SpringBoot读取yml配置文件
目录
yaml介绍
yaml语法规则
yaml数据读取
yaml数据读取
Environment读取yaml全部属性数据
自定义对象封装指定数据
yaml介绍
YAML(YAML Ain't Markup Language),一种数据序列化格式
优点:
- 容易阅读
- 容易与脚本语言交互
- 以数据为核心,重数据轻格式
YANL文件扩展名
- .yml(主流)
- .yaml
几种数据格式比较
yaml语法规则
- 大小写敏感
- 属性层级关系使用多行描述,每行结尾使用冒号结束
- 使用缩进表示层级关系,同层级左侧对齐,只允许使用空格(不允许使用Tab键)
- 属性值前面添加空格(属性名与属性值之间使用冒号+空格作为分隔)
- #表示注释
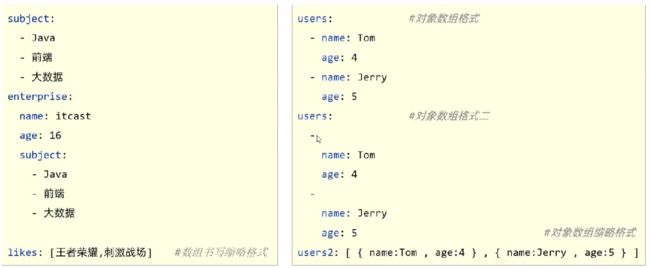
示例:
user:
name: zhangsan
age: 12
users:
-
name: lisi
age: 13
-
name: wangwu
age: 18
likes: [game,play,having]
users1: [{name:zhangsan,age:12},{name:lisi,age:12}]
字面值表示方式
数组表示方式:在属性名书写位置的下方使用减号作为数据开始符号,每行书写一个数据,减号与数据键空格分隔
yaml数据读取
使用@Value读取单个数据,属性名引用方式:${一级属性名.二级属性名}
controller下
package com.springboot01_02.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/SpringBoot")
public class TestController {
@Value("${user.name1}")
private String username1;
@Value("${users[0].age}")
private String userage2;
@Value("${person.hobby[0]}")
private String personHobbyEat;
@Value("${person.hobby[1]}")
private String personHobbyPlay;
@Value("${users1[0].age}")
private String usersAge;
@RequestMapping("/test")
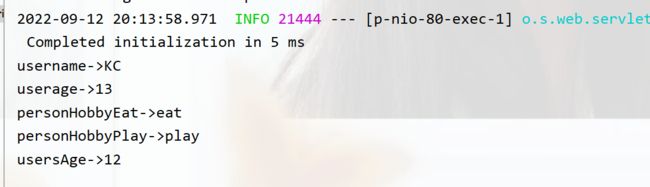
public String Test(){
System.out.println("username->"+username1);
System.out.println("userage->"+userage2);
System.out.println("personHobbyEat->"+personHobbyEat);
System.out.println("personHobbyPlay->"+personHobbyPlay);
System.out.println("usersAge->"+usersAge);
return "springboot is good";
}
}
yml配置文件
user:
name1: KC
age: 12
users:
-
name: lisi
age: 13
-
name: wangwu
age: 18
person:
name: ZH
age: 19
tel: 152161
hobby:
- eat
- play
- run
users1: [{name: zhangsan,age: 12},{name: lisi,age: 12}]
likes: [game,play,having]
运行结果:
yaml数据读取
在配置文件中可以使用属性名引用方式引用属性
在配置文件中
package com.springboot01_02.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/SpringBoot")
public class TestController {
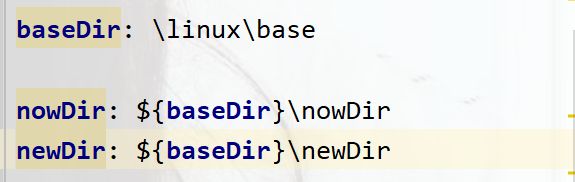
@Value("${nowDir}")
private String nowDir1;
@Value("${tewDir}")
private String tewDir1;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String Test(){
System.out.println("nowDir->"+nowDir1);
System.out.println("towDir->"+tewDir1);
return "springboot is good";
}
}
运行结果:
可以发现,要想让转义字符生效,就得加上双引号不然还是以字符串的形式打印出
Environment读取yaml全部属性数据
package com.springboot01_02.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/SpringBoot")
public class TestController {
//使用自动装配将所有数据封装到一个Environment中
@Autowired
private Environment evn;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String Test(){
System.out.println("----------------");
System.out.println(evn.getProperty("nowDir"));
System.out.println(evn.getProperty("users1[0].age"));
return "springboot is good";
}
}
运行结果:
小结:
使用Environment对象封装全部配置信息
使用@Autowired自动装配数据到Environment对象中
自定义对象封装指定数据
application.yaml配置文件中的信息
#创建类,用于封装下面的数据
#有spring带我们去加载数据到对象中,且告诉spring加载这组信息
#使用时从spring中直接获取信息使用
datasource:
driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost/love
username: kongchao
password: zenghui
自定义一个类
package com.springboot01_02.datesource;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
//1、定义数据类型模型封装yaml文件中对应的数据
//2、定义为spring管控的bean
@Component
//3、指定加载的数据
@ConfigurationProperties("datasource")
//4、设置getSet方法等
@Data
public class MyDateSource {
private String driver;
private String url;
private String username;
private String password;
}
使用了@Date,在pom.xml中导入lombok
org.projectlombok
lombok
1.16.10
测试类下
package com.springboot01_02.controller;
import com.springboot01_02.datesource.MyDateSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/SpringBoot")
public class TestController {
@Autowired
private MyDateSource dateSource;
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String Test(){
System.out.println(dateSource);
return "springboot is good";
}
}
运行访问localhost/SpringBoot/test即可得到:
小结:
使用@ConfigurationProperties注解绑定配置信息到封装类中
封装类需要定义为Spring管理的bean(使用注解@Component),否则无法进行属性注入