利用python求解tsp问题
我使用的TSP数据集在这里
TSP数据集
用到的python库有这些
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import re
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
我使用的是具有51个城市的数据集,一开始要对其进行数据上的整理(因为它每个城市的x,y轴都挤在了一个单元格里面)
整理的代码如下
1.整理excel表格
df=pd.read_excel(r'C:\Users\17115\Desktop\校赛A题\tsp.xlsx')
# print(df)
#将csv一列数据挤在了一起将其拆分
#创建数组
f=np.zeros((51,3))
c=0
for i in range(0,51,1):
#利用正则表达式拆开数据,分别放到不同的单元格里面
k=re.findall(r'\d+(?:\.\d+)?', df["a"][i])
f[c][0]=k[0]
f[c][1] = k[1]
f[c][2] = k[2]
c=c+1
# print(f)
#将f写入新的xslx当中,numpy不能使用直接使用toexcel
data=pd.DataFrame(f)
data.to_excel(r'C:\Users\17115\Desktop\1.xlsx',index=0)
2.整理好excel表格以后,计算距离矩阵(matrix使用了全局变量因为,有个juli函数会调用)
#全局变量
df1 = pd.read_excel(r'C:\Users\17115\Desktop\1.xlsx')
matrix = np.zeros((51, 51))
for i in range(0, 51, 1):
for j in range(0, 51, 1):
matrix[i][j] = np.sqrt((df1[1][i] - df1[1][j]) ** 2 + (df1[2][i] - df1[2][j]) ** 2)
print(df1)
def juli(a,b):
return matrix[a][b]
通过蒙特卡罗算法
3.主函数,生成100000个随机解进行比较,求出最优路径
#创建数组
f=np.zeros((51,3))
c=0
for i in range(0,51,1):
k=re.findall(r'\d+(?:\.\d+)?', df["a"][i])
f[c][0]=k[0]
f[c][1] = k[1]
f[c][2] = k[2]
c=c+1
# print(f)
#将f写入新的xslx当中,numpy不能使用直接使用toexcel
data=pd.DataFrame(f)
data.to_excel(r'C:\Users\17115\Desktop\1.xlsx',index=0)
#初始化最短路径
min_result=float("inf")
min_path=np.arange(0,51,1)
#并且要在末尾添加一个返回值
min_path=np.append(min_path,min_path[0])
#蒙特卡罗模拟次数
N=1000
for i in range(1,N,1):
#初始化,走过的路程为0
walk=0
s=np.arange(0,51,1)
# print(s)
random.shuffle(s)
# print(s[0])
#调用函数,更新走过的路程
for i in range(0,50,1):
walk=walk+juli(s[i],s[i+1])
#加上最后一个城市返回第一个城市的距离
walk=walk+juli(s[i],s[0])
# print("i" + str(i))
if walk<min_result:
min_result=walk
min_path=s
#最后一个城市要回到第一个城市,添加path(0),构成封闭
# m=min_path.tolist()
# print(s[0])
# m=m.append(s[0])
# print(type(m))
# print("s[0]"+str(s[0]))
#np.append()
min_path=np.append(min_path,s[0])
#输出结果
print("输出的路径为:")
print(min_path)
print("输出的结果为:")
print(min_result)
##作图
#利用坐标作图
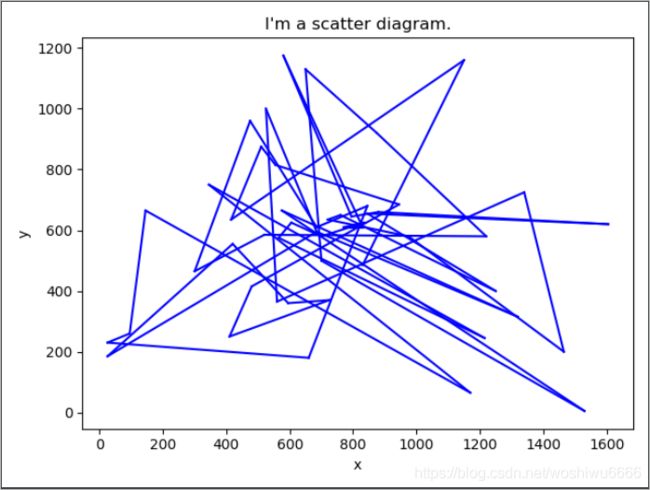
plt.title("I'm a scatter diagram.")
# plt.xlim(xmax=10,xmin=0)
# plt.ylim(ymax=10,ymin=0)
#箭头
# plt.annotate("(3,6)", xy = (3, 6), xytext = (4, 5), arrowprops = dict(facecolor = 'black', shrink = 0.1))
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
for i in range(0,50,1):
# plt.plot([[df1[1][min_path[i]],df1[1][min_path[i+1]]]],[[df1[2][min_path[i]],df1[2][min_path[i+1]]]],'k-',lw=1)
# print([[df1[1][min_path[i]],df1[1][min_path[i+1]]]])
# print([[df1[2][min_path[i]],df1[2][min_path[i+1]]]])
plt.plot([df1[1][min_path[i]],df1[1][min_path[i+1]]],[df1[2][min_path[i]],df1[2][min_path[i+1]]],color='b')
# plt.plot([[df1[1][min_path[i]],df1[1][min_path[i+1]]]],[[df1[2][min_path[i]],df1[2][min_path[i+1]]]], color='b')
plt.show()
最优路径为
[17 7 14 24 3 33 21 41 20 22 11 34 46 26 35 42 16 30 15 43 29 38 25 45
5 13 50 39 6 31 48 23 27 47 37 49 2 1 9 19 10 4 0 36 44 32 40 28
12 18 8 17]
路径长度为
25436.257985759978
再使用模拟退火算法去求解
模拟退火的参数设置如下
#模拟退火参数初始化
T=1000#初始化温度
MAX=1000#最大迭代次数
MAX1=500#每个温度下的迭代次数
alpfa=0.95#温度衰减系数
代码如下
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import re
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import random
import math
#全局变量
df1 = pd.read_excel(r'C:\Users\17115\Desktop\1.xlsx')
matrix = np.zeros((51, 51))
for i in range(0, 51, 1):
for j in range(0, 51, 1):
matrix[i][j] = np.sqrt((df1[1][i] - df1[1][j]) ** 2 + (df1[2][i] - df1[2][j]) ** 2)
# print(df1)
#生成新路径的函数
def gen_new_path(path):
#随机选择两种方式产生新路径
p1=0.33#使用交换法产生新路径概率
p2=0.33#使用位移法产生新路径概率
r=random.random()#生成一个0-1之间的随机数
# 使用交换法生成路径
if r<p1:
#生成0-50的随机整数
c1=random.randint(0,50)
# 生成0-50的随机整数
c2= random.randint(0, 50)
#python数组赋值是共用??
path1=path
k=path1[c1]
path1[c1]=path[c2]
path1[c2]=k
# 使用移位法产生新路径
#这个好像没有用
elif r<p1+p2:
path1=0
c1=random.randint(0,50)
c2 = random.randint(0, 50)
c3 = random.randint(0, 50)
list=[c1,c2,c3]
list.sort()
c1=list[0]
c2=list[1]
c3=list[2]
#利用切片分段
#最后那个值不一定与它前面的那个起点相同
tem1=path[0:c1]
tem2=path[c1:c2]
tem3=path[c2:c3]
tem4=path[c3:51]
path1=np.append(path1,tem1)
path1=np.append(path1,tem3)
path1 = np.append(path1, tem2)
path1 = np.append(path1, tem4)
path1 = path1[1:52]
else:
path1=0
#随机数(0,50)取50,后面的j有可能等于52,而序列为0-51(52个数),52超出范围
c1=random.randint(0,50)
c2 = random.randint(0, 50)
if c1>c2:
tem=c2
c2=c1
c1=tem
tem1=path[0:c1]
tem2=path[c1:c2]
#对tem2进行fliplr操作,左右翻转
#翻转这里有问题
f=c2-c1+1
j=c2-1
for i in (c1,(int)(f/2),1):
k = path[i]
path[i] = path[j]
path[j] = k
j = j - 1
tem3=path[c2:52]
path1 = np.append(path1, tem1)
path1 = np.append(path1, tem2)
path1 = np.append(path1, tem3)
path1=path1[1:52]
# print("path1:")
# print(path1)
# print(path1.shape())
return path1
#计算距离函数
def caculate(path0):
walk=0
# print("path0:")
# print(path0)
for i in range(0,50,1):
walk=walk+matrix[path0[i],path0[i+1]]
#加上最后一个城市返回第一个城市的距离
walk=walk+matrix[path0[i],path0[0]]
return walk
#模拟退火参数初始化
T=1000#初始化温度
MAX=1000#最大迭代次数
MAX1=500#每个温度下的迭代次数
alpfa=0.95#温度衰减系数
#初始化最短路径
min_result=float("inf")
result0=float("inf")
min_path=np.arange(0,51,1)
# min_path=np.append(min_path,0)
path0=min_path
#模拟退火过程
for i in range(1,MAX,1):
for j in range(1,MAX1,1):
#拿path0去生成新的路径,距离
#传0到50进去,51不用传进去
path1=gen_new_path(path0[0:51])
# print(path1)
path1=np.append(path1,path1[0])
# print("path1:")
# print(path1)
result=caculate(path1)
#与前一个解的最小距离进行比较
if result<result0:
path0=path1
result0=result
else:
#计算不符合if中的条件,接收新解的概率
p=math.exp(-(result-min_result)/T)
if random.random()<p:
path0=path1
result0 = result
#与前面所有解中的最小距离进行比较
if result0<min_result:
min_result=result0
min_path=path0
T=alpfa*T
#输出最优路径
print("最优路径:")
print(min_path)
#输出最优距离的结果
print("最优距离:")
print(min_result)
#作图
#利用坐标作图
plt.title("I'm a scatter diagram.")
plt.xlabel("x")
plt.ylabel("y")
#一共有51个城市,52个点
for i in range(0,51,1):
plt.plot([df1[1][min_path[i]],df1[1][min_path[i+1]]],[df1[2][min_path[i]],df1[2][min_path[i+1]]],color='b')
plt.show()
最优路径
[45 32 17 18 44 3 22 29 15 49 30 1 34 26 31 13 43 9 42 11 21 20 40 35
14 28 6 41 16 46 2 25 0 48 33 23 36 47 8 37 5 10 4 27 39 38 24 12
50 19 7 34]
最优距离
20413.542699599373