基于麻雀算法求解函数最优解
1.原理
麻雀算法是在2020年兴起的一种新型的智能搜索算法,其主要思想来源于麻雀的觅食以及反捕食的行为。
2.发现者的位置更新公式
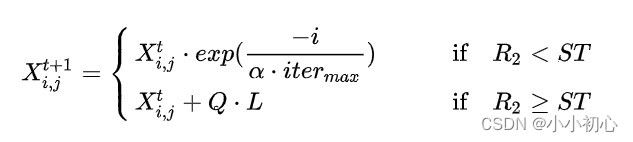
3.加入者的位置更新公式

4.麻雀算法的数学表达式

5.用于测试的函数

6.算法代码
function [fMin,bestX,Convergence_curve]=SSA(M,pop,c,d,dim,f1)
%pop是种群,M是迭代次数,fobj是用来计算适应度的函数
%pNum是生产者
P_percent = 0.2; % The population size of producers accounts for "P_percent" percent of the total population size
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
pNum = round( pop * P_percent ); % The population size of the producers
lb= c.*ones( 1,dim ); % Lower limit/bounds/ a vector
ub= d.*ones( 1,dim ); % Upper limit/bounds/ a vector
%Initialization
for i = 1 : pop
x( i, : ) = lb + (ub - lb) .* rand( 1, dim );
fit( i ) = f1( x( i, : ) ) ;
end
pFit = fit;
pX = x; % The individual's best position corresponding to the pFit
[ fMin, bestI ] = min( fit ); % fMin denotes the global optimum fitness value
bestX = x( bestI, : ); % bestX denotes the global optimum position corresponding to fMin
% Start updating the solutions.
for t = 1 : M
[ ans, sortIndex ] = sort( pFit );% Sort.
[fmax,B]=max( pFit );
worse= x(B,:);
r2=rand(1);
%%%%%%%%%%%%%5%%%%%%这一部位为发现者(探索者)的位置更新%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
if(r2<0.8)%预警值较小,说明没有捕食者出现
for i = 1 : pNum %r2小于0.8的发现者的改变(1-20) % Equation (3)
r1=rand(1);
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = pX( sortIndex( i ), : )*exp(-(i)/(r1*M));%对自变量做一个随机变换
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex( i ), : ), lb, ub );%对超过边界的变量进行去除
fit( sortIndex( i ) ) = f1( x( sortIndex( i ), : ) ); %就算新的适应度值
end
else %预警值较大,说明有捕食者出现威胁到了种群的安全,需要去其它地方觅食
for i = 1 : pNum %r2大于0.8的发现者的改变
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = pX( sortIndex( i ), : )+randn(1)*ones(1,dim);
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex( i ), : ), lb, ub );
fit( sortIndex( i ) ) = f1( x( sortIndex( i ), : ) );
end
end
[ fMMin, bestII ] = min( fit );
bestXX = x( bestII, : );
%%%%%%%%%%%%%5%%%%%%这一部位为加入者(追随者)的位置更新%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
for i = ( pNum + 1 ) : pop %剩下20-100的个体的变换 % Equation (4)
A=floor(rand(1,dim)*2)*2-1;
if( i>(pop/2))%这个代表这部分麻雀处于十分饥饿的状态(因为它们的能量很低,也是是适应度值很差),需要到其它地方觅食
x( sortIndex(i ), : )=randn(1)*exp((worse-pX( sortIndex( i ), : ))/(i)^2);
else%这一部分追随者是围绕最好的发现者周围进行觅食,其间也有可能发生食物的争夺,使其自己变成生产者
x( sortIndex( i ), : )=bestXX+(abs(( pX( sortIndex( i ), : )-bestXX)))*(A'*(A*A')^(-1))*ones(1,dim);
end
x( sortIndex( i ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex( i ), : ), lb, ub );%判断边界是否超出
fit( sortIndex( i ) ) = f1( x( sortIndex( i ), : ) );%计算适应度值
end
%%%%%%%%%%%%%5%%%%%%这一部位为意识到危险(注意这里只是意识到了危险,不代表出现了真正的捕食者)的麻雀的位置更新%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
c=randperm(numel(sortIndex));%%%%%%%%%这个的作用是在种群中随机产生其位置(也就是这部分的麻雀位置一开始是随机的,意识到危险了要进行位置移动,
%处于种群外围的麻雀向安全区域靠拢,处在种群中心的麻雀则随机行走以靠近别的麻雀)
b=sortIndex(c(1:round(pop*0.2)));
for j = 1 : length(b) % Equation (5)
if( pFit( sortIndex( b(j) ) )>(fMin) ) %处于种群外围的麻雀的位置改变
x( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )=bestX+(randn(1,dim)).*(abs(( pX( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) -bestX)));
else %处于种群中心的麻雀的位置改变
x( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) =pX( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )+(2*rand(1)-1)*(abs(pX( sortIndex( b(j) ), : )-worse))/ ( pFit( sortIndex( b(j) ) )-fmax+1e-50);
end
x( sortIndex(b(j) ), : ) = Bounds( x( sortIndex(b(j) ), : ), lb, ub );
fit( sortIndex( b(j) ) ) = f1( x( sortIndex( b(j) ), : ) );
end
for i = 1 : pop
if ( fit( i ) < pFit( i ) )
pFit( i ) = fit( i );
pX( i, : ) = x( i, : );
end
if( pFit( i ) < fMin )
fMin= pFit( i );
bestX = pX( i, : );
end
end
Convergence_curve(t)=fMin;
end

