第十九周的算法总结-2022
第十九周的算法总结-2022
- 5.1 两题(动态+数据结构)
-
- 139. **单词拆分**
-
- 个人总结(需要回顾)(suc)
- **基础知识总结**
- 官方解法
- 推荐解法
- 21. 合并两个有序链表 (suc)
-
- 个人解法(suc)
- 官方解法
- 推荐解法
- 5.2 NULL
- 5.3
-
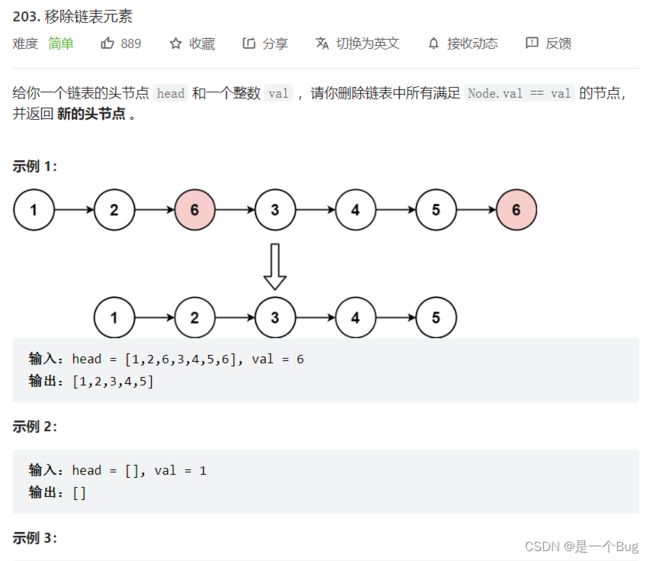
- 203. 移除链表元素
-
- 个人总结(suc)
- 迭代解法 和 个人尝试(回顾)
- 迭代解法
- 144. 二叉树的前序遍历
-
- 个人总结(suc)
- 官方解法
- 对树进行debug
- 94. 二叉树的中序遍历
-
- 个人总结(suc)
- 官方解法
- 推荐解法
- 145. 二叉树的后序遍历
-
- 个人总结(suc)
- 官方解法
- 推荐解法
- 5.4 剑指 Offer
-
- 30. **包含min函数的栈**
-
- 个人解法(lose)
- 官方解法
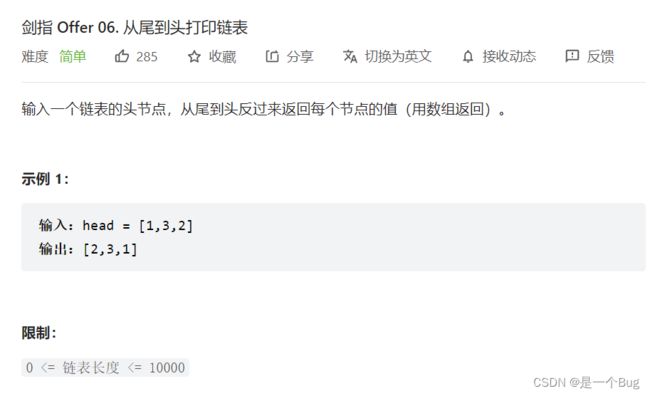
- 06. 从尾到头打印链表
-
- 个人解法(suc)
- 官方解法
- 24. 反转链表
-
- 个人总结(suc)
- 官方解法
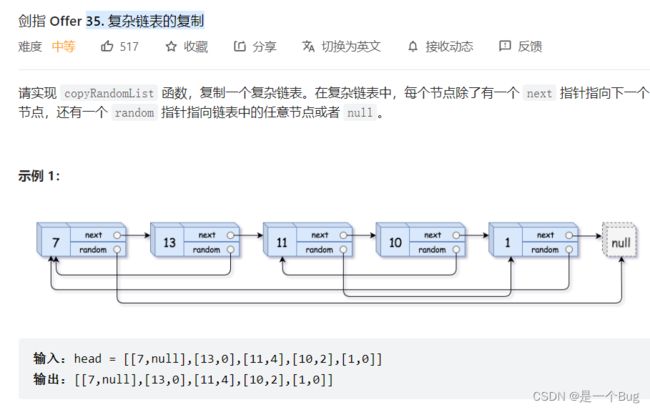
- 35. **复杂链表的复制**
-
- 个人解法(lose)
- 官方解法
- 推荐解法
- 5.5 剑指 Offer
-
- 05. 替换空格
-
- 个人解法
- 官方解法
- 重做-总结
-
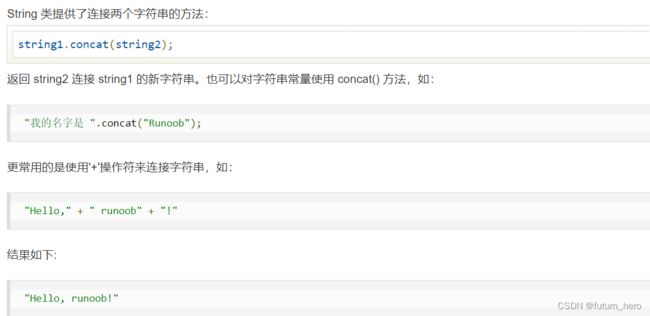
- 单引号和双引号
- new String(b, 0, len)
- 58 - II. 左旋转字符串
-
- 个人解法(suc)
- 官方解法
- 03. 数组中重复的数字
-
- 个人解法(suc)(Map)
- 个人解法(suc)(Set)
- 53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
-
- 个人总结
- 53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
-
- 个人总结
- 官方解法
- 5.6 剑指 Offer
-
- 11. 旋转数组的最小数字
-
- 个人解法
- 官方解法
- 50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
-
- 个人解法
- 官方解法
- 推荐解法
- 04. 二维数组中的查找
-
- 个人解法
- 官方解法
-
- 暴力
- 线性查找
- 推荐解法
- 5.7 是凌晨一点的补习
-
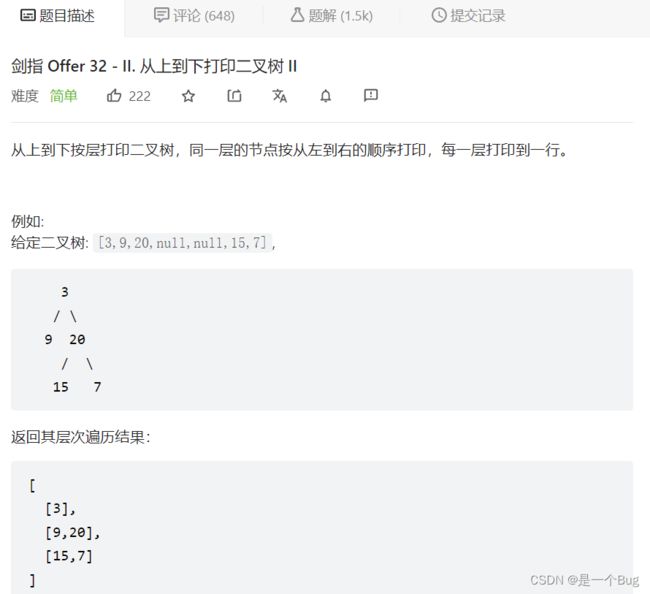
- 32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
-
- 个人解法
- 5.8 是改论文得第365天
-
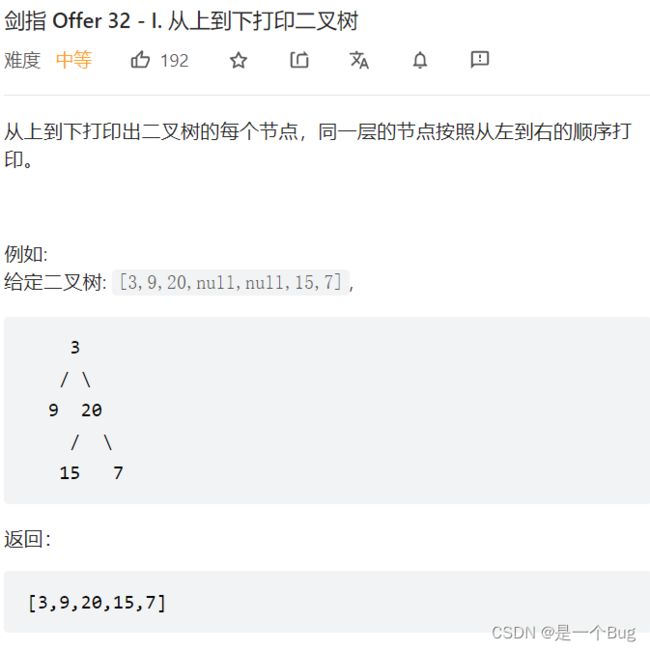
- 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
-
- 个人解法 BFS(suc)
- 官方解法
- queue
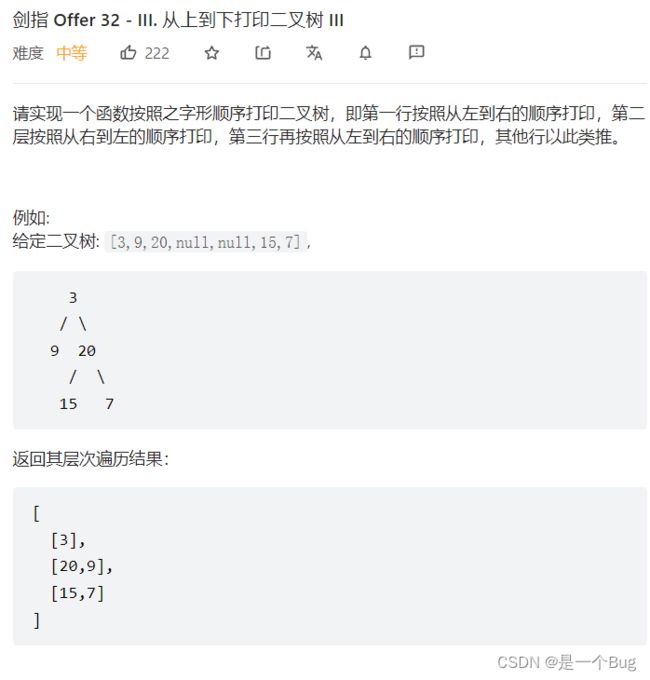
- 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III(回顾)
-
- 个人解法
- 官方解法
- 推荐解法
- 第一题
-
- 个人解法
- 官方解法
- 推荐解法
5.1 两题(动态+数据结构)
本周打算处理下数据结构方面的习题,对链表,树进行回顾和整理
数据结构的题型会占到15道左右,算法的大概5道的样子;
139. 单词拆分
个人总结(需要回顾)(suc)
我对字符串类型的都不是很熟悉,对String的方法掌握的也不好,希望通过者一周的练习,提升自己对字符串的处理。
这道题的解体思路就是对于这个字符串的每一个字串都能分辨
即:从前往后分为 dp(j)和dp(n)两个部分;
只要满足动态转移公式
dp(n) = dp(j) && dp(j,...,n-1);
则最后的dp(n) = true;
class Solution {
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
boolean[] result = new boolean[s.length() +1 ];
result[0] = true;
for(int i=0;i<=s.length();i++){
for(int j=0; j<i;j++){
if(result[j] && wordDict.contains(s.substring(j,i))){
result[i]=true;
break;
}
}
}
return result[s.length()];
}
}
基础知识总结
官方解法
public class Solution {
public boolean wordBreak(String s, List<String> wordDict) {
Set<String> wordDictSet = new HashSet(wordDict);
boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
dp[0] = true;
for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (dp[j] && wordDictSet.contains(s.substring(j, i))) {
dp[i] = true;
break;
}
}
}
return dp[s.length()];
}
}
推荐解法
21. 合并两个有序链表 (suc)
个人解法(suc)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {
int len1 = 0;
int len2 = 0;
if(list1==null && list2==null){
return null;
}
ListNode cur1 = list1;
ListNode cur12 = list2;
List<Integer> newlist = new ArrayList<>();
while(list1!=null){
len1++;
newlist.add(list1.val);
list1 = list1.next;
}
list1 = cur1;
while(list2!=null){
len2++;
newlist.add(list2.val);
list2 = list2.next;
}
list2 = cur12;
System.out.println(newlist);
int[] list = new int[newlist.size()];
for(int i=0;i<newlist.size();i++){
list[i] = newlist.get(i);
}
Arrays.sort(list);
String a = Arrays.toString(list);
System.out.println(a);
int len = newlist.size()-1;
ListNode cur = new ListNode(list[0]);
ListNode cur3 = cur;
int i = 0;
while(len!=0){
len--;
cur.next = new ListNode(list[i+1]);
cur = cur.next;
i++;
}
return cur3;
}
}
官方解法
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) {
return l2;
} else if (l2 == null) {
return l1;
} else if (l1.val < l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
推荐解法
5.2 NULL
5.3
203. 移除链表元素
个人总结(suc)
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode cur = head;
if(cur==null){
return null;
}
while(cur.next!=null){
if(cur.next.val == val){
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}else{
cur = cur.next;
}
}
if(head.val == val){
if(head.next == null){
return null;
}else{
head = head.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}
迭代解法 和 个人尝试(回顾)
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
/**如果使用递归,需要判断
1.递归什么时候停止,
2.递归返回的参数是什么和递归的连续性
3. 条件限定
*/
// 1.递归什么时候停止,
if(head == null){
return head;
}
// 2.递归返回的参数是什么和递归的连续性: 这里就是head = head.next; 参数为head.next
head.next = removeElements(head.next, val);
//3.递归的条件限定
if(head.val==val){
return head.next;
}else{
return head;
}
}
}
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return head;
}
head.next = removeElements(head.next, val);
return head.val == val ? head.next : head;
}
}
迭代解法
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode temp = dummyHead;
while (temp.next != null) {
if (temp.next.val == val) {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
} else {
temp = temp.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
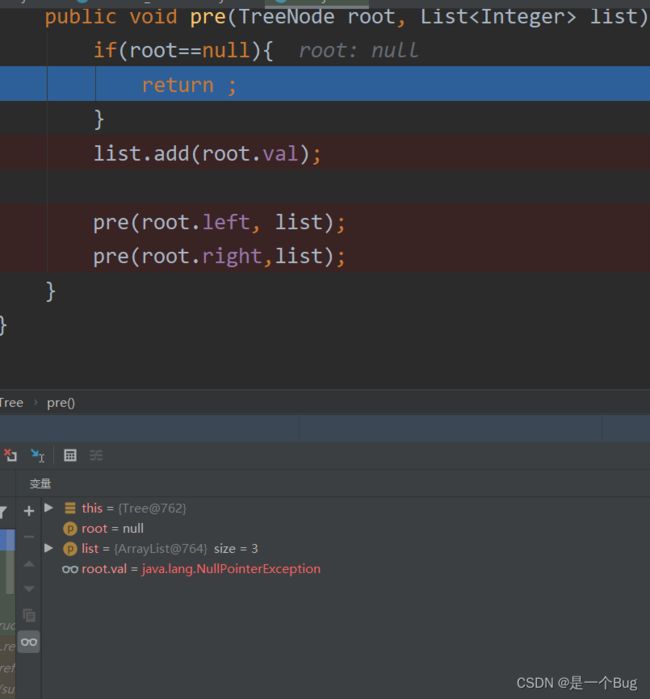
144. 二叉树的前序遍历
个人总结(suc)
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
pre(root,list);
return list;
}
public void pre(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if(root==null){
return ;
}
list.add(root.val);
pre(root.left, list);
pre(root.right,list);
}
}
官方解法
对树进行debug
class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode() {}
TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
this.val = val;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
public class Tree {
@Test
public void preorderTraversal() {
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(1);
root.left = new TreeNode(2);
root.left.left = new TreeNode(3);
root.left.right = new TreeNode(4);
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
pre(root,list);
System.out.println(list);
}
// 返回条件就是走到null,
public void pre(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) {
if(root==null){
return ;
}
list.add(root.val);
pre(root.left, list);
pre(root.right,list);
}
}

递归就是当 root.left.left==null; return 上一个节点root.left递归到root.left.right


94. 二叉树的中序遍历
个人总结(suc)
class Solution {
//中序 就是 左中右
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
mid(root,list);
return list;
}
public void mid(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
mid(root.left,list);
list.add(root.val);
mid(root.right,list);
}
}
官方解法
推荐解法
145. 二叉树的后序遍历
个人总结(suc)
class Solution {
public List<Integer> postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
mid(root,list);
return list;
}
public void mid(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list){
if(root == null){
return;
}
mid(root.left,list);
mid(root.right,list);
list.add(root.val);
}
}
官方解法
推荐解法
5.4 剑指 Offer
30. 包含min函数的栈
个人解法(lose)
public class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> integer = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> minlist = new Stack<>();
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
//栈,后入先出
}
public void push(int x) {
integer.push(x);
int min = fuzu();
minlist.push(min);
}
public void pop() {
integer.pop();
minlist.pop();
}
public int top() {
return integer.peek();
}
public int min(){
return minlist.peek();
}
public int fuzu() {
Stack<Integer> integer1 = (Stack<Integer>) integer.clone();
int min = integer1.peek();
int temp = 0;
while(integer1.empty()==false){
temp = integer1.pop();
if (temp<min){
min = temp;
}
}
return min;
}
}
官方解法
我的解法超过了要求的时间复杂度
所以依照题目要求,
需要建立两个栈
其中一个作为存放每次push时的最小值;
class MinStack {
Stack<Integer> xStack = new Stack<>();
Stack<Integer> minStack = new Stack<>();
/** initialize your data structure here. */
public MinStack() {
xStack =new Stack<>();
minStack =new Stack<>();
minStack.push(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public void push(int x) {
xStack.push(x);
minStack.push(Math.min(minStack.peek(), x));
}
public void pop() {
xStack.pop();
minStack.pop();
}
public int top() {
return xStack.peek();
}
public int min() {
return minStack.peek();
}
}
06. 从尾到头打印链表
个人解法(suc)
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
List<Integer> list = new LinkedList<>();
while(head!=null){
list.add(head.val);
head = head.next;
}
int[] arr = new int[list.size()];
int i = 0;
while(i<list.size()){
arr[i] = list.get(list.size()-i-1);
i++;
}
return arr;
}
}
官方解法
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<ListNode>();
ListNode temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
stack.push(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
int size = stack.size();
int[] print = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
print[i] = stack.pop().val;
}
return print;
}
}
24. 反转链表
个人总结(suc)
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null||head.next==null){
return head;
}
ListNode cur = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return cur;
}
}
官方解法
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode curr = head;
while (curr != null) {
ListNode next = curr.next;
curr.next = prev;
prev = curr;
curr = next;
}
return prev;
}
}
35. 复杂链表的复制
个人解法(lose)
官方解法
class Solution {
Map<Node, Node> cachedNode = new HashMap<Node, Node>();
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
if (!cachedNode.containsKey(head)) {
Node headNew = new Node(head.val);
cachedNode.put(head, headNew);
headNew.next = copyRandomList(head.next);
headNew.random = copyRandomList(head.random);
}
return cachedNode.get(head);
}
}
推荐解法
5.5 剑指 Offer
05. 替换空格
个人解法
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
String sa = "";
int i =0;
for (String retval: s.split(" ")){
if(i>=1){
sa = sa.concat("%20");
}
sa = sa.concat(retval);
i++;
}
return sa;
}
官方解法
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
int length = s.length();
char[] array = new char[length * 3];
int size = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
char c = s.charAt(i);
if (c == ' ') {
array[size++] = '%';
array[size++] = '2';
array[size++] = '0';
} else {
array[size++] = c;
}
}
String newStr = new String(array, 0, size);
return newStr;
}
}
重做-总结
@Test
public void replaceSpace() {
String s = "We are happy.";
int len = s.length();
char[] chars = new char[len*3];
int size = 0;
char cur;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
cur = s.charAt(i);
if(cur == ' '){
chars[size++] = '%';
chars[size++] = '2';
chars[size++] = '0';
}else {
chars[size++] = cur;
}
}
String list = new String(chars,0,size);
System.out.println(list);
}
单引号和双引号
- 单引号引的数据 是char类型的 单引号只能引一个字符(表示单个字符)
- 双引号引的数据 是String类型的 而双引号可以引0个及其以上(引用字符串)
char类型的值用单引号引起来的单个字符
如: char a = 'b'
而java中的双引号 表示字符串 一个或多个字符
如 String c = "abc"
String d="a"
和char d='a'
new String(b, 0, len)
就是 new一个String类型的对象 取值是从地0个 长度为数值的长度 取的是b数组
58 - II. 左旋转字符串
个人解法(suc)
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
int len = s.length();
char cur;
char[] list = new char[len];
for (int i = n; i < len; i++) {
cur = s.charAt(i);
list[i-n] = cur;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
cur = s.charAt(i);
list[len-n+i] = cur;
}
String l = new String(list, 0, len);
return l;
}
}
官方解法
class Solution {
public String reverseLeftWords(String s, int n) {
return s.substring(n, s.length()) + s.substring(0, n);
}
}
03. 数组中重复的数字
个人解法(suc)(Map)
这里用map其实不太好,建议直接使用set,然后随意输出就可以了
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(map.get(nums[i])==null){
map.put(nums[i],1);
}else{
map.put(nums[i],map.get(nums[i]) + 1);
}
}
Set<Integer> set= map.keySet();
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Integer obj: set) {
if(map.get(obj)>1){
list.add(obj);
}
}
// int[] arr = new int[list.size()];
// for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
// arr[i] = list.get(i);
// }
return list.get(0);
}
}
个人解法(suc)(Set)
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new LinkedHashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(!set.add(nums[i])){
return (nums[i]);
}
}
return 0;
}
}
53 - I. 在排序数组中查找数字 I
个人总结
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int time = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] == target){
time++;
}
}
return (time);
}
}
53 - II. 0~n-1中缺失的数字
个人总结
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
for(int i =0; i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i] != i){
return i;
}
}
return nums.length;
}
}
官方解法
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] == m) i = m + 1;
else j = m - 1;
}
return i;
}
}
5.6 剑指 Offer
11. 旋转数组的最小数字
个人解法
我的解法肯定不对,有问题,应该是根据旋转数组来进行考虑
关注点可以去看下题解
我需要回顾一下查找算法补充到小张的算法基础中去
链接: link.
class Solution {
public int minArray(int[] numbers) {
// if(numbers==null){
// return -1;
// }
int minV = numbers[0];
for(int i =0; i<numbers.length;i++){
if(numbers[i] < minV){
minV = numbers[i];
}
}
return minV;
}
}
官方解法
class Solution {
public int minArray(int[] numbers) {
int low = 0;
int high = numbers.length - 1;
while (low < high) {
int pivot = low + (high - low) / 2;
if (numbers[pivot] < numbers[high]) {
high = pivot;
} else if (numbers[pivot] > numbers[high]) {
low = pivot + 1;
} else {
high -= 1;
}
}
return numbers[low];
}
}
50. 第一个只出现一次的字符
个人解法
class Solution {
public char firstUniqChar(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> map = new LinkedHashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
char one = s.charAt(i);
if(map.get(one)==null){
map.put(one,1);
}else {
map.put(one, map.get(one) + 1);
}
}
Set<Character> set = map.keySet();
for(Character a:set){
if(map.get(a)==1){
return (a);
}
}
return ' ';
}
}
官方解法
class Solution {
public char firstUniqChar(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> frequency = new HashMap<Character, Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
char ch = s.charAt(i);
frequency.put(ch, frequency.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
if (frequency.get(s.charAt(i)) == 1) {
return s.charAt(i);
}
}
return ' ';
}
}
推荐解法
这里26个英文字符可以用过char字符之间的排列关系得到。
class Solution {
// 计数数组
public char firstUniqChar(String s) {
int[] count = new int[26];
char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
for (char c : chars) count[c - 'a']++;
for (char c : chars) {
if (count[c - 'a'] == 1) return c;
}
return ' ';
}
}
04. 二维数组中的查找
个人解法
其实这里用深度优先遍历和广度优先遍历是可以的
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if(matrix.length == 1){
if(matrix[0].length < 1){
return (false);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
if(matrix[i][0]>target){
return (false);
}
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j]>target){
break;
}
if(matrix[i][j] == target){
return (true);
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
官方解法
暴力
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < columns; j++) {
if (matrix[i][j] == target) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
线性查找
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
int row = 0, column = columns - 1;
while (row < rows && column >= 0) {
int num = matrix[row][column];
if (num == target) {
return true;
} else if (num > target) {
column--;
} else {
row++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
推荐解法
5.7 是凌晨一点的补习
做的太慢,及时补上,但是论文的回稿到了,这两天需要提交,希望导师和审稿人都可以满意!
32 - II. 从上到下打印二叉树 II
个人解法
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root!=null){
queue.add(root);
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
List<Integer> arr = new LinkedList<>();
for (int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--) {
root = queue.poll();
arr.add(root.val);
if(root.left!=null)queue.add(root.left);
if(root.right!=null)queue.add(cur.right);
}
list.add(arr);
}
return list;
}
}
5.8 是改论文得第365天
32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
个人解法 BFS(suc)
- Breadth First Search
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
if(root!=null){
queue.add(root);
}
List<Integer> arr = new LinkedList<>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
for (int i = queue.size(); i > 0; i--) {
root = queue.poll();
arr.add(root.val);
if(root.left!=null)queue.add(root.left);
if(root.right!=null)queue.add(root.right);
}
}
int[] r = new int[arr.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); i++) {
r[i] = arr.get(i);
}
return r;
}
}
官方解法
class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) return new int[0];
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(){{ add(root); }};
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
ans.add(node.val);
if(node.left != null) queue.add(node.left);
if(node.right != null) queue.add(node.right);
}
int[] res = new int[ans.size()];
for(int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)
res[i] = ans.get(i);
return res;
}
}
queue
队列是一种特殊的线性表,它只允许在表的前端进行删除操作,而在表的后端进行插入操作。
LinkedList类实现了Queue接口,因此我们可以把LinkedList当成Queue来用。
- add(E e) : 将元素e插入到队列末尾,如果插入成功,则返回true;如果插入失败(即队列已满),则会抛出异常;
- remove() :移除队首元素,若移除成功,则返回true;如果移除失败(队列为空),则会抛出异常;
- offer(E e) :将元素e插入到队列末尾,如果插入成功,则返回true;如果插入失败(即队列已满),则返回false;
- poll() :移除并获取队首元素,若成功,则返回队首元素;否则返回null;
peek() :获取队首元素,若成功,则返回队首元素;否则返回nul
32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III(回顾)
个人解法
官方解法
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root != null) deque.add(root);
while(!deque.isEmpty()) {
// 打印奇数层
List<Integer> tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = deque.size(); i > 0; i--) {
// 从左向右打印
TreeNode node = deque.removeFirst();
tmp.add(node.val);
// 先左后右加入下层节点
if(node.left != null) deque.addLast(node.left);
if(node.right != null) deque.addLast(node.right);
}
res.add(tmp);
if(deque.isEmpty()) break; // 若为空则提前跳出
// 打印偶数层
tmp = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = deque.size(); i > 0; i--) {
// 从右向左打印
TreeNode node = deque.removeLast();
tmp.add(node.val);
// 先右后左加入下层节点
if(node.right != null) deque.addFirst(node.right);
if(node.left != null) deque.addFirst(node.left);
}
res.add(tmp);
}
return res;
}
}