YOLOV5模型转onnx并推理
YOLOV5模型转onnx并推理
- 模型转onnx
-
- 普通模型转onnx
- yolov5模型转onnx
- onnx 推理
-
- 普通模型
- yolov5模型
-
- 一、推理
- 二、坐标转换
- 三、非极大值抑制
- 四、根据置信度过滤无用框
- 五、画图
- 六、总代码
模型转onnx
普通模型转onnx
- 加载模型,需要是torch.save保存的模型
- 指定输入输出的名字
- 指定输入size
- 导出静态模型
- 导出动态维度模型
import torch
import torch.nn
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 加载模型,需要是torch.save保存的模型
#-------------------------------------------------------
model = torch.load('yolov5s.pt',map_location=torch.device('cpu'))
model.eval()
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 指定输入输出的名字
#-------------------------------------------------------
input_names = ['input']
output_names = ['output']
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 指定输入size
#-------------------------------------------------------
x = torch.randn(1,3,640,640,requires_grad=True)
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 导出静态模型
#-------------------------------------------------------
torch.onnx.export(model,
x,
"model.onnx",
export_params=True,
opset_version=10,
do_constant_folding=True,
input_names=input_names,
output_names=output_names )
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 导出动态维度模型
#-------------------------------------------------------
torch.onnx.export(model,
x,
"model2.onnx",
export_params=True,
opset_version=10,
do_constant_folding=True,
input_names=input_names,
output_names=input_names,
dynamic_axes= {
input_names: {0: 'batch_size', 2 : 'in_width', 3: 'int_height'},
output_names: {0: 'batch_size', 2: 'out_width', 3:'out_height'}})
yolov5模型转onnx
由于yolov5的模型和整个项目相互关联,所以转onnx无法用常规方法,只能用内部的转onnx方法
1.静态模型
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include onnx
2.动态模型
python export.py --weights yolov5s.pt --include onnx --dynamic
动态模型如下图所示
batch、width、height为动态的

onnx 推理
普通模型
x = torch.randn(1,3,640,640,requires_grad=True)
onnx_model = onnxruntime.InferenceSession("model.onnx")
print(onnx_model.get_inputs()[0].name)
inputs = {onnx_model.get_inputs()[0].name: x.cpu().numpy()}
outs = onnx_model.run(None, inputs)
print(outs[0])
yolov5模型
一、推理
1.cv2读取图像并resize
2.图像转BGR2RGB和HWC2CHW
3.图像归一化
4.图像增加维度
5.onnx_session 推理
class YOLOV5():
def __init__(self,onnxpath):
self.onnx_session=onnxruntime.InferenceSession(onnxpath)
self.input_name=self.get_input_name()
self.output_name=self.get_output_name()
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 获取输入输出的名字
#-------------------------------------------------------
def get_input_name(self):
input_name=[]
for node in self.onnx_session.get_inputs():
input_name.append(node.name)
return input_name
def get_output_name(self):
output_name=[]
for node in self.onnx_session.get_outputs():
output_name.append(node.name)
return output_name
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 输入图像
#-------------------------------------------------------
def get_input_feed(self,img_tensor):
input_feed={}
for name in self.input_name:
input_feed[name]=img_tensor
return input_feed
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 1.cv2读取图像并resize
# 2.图像转BGR2RGB和HWC2CHW
# 3.图像归一化
# 4.图像增加维度
# 5.onnx_session 推理
#-------------------------------------------------------
def inference(self,img_path):
img=cv2.imread(img_path)
or_img=cv2.resize(img,(640,640))
img=or_img[:,:,::-1].transpose(2,0,1) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHW
img=img.astype(dtype=np.float32)
img/=255.0
img=np.expand_dims(img,axis=0)
input_feed=self.get_input_feed(img)
pred=self.onnx_session.run(None,input_feed)[0]
return pred,or_img
二、坐标转换
将中心点坐标转换为左上角右下角坐标
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2]
y = np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2
return y
三、非极大值抑制
1.计算框的面积
2.计算相交面积(相交、不相交)
3.计算该框与其它框的IOU,去除掉重复的框,即IOU值大的框
4.IOU小于thresh的框保留下来
#dets: array [x,6] 6个值分别为x1,y1,x2,y2,score,class
#thresh: 阈值
def nms(dets, thresh):
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 计算框的面积
# 置信度从大到小排序
#-------------------------------------------------------
areas = (y2 - y1 + 1) * (x2 - x1 + 1)
scores = dets[:, 4]
keep = []
index = scores.argsort()[::-1]
while index.size > 0:
i = index[0]
keep.append(i)
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 计算相交面积
# 1.相交
# 2.不相交
#-------------------------------------------------------
x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]])
y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0, x22 - x11 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, y22 - y11 + 1)
overlaps = w * h
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 计算该框与其它框的IOU,去除掉重复的框,即IOU值大的框
# IOU小于thresh的框保留下来
#-------------------------------------------------------
ious = overlaps / (areas[i] + areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)
idx = np.where(ious <= thresh)[0]
index = index[idx + 1]
return keep
四、根据置信度过滤无用框
1.删除置信度小于conf_thres的BOX
2.通过argmax获取置信度最大的类别
3.分别对每个类别进行过滤
def filter_box(org_box,conf_thres,iou_thres): #过滤掉无用的框
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 删除为1的维度
# 删除置信度小于conf_thres的BOX
#-------------------------------------------------------
org_box=np.squeeze(org_box)
conf = org_box[..., 4] > conf_thres
box = org_box[conf == True]
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 通过argmax获取置信度最大的类别
#-------------------------------------------------------
cls_cinf = box[..., 5:]
cls = []
for i in range(len(cls_cinf)):
cls.append(int(np.argmax(cls_cinf[i])))
all_cls = list(set(cls))
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 分别对每个类别进行过滤
# 1.将第6列元素替换为类别下标
# 2.xywh2xyxy 坐标转换
# 3.经过非极大抑制后输出的BOX下标
# 4.利用下标取出非极大抑制后的BOX
#-------------------------------------------------------
output = []
for i in range(len(all_cls)):
curr_cls = all_cls[i]
curr_cls_box = []
curr_out_box = []
for j in range(len(cls)):
if cls[j] == curr_cls:
box[j][5] = curr_cls
curr_cls_box.append(box[j][:6])
curr_cls_box = np.array(curr_cls_box)
# curr_cls_box_old = np.copy(curr_cls_box)
curr_cls_box = xywh2xyxy(curr_cls_box)
curr_out_box = pynms(curr_cls_box,iou_thres)
for k in curr_out_box:
output.append(curr_cls_box[k])
output = np.array(output)
return output
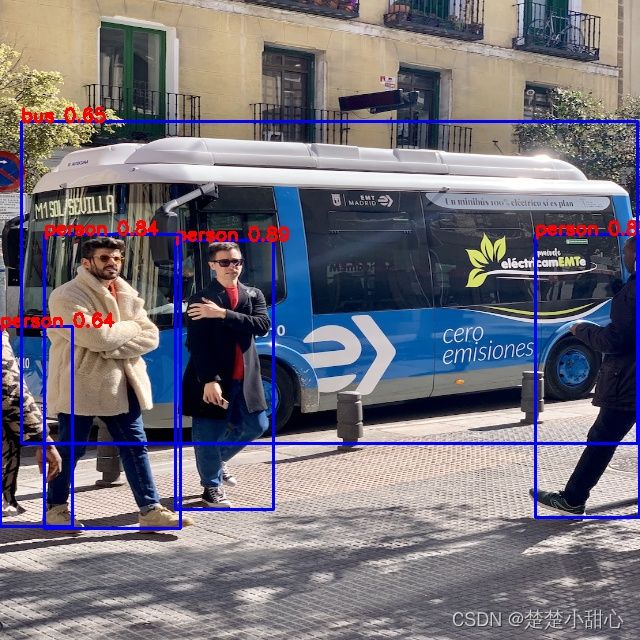
五、画图
def draw(image,box_data):
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 取整,方便画框
#-------------------------------------------------------
boxes=box_data[...,:4].astype(np.int32)
scores=box_data[...,4]
classes=box_data[...,5].astype(np.int32)
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = box
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(top, left, right, bottom))
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
(top, left ),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
六、总代码
import os
import cv2
import numpy as np
import onnxruntime
import time
CLASSES=['person', 'bicycle', 'car', 'motorcycle', 'airplane', 'bus', 'train', 'truck', 'boat', 'traffic light',
'fire hydrant', 'stop sign', 'parking meter', 'bench', 'bird', 'cat', 'dog', 'horse', 'sheep', 'cow',
'elephant', 'bear', 'zebra', 'giraffe', 'backpack', 'umbrella', 'handbag', 'tie', 'suitcase', 'frisbee',
'skis', 'snowboard', 'sports ball', 'kite', 'baseball bat', 'baseball glove', 'skateboard', 'surfboard',
'tennis racket', 'bottle', 'wine glass', 'cup', 'fork', 'knife', 'spoon', 'bowl', 'banana', 'apple',
'sandwich', 'orange', 'broccoli', 'carrot', 'hot dog', 'pizza', 'donut', 'cake', 'chair', 'couch',
'potted plant', 'bed', 'dining table', 'toilet', 'tv', 'laptop', 'mouse', 'remote', 'keyboard', 'cell phone',
'microwave', 'oven', 'toaster', 'sink', 'refrigerator', 'book', 'clock', 'vase', 'scissors', 'teddy bear',
'hair drier', 'toothbrush'] #coco80类别
class YOLOV5():
def __init__(self,onnxpath):
self.onnx_session=onnxruntime.InferenceSession(onnxpath)
self.input_name=self.get_input_name()
self.output_name=self.get_output_name()
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 获取输入输出的名字
#-------------------------------------------------------
def get_input_name(self):
input_name=[]
for node in self.onnx_session.get_inputs():
input_name.append(node.name)
return input_name
def get_output_name(self):
output_name=[]
for node in self.onnx_session.get_outputs():
output_name.append(node.name)
return output_name
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 输入图像
#-------------------------------------------------------
def get_input_feed(self,img_tensor):
input_feed={}
for name in self.input_name:
input_feed[name]=img_tensor
return input_feed
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 1.cv2读取图像并resize
# 2.图像转BGR2RGB和HWC2CHW
# 3.图像归一化
# 4.图像增加维度
# 5.onnx_session 推理
#-------------------------------------------------------
def inference(self,img_path):
img=cv2.imread(img_path)
or_img=cv2.resize(img,(640,640))
img=or_img[:,:,::-1].transpose(2,0,1) #BGR2RGB和HWC2CHW
img=img.astype(dtype=np.float32)
img/=255.0
img=np.expand_dims(img,axis=0)
input_feed=self.get_input_feed(img)
pred=self.onnx_session.run(None,input_feed)[0]
return pred,or_img
#dets: array [x,6] 6个值分别为x1,y1,x2,y2,score,class
#thresh: 阈值
def nms(dets, thresh):
x1 = dets[:, 0]
y1 = dets[:, 1]
x2 = dets[:, 2]
y2 = dets[:, 3]
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 计算框的面积
# 置信度从大到小排序
#-------------------------------------------------------
areas = (y2 - y1 + 1) * (x2 - x1 + 1)
scores = dets[:, 4]
keep = []
index = scores.argsort()[::-1]
while index.size > 0:
i = index[0]
keep.append(i)
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 计算相交面积
# 1.相交
# 2.不相交
#-------------------------------------------------------
x11 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[index[1:]])
y11 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[index[1:]])
x22 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[index[1:]])
y22 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[index[1:]])
w = np.maximum(0, x22 - x11 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, y22 - y11 + 1)
overlaps = w * h
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 计算该框与其它框的IOU,去除掉重复的框,即IOU值大的框
# IOU小于thresh的框保留下来
#-------------------------------------------------------
ious = overlaps / (areas[i] + areas[index[1:]] - overlaps)
idx = np.where(ious <= thresh)[0]
index = index[idx + 1]
return keep
def xywh2xyxy(x):
# [x, y, w, h] to [x1, y1, x2, y2]
y = np.copy(x)
y[:, 0] = x[:, 0] - x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 1] = x[:, 1] - x[:, 3] / 2
y[:, 2] = x[:, 0] + x[:, 2] / 2
y[:, 3] = x[:, 1] + x[:, 3] / 2
return y
def filter_box(org_box,conf_thres,iou_thres): #过滤掉无用的框
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 删除为1的维度
# 删除置信度小于conf_thres的BOX
#-------------------------------------------------------
org_box=np.squeeze(org_box)
conf = org_box[..., 4] > conf_thres
box = org_box[conf == True]
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 通过argmax获取置信度最大的类别
#-------------------------------------------------------
cls_cinf = box[..., 5:]
cls = []
for i in range(len(cls_cinf)):
cls.append(int(np.argmax(cls_cinf[i])))
all_cls = list(set(cls))
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 分别对每个类别进行过滤
# 1.将第6列元素替换为类别下标
# 2.xywh2xyxy 坐标转换
# 3.经过非极大抑制后输出的BOX下标
# 4.利用下标取出非极大抑制后的BOX
#-------------------------------------------------------
output = []
for i in range(len(all_cls)):
curr_cls = all_cls[i]
curr_cls_box = []
curr_out_box = []
for j in range(len(cls)):
if cls[j] == curr_cls:
box[j][5] = curr_cls
curr_cls_box.append(box[j][:6])
curr_cls_box = np.array(curr_cls_box)
# curr_cls_box_old = np.copy(curr_cls_box)
curr_cls_box = xywh2xyxy(curr_cls_box)
curr_out_box = pynms(curr_cls_box,iou_thres)
for k in curr_out_box:
output.append(curr_cls_box[k])
output = np.array(output)
return output
def draw(image,box_data):
#-------------------------------------------------------
# 取整,方便画框
#-------------------------------------------------------
boxes=box_data[...,:4].astype(np.int32)
scores=box_data[...,4]
classes=box_data[...,5].astype(np.int32)
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
top, left, right, bottom = box
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(top, left, right, bottom))
cv2.rectangle(image, (top, left), (right, bottom), (255, 0, 0), 2)
cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
(top, left ),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
if __name__=="__main__":
onnx_path='yolov5s.onnx'
model=YOLOV5(onnx_path)
output,or_img=model.inference('bicycle_1_1.jpg')
outbox=filter_box(output,0.5,0.5)
draw(or_img,outbox)
cv2.imwrite('res.jpg',or_img)