深度神经网络进行各种预测任务,包括图像识别和自然语言处理。学生将通过源代码示例学习从网络架构设计、数据预处理到模型训练与评估的完整流程,并掌握深度学习的基本概念、组件及技巧。1.深度神经网络定义和在深度学习预测中的角色深度神经网络(DeepNeuralNetworks,DNNs)是深
- huggingface 笔记: Trainer
UQI-LIUWJ
笔记人工智能
Trainer是一个为Transformers中PyTorch模型设计的完整训练与评估循环只需将模型、预处理器、数据集和训练参数传入Trainer,其余交给它处理,即可快速开始训练自动处理以下训练流程:根据batch计算loss使用backward()计算梯度根据梯度更新权重重复上述流程直到达到指定的epoch数1配置TrainingArguments使用TrainingArguments定义训练
- 【机器学习】解密计算机视觉:CNN、目标检测与图像识别核心技术(第25天)
吴师兄大模型
0基础实现机器学习入门到精通机器学习计算机视觉cnn人工智能目标检测图像识别pytorch
Langchain系列文章目录01-玩转LangChain:从模型调用到Prompt模板与输出解析的完整指南02-玩转LangChainMemory模块:四种记忆类型详解及应用场景全覆盖03-全面掌握LangChain:从核心链条构建到动态任务分配的实战指南04-玩转LangChain:从文档加载到高效问答系统构建的全程实战05-玩转LangChain:深度评估问答系统的三种高效方法(示例生成、手
- 【深度学习-Day 35】实战图像数据增强:用PyTorch和TensorFlow扩充你的数据集
吴师兄大模型
深度学习入门到精通深度学习pytorchtensorflow人工智能python大模型LLM
Langchain系列文章目录01-玩转LangChain:从模型调用到Prompt模板与输出解析的完整指南02-玩转LangChainMemory模块:四种记忆类型详解及应用场景全覆盖03-全面掌握LangChain:从核心链条构建到动态任务分配的实战指南04-玩转LangChain:从文档加载到高效问答系统构建的全程实战05-玩转LangChain:深度评估问答系统的三种高效方法(示例生成、手
- PyTorch+CNN进行猫狗识别项目
任务介绍数据结构为:big_data├──train│└──cat│└──XXX.jpg(每个文件夹含若干张图像)│└──dog│└──XXX.jpg(每个文件夹含若干张图像)├──val│└──cat│└──XXX.jpg(每个文件夹含若干张图像)│└──dog└─────└──XXX.jpg(每个文件夹含若干张图像)需要对train数据集进行训练,达到给定val数据集中的一张猫/狗的图片,识别
- 人体坐姿检测系统开发实战(YOLOv8+PyTorch+可视化)
Loving_enjoy
计算机学科论文创新点人工智能深度学习迁移学习经验分享
本文将手把手教你构建智能坐姿检测系统,结合目标检测与姿态估计技术,实现不良坐姿的实时识别与预警###一、项目背景与价值现代人每天平均坐姿时间超过8小时,不良坐姿会导致:-脊椎压力增加300%-颈椎病发病率提升45%-腰椎间盘突出风险增加60%本系统通过计算机视觉技术实时监测坐姿状态,对驼背、侧倾、前倾等不良姿势进行智能识别和预警。相较于传统传感器方案,我们的视觉方案具有非接触、低成本、易部署的优势
- 312个免费高速HTTP代理IP(能隐藏自己真实IP地址)
yangshangchuan
高速免费superwordHTTP代理
124.88.67.20:843
190.36.223.93:8080
117.147.221.38:8123
122.228.92.103:3128
183.247.211.159:8123
124.88.67.35:81
112.18.51.167:8123
218.28.96.39:3128
49.94.160.198:3128
183.20
- pull解析和json编码
百合不是茶
androidpull解析json
n.json文件:
[{name:java,lan:c++,age:17},{name:android,lan:java,age:8}]
pull.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<stu>
<name>java
- [能源与矿产]石油与地球生态系统
comsci
能源
按照苏联的科学界的说法,石油并非是远古的生物残骸的演变产物,而是一种可以由某些特殊地质结构和物理条件生产出来的东西,也就是说,石油是可以自增长的....
那么我们做一个猜想: 石油好像是地球的体液,我们地球具有自动产生石油的某种机制,只要我们不过量开采石油,并保护好
- 类与对象浅谈
沐刃青蛟
java基础
类,字面理解,便是同一种事物的总称,比如人类,是对世界上所有人的一个总称。而对象,便是类的具体化,实例化,是一个具体事物,比如张飞这个人,就是人类的一个对象。但要注意的是:张飞这个人是对象,而不是张飞,张飞只是他这个人的名字,是他的属性而已。而一个类中包含了属性和方法这两兄弟,他们分别用来描述对象的行为和性质(感觉应该是
- 新站开始被收录后,我们应该做什么?
IT独行者
PHPseo
新站开始被收录后,我们应该做什么?
百度终于开始收录自己的网站了,作为站长,你是不是觉得那一刻很有成就感呢,同时,你是不是又很茫然,不知道下一步该做什么了?至少我当初就是这样,在这里和大家一份分享一下新站收录后,我们要做哪些工作。
至于如何让百度快速收录自己的网站,可以参考我之前的帖子《新站让百
- oracle 连接碰到的问题
文强chu
oracle
Unable to find a java Virtual Machine--安装64位版Oracle11gR2后无法启动SQLDeveloper的解决方案
作者:草根IT网 来源:未知 人气:813标签:
导读:安装64位版Oracle11gR2后发现启动SQLDeveloper时弹出配置java.exe的路径,找到Oracle自带java.exe后产生的路径“C:\app\用户名\prod
- Swing中按ctrl键同时移动鼠标拖动组件(类中多借口共享同一数据)
小桔子
java继承swing接口监听
都知道java中类只能单继承,但可以实现多个接口,但我发现实现多个接口之后,多个接口却不能共享同一个数据,应用开发中想实现:当用户按着ctrl键时,可以用鼠标点击拖动组件,比如说文本框。
编写一个监听实现KeyListener,NouseListener,MouseMotionListener三个接口,重写方法。定义一个全局变量boolea
- linux常用的命令
aichenglong
linux常用命令
1 startx切换到图形化界面
2 man命令:查看帮助信息
man 需要查看的命令,man命令提供了大量的帮助信息,一般可以分成4个部分
name:对命令的简单说明
synopsis:命令的使用格式说明
description:命令的详细说明信息
options:命令的各项说明
3 date:显示时间
语法:date [OPTION]... [+FORMAT]
- eclipse内存优化
AILIKES
javaeclipsejvmjdk
一 基本说明 在JVM中,总体上分2块内存区,默认空余堆内存小于 40%时,JVM就会增大堆直到-Xmx的最大限制;空余堆内存大于70%时,JVM会减少堆直到-Xms的最小限制。 1)堆内存(Heap memory):堆是运行时数据区域,所有类实例和数组的内存均从此处分配,是Java代码可及的内存,是留给开发人
- 关键字的使用探讨
百合不是茶
关键字
//关键字的使用探讨/*访问关键词private 只能在本类中访问public 只能在本工程中访问protected 只能在包中和子类中访问默认的 只能在包中访问*//*final 类 方法 变量 final 类 不能被继承 final 方法 不能被子类覆盖,但可以继承 final 变量 只能有一次赋值,赋值后不能改变 final 不能用来修饰构造方法*///this()
- JS中定义对象的几种方式
bijian1013
js
1. 基于已有对象扩充其对象和方法(只适合于临时的生成一个对象):
<html>
<head>
<title>基于已有对象扩充其对象和方法(只适合于临时的生成一个对象)</title>
</head>
<script>
var obj = new Object();
- 表驱动法实例
bijian1013
java表驱动法TDD
获得月的天数是典型的直接访问驱动表方式的实例,下面我们来展示一下:
MonthDaysTest.java
package com.study.test;
import org.junit.Assert;
import org.junit.Test;
import com.study.MonthDays;
public class MonthDaysTest {
@T
- LInux启停重启常用服务器的脚本
bit1129
linux
启动,停止和重启常用服务器的Bash脚本,对于每个服务器,需要根据实际的安装路径做相应的修改
#! /bin/bash
Servers=(Apache2, Nginx, Resin, Tomcat, Couchbase, SVN, ActiveMQ, Mongo);
Ops=(Start, Stop, Restart);
currentDir=$(pwd);
echo
- 【HBase六】REST操作HBase
bit1129
hbase
HBase提供了REST风格的服务方便查看HBase集群的信息,以及执行增删改查操作
1. 启动和停止HBase REST 服务 1.1 启动REST服务
前台启动(默认端口号8080)
[hadoop@hadoop bin]$ ./hbase rest start
后台启动
hbase-daemon.sh start rest
启动时指定
- 大话zabbix 3.0设计假设
ronin47
What’s new in Zabbix 2.0?
去年开始使用Zabbix的时候,是1.8.X的版本,今年Zabbix已经跨入了2.0的时代。看了2.0的release notes,和performance相关的有下面几个:
:: Performance improvements::Trigger related da
- http错误码大全
byalias
http协议javaweb
响应码由三位十进制数字组成,它们出现在由HTTP服务器发送的响应的第一行。
响应码分五种类型,由它们的第一位数字表示:
1)1xx:信息,请求收到,继续处理
2)2xx:成功,行为被成功地接受、理解和采纳
3)3xx:重定向,为了完成请求,必须进一步执行的动作
4)4xx:客户端错误,请求包含语法错误或者请求无法实现
5)5xx:服务器错误,服务器不能实现一种明显无效的请求
- J2EE设计模式-Intercepting Filter
bylijinnan
java设计模式数据结构
Intercepting Filter类似于职责链模式
有两种实现
其中一种是Filter之间没有联系,全部Filter都存放在FilterChain中,由FilterChain来有序或无序地把把所有Filter调用一遍。没有用到链表这种数据结构。示例如下:
package com.ljn.filter.custom;
import java.util.ArrayList;
- 修改jboss端口
chicony
jboss
修改jboss端口
%JBOSS_HOME%\server\{服务实例名}\conf\bindingservice.beans\META-INF\bindings-jboss-beans.xml
中找到
<!-- The ports-default bindings are obtained by taking the base bindin
- c++ 用类模版实现数组类
CrazyMizzz
C++
最近c++学到数组类,写了代码将他实现,基本具有vector类的功能
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<cassert>
using namespace std;
template<class T>
class Array
{
public:
//构造函数
- hadoop dfs.datanode.du.reserved 预留空间配置方法
daizj
hadoop预留空间
对于datanode配置预留空间的方法 为:在hdfs-site.xml添加如下配置
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.du.reserved</name>
<value>10737418240</value>
- mysql远程访问的设置
dcj3sjt126com
mysql防火墙
第一步: 激活网络设置 你需要编辑mysql配置文件my.cnf. 通常状况,my.cnf放置于在以下目录: /etc/mysql/my.cnf (Debian linux) /etc/my.cnf (Red Hat Linux/Fedora Linux) /var/db/mysql/my.cnf (FreeBSD) 然后用vi编辑my.cnf,修改内容从以下行: [mysqld] 你所需要: 1
- ios 使用特定的popToViewController返回到相应的Controller
dcj3sjt126com
controller
1、取navigationCtroller中的Controllers
NSArray * ctrlArray = self.navigationController.viewControllers;
2、取出后,执行,
[self.navigationController popToViewController:[ctrlArray objectAtIndex:0] animated:YES
- Linux正则表达式和通配符的区别
eksliang
正则表达式通配符和正则表达式的区别通配符
转载请出自出处:http://eksliang.iteye.com/blog/1976579
首先得明白二者是截然不同的
通配符只能用在shell命令中,用来处理字符串的的匹配。
判断一个命令是否为bash shell(linux 默认的shell)的内置命令
type -t commad
返回结果含义
file 表示为外部命令
alias 表示该
- Ubuntu Mysql Install and CONF
gengzg
Install
http://www.navicat.com.cn/download/navicat-for-mysql
Step1: 下载Navicat ,网址:http://www.navicat.com/en/download/download.html
Step2:进入下载目录,解压压缩包:tar -zxvf navicat11_mysql_en.tar.gz
- 批处理,删除文件bat
huqiji
windowsdos
@echo off
::演示:删除指定路径下指定天数之前(以文件名中包含的日期字符串为准)的文件。
::如果演示结果无误,把del前面的echo去掉,即可实现真正删除。
::本例假设文件名中包含的日期字符串(比如:bak-2009-12-25.log)
rem 指定待删除文件的存放路径
set SrcDir=C:/Test/BatHome
rem 指定天数
set DaysAgo=1
- 跨浏览器兼容的HTML5视频音频播放器
天梯梦
html5
HTML5的video和audio标签是用来在网页中加入视频和音频的标签,在支持html5的浏览器中不需要预先加载Adobe Flash浏览器插件就能轻松快速的播放视频和音频文件。而html5media.js可以在不支持html5的浏览器上使video和audio标签生效。 How to enable <video> and <audio> tags in
- Bundle自定义数据传递
hm4123660
androidSerializable自定义数据传递BundleParcelable
我们都知道Bundle可能过put****()方法添加各种基本类型的数据,Intent也可以通过putExtras(Bundle)将数据添加进去,然后通过startActivity()跳到下一下Activity的时候就把数据也传到下一个Activity了。如传递一个字符串到下一个Activity
把数据放到Intent
- C#:异步编程和线程的使用(.NET 4.5 )
powertoolsteam
.net线程C#异步编程
异步编程和线程处理是并发或并行编程非常重要的功能特征。为了实现异步编程,可使用线程也可以不用。将异步与线程同时讲,将有助于我们更好的理解它们的特征。
本文中涉及关键知识点
1. 异步编程
2. 线程的使用
3. 基于任务的异步模式
4. 并行编程
5. 总结
异步编程
什么是异步操作?异步操作是指某些操作能够独立运行,不依赖主流程或主其他处理流程。通常情况下,C#程序
- spark 查看 job history 日志
Stark_Summer
日志sparkhistoryjob
SPARK_HOME/conf 下:
spark-defaults.conf 增加如下内容
spark.eventLog.enabled true spark.eventLog.dir hdfs://master:8020/var/log/spark spark.eventLog.compress true
spark-env.sh 增加如下内容
export SP
- SSH框架搭建
wangxiukai2015eye
springHibernatestruts
MyEclipse搭建SSH框架 Struts Spring Hibernate
1、new一个web project。
2、右键项目,为项目添加Struts支持。
选择Struts2 Core Libraries -<MyEclipes-Library>
点击Finish。src目录下多了struts