动手学习pytorch之【CNN】——基础模型代码实现
Convolutional-NN
Simple-CNN
如果想看原理的话,请看我的同专栏下的文章
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
# 自定义的二维互相关操作
def corr2d(X, K):
h, w = K.shape
Y = torch.zeros((X.shape[0] - h + 1, X.shape[1] - w + 1))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]):
for j in range(Y.shape[1]):
Y[i, j] = (X[i:i + h, j:j + w] * K).sum()
return Y
# 自定义卷积层
class Conv2D(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, kernel_size): # kernel_size 是二维的
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(kernel_size))
self.bias = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1)) # 广播
def forward(self, x):
return corr2d(x, self.weight) + self.bias
# Part A 单通道卷积
X = torch.ones((6, 8))
X[:, 2:6] = 0
K = torch.tensor([[1.0, -1.0]])
Y = corr2d(X, K) # 目标值
# 二维卷积层一般都使用四维输入和输出格式(批量大小、通道、高度、宽度)
X = X.reshape((1, 1, 6, 8)) # # 其中批量大小和通道数都为1
Y = Y.reshape((1, 1, 6, 7))
lr = 3e-2 # 学习率
# 实现自学习的卷积核(忽略偏置),这里调用nn模块中的类
# 二维卷积,输入和输出通道都是1,相当于P=D=1,U和V通过结合kernel_size计算得到
# padding = P, stride = S, output: ( − + 2) / + 1
conv2d = nn.Conv2d(1, 1, kernel_size=(1, 2), bias=False)
for i in range(10):
Y_hat = conv2d(X)
l = (Y_hat - Y) ** 2
conv2d.zero_grad()
l.sum().backward()
# 迭代卷积核,注意要data
# 之前都是直接updatar.step(),因为迭代器中有根据grad更新参数的代码
conv2d.weight.data[:] -= lr * conv2d.weight.grad
if (i + 1) % 2 == 0:
print(f'epoch {i + 1}, loss {l.sum():.3f}')
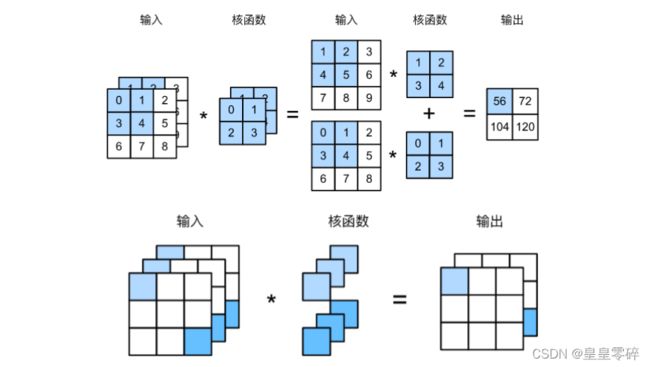
# Part B 多通道卷积
# 实现多输入通道的互相关操作,遍历每个通道维度后相加
def corr2d_multi_in(X, K):
return sum(d2l.corr2d(x, k) for x, k in zip(X, K))
# 实现多输出通道的互相关操作,将每组卷积核卷积后的结果拼接起来
def corr2d_multi_in_out(X, K):
# 沿着一个新维度对输入张量序列进行连接, dim=0指第0维(如1*2*2 拼接成 n*2*2)
return torch.stack([corr2d_multi_in(X, k) for k in K], 0)
# 用全连接层实现1*1卷积
def corr2d_multi_in_out_1x1(X, K):
c_i, h, w = X.shape # torch.Size([3, 3, 3])
c_o = K.shape[0] # torch.Size([2, 3, 1, 1])
X = X.reshape((c_i, h * w)) # torch.Size([3, 9])
K = K.reshape((c_o, c_i)) # torch.Size([2, 3])
# 全连接层中的矩阵乘法
Y = torch.matmul(K, X)
return Y.reshape((c_o, h, w)) # torch.Size([2, 9]) / 2*(3*3)
X = torch.normal(0, 1, (3, 3, 3)) # in_channel = 3
K = torch.normal(0, 1, (2, 3, 1, 1)) # out_channel = 2
Y1 = corr2d_multi_in_out_1x1(X, K)
Y2 = corr2d_multi_in_out(X, K)
assert float(torch.abs(Y1 - Y2).sum()) < 1e-6
# Part C 汇聚层
def pool2d(X, pool_size, mode='max'):
p_h, p_w = pool_size
Y = torch.zeros((X.shape[0] - p_h + 1, X.shape[1] - p_w + 1))
for i in range(Y.shape[0]):
for j in range(Y.shape[1]):
if mode == 'max':
Y[i, j] = X[i: i + p_h, j: j + p_w].max()
elif mode == 'avg':
Y[i, j] = X[i: i + p_h, j: j + p_w].mean()
return Y
# 默认情况下深度学习框架中的步幅与汇聚窗口的大小相同
X = torch.arange(16, dtype=torch.float32).reshape((1, 1, 4, 4))
pool2d = nn.MaxPool2d((2, 3), stride=(2, 3), padding=(0, 1)) # 手动设置
Lanet模型实现:(这里暂且去掉最后一层高斯激活,用到了GPU)
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-sybPqgnP-1650811705618)(C:\Users\86130\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220423183942117.png)]
net = nn.Sequential( # (M-K+2P)/S+1
nn.Conv2d(1, 6, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.Sigmoid(), # C1: 6@28*28
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # S2: 6@14*14
nn.Conv2d(6, 16, kernel_size=5), nn.Sigmoid(), # C3: 16@10*10
nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2), # S4: 16@5*5
nn.Flatten(), # 展平,以进行全连接 1*400
nn.Linear(16*5*5, 120), nn.Sigmoid(), # 全连接层F5: 400*120
nn.Linear(120, 84), nn.Sigmoid(), # 全连接层F6: 120*84
nn.Linear(84, 10)) # 输出out: 84*10
# 使用GPU计算模型在数据集上的精度
def evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, data_iter, device=None):
if isinstance(net, nn.Module):
net.eval() # 设置为评估模式
if not device:
device = next(iter(net.parameters())).device
# 正确预测的数量,总预测的数量
metric = d2l.Accumulator(2)
with torch.no_grad():
for X, y in data_iter:
if isinstance(X, list):
# BERT微调所需的
X = [x.to(device) for x in X]
else:
X = X.to(device)
y = y.to(device)
metric.add(d2l.accuracy(net(X), y), y.numel())
return metric[0] / metric[1]
# 用GPU训练模型
def train_ch(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, device):
def init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear or type(m) == nn.Conv2d:
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(m.weight)
net.apply(init_weights)
print('training on', device)
net.to(device) # z
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=lr)
loss = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
animator = d2l.Animator(xlabel='epoch', xlim=[1, num_epochs],
legend=['train loss', 'train acc', 'test acc'])
timer, num_batches = d2l.Timer(), len(train_iter)
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# 训练损失之和,训练准确率之和,样本数
metric = d2l.Accumulator(3)
net.train()
for i, (X, y) in enumerate(train_iter):
timer.start()
optimizer.zero_grad()
X, y = X.to(device), y.to(device)
y_hat = net(X)
l = loss(y_hat, y)
l.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
metric.add(l * X.shape[0], d2l.accuracy(y_hat, y), X.shape[0])
timer.stop()
train_l = metric[0] / metric[2]
train_acc = metric[1] / metric[2]
if (i + 1) % (num_batches // 5) == 0 or i == num_batches - 1:
animator.add(epoch + (i + 1) / num_batches,
(train_l, train_acc, None))
test_acc = evaluate_accuracy_gpu(net, test_iter)
animator.add(epoch + 1, (None, None, test_acc))
print(f'loss {train_l:.3f}, train acc {train_acc:.3f}, '
f'test acc {test_acc:.3f}')
print(f'{metric[2] * num_epochs / timer.sum():.1f} examples/sec '
f'on {str(device)}')
X = torch.rand(size=(1, 1, 28, 28), dtype=torch.float32)
for layer in net:
X = layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__, 'output shape: \t', X.shape)
batch_size = 256
train_iter, test_iter = load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size=batch_size)
lr, num_epochs = 0.9, 10
train_ch(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())