基于Detectron2和LSTM的人体动作识别
人体动作识别通过分析视频来预测或分类视频中人物的各种动作。它被广泛应用于监测、体育、健身、防御等各个领域。
假设你想创建一个在线教授瑜伽的应用程序。它应该提供一个预先录制的瑜伽视频列表供用户观看。用户在应用程序上观看视频后,可以上传自己的个人练习视频。然后app评估他们的表现,并根据用户的各种瑜伽体式(或姿势)的表现给出反馈。使用动作识别来自动评估视频不是很好吗?你可以用它做更多的事。看看下面的视频。
下面展示在瑜伽app中使用人体姿势估计来识别每个瑜伽姿势。

通过人体上关键来识别瑜伽姿势(Natarajasana, Trikonasana或Virabhadrasana)。
在这篇博文中,我们将解释如何使用姿势估计和LSTM (Long - term Memory)创建一个用于人类动作识别(或分类)的App。我们将创建一个web应用程序,它接收一个视频,并生成一个带有标识动作类注释的输出视频。我们将在web应用程序中使用Flask框架,并使用PyTorch lightning进行模型训练和验证。
Detectron2
Detectron2是Facebook AI Research的开源平台,用于目标检测、人体姿态估计、分割和其他视觉识别任务。这个平台现在是在PyTorch中实现的,不像之前的版本Detectron是在caff2中实现的。
在这里,我们使用了一个来自Detectron2 model zoo的预训练的“R50-FPN”模型来进行姿态估计。这个模型已经在包含20多万张图片和25万个任务实例的COCO数据集上进行了训练,这些数据集被标记为关键点。模型对输入图像帧中的每个人输出17个关键点,如下图所示。

人体有17个关键点。图片的左边显示的是一个人,中间部分显示的是一个关键点列表,右边显示的是关键点在人身上的位置
LSTM
LSTM网络是一种递归神经网络(RNN),在序列预测问题中具有学习顺序依赖的能力。如下图所示,RNN有一个重复的神经网络模块链。
递归神经网络及其重复神经网络模块链
在神经网络(NN)中:
- X 0 , X 1 , … , X t X_{0}, X_1,…,X_t X0,X1,…,Xt是输入, h 0 , h 1 , … , h t h_0 ,h_1,…,h_t h0,h1,…,ht是预测。
- 每一时刻 t ( h t ) t_(ht) t(ht)的预测都依赖于之前的预测和当前输入 X t X_t Xt。
RNN记住之前的信息,并利用它来优化处理当前的输入。但是RNN的缺点是不能记住长期的依赖关系,具体梯度消失和爆炸的问题。
LSTM也有类似的链式结构,但它的神经网络模块可以轻松处理长期依赖关系。
我们使用LSTM对一段视频中的一系列关键点进行动作分类。
Dataset
为了训练LSTM模型,我们使用这个数据集。
这个数据集有什么特别之处?它由关键点检测组成,使用OpenPose深度学习模型,是伯克利多模态人类行为数据库(MHAD)数据集的中的一个子数据集。
OpenPose是第一个在单个图像上联合检测人体、手、面部和脚关键点(总共135个关键点)的实时多人系统。对12名受试者(从4个角度拍摄)的视频进行关键点检测,做以下6个动作,重复5次
来自MHAD数据集子集的一系列6个人类动作(JUMPING, JUMPING_JACKS, BOXING, WAVING_2HANDS, WAVING_1HAND, CLAPPING_HANDS)。
- JUMPING
- JUMPING_JACKS
- BOXING
- WAVING_2HANDS
- WAVING_1HAND
- CLAPPING_HANDS
Flask
Flask是一个流行的Python web框架,用于开发多个web应用程序。该应用程序内部使用Detectron2和LSTM模型来识别动作。
人体动作识别的高级方法
要对一个动作进行分类,我们首先需要在每一帧中定位身体的各个部位,然后分析身体部位随时间的变化。
- 第一步是使用Detectron2,在观察视频中的一帧后输出身体姿态(17个关键点)。
- 第二步是利用LSTM网络分析物体随时间的运动并做出预测。因此,将一组帧中的关键点发送到LSTM进行动作分类,如下图所示。
端到端动作识别工作流,使用Detectron2和LSTM
动作识别的ML模型训练
-
1.正如我们之前提到的,对于关键点检测,我们使用了Detectron2 model zoo.中预先训练好的“R50-FPN”模型。所以不需要进一步的训练。
-
2.使用pytorch lightning训练用于基于关键点的动作分类的LSTM模型。
训练输入数据包含一系列关键点(每帧17个关键点)和相关的动作标签。一个连续的32帧序列被用来识别一个特定的动作。32帧的样本序列将是一个大小为32×34的多维数组,如下所示:
每行包含17个关键点值。每个关键点都表示为(x,y)值,因此每行总共有34个值。
**注意:**与OpenPose模型在原始数据集中检测到的18个人体关键点不同,我们的应用程序只有17个关键点被Detectron2检测到。因此,在训练我们的LSTM模型之前,我们要转换成17个关键点的格式。
我们对模型进行了400个epoch的训练,得到了0.913的验证精度。验证精度和损失曲线如下图所示。训练后的模型被存入到代码库中,并在推理过程中使用相同的模型。

模型推理
推理管道由Detectron2模型和自定义LSTM模型组成。
- 我们的应用程序接受视频输入,迭代帧,然后使用Detectron2对每一帧进行关键点检测。
- 然后将关键点结果追加到大小为32的缓冲区,该缓冲区以滑动窗口的方式操作。
- 缓冲区的内容最终被发送到我们训练过的LSTM模型进行动作识别。
- 此外,基于flas web应用程序有一个UI来接受用户的视频输入。
我们的推理管道检测到的动作会在视频上加注释,并显示为结果。
在“Tesla T4”GPU上的测试表明,Detectron2和LSTM的推理时间分别为0.14秒和0.002秒。因此,如果我们处理视频中的每一帧,那么我们的推断管道执行的组合FPS(帧/秒)大约是每秒6帧。
上述FPS速率可能适用于离线视频分析的应用程序。但如果你是在实时视频流上进行推断呢?一般来说,实时视频流的帧率为30fps或更高(取决于相机)。在这种情况下,推断管道的FPS必须高于或至少等于视频流的FPS,以处理帧没有任何延迟。虽然当前FPS很低,但你确实可以选择改善推断管道的FPS。
- 对模型进行剪枝和量化可以加快模型的执行速度。
- 跳过帧和间隔推断:你甚至可以跳过几个帧,选择间隔帧推断。例如,我们的测试显示,当在序列中每5帧进行推断时,FPS会增加到每秒27帧。但是我们发现准确性下降了,因此需要选择一个区间。
- 多线程:有单独的线程接收视频和推断。
- 接收线程可以专注于从流中读取视频帧,并将它们添加到队列中。
- 独立的子线程可以从队列中读取帧来进行推断。子线程在处理帧时可能会滞后,但它不会阻止接收线程读取视频流
基于Web 应用的视频分析Detectron2, LSTM 模型代码
1. Detectron2姿态估计模型
我们使用的是预先训练好的Detectron2模型,如下图所示。
# obtain detectron2's default config
cfg = get_cfg()
# load the pre trained model from Detectron2 model zoo
cfg.merge_from_file(model_zoo.get_config_file("COCO-Keypoints/keypoint_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml"))
# set confidence threshold for this model
cfg.MODEL.ROI_HEADS.SCORE_THRESH_TEST = 0.5
# load model weights
cfg.MODEL.WEIGHTS = model_zoo.get_checkpoint_url("COCO-Keypoints/keypoint_rcnn_R_50_FPN_3x.yaml")
# create the predictor for pose estimation using the config
pose_detector = DefaultPredictor(cfg)
2. LSTM模型定义
我们的LSTM模型初始化隐藏维度(hidden_dim)为50,并使用PyTorch Lightning进行训练。我们使用了Adam优化器,还配置了ReduceLROnPlateau调度器,以根据val_loss的值降低学习速率。
# We have 6 output action classes.
TOT_ACTION_CLASSES = 6
#lstm classifier definition
class ActionClassificationLSTM(pl.LightningModule):
# initialise method
def __init__(self, input_features, hidden_dim, learning_rate=0.001):
super().__init__()
# save hyperparameters
self.save_hyperparameters()
# The LSTM takes word embeddings as inputs, and outputs hidden states
# with dimensionality hidden_dim.
self.lstm = nn.LSTM(input_features, hidden_dim, batch_first=True)
# The linear layer that maps from hidden state space to classes
self.linear = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, TOT_ACTION_CLASSES)
def forward(self, x):
# invoke lstm layer
lstm_out, (ht, ct) = self.lstm(x)
# invoke linear layer
return self.linear(ht[-1])
def training_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
# get data and labels from batch
x, y = batch
# reduce dimension
y = torch.squeeze(y)
# convert to long
y = y.long()
# get prediction
y_pred = self(x)
# calculate loss
loss = F.cross_entropy(y_pred, y)
# get probability score using softmax
prob = F.softmax(y_pred, dim=1)
# get the index of the max probability
pred = prob.data.max(dim=1)[1]
# calculate accuracy
acc = torchmetrics.functional.accuracy(pred, y)
dic = {
'batch_train_loss': loss,
'batch_train_acc': acc
}
# log the metrics for pytorch lightning progress bar or any other operations
self.log('batch_train_loss', loss, prog_bar=True)
self.log('batch_train_acc', acc, prog_bar=True)
#return loss and dict
return {'loss': loss, 'result': dic}
def training_epoch_end(self, training_step_outputs):
# calculate average training loss end of the epoch
avg_train_loss = torch.tensor([x['result']['batch_train_loss'] for x in training_step_outputs]).mean()
# calculate average training accuracy end of the epoch
avg_train_acc = torch.tensor([x['result']['batch_train_acc'] for x in training_step_outputs]).mean()
# log the metrics for pytorch lightning progress bar and any further processing
self.log('train_loss', avg_train_loss, prog_bar=True)
self.log('train_acc', avg_train_acc, prog_bar=True)
def validation_step(self, batch, batch_idx):
# get data and labels from batch
x, y = batch
# reduce dimension
y = torch.squeeze(y)
# convert to long
y = y.long()
# get prediction
y_pred = self(x)
# calculate loss
loss = F.cross_entropy(y_pred, y)
# get probability score using softmax
prob = F.softmax(y_pred, dim=1)
# get the index of the max probability
pred = prob.data.max(dim=1)[1]
# calculate accuracy
acc = torchmetrics.functional.accuracy(pred, y)
dic = {
'batch_val_loss': loss,
'batch_val_acc': acc
}
# log the metrics for pytorch lightning progress bar and any further processing
self.log('batch_val_loss', loss, prog_bar=True)
self.log('batch_val_acc', acc, prog_bar=True)
#return dict
return dic
def validation_epoch_end(self, validation_step_outputs):
# calculate average validation loss end of the epoch
avg_val_loss = torch.tensor([x['batch_val_loss']
for x in validation_step_outputs]).mean()
# calculate average validation accuracy end of the epoch
avg_val_acc = torch.tensor([x['batch_val_acc']
for x in validation_step_outputs]).mean()
# log the metrics for pytorch lightning progress bar and any further processing
self.log('val_loss', avg_val_loss, prog_bar=True)
self.log('val_acc', avg_val_acc, prog_bar=True)
def configure_optimizers(self):
# adam optimiser
optimizer = optim.Adam(self.parameters(), lr=self.hparams.learning_rate)
# learning rate reducer scheduler
scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer, mode='min', factor=0.5, patience=10, min_lr=1e-15, verbose=True)
# scheduler reduces learning rate based on the value of val_loss metric
return {"optimizer": optimizer,
"lr_scheduler": {"scheduler": scheduler, "interval": "epoch", "frequency": 1, "monitor": "val_loss"}}
3. Web 应用
我们的web应用程序有几个已定义的路由。下面的程序处理输入视频。当用户从网页中提交视频进行分析时,该路由将被调用。
# route definition for video upload for analysis
@app.route('/analyze/' )
def analyze(filename):
# invokes method analyse_video
return Response(analyse_video(pose_detector, lstm_classifier, filename), mimetype='text/event-stream')
4. 视频分析
一旦我们的web应用程序接收到用户发来的视频,
- 下面的函数对视频进行解析,调用:关键点检测调用Dectron2,动作分类调用LSTM。你可以看到,我们已经使用
' buffer_window '来存储帧的32个连续的关键点结果,同样也用于推断动作类。 - 接下来,我们使用OpenCV读取输入视频,并根据分类结果和姿态估计结果创建输出视频
如果你想要一个更高的FPS速率用于视频分析,你可以为SKIP_FRAME_COUNT配置一个更高的值。
# how many frames to skip while inferencing
# configuring a higher value will result in better FPS (frames per rate), but accuracy might get impacted
SKIP_FRAME_COUNT = 0
# analyse the video
def analyse_video(pose_detector, lstm_classifier, video_path):
# open the video
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video_path)
# width of image frame
width = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_WIDTH))
# height of image frame
height = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_HEIGHT))
# frames per second of the input video
fps = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS))
# total number of frames in the video
tot_frames = int(cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT))
# video output codec
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'mp4v')
# extract the file name from video path
file_name = ntpath.basename(video_path)
# video writer
vid_writer = cv2.VideoWriter('res_{}'.format(
file_name), fourcc, 30, (width, height))
# counter
counter = 0
# buffer to keep the output of detectron2 pose estimation
buffer_window = []
# start time
start = time.time()
label = None
# iterate through the video
while True:
# read the frame
ret, frame = cap.read()
# return if end of the video
if ret == False:
break
# make a copy of the frame
img = frame.copy()
if(counter % (SKIP_FRAME_COUNT+1) == 0):
# predict pose estimation on the frame
outputs = pose_detector(frame)
# filter the outputs with a good confidence score
persons, pIndicies = filter_persons(outputs)
if len(persons) >= 1:
# pick only pose estimation results of the first person.
# actually, we expect only one person to be present in the video.
p = persons[0]
# draw the body joints on the person body
draw_keypoints(p, img)
# input feature array for lstm
features = []
# add pose estimate results to the feature array
for i, row in enumerate(p):
features.append(row[0])
features.append(row[1])
# append the feature array into the buffer
# not that max buffer size is 32 and buffer_window operates in a sliding window fashion
if len(buffer_window) < WINDOW_SIZE:
buffer_window.append(features)
else:
# convert input to tensor
model_input = torch.Tensor(np.array(buffer_window, dtype=np.float32))
# add extra dimension
model_input = torch.unsqueeze(model_input, dim=0)
# predict the action class using lstm
y_pred = lstm_classifier(model_input)
prob = F.softmax(y_pred, dim=1)
# get the index of the max probability
pred_index = prob.data.max(dim=1)[1]
# pop the first value from buffer_window and add the new entry in FIFO fashion, to have a sliding window of size 32.
buffer_window.pop(0)
buffer_window.append(features)
label = LABELS[pred_index.numpy()[0]]
#print("Label detected ", label)
# add predicted label into the frame
If label is not None:
cv2.putText(img, 'Action: {}'.format(label),
(int(width-400), height-50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_COMPLEX, 0.9, (102, 255, 255), 2)
# increment counter
counter += 1
# write the frame into the result video
vid_writer.write(img)
# compute the completion percentage
percentage = int(counter*100/tot_frames)
# return the completion percentage
yield "data:" + str(percentage) + "\n\n"
analyze_done = time.time()
print("Video processing finished in ", analyze_done - start)
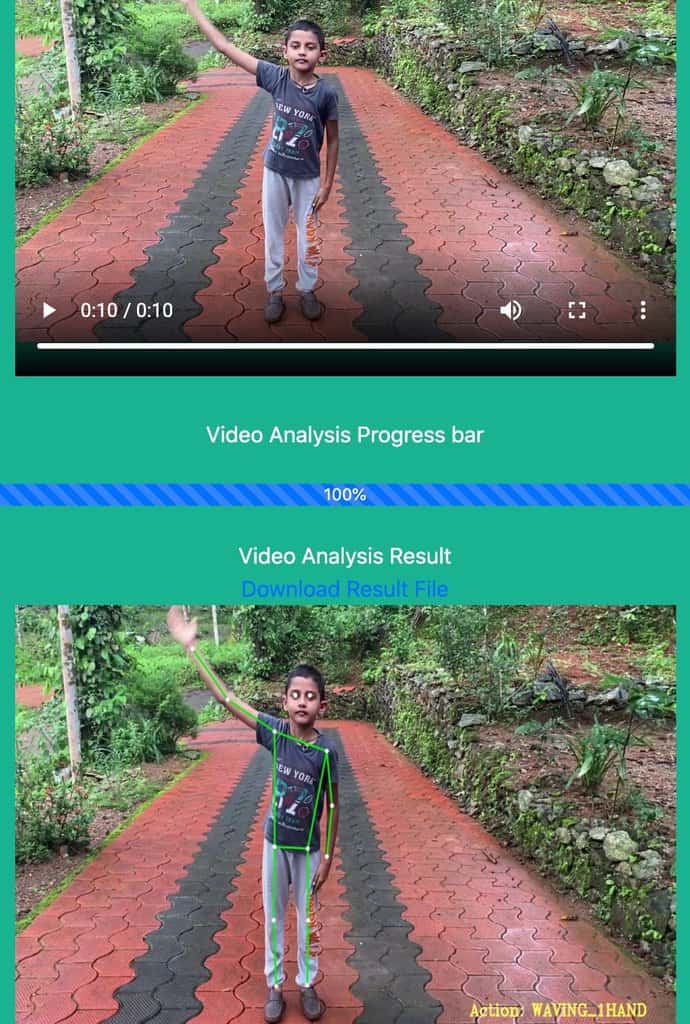
应用程序运行结果
结论
- 学习了所有与人类行为识别有关的知识,也了解了它们的各种应用
- 接下来,我们讨论了如何创建用于动作识别的应用程序。
- 当我们详细介绍了Detectron2和LSTM的性能后,您很清楚我们为什么选择它们作为我们的解决方案。
- 然后,您学习了使用PyTorch Lightning根据关键点训练LSTM模型进行动作分类。你看到了32帧连续序列如何帮助识别特定的动作。
- 然后我们使用Detectron2和LSTM的组合进行推理。您了解到,所显示的结果实际上是由在输入视频上注释的推理管道检测到的操作。
- 理解为什么FPS必须为实时视频流推断而优化。为此,您探索了各种方法,如模型的修剪和量化、间隔跳过帧和推断,以及多线程。
- 接下来,您详细研究了应用程序中所有重要组件的给定代码。
- 最后,我们构建了一个基于flask的示例web应用程序,用于对任何视频输入进行推理。



![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-EDH9DXeY-1653124688436)(https://learnopencv.com/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-03e64c7a975c61e3f419ad675e3c51ca_l3.png)]](http://img.e-com-net.com/image/info8/c01477f3d4c042aca5e72e04aa0c19b9.jpg)