【Web开发】Python实现Web表格功能(D-Tale, Pandas, Flask)
Web服务器系列相关文章编写如下:
- 【Web开发】Node.js实现Web服务器(http模块)
- 【Web开发】Node.js实现Web服务器(express模块)
- 【Web开发】Python实现Web服务器(Flask快速入门)
- 【Web开发】Python实现Web服务器(Flask案例测试)
- 【Web开发】Python实现Web服务器(Flask部署上线)
- 【Web开发】Python实现Web服务器(Tornado入门)
- 【Web开发】Python实现Web服务器(Tornado+flask+nginx)
- 【Web开发】Python实现Web服务器(FastAPI)
- 【Web开发】Python实现Web服务器(Bottle)
文章目录
- 1、D-Tale
-
- 1.1 D-Tale简介
- 1.2 D-Tale安装
- 1.3 D-Tale测试
- 2、ngrok代理
-
- 2.1 简介
- 2.2 安装
- 2.3 测试
- 3、Python线程
-
- 3.1 _thread模块
- 3.2 threading模块
- 结语
1、D-Tale
1.1 D-Tale简介
D-Tale 是 Flask 后端和 React 前端的组合,为您提供查看和分析 Pandas 数据结构的简单方法。它与 ipython 笔记本和 python/ipython 终端无缝集成。目前该工具支持 DataFrame、Series、MultiIndex、DatetimeIndex 和 RangeIndex 等 Pandas 对象。
D-Tale 是 SAS 到 Python 转换的产物。最初是基于 SAS功能 insight 的 perl 脚本包装器,现在是基于 Pandas 数据结构的轻量级 Web 客户端。
1.2 D-Tale安装
pip install dtale
# conda
conda install dtale -c conda-forge
# if you want to also use "Export to PNG" for charts
conda install -c plotly python-kaleido
1.3 D-Tale测试
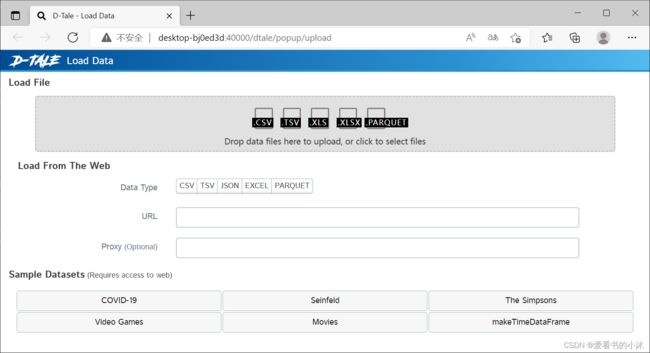
D-Tale支持多种文件格式,包括CSV、TSV、XLS、XLSX。它是一个以Flask 为后端,React 作为前端构建的,通过pip安装即可。数据的导入主要有如下几种方式:
(1)从文件加载数据
(2)从网站加载数据。需要传递网站的链接,可以从中获取 CSV、JSON、TSV 或 Excel 等文件。
(3)加载示例数据集。这些数据集可能需要一些后台下载才能从服务器获取数据集。
- (1)入门例子
import dtale
dtale.show(open_browser=True)
- (2)显示数组
import dtale
import pandas as pd
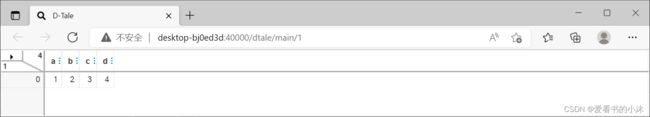
df = pd.DataFrame([dict(a=1,b=2,c=3), dict(a=123.732,b=1.414,c=3.1415)])
dtale.show(df, open_browser=True)
- (3)展示excel文件
import dtale
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_csv('d:/iris.csv')
dtale.show(df, open_browser=True)
- (4)显示网络数据
import dtale
import seaborn as sns
df=sns.load_dataset('planets')
dtale.show(df, ignore_duplicate=True, open_browser=True)
- (5)复杂例子
import dtale
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame([dict(a=1,b=2,c=3)])
# Assigning a reference to a running D-Tale process
d = dtale.show(df)
# Accessing data associated with D-Tale process
tmp = d.data.copy()
tmp['d'] = 4
# Altering data associated with D-Tale process
# FYI: this will clear any front-end settings you have at the time for this process (filter, sorts, formatting)
d.data = tmp
# Shutting down D-Tale process
d.kill()
# using Python's `webbrowser` package it will try and open your server's default browser to this process
d.open_browser()
# There is also some helpful metadata about the process
d._data_id # the process's data identifier
d._url # the url to access the process
d2 = dtale.get_instance(d._data_id) # returns a new reference to the instance running at that data_id
dtale.instances() # prints a list of all ids & urls of running D-Tale sessions
2、ngrok代理
2.1 简介
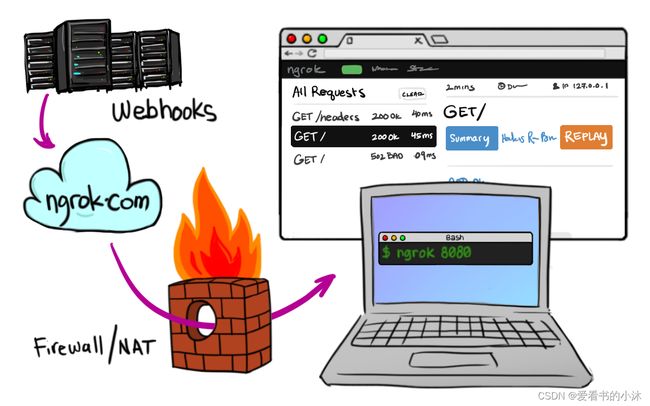
ngrok会在您计算机上的本地Web服务器上创建安全的公共URL(https://yourapp.ngrok.io)。快速迭代,立即反馈,不中断流量。
2.2 安装
-
(2)安装您的Authtoken:
ngrok.com服务的许多高级功能在后面的章节中描述要求您注册一个帐户。 注册后,您需要使用显示在信息中心上的authtoken配置ngrok。 这将授予您访问仅限帐户功能的权限。 ngrok有一个简单的“authtoken”命令,使这很容易。 在引擎盖下,所有的authtoken命令是添加(或修改)authtoken属性在您的ngrok配置文件。
ngrok authtoken <YOUR_AUTHTOKEN>
2.3 测试
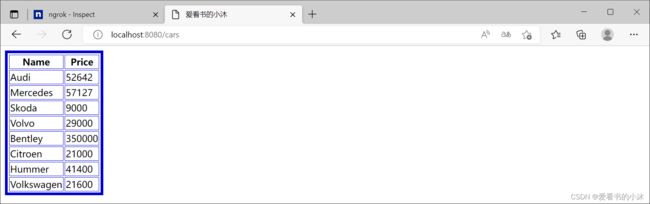
- (1)将本地计算机的端口80上的Web服务器公开到互联网:
ngrok http 8080
- (2)ngrok提供了一个实时的Web UI,您可以在其中内省您的隧道上运行的所有HTTP流量。在启动ngrok之后,只需在Web浏览器中打开http://localhost:4040即可检查请求详细信息。
http://localhost:4040/
http://localhost:8080/cars
3、Python线程
3.1 _thread模块
_thread实现多线程主要通过:
_thread.start_new(执行的方法的名称,当前执行方法需要的参数)
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import _thread
import time
def print_time(thread_name, delay):
count = 0
while count < 5:
time.sleep(delay)
count += 1
print("线程名:{0},当前的时间为:{1}".format(thread_name,
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())))
# 创建两个线程
try:
_thread.start_new_thread(print_time, ("Thread-1", 2))
_thread.start_new_thread(print_time, ("Thread-2", 4))
except:
print("Error :线程无法启动线程")
while 1:
pass
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import _thread
from time import sleep, ctime
loop_times = [4, 2]
def loop_func(nloop, nsec, lock):
print("start loop: {0}, at:{1}".format(nloop, ctime()))
sleep(nsec)
print("end loop: {0}, at :{1}".format(nloop, ctime()))
lock.release() # 这里是释放锁
def main():
print("starting at:{0}".format(ctime()))
loop_locks = []
nloops = range(len(loop_times))
for i in nloops:
lock = _thread.allocate_lock() # 获得线程的本地锁
lock.acquire() # 开始加锁,获得锁并加锁
loop_locks.append(lock) # 项当前的锁集合中添加该锁
for i in nloops:
_thread.start_new(loop_func,(i, loop_times[i], loop_locks[i]))
# 反复检查锁是否被锁住,如果被锁住就一直死循环,否者停止循环检查
for i in nloops:
while loop_locks[i].locked(): pass
print("all DONE at:{0}".format(ctime()))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
3.2 threading模块
更高级的threading模块。
通过threading.Thread(执行的函数,name=“执行线程的名称”,args=(执行函数需要的参数))创建一个可执行的线程。
#!/usr/bin/env python3
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import threading
import time
class Sum:
count = 0
#thread_lock = threading.Lock()
def loop_func():
while Sum.count < 10:
time.sleep(1)
#Sum.thread_lock.acquire() # 使用锁的方式实现线程安全以及同步
Sum.count += 1
current_name = threading.currentThread().getName()
current_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", time.localtime())
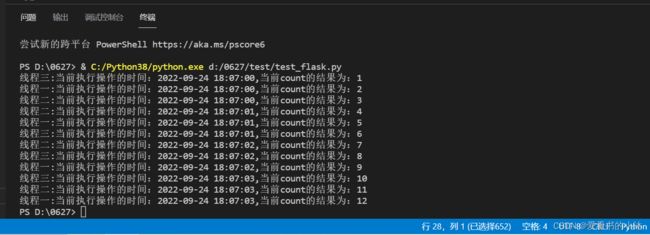
print("{0}:当前执行操作的时间:{1},当前count的结果为:{2}".format(current_name, current_time, Sum.count))
#Sum.thread_lock.release() # 释放锁
def main():
threading.Thread(target=loop_func, name="线程一").start()
threading.Thread(target=loop_func, name="线程二").start()
threading.Thread(target=loop_func, name="线程三").start()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
结语
如果您觉得该方法或代码有一点点用处,可以给作者点个赞,或打赏杯咖啡;╮( ̄▽ ̄)╭
如果您感觉方法或代码不咋地//(ㄒoㄒ)//,就在评论处留言,作者继续改进;o_O???
如果您需要相关功能的代码定制化开发,可以留言私信作者;(✿◡‿◡)
感谢各位大佬童鞋们的支持!( ´ ▽´ )ノ ( ´ ▽´)っ!!!