IOU GIOU DIOU CIOU 及代码实现
总体发展过程:
IOU
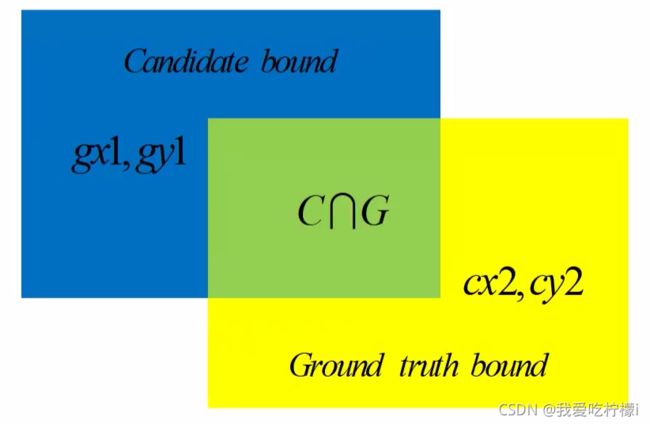
IOU(交并比)顾名思义就是两个框的交集除以他们的并集。
IOU Loss:IOU Loss = 1 -IOU(比较常用)
IOU 的优点:1.能够很好的反应重合的程度 2.具有尺度不变性
缺点: 当不相交时候loss为0 (IOU Loss = 1 - IOU)
GIOU
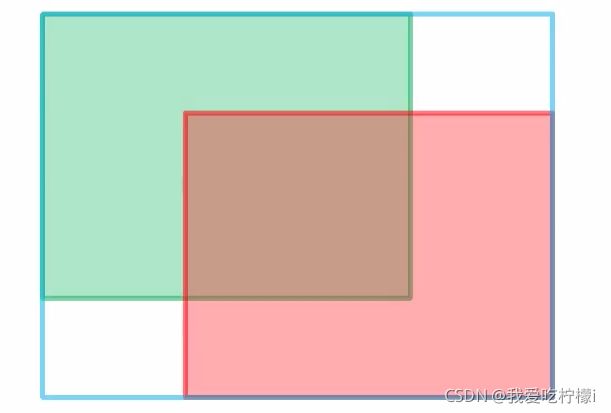
如图绿色边界框为真实的边界框,红色边界框为网络预测的边界框,蓝色边界框为用最小的矩形把两个边界框给框住。 ![]() = 蓝色目标边界框面积。u=两个边界框并集的面积。取两个极限的例子,当两个目标边界框重合时,
= 蓝色目标边界框面积。u=两个边界框并集的面积。取两个极限的例子,当两个目标边界框重合时,![]() - u = 0。此时GIOU = IOU。此时IOU = 1。当两个边界框无穷远时
- u = 0。此时GIOU = IOU。此时IOU = 1。当两个边界框无穷远时![]() 趋近于1 ,GIOU = IOU - 1,此时IOU = 0,所以此时的GIOU = -1。GIOU的范围在-1到1之间。对比IOU当两个目标框不相交时也能提供损失。
趋近于1 ,GIOU = IOU - 1,此时IOU = 0,所以此时的GIOU = -1。GIOU的范围在-1到1之间。对比IOU当两个目标框不相交时也能提供损失。
GIOU Loss:1 - GIOU
特殊情况下GIOU会变为IOU:
DIOU:
IOU和GIOU有两个很大的缺点:1.收敛特别慢 2.回归的不够准确。为此作者提出了DIOU
DIOU能够更好地反映两个框的相交情况,将其用于计算网络的损失函数可以直接最小化两框之间的距离,收敛速度更快。
其中![]() 代表两者之间的欧氏距离。
代表两者之间的欧氏距离。![]() 为黑色框代表预测的边界框,
为黑色框代表预测的边界框,![]() 为绿色框代表真实框。
为绿色框代表真实框。![]() 。
。![]() 为两个边界框最小外界框的对角线的长度。同GIOU的计算方法,可以算出DIOU 的取值范围。
为两个边界框最小外界框的对角线的长度。同GIOU的计算方法,可以算出DIOU 的取值范围。
DIOU 损失能够直接最小化两个boxes之间的距离,因此收敛的速度更快。
DIOU Loss: 1 - DIOU
CIOU:
作者认为对于一个优秀的回归定位损失应该考虑到3种几何参数:重叠面积 中心点距离 长宽比。因此作者在DIOU的基础上加上了长宽比。
CIOU Loss = 1 - CIOU
CIOU(D) : 将CIOU中的IOU换成DIOU
代码:
class IOUloss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, reduction="none", loss_type="diou"):
super(IOUloss, self).__init__()
self.reduction = reduction
self.loss_type = loss_type
def forward(self, pred, target):
assert pred.shape[0] == target.shape[0]
pred = pred.view(-1, 4)
target = target.view(-1, 4)
tl = torch.max(
(pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
br = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2)
)
area_p = torch.prod(pred[:, 2:], 1)
area_g = torch.prod(target[:, 2:], 1)
en = (tl < br).type(tl.type()).prod(dim=1)
area_i = torch.prod(br - tl, 1) * en
area_u = area_p + area_g - area_i
iou = (area_i) / (area_u + 1e-16)
#########################################siou#########################################
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心的差距
# ----------------------------------------------------#
center_wh = (pred[:, :2] - target[:, :2]) # 中心距离
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 找到包裹两个框的最小框的左上角和右下角
# ----------------------------------------------------#
b1_wh = pred[:, 2:]
b2_wh = target[:, 2:]
# b1_mins = pred[:, :2] - (pred[:, 2:] / 2) # 预测框的左上角
# b2_mins = target[:, :2] - (target[:, 2:] / 2) # 真实框的左上角
# b1_maxes = pred[:, :2] + (pred[:, 2:] / 2) # 预测框的左上角
# b2_maxes = target[:, :2] + (target[:, 2:] / 2) # 真实框的右下角
# intersect_maxes = torch.min(b1_maxes, b2_maxes) # 交集右下角坐标
intersect_maxes = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2) # 两框右下角最大点(x为基准)
)
# enclose_mins = torch.min(b1_mins, b2_mins)
# enclose_maxes = torch.max(b1_maxes, b2_maxes)
enclose_mins = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2) # 两框左上角最小点(x为基准)
)
enclose_maxes = torch.max(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2) # 两框右下角最大点(x为基准)
)
enclose_wh = torch.max(enclose_maxes - enclose_mins, torch.zeros_like(intersect_maxes)) # torch.zeros_like:产生一个与a相同shape的Tensor.
#########################################siou#########################################
if self.loss_type == "iou":
loss = 1 - iou ** 2
print('loss = ', loss)
elif self.loss_type == "diou": # xywh
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心的距离
# ----------------------------------------------------#
center_distance = torch.sum(torch.pow(center_wh, 2), axis=-1) # x平方+y平方 ρ方(b,bgt)
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算对角线距离
# ----------------------------------------------------#
enclose_diagonal = torch.sum(torch.pow(enclose_wh, 2), axis=-1) # x平方+y平方
diou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / torch.clamp(enclose_diagonal, min=1e-6) # torch.clamp:限制最小值为1e-6
loss = 1 - diou
elif self.loss_type == "giou": # xywh
c_tl = torch.min(
(pred[:, :2] - pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] - target[:, 2:] / 2) # 两框左上角最小点(x为基准)
)
c_br = torch.max(
(pred[:, :2] + pred[:, 2:] / 2), (target[:, :2] + target[:, 2:] / 2) # 两框右下角最大点(x为基准)
)
area_c = torch.prod(c_br - c_tl, 1) # torch.prod:在1维度上,返回 input 张量中所有元素的乘积。
giou = iou - (area_c - area_u) / area_c.clamp(1e-16)
loss = 1 - giou.clamp(min=-1.0, max=1.0) # clamp:限制在-1到1中间
print('loss = ', loss)
elif self.loss_type == "ciou": # xywh
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心的距离
# ----------------------------------------------------#
center_distance = torch.sum(torch.pow(center_wh, 2), axis=-1) # x平方+y平方 ρ方(b,bgt)
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算对角线距离
# ----------------------------------------------------#
enclose_diagonal = torch.sum(torch.pow(enclose_wh, 2), axis=-1) # x平方+y平方
ciou = iou - 1.0 * (center_distance) / torch.clamp(enclose_diagonal, min=1e-6) # torch.clamp:限制最小值为1e-6
# v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(
# pred[:, 2] / torch.clamp(pred[:, 3], min=1e-6)) - torch.atan(target[:, 2] / torch.clamp(target[:, 3], min=1e-6))), 2) # torch.atan:包含输入input张量每个元素的反正切函数。
v = (4 / (math.pi ** 2)) * torch.pow((torch.atan(
b1_wh[..., 0] / torch.clamp(b1_wh[..., 1], min=1e-6)) - torch.atan(
b2_wh[..., 0] / torch.clamp(b2_wh[..., 1], min=1e-6))), 2)
alpha = v / torch.clamp((1.0 - iou + v), min=1e-6)
out = ciou - alpha * v
loss = 1 - out
elif self.loss_type == 'siou':
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# Angle cost
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 计算中心的距离
# ----------------------------------------------------#
sigma = torch.pow(torch.sum(torch.pow(center_wh, 2), axis=-1), 0.5)
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 求h和w方向上的sin比值
# ----------------------------------------------------#
sin_alpha_1 = torch.clamp(torch.abs(center_wh[:, 0]) / torch.clamp(sigma, min=1e-6), min=0, max=1)
sin_alpha_2 = torch.clamp(torch.abs(center_wh[:, 1]) / torch.clamp(sigma, min=1e-6), min=0, max=1)
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# 求门限,二分之根号二,0.707
# 如果门限大于0.707,代表某个方向的角度大于45°
# 此时取另一个方向的角度
# ----------------------------------------------------#
threshold = pow(2, 0.5) / 2
sin_alpha = torch.where(sin_alpha_1 > threshold, sin_alpha_2, sin_alpha_1)
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# alpha越接近于45°,angle_cost越接近于1,gamma越接近于1
# alpha越接近于0°,angle_cost越接近于0,gamma越接近于2
# ----------------------------------------------------#
angle_cost = torch.cos(torch.asin(sin_alpha) * 2 - math.pi / 2)
gamma = 2 - angle_cost
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# Distance cost
# 求中心与外包围举行高宽的比值
# ----------------------------------------------------#
rho_x = (center_wh[:, 0] / torch.clamp(enclose_wh[:, 0], min=1e-6)) ** 2
rho_y = (center_wh[:, 1] / torch.clamp(enclose_wh[:, 1], min=1e-6)) ** 2
distance_cost = 2 - torch.exp(-gamma * rho_x) - torch.exp(-gamma * rho_y)
# ----------------------------------------------------#
# Shape cost
# 真实框与预测框的宽高差异与最大值的比值
# 差异越小,costshape_cost越小
# ----------------------------------------------------#
omiga_w = torch.abs(b1_wh[:, 0] - b2_wh[:, 0]) / torch.clamp(torch.max(b1_wh[:, 0], b2_wh[:, 0]),
min=1e-6)
omiga_h = torch.abs(b1_wh[:, 1] - b2_wh[:, 1]) / torch.clamp(torch.max(b1_wh[:, 1], b2_wh[:, 1]),
min=1e-6)
shape_cost = torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_w), 4) + torch.pow(1 - torch.exp(-1 * omiga_h), 4)
out = iou - 0.5 * (distance_cost + shape_cost)
loss = 1 - out
if self.reduction == "mean":
loss = loss.mean()
elif self.reduction == "sum":
loss = loss.sum()
return loss