MySQL习题集强化练习(50题)
文章目录
- SQL习题集强化练习(50题)
- 1.0检索数据
-
- 1.1从 Customers 表中检索所有的 ID(1)
- 1.2检索并列出已订购产品的清单(2)
- 1.3检索所有列(3)
- 2.0排序检索数据
-
- 2.1检索顾客名称并且排序(4)
- 2.2对顾客D和日期排序(5)
- 2.3按照数量和价格排序(6)
- 2.4检查SQL语句(7)
- 3.0过滤数据
-
- 3.1返回固定价格的产品(8)
- 3.2返回更高价格的产品(9)
- 3.3返回产品并且按照价格排序(10)
- 3.4返回更多的产品(11)
- 4.0高级数据过滤
-
- 4.1检索供应商名称(12)
- 4.2检索并列出已订购产品的清单(13)
- 4.3返回所有价格在3美元到6美元之间的产品的名称和价格(14)
- 4.4纠错2(15)
- 5.0用通配符进行过滤
-
- 5.1检索产品名称和描述(一)(16)
- 5.2检索产品名称和描述(二)(17)
- 5.3检索产品名称和描述(三)(18)
- 5.4检索产品名称和描述(四)(19)
- 6.0创建计算字段
-
- 6.1别名(20)
- 6.2打折(21)
- 7.0使用函数处理数据
-
- 7.1顾客登录名(22)
- 7.2返回2020年1月的所有订单的订单号和订单日期(23)
- 8.0汇总数据
-
- 8.1确定已售出产品的总数(24)
- 8.2确定已售出产品项BR01的总数(25)
- 8.3确定Products表中价格不超过10美元的最贵产品的价格(26)
- 9.0分组数据
-
- 9.1返回每个订单号各有多少行数(27)
- 9.2每个供应商成本最低的产品(28)
- 9.3确定最佳顾客(29)
- 9.4确定最佳顾客的另一种方式(一)(30)
- 9.5纠错3(31)
- 10.0使用子查询
-
- 10.1返回购买价格为10美元或以上产品的顾客列表(32)
- 10.2确定哪些订单购买了prod id为BR01的产品(一)(33)
- 10.3返回购买prod id为BR01的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(一)(34)
- 10.4返回每个顾客不同订单的总金额(35)
- 10.5从Products表中检索所有的产品名称以及对应的销售总数(36)
- 11.0联结表
-
- 11.1返回顾客名称和相关订单号(37)
- 11.2返回顾客名称和相关订单号以及每个订单的总价(38)
- 11.3确定哪些订单购买了prod id为BR01的产品(二)(39)
- 11.4反回购买prod id为BR01的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(二)(40)
- 11.5确定最佳顾客的另一种方式(二)(41)
- 12.0创建高级链结
-
- 12.1检索每个顾客的名称和所有的订单号(一)(42)
- 12.2检索每个顾客的名称和所有的订单号(二)(43)
- 12.3返回产品名称和与之相关的订单号(44)
- 12.4返回产品名称和每一项产品的总订单数(45)
- 12.5列出供应商及其可供产品的数量(46)
- 13.0组合查询
-
- 13.1将两个SELECT语句结合起来(一)(47)
- 13.2将两个SELECT语句结合起来(二)(48)
- 13.3组合Products表中的产品名称和Customers表中的顾客名称(49)
- 13.4纠错4(50)
SQL习题集强化练习(50题)
本文题目来源于牛客网,如需在线练习:【点击访问】
SQL速查手册常用关键字函数说明:【点击访问】
SQL快速入门39题(含涉及知识点总结):【点击访问】
1.0检索数据
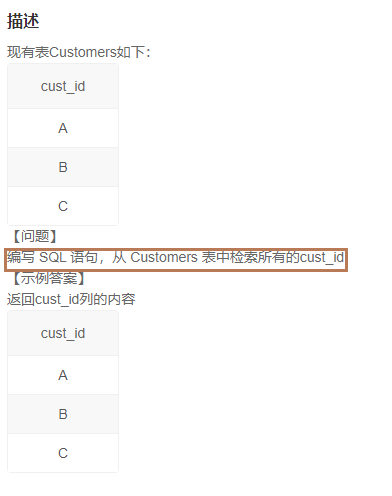
1.1从 Customers 表中检索所有的 ID(1)
1️⃣题解:
Select cust_id from Customers;
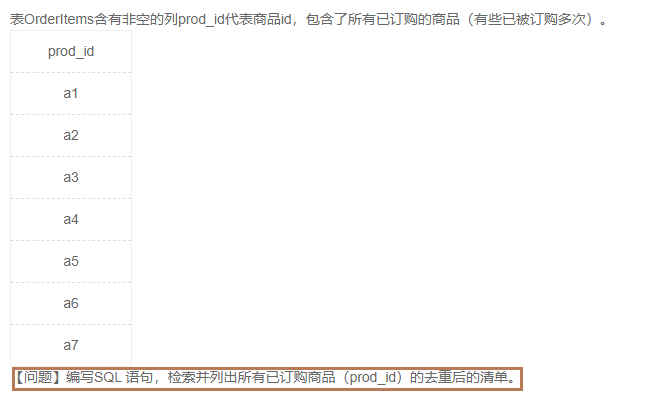
1.2检索并列出已订购产品的清单(2)
1️⃣题解:
select distinct prod_id
from OrderItems
where prod_id is not null
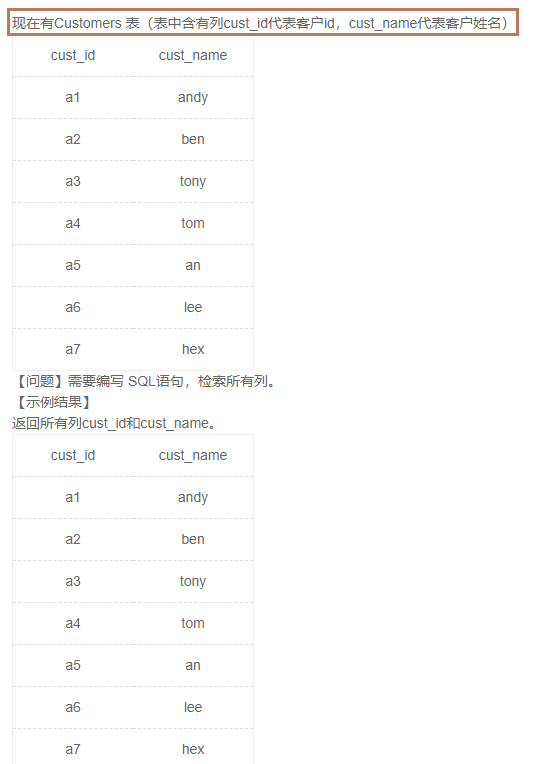
1.3检索所有列(3)
1️⃣题解:
select * from Customers
2.0排序检索数据
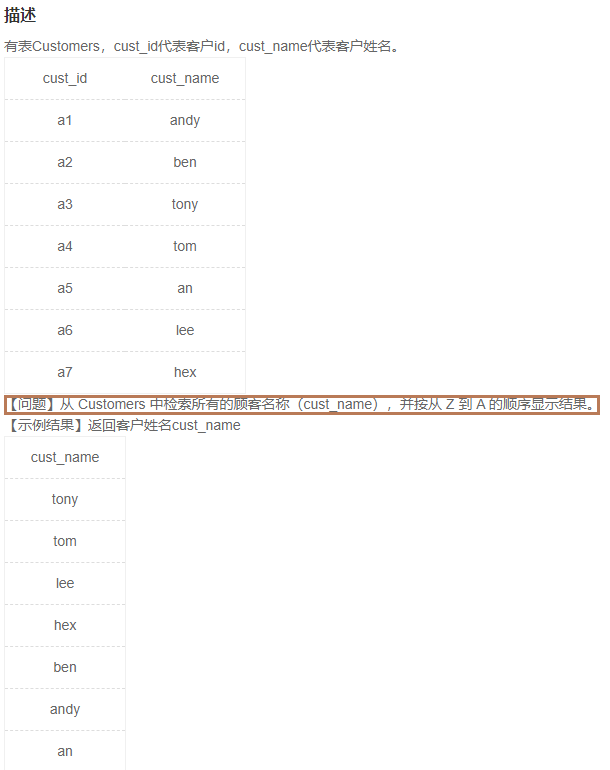
2.1检索顾客名称并且排序(4)
1️⃣题解:
select cust_name
from Customers
order by cust_name desc
2.2对顾客D和日期排序(5)
1️⃣题解:
select cust_id,order_num
from Orders
order by cust_id,order_date desc
2.3按照数量和价格排序(6)
1️⃣题解:
select *
FROM OrderItems
ORDER BY quantity DESC,item_price DESC
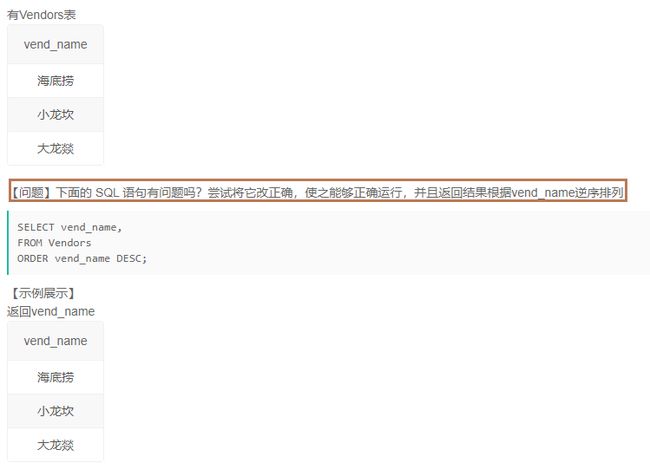
2.4检查SQL语句(7)
1️⃣题解:
select vend_name
from Vendors
order by vend_name Desc;
3.0过滤数据
3.1返回固定价格的产品(8)
1️⃣题解:
select prod_id,prod_name
from Products
where prod_price=9.49
3.2返回更高价格的产品(9)
1️⃣题解:
select prod_id,prod_name
from Products
where prod_price>=9
3.3返回产品并且按照价格排序(10)
1️⃣题解:
select prod_name,prod_price
from Products
where prod_price >=3 and prod_price<=6
order by prod_price
3.4返回更多的产品(11)
1️⃣题解:
select vend_name
FROM Vendors
Where vend_country='USA' AND vend_state='CA'
4.0高级数据过滤
4.1检索供应商名称(12)
1️⃣题解:
SELECT prod_name, prod_price
FROM Products
WHERE prod_price >= 3 AND prod_price <= 6
ORDER BY prod_price
4.2检索并列出已订购产品的清单(13)
1️⃣题解:
SELECT vend_name
FROM Vendors
WHERE vend_country = 'USA' AND vend_state = 'CA'
ORDER BY vend_name;
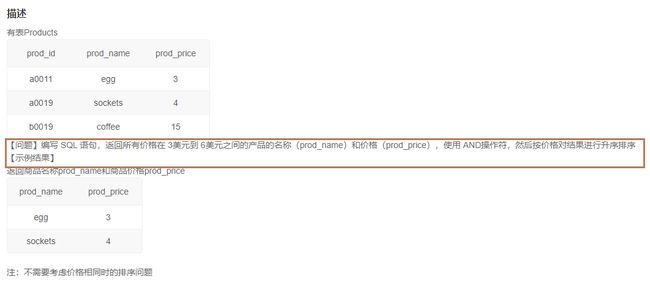
4.3返回所有价格在3美元到6美元之间的产品的名称和价格(14)
1️⃣题解:
SELECT prod_name, prod_price
FROM Products
WHERE prod_price >= 3 AND prod_price <= 6
ORDER BY prod_price
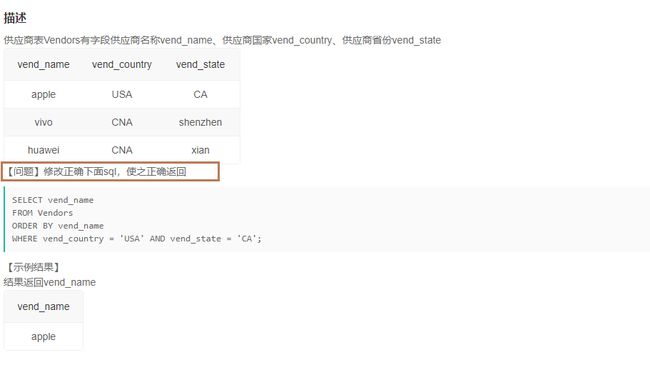
4.4纠错2(15)
1️⃣题解:
SELECT vend_name
FROM Vendors
WHERE vend_country = 'USA' AND vend_state = 'CA'
ORDER BY vend_name;
5.0用通配符进行过滤
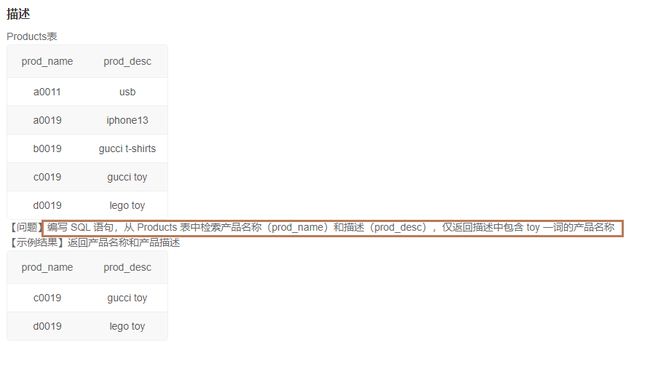
5.1检索产品名称和描述(一)(16)
1️⃣题解:
select prod_name,prod_desc
from Products
where prod_desc like '%toy'
5.2检索产品名称和描述(二)(17)
1️⃣题解:
SELECT prod_name,prod_desc
from Products
where prod_desc not like '%toy%'
5.3检索产品名称和描述(三)(18)
1️⃣题解:
select prod_name,prod_desc
from Products
where prod_desc like '%toy%' and prod_desc like "%carrots%"
5.4检索产品名称和描述(四)(19)
1️⃣题解:
select prod_name,prod_desc
from Products
where prod_desc like "%toy%carrots%"
6.0创建计算字段
6.1别名(20)
1️⃣题解:
select vend_id,
vend_name as vname,
vend_address as vaddress,
vend_city as vcity
From Vendors
order by vend_name
6.2打折(21)
1️⃣题解:
select prod_id,prod_price,prod_price*0.9 as sale_price
from Products
7.0使用函数处理数据
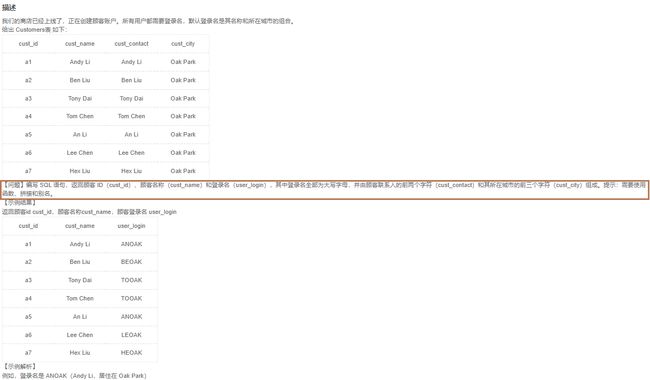
7.1顾客登录名(22)
1️⃣题解:
select cust_id,cust_name,upper(concat(left(cust_name,2),left(cust_city,3))) as user_login
from Customers
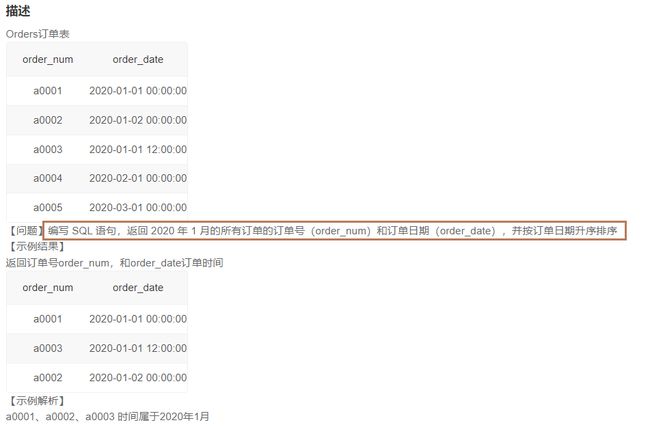
7.2返回2020年1月的所有订单的订单号和订单日期(23)
1️⃣题解:
select order_num,order_date
from Orders
where order_date like '2020-01%'
order by order_date
8.0汇总数据
8.1确定已售出产品的总数(24)
1️⃣题解:
select sum(quantity) as items_ordered
from OrderItems
8.2确定已售出产品项BR01的总数(25)
1️⃣题解:
select sum(quantity) as items_ordered
from OrderItems
where prod_id="BR01"
8.3确定Products表中价格不超过10美元的最贵产品的价格(26)
1️⃣题解:
select sum(quantity) as items_ordered
from OrderItems
where prod_id="BR01"
9.0分组数据
9.1返回每个订单号各有多少行数(27)
1️⃣题解:
select order_num,count(1) as order_lines
from OrderItems
group by order_num
order by order_lines
9.2每个供应商成本最低的产品(28)
1️⃣题解:
select vend_id,min(prod_price) as cheapest_item
from Products
Group by vend_id
Order by cheapest_item
9.3确定最佳顾客(29)
1️⃣题解:
select order_num
from OrderItems
group by order_num having sum(quantity)>=100
order by order_num
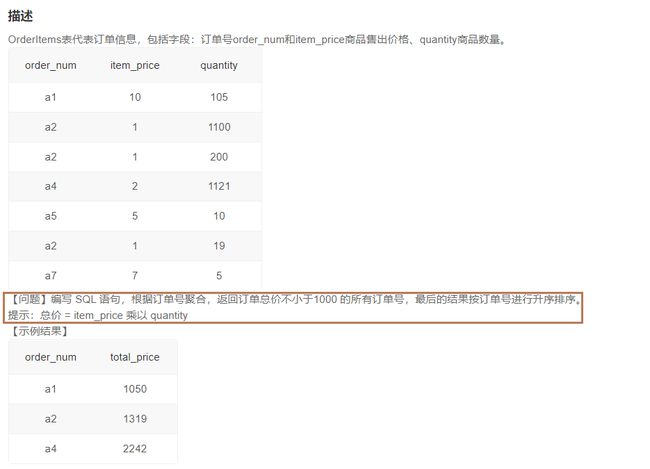
9.4确定最佳顾客的另一种方式(一)(30)
1️⃣题解:
select order_num,sum(item_price*quantity) total_price
from OrderItems
group by order_num
having total_price>=1000
order by order_num
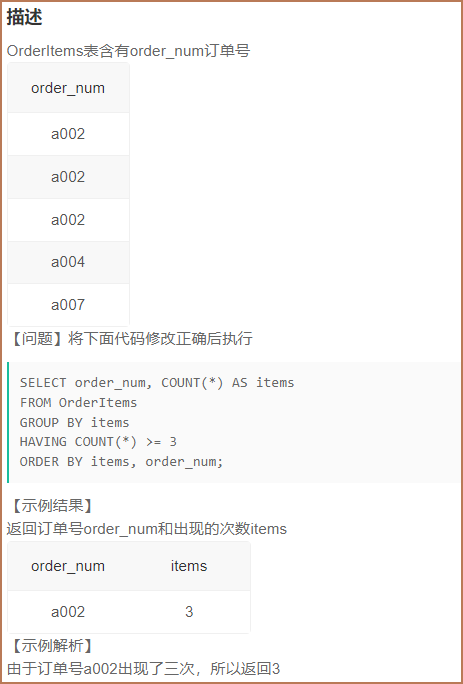
9.5纠错3(31)
1️⃣题解:
SELECT order_num, COUNT(order_num) AS items
FROM OrderItems
GROUP BY order_num
HAVING items >= 3
ORDER BY items, order_num;
10.0使用子查询
10.1返回购买价格为10美元或以上产品的顾客列表(32)
OrderItems表示订单商品表,含有字段订单号:order_num、订单价格:item_price;Orders表代表订单信息表,含有顾客id:cust_id和订单号:order_num
OrderItems表
| order_num | item_price |
|---|---|
| a1 | 10 |
| a2 | 1 |
| a2 | 1 |
| a4 | 2 |
| a5 | 5 |
| a2 | 1 |
| a7 | 7 |
Orders表
| order_num | cust_id |
|---|---|
| a1 | cust10 |
| a2 | cust1 |
| a2 | cust1 |
| a4 | cust2 |
| a5 | cust5 |
| a2 | cust1 |
| a7 | cust7 |
【问题】使用子查询,返回购买价格为 10 美元或以上产品的顾客列表,结果无需排序。
注意:你需要使用 OrderItems 表查找匹配的订单号(order_num),然后使用Order 表检索这些匹配订单的顾客 ID(cust_id)。
【示例结果】返回顾客id cust_id
| cust_id |
|---|
| cust10 |
【示例解析】
cust10顾客下单的订单为a1,a1的售出价格大于等于10
1️⃣题解:
select cust_id
from Orders
where order_num in(
select order_num cust_id
from OrderItems
where item_price>=10
)
10.2确定哪些订单购买了prod id为BR01的产品(一)(33)
表OrderItems代表订单商品信息表,prod_id为产品id;Orders表代表订单表有cust_id代表顾客id和订单日期order_date
OrderItems表
| prod_id | order_num |
|---|---|
| BR01 | a0001 |
| BR01 | a0002 |
| BR02 | a0003 |
| BR02 | a0013 |
Orders表
| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
|---|---|---|
| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
【问题】
编写 SQL 语句,使用子查询来确定哪些订单(在 OrderItems 中)购买了 prod_id 为 “BR01” 的产品,然后从 Orders 表中返回每个产品对应的顾客 ID(cust_id)和订单日期(order_date),按订购日期对结果进行升序排序。
【示例结果】返回顾客id cust_id和定单日期order_date。
| cust_id | order_date |
|---|---|
| cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
| cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
【示例解析】
产品id为"BR01"的订单a0001和a002的下单顾客cust10和cust1的下单时间分别为2022-01-01 00:00:00和2022-01-01 00:01:00
1️⃣题解:
select cust_id,order_date
from Orders
where order_num in(
select order_num
from OrderItems
where prod_id="BR01"
)
order by order_date
10.3返回购买prod id为BR01的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(一)(34)
你想知道订购 BR01 产品的日期,有表OrderItems代表订单商品信息表,prod_id为产品id;Orders表代表订单表有cust_id代表顾客id和订单日期order_date;Customers表含有cust_email 顾客邮件和cust_id顾客id
OrderItems表
| prod_id | order_num |
|---|---|
| BR01 | a0001 |
| BR01 | a0002 |
| BR02 | a0003 |
| BR02 | a0013 |
Orders表
| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
|---|---|---|
| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
Customers表代表顾客信息,cust_id为顾客id,cust_email为顾客email
| cust_id | cust_email |
|---|---|
| cust10 | [email protected] |
| cust1 | [email protected] |
| cust2 | [email protected] |
【问题】返回购买 prod_id 为BR01 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(Customers 表中的 cust_email),结果无需排序。
提示:这涉及 SELECT 语句,最内层的从 OrderItems 表返回 order_num,中间的从 Customers 表返回 cust_id。
【示例结果】
返回顾客email cust_email
| cust_email |
|---|
| [email protected] |
| [email protected] |
【示例解析】
产品id为BR01的订单a0001和a002的下单顾客cust10和cust1的顾客email cust_email分别是:[email protected] 、[email protected]
1️⃣题解:
select cust_email
from Customers
where cust_id in(
select cust_id
from Orders
where order_num in(
select order_num
from OrderItems
where prod_id='BR01'
)
)
10.4返回每个顾客不同订单的总金额(35)
我们需要一个顾客 ID 列表,其中包含他们已订购的总金额。
OrderItems表代表订单信息,OrderItems表有订单号:order_num和商品售出价格:item_price、商品数量:quantity。
| order_num | item_price | quantity |
|---|---|---|
| a0001 | 10 | 105 |
| a0002 | 1 | 1100 |
| a0002 | 1 | 200 |
| a0013 | 2 | 1121 |
| a0003 | 5 | 10 |
| a0003 | 1 | 19 |
| a0003 | 7 | 5 |
Orders表订单号:order_num、顾客id:cust_id
| order_num | cust_id |
|---|---|
| a0001 | cust10 |
| a0002 | cust1 |
| a0003 | cust1 |
| a0013 | cust2 |
【问题】
编写 SQL语句,返回顾客 ID(Orders 表中的 cust_id),并使用子查询返回total_ordered 以便返回每个顾客的订单总数,将结果按金额从大到小排序。
提示:你之前已经使用 SUM()计算订单总数。
【示例结果】返回顾客id cust_id和total_order下单总额
| cust_id | total_ordered |
|---|---|
| cust2 | 2242 |
| cust1 | 1300 |
| cust10 | 1050 |
| cust2 | 104 |
【示例解析】cust2在Orders里面的订单a0013,a0013的售出价格是2售出数量是1121,总额是2242,最后返回cust2的支付总额是2242。
1️⃣题解:
select cust_id,sum(item_price*quantity) as total_ordered
from OrderItems,Orders
where Orders.order_num=OrderItems.order_num
group by cust_id
order by total_ordered desc
10.5从Products表中检索所有的产品名称以及对应的销售总数(36)
Products 表中检索所有的产品名称:prod_name、产品id:prod_id
| prod_id | prod_name |
|---|---|
| a0001 | egg |
| a0002 | sockets |
| a0013 | coffee |
| a0003 | cola |
OrderItems代表订单商品表,订单产品:prod_id、售出数量:quantity
| prod_id | quantity |
|---|---|
| a0001 | 105 |
| a0002 | 1100 |
| a0002 | 200 |
| a0013 | 1121 |
| a0003 | 10 |
| a0003 | 19 |
| a0003 | 5 |
【问题】
编写 SQL 语句,从 Products 表中检索所有的产品名称(prod_name),以及名为 quant_sold 的计算列,其中包含所售产品的总数(在 OrderItems 表上使用子查询和 SUM(quantity)检索)。
【示例结果】返回产品名称prod_name和产品售出数量总和
| prod_name | quant_sold |
|---|---|
| egg | 105 |
| sockets | 1300 |
| coffee | 1121 |
| cola | 34 |
【示例解析】prod_name是cola的prod_id为a0003,quantity总量为34,返回结果无需排序。
1️⃣题解:
select a.prod_name,SUM(b.quantity)
from Products a,OrderItems b
where a.prod_id=b.prod_id
group by a.prod_name
11.0联结表
11.1返回顾客名称和相关订单号(37)
Customers 表有字段顾客名称cust_name、顾客id cust_id
| cust_id | cust_name |
|---|---|
| cust10 | andy |
| cust1 | ben |
| cust2 | tony |
| cust22 | tom |
| cust221 | an |
| cust2217 | hex |
Orders订单信息表,含有字段order_num订单号、cust_id顾客id
| order_num | cust_id |
|---|---|
| a1 | cust10 |
| a2 | cust1 |
| a3 | cust2 |
| a4 | cust22 |
| a5 | cust221 |
| a7 | cust2217 |
【问题】
编写 SQL 语句,返回 Customers 表中的顾客名称(cust_name)和Orders 表中的相关订单号(order_num),并按顾客名称再按订单号对结果进行升序排序。你可以尝试用两个不同的写法,一个使用简单的等联结语法,另外一个使用 INNER JOIN。
【示例结果】cust_name代表用户名称cust_name和订单号order_num。
| cust_name | order_num |
|---|---|
| an | a5 |
| andy | a1 |
| ben | a2 |
| hex | a7 |
| tom | a4 |
| tony | a3 |
【示例解析】顾客名称为an的cust_id为cust221,他的订单号为a5。
1️⃣题解:
select cust_name,order_num
from Customers a,Orders b
where a.cust_id=b.cust_id
order by cust_name,order_num
11.2返回顾客名称和相关订单号以及每个订单的总价(38)
Customers 表有字段,顾客名称:cust_name、顾客id:cust_id
| cust_id | cust_name |
|---|---|
| cust10 | andy |
| cust1 | ben |
| cust2 | tony |
| cust22 | tom |
| cust221 | an |
| cust2217 | hex |
Orders订单信息表,含有字段,订单号:order_num、顾客id:cust_id
| order_num | cust_id |
|---|---|
| a1 | cust10 |
| a2 | cust1 |
| a3 | cust2 |
| a4 | cust22 |
| a5 | cust221 |
| a7 | cust2217 |
OrderItems表有字段,商品订单号:order_num、商品数量:quantity、商品价格:item_price
| order_num | quantity | item_price |
|---|---|---|
| a1 | 1000 | 10 |
| a2 | 200 | 10 |
| a3 | 10 | 15 |
| a4 | 25 | 50 |
| a5 | 15 | 25 |
| a7 | 7 | 7 |
【问题】
除了返回顾客名称和订单号,返回 Customers 表中的顾客名称(cust_name)和Orders 表中的相关订单号(order_num),添加第三列 OrderTotal,其中包含每个订单的总价,并按顾客名称再按订单号对结果进行升序排序。
【示例结果】返回顾客名称 cust_name、订单号order_num、订单总额OrderTotal
| cust_name | order_num | OrderTotal |
|---|---|---|
| an | a5 | 375 |
| andy | a1 | 10000 |
| ben | a2 | 2000 |
| hex | a7 | 49 |
| tom | a4 | 1250 |
| tony | a3 | 150 |
【示例解析】
例如顾客名称cust_name为an的顾客的订单a5的订单总额为quantity*item_price = 15 * 25 = 375,最后以cust_name和order_num来进行升序排序。
1️⃣题解:
select cust_name, OrderItems.order_num, sum(quantity*item_price) as OrderTotal
from OrderItems join Orders on OrderItems.order_num = Orders.order_num
join Customers on Orders.cust_id = Customers.cust_id
GROUP BY cust_name, OrderItems.order_num
order by cust_name
11.3确定哪些订单购买了prod id为BR01的产品(二)(39)
表OrderItems代表订单商品信息表,prod_id为产品id;Orders表代表订单表有cust_id代表顾客id和订单日期order_date
OrderItems表
| prod_id | order_num |
|---|---|
| BR01 | a0001 |
| BR01 | a0002 |
| BR02 | a0003 |
| BR02 | a0013 |
Orders表
| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
|---|---|---|
| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
【问题】
编写 SQL 语句,使用子查询来确定哪些订单(在 OrderItems 中)购买了 prod_id 为 “BR01” 的产品,然后从 Orders 表中返回每个产品对应的顾客 ID(cust_id)和订单日期(order_date),按订购日期对结果进行升序排序。
提示:这一次使用联结和简单的等联结语法。
【示例结果】
返回顾客id cust_id和定单日期order_date
| cust_id | order_date |
|---|---|
| cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
| cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
【示例解析】
产品id为BR01的订单a0001和a002的下单顾客cust10和cust1的下单时间分别为2022-01-01 00:00:00和2022-01-01 00:01:00
1️⃣题解:
select cust_id,order_date
from Orders left join OrderItems using(order_num)
where prod_id='BR01'
order by order_date
11.4反回购买prod id为BR01的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(二)(40)
有表OrderItems代表订单商品信息表,prod_id为产品id;Orders表代表订单表有cust_id代表顾客id和订单日期order_date;Customers表含有cust_email 顾客邮件和cust_id顾客id
OrderItems表
| prod_id | order_num |
|---|---|
| BR01 | a0001 |
| BR01 | a0002 |
| BR02 | a0003 |
| BR02 | a0013 |
Orders表
| order_num | cust_id | order_date |
|---|---|---|
| a0001 | cust10 | 2022-01-01 00:00:00 |
| a0002 | cust1 | 2022-01-01 00:01:00 |
| a0003 | cust1 | 2022-01-02 00:00:00 |
| a0013 | cust2 | 2022-01-01 00:20:00 |
Customers表代表顾客信息,cust_id为顾客id,cust_email为顾客email
| cust_id | cust_email |
|---|---|
| cust10 | [email protected] |
| cust1 | [email protected] |
| cust2 | [email protected] |
【问题】返回购买 prod_id 为BR01 的产品的所有顾客的电子邮件(Customers 表中的 cust_email),结果无需排序。
提示:涉及到 SELECT 语句,最内层的从 OrderItems 表返回 order_num,中间的从 Customers 表返回 cust_id,但是必须使用 INNER JOIN 语法。
【示例结果】返回顾客email cust_email
| cust_email |
|---|
| [email protected] |
| [email protected] |
【示例解析】
产品id为BR01的订单a0001和a002的下单顾客cust10和cust1的顾客email cust_email分别是:[email protected] 、[email protected]
1️⃣题解:
select cust_email
from OrderItems join Orders using(order_num)
join Customers using(cust_id)
where prod_id='BR01'
11.5确定最佳顾客的另一种方式(二)(41)
OrderItems表代表订单信息,确定最佳顾客的另一种方式是看他们花了多少钱,OrderItems表有订单号order_num和item_price商品售出价格、quantity商品数量
| order_num | item_price | quantity |
|---|---|---|
| a1 | 10 | 105 |
| a2 | 1 | 1100 |
| a2 | 1 | 200 |
| a4 | 2 | 1121 |
| a5 | 5 | 10 |
| a2 | 1 | 19 |
| a7 | 7 | 5 |
Orders表含有字段order_num 订单号、cust_id顾客id
| order_num | cust_id |
|---|---|
| a1 | cust10 |
| a2 | cust1 |
| a3 | cust2 |
| a4 | cust22 |
| a5 | cust221 |
| a7 | cust2217 |
顾客表Customers有字段cust_id 客户id、cust_name 客户姓名
| cust_id | cust_name |
|---|---|
| cust10 | andy |
| cust1 | ben |
| cust2 | tony |
| cust22 | tom |
| cust221 | an |
| cust2217 | hex |
【问题】编写 SQL 语句,返回订单总价不小于1000 的客户名称和总额(OrderItems 表中的order_num)。
提示:需要计算总和(item_price 乘以 quantity)。按总额对结果进行排序,请使用INNER JOIN 语法。
【示例结果】
| cust_name | total_price |
|---|---|
| andy | 1050 |
| ben | 1319 |
| tom | 2242 |
【示例解析】
总额(item_price 乘以 quantity)大于等于1000的订单号,例如a2对应的顾客id为cust1,cust1的顾客名称cust_name是ben,最后返回ben作为order_num a2的quantity * item_price总和的结果1319。
1️⃣题解:
select cust_name, sum(item_price * quantity) as total_price
from Orders o
inner join OrderItems oi on o.order_num = oi.order_num
inner join Customers c on o.cust_id = c.cust_id
group by mcust_name
having total_price >= 1000
12.0创建高级链结
12.1检索每个顾客的名称和所有的订单号(一)(42)
Customers表代表顾客信息含有顾客id cust_id和 顾客名称 cust_name
| cust_id | cust_name |
|---|---|
| cust10 | andy |
| cust1 | ben |
| cust2 | tony |
| cust22 | tom |
| cust221 | an |
| cust2217 | hex |
Orders表代表订单信息含有订单号order_num和顾客id cust_id
| order_num | cust_id |
|---|---|
| a1 | cust10 |
| a2 | cust1 |
| a3 | cust2 |
| a4 | cust22 |
| a5 | cust221 |
| a7 | cust2217 |
【问题】使用 INNER JOIN 编写 SQL语句,检索每个顾客的名称(Customers表中的 cust_name)和所有的订单号(Orders 表中的 order_num),最后根据顾客姓名cust_name升序返回。
【示例结果】返回顾客名称cust_name和订单号order_num
| cust_name | order_num |
|---|---|
| an | a5 |
| andy | a1 |
| ben | a2 |
| hex | a7 |
| tom | a4 |
| tony | a3 |
1️⃣题解:
select cust_name,order_num
from Customers
join Orders using(cust_id)
order by cust_name
12.2检索每个顾客的名称和所有的订单号(二)(43)
Orders表代表订单信息含有订单号order_num和顾客id cust_id
| order_num | cust_id |
|---|---|
| a1 | cust10 |
| a2 | cust1 |
| a3 | cust2 |
| a4 | cust22 |
| a5 | cust221 |
| a7 | cust2217 |
Customers表代表顾客信息含有顾客id cust_id和 顾客名称 cust_name
| cust_id | cust_name |
|---|---|
| cust10 | andy |
| cust1 | ben |
| cust2 | tony |
| cust22 | tom |
| cust221 | an |
| cust2217 | hex |
| cust40 | ace |
【问题】检索每个顾客的名称(Customers表中的 cust_name)和所有的订单号(Orders 表中的 order_num),列出所有的顾客,即使他们没有下过订单。最后根据顾客姓名cust_name升序返回。
【示例结果】
返回顾客名称cust_name和订单号order_num
| cust_name | order_num |
|---|---|
| ace | NULL |
| an | a5 |
| andy | a1 |
| ben | a2 |
| hex | a7 |
| tom | a4 |
| tony | a3 |
【示例解析】
基于两张表,返回订单号a1的顾客名称andy等人,没有下单的顾客ace也统计了进来
1️⃣题解:
SELECT cust_name, order_num
FROM Customers LEFT JOIN Orders
USING(cust_id)
Order by cust_name
12.3返回产品名称和与之相关的订单号(44)
Products表为产品信息表含有字段prod_id产品id、prod_name产品名称
| prod_id | prod_name |
|---|---|
| a0001 | egg |
| a0002 | sockets |
| a0013 | coffee |
| a0003 | cola |
| a0023 | soda |
OrderItems表为订单信息表含有字段order_num订单号和产品id prod_id
| prod_id | order_num |
|---|---|
| a0001 | a105 |
| a0002 | a1100 |
| a0002 | a200 |
| a0013 | a1121 |
| a0003 | a10 |
| a0003 | a19 |
| a0003 | a5 |
【问题】
使用 OUTER JOIN 联结 Products 表和 OrderItems 表,返回产品名称(prod_name)和与之相关的订单号(order_num)的列表,并按照产品名称升序排序。
【示例结果】
返回产品名称prod_name和订单号order_num
| prod_name | order_num |
|---|---|
| coffee | a1121 |
| cola | a5 |
| cola | a19 |
| cola | a10 |
| egg | a105 |
| sockets | a200 |
| sockets | a1100 |
| soda | NULL |
【示例解析】
返回产品和对应实际支付订单的订单号,但是无实际订单的产品soda也返回,最后根据产品名称升序排序。
1️⃣题解:
select prod_name,order_num
from Products
LEFT JOIN OrderItems using(prod_id)
order by prod_name
12.4返回产品名称和每一项产品的总订单数(45)
Products表为产品信息表含有字段prod_id产品id、prod_name产品名称
| prod_id | prod_name |
|---|---|
| a0001 | egg |
| a0002 | sockets |
| a0013 | coffee |
| a0003 | cola |
| a0023 | soda |
OrderItems表为订单信息表含有字段order_num订单号和产品id prod_id
| prod_id | order_num |
|---|---|
| a0001 | a105 |
| a0002 | a1100 |
| a0002 | a200 |
| a0013 | a1121 |
| a0003 | a10 |
| a0003 | a19 |
| a0003 | a5 |
【问题】
使用 OUTER JOIN 联结 Products 表和 OrderItems 表,返回产品名称(prod_name)和每一项产品的总订单数(不是订单号),并按产品名称升序排序。
【示例结果】
返回产品名称prod_name和订单号订单数orders
| prod_name | orders |
|---|---|
| coffee | 1 |
| cola | 3 |
| egg | 1 |
| sockets | 2 |
| soda | 0 |
【示例解析】
返回产品和产品对应的实际支付的订单数,但是无实际订单的产品soda也返回,最后根据产品名称升序排序。
1️⃣题解:
select prod_name,count(order_num) as orders
from Products
left join OrderItems
using(prod_id)
group by prod_name
order by prod_name
12.5列出供应商及其可供产品的数量(46)
有Vendors表含有vend_id供应商id.
| vend_id |
|---|
| a0002 |
| a0013 |
| a0003 |
| a0010 |
有Products表含有供应商id和供应产品id
| vend_id | prod_id |
|---|---|
| a0001 | egg |
| a0002 | prod_id_iphone |
| a00113 | prod_id_tea |
| a0003 | prod_id_vivo phone |
| a0010 | prod_id_huawei phone |
【问题】
列出供应商(Vendors 表中的 vend_id)及其可供产品的数量,包括没有产品的供应商。你需要使用 OUTER JOIN 和 COUNT()聚合函数来计算 Products 表中每种产品的数量,最后根据vend_id 升序排序。
注意:vend_id 列会显示在多个表中,因此在每次引用它时都需要完全限定它。
【示例结果】
返回供应商id和对应供应商供应的产品的个数
| vend_id | prod_id |
|---|---|
| a0002 | 1 |
| a0013 | 0 |
| a0003 | 1 |
| a0010 | 1 |
【示例解析】
供应商a00013供应的商品不在Products表中所以为0,其他供应商供应的产品为1个。
1️⃣题解:
select a.vend_id, count(b.prod_id) prod_id
from Vendors a
left join Products b using(vend_id)
group by a.vend_id
order by a.vend_id asc
13.0组合查询
13.1将两个SELECT语句结合起来(一)(47)
表OrderItems包含订单产品信息,字段prod_id代表产品id、quantity代表产品数量
| prod_id | quantity |
|---|---|
| a0001 | 105 |
| a0002 | 100 |
| a0002 | 200 |
| a0013 | 1121 |
| a0003 | 10 |
| a0003 | 19 |
| a0003 | 5 |
| BNBG | 10002 |
【问题】
将两个 SELECT 语句结合起来,以便从 OrderItems表中检索产品 id(prod_id)和 quantity。其中,一个 SELECT 语句过滤数量为 100 的行,另一个 SELECT 语句过滤 id 以 BNBG 开头的产品,最后按产品 id 对结果进行升序排序。
【示例结果】
返回产品id prod_id和产品数量quantity
| prod_id | quantity |
|---|---|
| a0002 | 100 |
| BNBG | 10002 |
【示例解析】
产品id a0002因为数量等于100被选取返回;BNBG因为是以 BNBG 开头的产品所以返回;最后以产品id进行排序返回。
1️⃣题解:
select * from OrderItems where quantity=100
union all
select * from OrderItems where prod_id like 'BNBG%'
order by prod_id;
13.2将两个SELECT语句结合起来(二)(48)
表OrderItems包含订单产品信息,字段prod_id代表产品id、quantity代表产品数量。
| prod_id | quantity |
|---|---|
| a0001 | 105 |
| a0002 | 100 |
| a0002 | 200 |
| a0013 | 1121 |
| a0003 | 10 |
| a0003 | 19 |
| a0003 | 5 |
| BNBG | 10002 |
【问题】
将两个 SELECT 语句结合起来,以便从 OrderItems表中检索产品 id(prod_id)和 quantity。其中,一个 SELECT 语句过滤数量为 100 的行,另一个 SELECT 语句过滤 id 以 BNBG 开头的产品,最后按产品 id 对结果进行升序排序。
注意:这次仅使用单个 SELECT 语句。
【示例结果】
返回产品id prod_id和产品数量quantity
| prod_id | quantity |
|---|---|
| a0002 | 100 |
| BNBG | 10002 |
【示例解析】
产品id a0002因为数量等于100被选取返回;BNBG因为是以 BNBG 开头的产品所以返回;最后以产品id进行排序返回。
1️⃣题解:
select prod_id,quantity from OrderItems
where quantity=100 or prod_id like 'BNBG%'
order by prod_id;
13.3组合Products表中的产品名称和Customers表中的顾客名称(49)
Products表含有字段prod_name代表产品名称
| prod_name |
|---|
| flower |
| rice |
| ring |
| umbrella |
Customers表代表顾客信息,cust_name代表顾客名称
| cust_name |
|---|
| andy |
| ben |
| tony |
| tom |
| an |
| lee |
| hex |
【问题】
编写 SQL 语句,组合 Products 表中的产品名称(prod_name)和 Customers 表中的顾客名称(cust_name)并返回,然后按产品名称对结果进行升序排序。
【示例结果】
| prod_name |
|---|
| an |
| andy |
| ben |
| flower |
| hex |
| lee |
| rice |
| ring |
| tom |
| tony |
| umbrella |
【示例解析】
拼接cust_name和prod_name并根据结果升序排序
1️⃣题解:
select prod_name
from Products
union all
select cust_name
from Customers
order by prod_name
13.4纠错4(50)
表Customers含有字段cust_name顾客名、cust_contact顾客联系方式、cust_state顾客州、cust_email顾客email
| cust_name | cust_contact | cust_state | cust_email |
|---|---|---|---|
| cust10 | 8695192 | MI | [email protected] |
| cust1 | 8695193 | MI | [email protected] |
| cust2 | 8695194 | IL | [email protected] |
【问题】修正下面错误的SQL
SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
FROM Customers
WHERE cust_state = 'MI'
ORDER BY cust_name;
UNION
SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
|cust_name|cust_contact|cust_email |
|---------|------------|---------------|
|cust1 |8695193 |cust1@cust.com |
|cust10 |8695192 |cust10@cust.com|
|cust2 |8695194 |cust2@cust.com |
【示例解析】
返回住在"IL"和"MI"的顾客信息,最后根据顾客名称升序排序。
**:one:题解:**
```sql
SELECT cust_name, cust_contact, cust_email
FROM Customers
WHERE cust_state = 'MI'
OR cust_state = 'IL'
ORDER BY cust_name;