【论文阅读】ResNet——Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition
文章目录
-
-
- 论文阅读
-
- ResNetv2
- 模型图示
- 代码实现
-
- model
- train
- predict
- batch_predict
- 实验结果
-
论文阅读
感谢p导
有错误希望可以指正
论文中提出了残差思想、两种残差块
随着AlexNet出现之后,大家都开始来堆叠网络
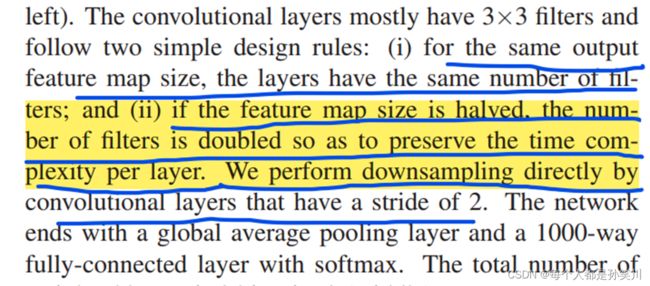
VGG得到的结果表明深度会提高准确率

之后在加深过程中碰到了一系列问题,梯度消失和梯度爆炸,GoogLeNet中为了解决这个问题导致的浅层部分训练不到添加了两个辅助分类器来计算loss,可以使用BN来进行解决。
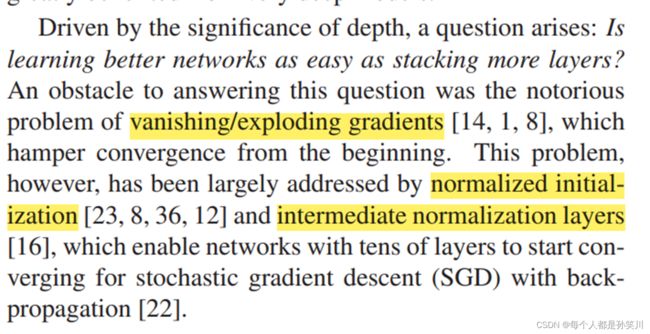
另外一个问题就是退化,这个问题不是由过拟合导致的,因为在训练集和测试集上面都出现了准确率比不了浅层网络的结果。

20层的网络准确率比56层的网络准确率还要高,这个在意料之外,如果后面的36层什么都不做,只是一个恒等映射的话,也不会出现准确率下降的结果,为了解决这个问题手动给它添加一个恒等映射,也就是残差连接(在深层网络中即使没有获得更深层次的特征,也不会让网络丢失数据的原本模样)

之后有一篇论文在讲ResNet是多个简单网络的集合

ResNetv2
2016年何凯明大神又改进了一下
ResNetv2
模型图示
代码实现
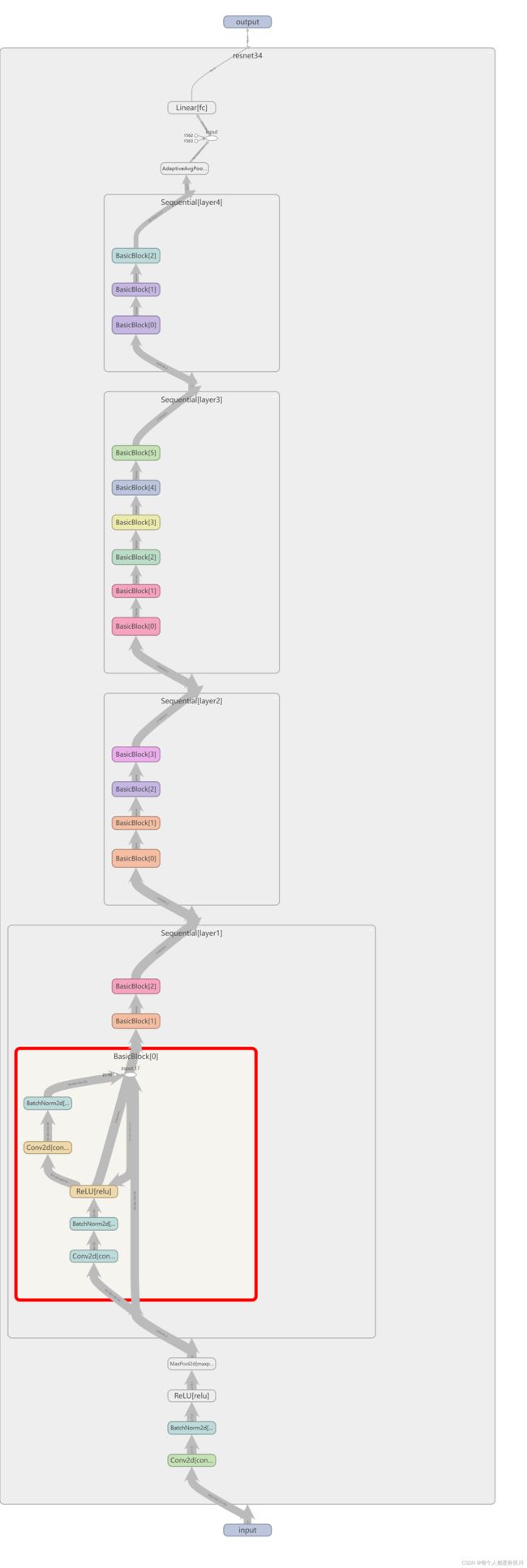
model
构建两种残差块结构BasicBlock、Bottleneck,之后构建resnet时候按照上面的表进行循环堆叠不同残差块即可
import torch.nn as nn
import torch
# 18、34层
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
expansion = 1
# expansion对应每个复合卷积层中卷积核个数有没有发生变化,18层和34层的每个卷积结构里面的卷积核个数没有变化:64、128、256、512
# 但是50、101、152对应的每个复合卷积层中卷积核个数会发生变化,第一个和第二个一样,第三个为1、2的4倍,在另一个残差块中expansion定义为4
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
# in_channel、out_channel对应每复合卷积层的输入通道数、输出通道数(卷积核个数)
# conv_3、4、5中第一个残差块都需要进行downsample,在虚线中。将输入的特征矩阵进行降维操作,进行相加
# stride=1对应实线的残差快(output=input)。=2时候对应虚线残差块(output=input/2)
# 也就是conv_2中stride==1,conv_2不需要进行下采样操作,conv_3、4、5都需要将stride设置为2
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
self.stride=stride
# BN放在conv和relu中间
# 不使用bias、因为要进行正则化操作
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.downsample = downsample
# 论文中进行下采样操作,设置搭配downsample参数进行操作
def forward(self, x):
# shortcut connection
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
# 50、101、152层
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion = 4
# 因为每个卷积层的最后一个卷积,为前面卷积核个数的4倍,这里设置为4
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, stride=1, downsample=None):
super(Bottleneck, self).__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel,
kernel_size=3, stride=stride, bias=False, padding=1)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel)
self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=out_channel, out_channels=out_channel*self.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=1, bias=False) # 升维
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channel*self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = downsample
def forward(self, x):
identity = x
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
# block为不同的残差结构,blocks_num为对应残差结构的数量,见论文列表
# 分类个数
def __init__(self,
block,
blocks_num,
num_classes=1000,
include_top=True,
):
super(ResNet, self).__init__()
self.include_top = include_top
self.in_channel = 64
# 224*224*3 转换为 112*112*64,之后通过最大池化变成56*56*64,进入复合卷积层
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, self.in_channel, kernel_size=7, stride=2,
padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(self.in_channel)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, blocks_num[0])
# 也就是第一个复合卷积层中stride==1,不需要进行下采样操作,第二三四个复合卷积层都需要将stride设置为2
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, blocks_num[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, blocks_num[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, blocks_num[3], stride=2)
if self.include_top:
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1)) # output size = (1, 1)
self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes) #通道数
# 卷积层初始化操作
for m in self.modules():
if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
nn.init.kaiming_normal_(
m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')
def _make_layer(self, block, channel, block_num, stride=1):
# channel为每个层第一个卷积操作的卷积核个数
# block_num为该层多少个残差结构(复合卷积层)
downsample = None
# 如果stride==2,对应的是后面三个复合卷积层,由于层与层之间的通道数和长宽不同,也需要进行下采样操作
# 如果expansion不为1,则说明在复合卷积层中进行了降维和升维操作,输出特征图的通道数与输入特征图的通道数不同,需要进行1*1卷积核的提升通道数和每个通道的降维
# 18,34层的第一个层会直接跳过这步
if stride != 1 or self.in_channel != channel * block.expansion:
# 用1*1卷积核,将每个通道的长和宽进行减半以及通道数量的变化
downsample = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(self.in_channel, channel * block.expansion,
kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(channel * block.expansion))
layers = []
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel,
downsample=downsample, stride=stride))
# 除了第一层之外剩下的in_channel为channel * block.expansion
# 如果是bottleneck残差块的话,例如:第一个残差块输出通道为256,第二个残差块的第一个卷积层的输出通道又要变成64,调整卷积层的输入通道为256
self.in_channel = channel * block.expansion
# 不需要下采样操作了
for _ in range(1, block_num):
layers.append(block(self.in_channel, channel))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
if self.include_top:
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
def resnet34(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth
return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet50(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
def resnet101(num_classes=1000, include_top=True):
# https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth
return ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], num_classes=num_classes, include_top=include_top)
train
import os
import json
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
from torchvision import transforms, datasets
from tqdm import tqdm
from model import resnet34
def main():
batch_size = 16
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("using {} device.".format(device))
# number of workers,windows下可能会有bug,碰到的话不给num_workers赋值即可
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8])
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(224),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])}
data_root = os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../"))
image_path = os.path.join(data_root, "data_set", "flower_data")
assert os.path.exists(
image_path), "{} path does not exist.".format(image_path)
train_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "train"),
transform=data_transform["train"])
validate_dataset = datasets.ImageFolder(root=os.path.join(image_path, "val"),
transform=data_transform["val"])
train_num = len(train_dataset)
val_num = len(validate_dataset)
print("using {} images for training, {} images for validation.".format(
train_num, val_num))
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True,
num_workers=nw)
validate_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(validate_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False,
num_workers=nw)
# {'daisy':0, 'dandelion':1, 'roses':2, 'sunflower':3, 'tulips':4}
flower_list = train_dataset.class_to_idx
cla_dict = dict((val, key) for key, val in flower_list.items())
# write dict into json file
json_str = json.dumps(cla_dict, indent=4)
with open('class_indices.json', 'w') as json_file:
json_file.write(json_str)
net = resnet34()
model_weight_path = "./resnet34-pre.pth"
net.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_weight_path, map_location=device))
in_channel = net.fc.in_features
net.fc = nn.Linear(in_channel, 5)# 误分类使用最后的为5个
net.to(device)
loss_function = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=0.0001)
epochs = 10
best_acc = 0.0
save_path = './resNet34.pth'
train_steps = len(train_loader)
for epoch in range(epochs):
# train
net.train()
running_loss = 0.0
train_bar = tqdm(train_loader)
for data in train_bar:
images, labels = data
optimizer.zero_grad()
logits = net(images.to(device))
loss = loss_function(logits, labels.to(device))
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
running_loss += loss.item()
train_bar.desc = "train epoch[{}/{}] loss:{:.3f}".format(epoch + 1,
epochs,
loss)
# validate
net.eval()
acc = 0.0 # accumulate accurate number / epoch
with torch.no_grad():
val_bar = tqdm(validate_loader)
for val_data in val_bar:
val_images, val_labels = val_data
outputs = net(val_images.to(device))
# loss = loss_function(outputs, test_labels)
predict_y = torch.max(outputs, dim=1)[1]
acc += torch.eq(predict_y, val_labels.to(device)).sum().item()
val_bar.desc = "valid epoch[{}/{}]".format(epoch + 1,
epochs)
val_accurate = acc / val_num
print('[epoch %d] train_loss: %.3f val_accuracy: %.3f' %
(epoch + 1, running_loss / train_steps, val_accurate))
if val_accurate > best_acc:
best_acc = val_accurate
torch.save(net.state_dict(), save_path)
print('Finished Training')
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
predict
import os
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from model import resnet34
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
# load image
img_path = "./tulip.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
json_file = open(json_path, "r")
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
# create model
model = resnet34(num_classes=5).to(device)
# load model weights
model.load_state_dict(torch.load("./resnet34-pre.pth", map_location=device))
# prediction
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
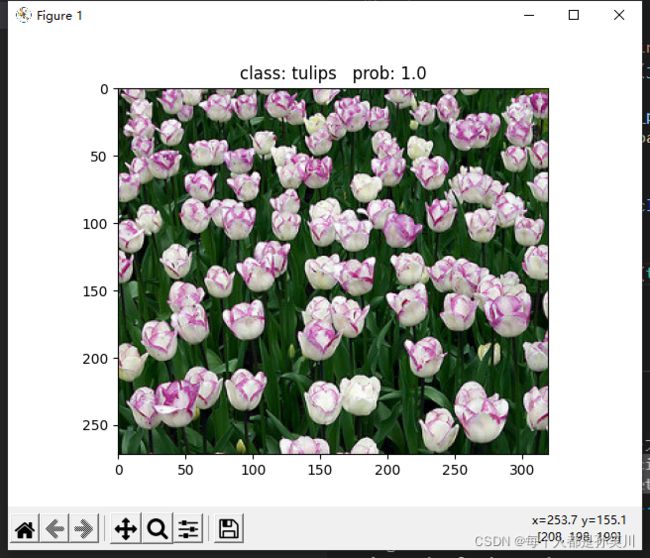
print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
print(print_res)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
batch_predict
import os
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
from model import resnet34
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize(256),
transforms.CenterCrop(224),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])
# load image
img_path_list = ["../tulip.jpg", "../rose.jpg"]
img_list = []
for img_path in img_path_list:
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
img = data_transform(img)
img_list.append(img)
# batch img
batch_img = torch.stack(img_list, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
json_file = open(json_path, "r")
class_indict = json.load(json_file)
# create model
model = resnet34(num_classes=5).to(device)
# load model weights
weights_path = "./resNet34.pth"
assert os.path.exists(weights_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(weights_path)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights_path, map_location=device))
# prediction
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = model(batch_img.to(device)).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=1)
probs, classes = torch.max(predict, dim=1)
for idx, (pro, cla) in enumerate(zip(probs, classes)):
print("image: {} class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(img_path_list[idx],
class_indict[str(cla.numpy())],
pro.numpy()))
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()