JavaScript笔记
JavaScript笔记
- 第一章 初识JavaScript
-
- 1.JavaScript的特点
- 2.JavaScript的组成
- 3.输入输出语句
- 4.JavaScript变量
- 第二章 JavaScript基础(上)
-
- 1.数据类型分类
- 2.数据类型检测
- 3.数据类型转换
-
- 1.转换成字符串型
- 2.转换为数字型
- 3.三元运算符
- 第三章 JavaScript基础(下)
-
- 1.数组
- 第四章 JavaScript函数
-
- 1.初识函数
- 2.函数参数的数量
- 3.arguments使用
- 4.作用域链
- 5.预解析
- 第五章 JavaScript对象
-
- 1.利用字面量创建对象
- 2.利用new Object 创建(普通的)对象
- 3.利用构造函数创建对象(类似Java的类)
- 4.遍历对象的属性和方法
- 5.内置对象
- 6.Math对象
- 7.日期对象
- 8.数组对象
-
- 1.筛选数组
- 2.数组排序
- 3.数组索引(从0开始索引)
- 4.数组转换为字符串
- 5.其他方法
- 9.字符串对象
-
- 1.根据字符返回位置
- 2.根据位置返回字符
- 3.字符串操作方法
- 10.值类型和引用对象
- 第六章 DOM(上)
-
- 1.获取元素
-
- 1.根据id获取元素
- 2.根据标签获取元素
- 3.根据name获取元素
- 4.根据类名获取(HTML5新增)
- 5.querySelector()和querySelectorAll()
- 6.document对象的属性
- 2.事件基础
- 3.操作元素
-
- 1.innerText和innerHTML的区别
- 2.操作元素属性
- 3.表单input元素的属性操作
- 4.操作元素样式
- 第七章 DOM(下)
-
- 1.排他操作
- 2.属性操作
-
- 1.获取属性值
- 2.设置属性值
- 3.移除属性
- 3.自定义属性
-
- 1.在HTML/JavaScript中设置自定义属性
- 2.获取属性值
- 4.节点基础
-
- 1.节点层级
- 2.获取父级节点
- 3.获取子级节点
- 4.获取兄弟节点
- 5.节点操作
-
- 1.创建 添加 删除 节点案例(简易留言板)
- 2.复制节点
- 6.事件进阶
-
- 1.注册事件
- 2.删除事件
- 3.DOM事件流
- 7.事件对象
-
- 1.事件对象的使用
- 2.e.target和this的区别
- 3.阻止默认行为
- 4.阻止事件冒泡
- 5.事件委托
- 8.鼠标事件
-
- 1.常用的鼠标事件
- 2.图片跟随鼠标移动案例
- 9.键盘事件
-
- 1.常用的键盘事件
- 2.文本提示信息
- 第八章 BOM
-
- 1.BOM简介
- 2.窗口加载事件
- 3.调整窗口大小事件
- 4.定时器
-
- 1.setTimeout定时器
- 2.clearTimeout停止定时器
- 3.setInterval定时器
- 4.clearterval清除定时器
- 5.验证码定时器
- 5.this指向问题
- 6.JavaScript执行机制
- 7.location对象
-
- 1.案例 5s后跳转页面
- 2.获取URL参数
- 3.location的常用方法
- 8.navigator对象
- 9.history对象
- 第十章 jQuery(上)
-
- 1.jQuery的入口函数
- 2.jQuery与DOM
- 3.jQuery选择器
- 4.隐式迭代
- 5.jQuery筛选选择器
- 6.排他思想
- 7.链式编程
- 8.jQuery样式操作
-
- 1.类操作
- 9.jQuery动画
-
- 1.显示与隐藏效果
- 2.滑动效果
- 3.停止动画
- 4.淡入淡出
- 5.自定义动画
第一章 初识JavaScript
1.JavaScript的特点
1.JavaScript是一种脚本语言
2.JavaScript可以跨平台
3.JavaScript支持面向对象
2.JavaScript的组成
JavaScript
ECMAScipt
DOM
BOM
3.输入输出语句
| 语句 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| alter(‘msg’) | 浏览器弹出警告框 |
| console.log(‘msg’) | 浏览器控制台输出信息 |
| promote | 浏览器弹出输入框,用户可以输入信息 |
4.JavaScript变量
var age; //声明一个名称为age的变量
第二章 JavaScript基础(上)
1.数据类型分类
数据类型
基本数据类型
复杂数据类型:Object
Boolean布尔型
String字符串型
Number数字型
Null空型
Undefind未定义型
2.数据类型检测
console.log(typeof null); //输出结果:object
typeof检测null值时返回的是object,而不是null.
3.数据类型转换
1.转换成字符串型
null和undefined无法使用toString()方式进行转换
var num=3.14;
//方法1.利用"+"拼接
var str=num+'+';
console.log(str,typeof str) //输出结果:3.14 string
//方法2.利用toString()转换成字符串
var str=num.toString();
console.log(str,typeof str) //输出结果:3.14 string
//方法3:利用String()转换成字符串
var str=String(num);
console.log(str,typeof str) //输出结果:3.14 string
//Ps:toString()可以将传入的参数进行进制转化
var num=5;
num.toString(2); //将5转化为二进制,结果为101
2.转换为数字型
//方法1.使用parseInt()将字符串转为整数
console.log(parseInt('69'); //输出结果:69
console.log(parseInt('03.14'); //输出结果:3
console.log(parseInt('12px'); //输出结果:12
console.log(parseInt('-12px'); //输出结果:-12
console.log(parseInt('a12'); //输出结果:NaN
console.log(parseInt('F',16); //输出结果:15 将F转化为16进制数
//方法2.使用parseFloat()将字符串转为浮点数
console.log(parseFloat('12.34'); //输出结果:12.34
//方法3.使用Number()将字符串转为数字型
console.log(Number('1.23'); //输出结果:1.23
//方法4.利用算术运算符(-、*、/)隐式转换
cosole.log('12'-1); //输出结果:11
3.三元运算符
条件表达式 ? 表达式1: 表达式2
var age=prompt('请输入需要判断的年龄:');
var s=age>=18? '已成年':'未成年';
console.log(s);
第三章 JavaScript基础(下)
1.数组
1.使用new Array()创造数组
var arr1=new Array();
var arr2=new Array(123,'狗',null);
2.使用字面量来创造数组
var arr1=[123,'狗',null];
var arr2=[];
第四章 JavaScript函数
1.初识函数
function 函数名(){
//函数体代码
}
var fun=function(a){
console.log('我是谁');
console.log(a);
}
fun('人');
2.函数参数的数量
function getSum(num1,num2){
console.log(num1,num2);
}
getSum(1,2); //实参数量等于形参数量,输出结果:1,2
getSum(1) //实参数量小于形参数量,输出结果:1 undefined
3.arguments使用
function fn(){
console.log(arguments); //结果输出:Arguments(3)[1,2,3]
console.log(arguments.length); //结果输出:3
console.log(arguments[1]); //结果输出:2
}
fn(1,2,3);
//特性
//1.伪数组
//2.具有length属性
//3.他没有数组一些方法pop() push() 等
4.作用域链
var a=1;
function fn1() {
var a=2;
var b='22'
fn2();
function fn2() {
var a=3;
fn3();
function fn3(){
var a=4;
console.log(a);
console.log(b);
}
}
}
fn1();//输出结果为:4 22
//就近原则
5.预解析
预解析 js引擎会把js所有的var还有function提升到作用域最前面
1.
console.log(num); //输出结果:undefined
var num=10;
// 相当于执行了以下代码
var num;
console.log(num);
num=10;
2.
fun(); //输出结果:undefined
var fun=function(){
console.log(22);
}
// 相当于执行了以下代码
var fun;
fun();
fun=function(){
console.log(22);
}
第五章 JavaScript对象
1.利用字面量创建对象
//创建一个空对象
var obj={};
//创建一个学生对象
var stu1={
name:'电棍',
age:24,
sex:'男',
sayHi:function(){
console.log('大家好,我是电棍');
};
}
console.log(stu1.name);//写法1
console.log(stu1['name']);//写法2
stu1.sayHi();//写法1
stu1['sayHi']();//写法2
//为obj添加成员
obj.name='炫狗';
obj.sayHi=function(){
alert('我是'+this.name);
}
alert(obj.name); //输出结果:炫狗
obj.sayHi();//调用方法:我是炫狗
console.log(sex);//输出结果:undefined
2.利用new Object 创建(普通的)对象
var obj=new Object();
obj.name='电棍';
obj.age='24';
obj.sex='男';
obj.talking=function(){
console.log('欧西给欧西给');
}
3.利用构造函数创建对象(类似Java的类)
function People(name,age){
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.talking=function(){
console.log('大家好我叫'+this.name);
};
}
//创建一个静态方法
function Student(){
}
var one1=new People('电棍',24)
console.log(one1.name);//输出结果:电棍
console.log(one1.talking());//输出结果:大家好我叫电棍
var one2=new People('炫狗',21)
console.log(one2.name);//输出结果:炫狗
console.log(one2.talking());//输出结果:大家好我叫炫狗
Student.school='福州十六中';
Student.talking=function(){
console.log('许昊龙被踩头');
};
console.log(Student.school);
Student.talking();
4.遍历对象的属性和方法
//准备一个待遍历的对象
var obj={
name:'炫狗',
age:21,
talk:'汪汪汪汪汪'
};
for(var k in obj){
console.log(k);//依次输出:name age talk(键)
console.log(obj[k]);//依次输出:炫狗 21 汪汪汪汪汪(值)
}
//判断对象成员是否存在
console.log('sex' in obj) //输出结果:false
console.log('name' in obj) //输出结果:true
5.内置对象
var myMath={
Pi:3.1415926
max:function(){
var max=arguments[0];
for(var i=1;i<arguments.length;i++){
if(arguments[i]>max){
max=arguments[i];
}
}
return max;
}
};
console.log(myMath.Pi); //输出结果:3.1415926
console.log(myMath.max(10,30,40)); //输出结果:40
6.Math对象
【案例】猜数字游戏
function getRandom(min,max){
return Math.floor(Math.random()*(max-min+1)+min);
}
// min ≤ 返回结果 < max
var random=new getRandom(1,10);
while(true){
var num=prompt('猜一个1~10的数字');
if(num>random){
alert('猜大了');
}
else if(num<random){
alert('猜小了');
}
else{
alert('猜对了');
break;
}
}
7.日期对象
【案例】倒计时
function countDown(time){
var nowTime =+ new Date(); //返回当前时间总毫秒数
var inputTime =+ new Date(time); //返回的是用户输入时间总毫秒数
var times= (inputTime-nowTime)/1000; //times是剩余时间总的秒数
var d= parseInt(times / 60 / 60 /24);
d = d < 10? '0' +d :d; //使其更美观
var h= parseInt(times / 60 / 60 %24);
h = h < 10? '0' +h :h;
var m= parseInt(times / 60 % 60);
m = m < 10? '0' +m :m;
var s= parseInt(times % 60);
s = s < 10? '0' +s :s;
return d +'天'+h+'时'+m+'分'+s+'秒';
}
console.log(countDown('2021-1-1 10:10:10'))
8.数组对象
数组类型检测
var arr=[];
var obj={};
console.log(arr instanceof Array);//结果返回true
console.log(obj instanceof Array);//结果返回false
console.log(Array.isArray(arr));//结果返回true
console.log(Array.isArray(obj));//结果返回false
一些数组对象的方法
| 方法名 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| push(参数) | 数组末尾添加一个或多个元素,会修改原数组 |
| unshift(参数) | 数组开头添加一个或多个元素,会修改原数组 |
| pop() | 删除数组的最后一个元素,若是空数组则返回undefined,会修改原数组 |
| shift() | 删除数组的第一个元素,若是空数组则返回undefined,会修改原数组 |
| reverse() | 颠倒数组中的元素的位置,该方法会改变原数组,返回新数组 |
| sort() | 对数组元素进行排序,该方法会改变原数组,返回新数组 |
| indexOf() | 返回数组中可以找到的定制的第一个索引,如果不存在返回-1 |
| lastindexOf() | 返回数组中可以找到的定制的最后一个索引,如果不存在返回-1 |
| toString() | 把数组转化成字符串,逗号分隔每一项 |
| join(‘分隔符’) | 将数组的所有元素链接到一个字符串中 |
| fill() | 用一个固定值填充数组中指定下标范围内的全部元素 |
| splice() | 数组删除,参数为splice(第几个开始,要输出的个数),返回被删除项目的新数组 |
| slice() | 数组截取,参数为slice(begin,end),返回呗截取项目的新数组 |
| concat() | 链接两个或多个数组,不影响原数组,返回一个新数组 |
1.筛选数组
var arr=[1000,1500,3000,3500,4000];
var newArr=[];
for(var i=0;i<arr.length;i++){
if(arr[i]<2000){
newArr.push(arr[i]);
}
}
console.log(newArr); //输出结果:[1000,1500]
2.数组排序
var arr[100,500,300];
arr.reverse();
console.log(arr); //输出结果:[300,500,100]
arr.sort(function(a,b)){
return b-a; //按降序排序
});
console.log(arr); //输出结果:[500,300,100]
3.数组索引(从0开始索引)
var arr[100,500,300,400,100];
console(arr.indexOf(100)); //输出结果:0
console(arr.lastindexOf(100)); //输出结果:4
4.数组转换为字符串
var arr=['a','b','c'];
console.log(arr.toString());//输出结果:a,b,c
console.log(arr.join('')); //输出结果:abc
console.log(arr.join('-')); //输出结果:a-b-c
5.其他方法
var arr=['a','b','c','d'];
arr.splice(2,2); //索引为2的位置开始 删除2个元素
console.log(arr); //输出结果:['a','b']
arr.splice(1,1,'e');//索引为1的位置开始 删除1个元素后 再添加元素e
console.log(arr); //输出结果:['a','e']
arr.splice(1,0,'f','g'); //索引为1的位置开始 添加元素
console.log(arr); //输出结果:['a','f','g','e']
9.字符串对象
var str=new String('apple');
console.log(str);//输出结果:String{"apple"}
console.log(str.length);//输出结果:5
console.log(typeof str);//输出结果:object
console.log(str instanceof String);//输出结果:true
var str2='hello'
console.log(typeof str2);//输出结果:string
console.log(str2 instanceof String);//输出结果:false
//使用new String()返回的str是一个对象 但普通的字符串变量并不是一个对象
| 成员 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|
| indexOf(searchValue) | 获取searchValue在字符串中首次出现的位置 |
| lastindexOf(searchValue) | 获取searchValue在字符串中最后出现的位置 |
| charAt(index) | 获取index位置的字符,位置从0开始计算 |
| charCodeAt(index) | 获取index位置的ASCII码 |
| str(index) | 获取指定位置处的字符 |
| concat(str1,str2…) | 连接多个字符串 |
| slice(start,[end]) | 截取从start位置到end位置之间的一个子字符串 |
| substring(start,[end]) | 截取从start位置到end位置之间的一个子字符串,基本和slice相同但不接收负值 |
| substr(start,[length]) | 截取从start位置开始到length长度的子字符串 |
| toLowerCase() | 获取字符串的小写模式 |
| toUpperCase() | 获取字符串的大写模式 |
| split([separator[,limit]) | 使用separator分隔符将字符串分隔成数组,limit用于限制数量 |
| replace(str1,str2) | 使用str2替换字符串中的str1,返回替换结果,只会替换第一个字符 |
1.根据字符返回位置
var str='hello';
str.indexOf('l'); //输出结果:2
str.lastindexOf('l'); //输出结果:3
2.根据位置返回字符
var str='hello';
console.log(str.charAt(1)); //输出结果:e
console.log(str.charCodeAt(1)); //输出结果:69(字符e的ASCII码为69)
console.log(str[0]); //输出结果:h
3.字符串操作方法
var str='helloworld';
str.concat('!'); //输出结果:helloworld!
str.slice(1,3); //输出结果:el
str.substring(5); //输出结果:world
str.substring(5,7) //输出结果:wo
str.substr(5) //输出结果:world
str.substr(5,7) //输出结果:wo
str.toLowerCase(); //输出结果:helloworld
str.toUpperCase(); //输出结果:HELLOWORLD
str.split('l'); //输出结果:["he","","owor","d"]
str.split('l',3); //输出结果:["he","","owor"]
str,replace('world','!'); //输出结果:"hello!"
10.值类型和引用对象
var obj1={name:'炫狗',age:'21'};
var obj2=obj1;
console.log(obj2==obj1);//输出结果:true
obj2.name='电棍';
console.log(obj1.name);//输出结果:电棍
//由于obj1 obj2引用同一个对象 无论两个变量操作对象 实际都是操作同一个对象
var obj1={name:'炫狗',age:'21'};
var obj2=obj1;
//此时obj1新创建一个对象
obj1={name:'电棍',age:'24'};
console.log(obj2.name); //输出结果:炫狗
function change(obj){
obj.name='炫狗';
}
var dog={name:'电棍',age:24};
change(dog);
console.log(dog.name); //输出结果:炫狗
第六章 DOM(上)
1.获取元素
1.根据id获取元素
<body>
<div id="box">哈哈</div>
<script>
var obox=document.getElementById('box');
console.log(obox);
//结果为:哈哈
console.log(typeof obox);
//结果为:object
console.dir(obox);
// 结果为:div#box
</script>
</body>
2.根据标签获取元素
<body>
<ul>
<li>苹果</li>
<li>西瓜</li>
<li>葡萄</li>
</ul>
<ol id="ol">
<li>红色</li>
<li>绿色</li>
<li>紫色</li>
</ol>
<script>
var lis=document.getElementsByTagName('li');
// 结果为:HTMLCollection(6) [li,li,li,li,li,li]
console.log(lis);
// 查看集合中索引为0的元素,结果为:苹果
console.log(lis[0]);
// 遍历集合中的所有元素
for(var i=0;i<lis.length;i++){
console.log[i];
}
// 通过元素对象获取元素
var ol=document.getElementById('ol');
// 结果为:HTMLCollection(3) [li,li,li]
console.log(ol.getElementsByTagName('li'));
</script>
</body>
3.根据name获取元素
<p>请选择你最喜欢的水果(多选)</p>
<label><input type="checkbox" name="fruit" value="苹果">苹果</label>
<label><input type="checkbox" name="fruit" value="西瓜">西瓜</label>
<label><input type="checkbox" name="fruit" value="香蕉">香蕉</label>
<script>
var fruits=document.getElementsByName('fruit');
fruits[0].checked=true;
</script>
4.根据类名获取(HTML5新增)
<body>
<span class="one">语文</span>
<span class="two">数学</span>
<span class="one">英语</span>
<span class="two">物理</span>
<script>
var ospan1=document.getElementsByClassName('one');
var ospan2=document.getElementsByClassName('two');
ospan1[0].style.fontWeight='bold';
ospan2[1].style.background='pink';
</script>
</body>
5.querySelector()和querySelectorAll()
<body>
<div class="box">盒子1</div>
<div class="box">盒子2</div>
<div id="nav">
<ul>
<li>首页</li>
<li>产品</li>
</ul>
</div>
<script>
var firstbox=document.querySelector('.box');
console.log(firstbox); //获取class为box的第一个div
var nav=document.querySelector('#nav');
console.log(nav); //获取id为nav的第一个div
var li=document.querySelector('li');
console.log(li); //获取匹配到的第一个li
var allbox=document.querySelectorAll('.box');
console.log(allbox); //获取class为box的所有div
var allli=document.querySelectorAll('li');
console.log(allli); //获取匹配到的所有li
</script>
</body>
6.document对象的属性
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| document.body | 返回文档的body元素 |
| document.title | 返回文档的title元素 |
| document.documentElement | 返回文档的html元素 |
| document.forms | 返回对文档中所有Form对象的引用 |
| document.images | 返回对文档中所有Image对象的引用 |
<body>
<script>
var bodyEle=document.body;
console.dir(bodyEle);
var htmlEle=document.documentElement;
console.log(htmlEle);
</script>
</body>
2.事件基础
事件三要素
1.事件源:触发事件的元素。(谁触发了事件)
2.事件类型:如click单击事件。(触发了什么事件)
3.事件处理程序:事件触发后要执行的代码,也称事件处理函数。(触发事件后要做什么)
<body>
<button id="btn">点击起飞</button>
<script>
var btn=document.getElementById('btn'); //1.获取事件源
//2.注册事件btn.onclick
btn.onclick=function(){
alert('芜湖');
};
</script>
</body>
3.操作元素
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| element.innerHTML | 设置或返回元素开始和结束标签之间的HTML,包括HTML标签,同时保留空格和换行 |
| element.innerText | 设置或返回元素的文本内容,在返回的时候会去除HTML标签和多余的空格、换行,在设置的时候回进行特殊字符转义 |
| element.textContent | 设置或返回指定节点的文本内容,同时保留空格和换行 |
1.innerText和innerHTML的区别
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
var div=document.querySelector('div');
div.innerText='今天是:2019年'; //会不识别标签
div.innerHTML='今天是:2019年';
</script>
</body>
2.操作元素属性
<body>
<button>刘德华</button>
<button>张学友</button><br>
<img src="ldh.jpg" alt="刘德华">
<script>
var ldh=document.getElementById('ldh');
var zxy=document.getElementById('zxy');
ldh.onclick=function(){
img.src=ldh.jpg;
img.title='刘德华';
};
zxy.onclick=function(){
img.src=zxy.jpg;
img.title='张学友';
};
</script>
</body>
3.表单input元素的属性操作
<body>
<button>按钮</button>
<input type="text" value="输入内容">
<script>
var btn=document.querySelector('button');
var input=document.querySelector('input');
btn.onclick=function(){
input.value='已被点击';
this.disabled=true; //this指向事件函数的调用者btn
}
</script>
</body>
4.操作元素样式
<body>
<input type="text" value="手机" style="color: #999;">
<script>
var text=document.querySelector('input');
//获得焦点事件 onfocus
text.onfocus=function(){
if(this.value==='手机'){
this.value='';
}
this.style.color='#333';
};
//失去焦点 onblur
text.onblur=function(){
if(this.value===''){
this.value='手机';
}
this.style.color='#999';
}
</script>
</body>
第七章 DOM(下)
1.排他操作
<body>
<button>按钮1</button>
<button>按钮2</button>
<button>按钮3</button>
<button>按钮4</button>
<script>
var btns=document.getElementsByTagName('button');
for(var i=0;i<btns.length;i++){
btns[i].onclick=function(){
for(var i=0;i<btns.length;i++){
btns[i].style.backgroundColor='';
}
this.style.backgroundColor='pink';
}
}
</script>
</body>
<body>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>代码</th>
<th>名称</th>
<th>最新公布净值</th>
<th>累计净值</th>
<th>前单位净值</th>
<th>净值增长率</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr>
<td>0035**</td>
<td>3个月定期开放证券</td>
<td>1.075</td>
<td>1.079</td>
<td>1.074</td>
<td>+0.047%</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>0035**</td>
<td>3个月定期开放证券</td>
<td>1.075</td>
<td>1.079</td>
<td>1.074</td>
<td>+0.047%</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>0035**</td>
<td>3个月定期开放证券</td>
<td>1.075</td>
<td>1.079</td>
<td>1.074</td>
<td>+0.047%</td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
<script>
var trs=document.querySelector('tbody').querySelectorAll('tr');
for(var i=0;i<trs.length;i++){
trs[i].onmouseover=function(){
this.style.backgroundColor='pink'; //此处也可提前style样式来调色
};
trs[i].onmouseout=function(){
this.style.backgroundColor='';
};
}
</script>
</body>
2.属性操作
1.获取属性值
<body>
<div id="demo" index="1" class="nav"></div>
<script>
var div=document.querySelector('div');
console.log(div.id);//结果为:demo
console.log(div.getAttribute('id'));//结果为:demo
console.log(div.getAttribute('index'));//结果为:1
</script>
</body>
2.设置属性值
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
var div=document.querySelector('div');
div.id='test';
div.className='navs';
div.setAttribute('index',2);
/* div.setAttribute('class','footer'); 设置元素类名*/
</script>
</body>
3.移除属性
<body>
<div id="test" class="footer" index="2"></div>
<script>
var div=document.querySelector('div');
div.removeAttribute('id');
div.removeAttribute('class');
div.removeAttribute('name');
</script>
</body>
3.自定义属性
1.在HTML/JavaScript中设置自定义属性
<body>
<div data-index="2"></div> //"data-*"开发者习惯自定义属性名前缀
<script>
var div=document.querySelector('div');
div.dataset.index='1';
div.setAttribute('data-name','haha');//设置属性值
console.log(div);
</script>
</body>
2.获取属性值
<body>
<div gettime="20" data-index="2" data-list-name="haha"></div>
<script>
var div=document.querySelector('div');
console.log(div.getAttribute('data-index')); // 输出结果:2
console.log(div.getAttribute('data-list-name')); //输出结果:haha
// 使用HTML5获取自定义属性方法,只能获取"data-"开头的属性
console.log(div.dataset); //DOMStringMap{index="2",listName:"haha"}
console.log(div.dataset.index); //输出结果:2
console.log(div.dataset['index']); //第二种写法
console.log(div.dataset.listName); //有多个-相连时 使用驼峰命名法
console.log(div.dataset['listName']); //输出结果:haha
</script>
</body>
4.节点基础
1.节点层级
2.获取父级节点
<body>
<div class="demo">
<div class="box">
<span class="child">123</span>
</div>
</div>
<script>
var child=document.querySelector('.child');
console.log(child.parentNode);
//返回最近的一个父节点 若无返回null
</script>
</body>
3.获取子级节点
(1) childNodes
使用该方法会获取文本节点 因此略
(2) children
<ol>
<li>我是1</li>
<li>我是1</li>
<li>我是1</li>
</ol>
<script>
var ol=document.querySelector('ol');
var lis=ol.querySelectorAll('li');
console.log(ol.children);
</script>
</body>
(3)获取第一个子元素和最后一个子元素
<body>
<ol>
<li>我是1</li>
<li>我是1</li>
<li>我是1</li>
</ol>
<script>
var ol=document.querySelector('ol');
// 1.此处会返回文本节点(空格)
console.log(ol.firstChild);
console.log(ol.lastChild);
// 2.firstElementChild 返回第一个子元素节点(有兼容性问题)
console.log(ol.firstElementChild);
console.log(ol.lastElementChild);
// 3.实际开发使用
console.log(ol.children[0]);
console.log(ol.children[ol.children.length-1]);
</script>
</body>
4.获取兄弟节点
<body>
<div>1</div>
<span>2</span>
<script>
var div=document.querySelector('div');
// 1.nextSibling和previousSibling 返回值包含其他节点
console.log(div.nextSibling);
console.log(div.previousSibling);
/* 2.nextElementSibling返回当前元素下一个兄弟元素节点
previousElementSibling则返回上一个兄弟元素节点 兼容性问题 */
console.log(div.nextElementSibling);
console.log(div.previousElementSibling);
// 实际开发使用封装一个兼容性的函数
function getNextElementSibling (element) {
var el=element;
while(el=el.nextSibling){
if(el.nodeType===1){ //判断是否为节点
return el;
}
}
return null;
}
</script>
</body>
5.节点操作
1.创建 添加 删除 节点案例(简易留言板)
<body>
<textarea name="" id="" cols="30" rows="10"></textarea>
<button>发布</button>
<ul></ul>
<script>
// 1.获取元素
var btn=document.querySelector('button');
var text=document.querySelector('textarea');
var ul=document.querySelector('ul');
// 2.注册事件
btn.onclick=function(){
if (text.value==''){
alert('没有输入内容');
return false;
}else{
// 1.创建元素
var li=document.createElement('li');
//阻止链接跳转可以使用'javascript:;'
li.innerHTML=text.value+"删除"
//
// 2.添加元素
ul.insertBefore(li,ul.children[0]);
}
// 3.删除元素
var as=document.querySelectorAll('a');
for(var i=0;i<as.length;i++){
as[i].onclick=function(){
// node.removeChild(child); 删除的是li 当前a所在的li 此时this指a
ul.removeChild(this.parentNode);
}
}
}
</script>
</body>
2.复制节点
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>2</li>
<li>3</li>
</ul>
<script>
var ul=document.querySelector('ul');
// 1.node.cloneNode() 括号为空或者为flase 浅拷贝 只复制标签不复制内容
// 2.node.cloneNode(true) 括号为true 深拷贝 复制标签里面的内容
var lili=ul.children[0].cloneNode(true);
ul.appendChild(lili);
</script>
</body>
6.事件进阶
1.注册事件
<body>
<button>传统</button>
<button>事件监听</button>
<button>before ie9</button>
<script>
var btns=document.querySelectorAll('button');
// 1.传统方式注册事件
btns[0].onclick=function(){
alert('123');
}
// 由于被下面的覆盖 所以只会弹出456
btns[0].onclick=function(){
alert('456');
}
// 2.事件监听注册事件addEventListener
// (1) 因为里面的事件类型是字符型 所有加引号 而且不带on
// (2) 同一个元素 同一个事件可以添加多个监听器 因此显示123后在显示456
btns[1].addEventListener('click',function(){
alert(123);
})
btns[1].addEventListener('click',function(){
alert(456);
})
// 3.attachEvent ie9以前的版本支持
btns[2].attachEvent('onclick',function(){
alert(123);
})
</script>
</body>
2.删除事件
<body>
<div>1</div>
<div>2</div>
<div>3</div>
<script>
var divs=document.querySelectorAll('div');
divs[0].onclick=function(){
alert(123);
// 1.传统方式删除事件
divs[0].onclick=null;
}
// 2. removeEventListener删除事件
divs[1].addEventListener('click',fn) //里面的fn不需要加小括号
function fn(){
alert(456);
divs[1].removeEventListener('click',fn);
}
// 3.datachEvent IE9之前使用的删除事件
divs[2].datachEvent('onclick',fn1);
function fn1(){
alert(789);
}
</script>
</body>
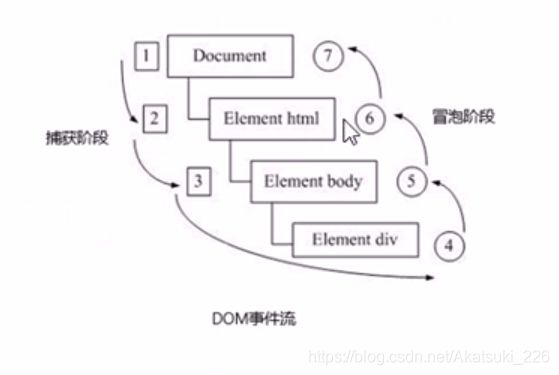
3.DOM事件流
7.事件对象
1.事件对象的使用
var 事件对象=window.event //早期IE内核浏览器
DOM对象 .事件=function(event){} //现在
2.e.target和this的区别
<body>
<div>1</div>
<ul>
<li>a</li>
<li>a</li>
<li>a</li>
</ul>
<script>
// 1.e.target 返回的是触发事件返回的对象(元素) this返回的是绑定事件的对象(元素)
// 区别:e.target点击哪个元素就返回哪个元素
// 谁绑定this 就返回谁
var div=document.querySelector('div');
div.addEventListener('click',function(e){
// 均输出div
console.log(e.target);
console.log(this);
})
var ul=document.querySelector('ul');
ul.addEventListener('click',function(e){
// 输出li
console.log(e.target);
// 输出ul
console.log(this);
})
</script>
</body>
3.阻止默认行为
<body>
<div>
<a href="www.baidu.com">百度</a>
</div>
<script>
var a=document.querySelector('a');
a.addEventListener('click',function(e){
e.preventDefault(); //DOM标准写法
});
// 传统方法
a.onclick=function(e){
e.preventDefault();
e.returnValue;
}
</script>
</body>
4.阻止事件冒泡
stopPropagation() //标准浏览器
cancelBubble=ture //早期浏览器
5.事件委托
<body>
<ul>
<li>1</li>
<li>1</li>
<li>1</li>
<li>1</li>
</ul>
<script>
//事件委托原理:给父节点添加监听器 利用事件冒泡影响每一个子节点
// 也可以用排他思想做
var ul=document.querySelector('ul');
ul.addEventListener('click',function(e){
e.target.style.backgroundColor='blue';
})
</script>
</body>
8.鼠标事件
1.常用的鼠标事件
<body>
123456
<script>
// 禁止鼠标右击菜单
document.addEventListener('contextmenu',function(e){
e.preventDefault();
});
// 禁止鼠标选中
document.addEventListener('selectstart',function(e){
e.preventDefault();
});
</script>
</body>
2.图片跟随鼠标移动案例
<style>
img{
position: absolute;
}
</style>
<body>
<img src="a.png">
<script>
var pic=document.querySelector('img');
document.addEventListener('mousemove',function(e){
var x=e.pageX;
var y=e.pageY;
pic.style.left=x-205+'px'; //图片长度%2为205
pic.style.top=y-211+'px'; //图片长度%2为211
})
</script>
</body>
9.键盘事件
1.常用的键盘事件
<body>
<script>
document.addEventListener('keyup',function(){
console.log('弹起');
})
document.addEventListener('keydown',function(){
console.log('按下');
})
// keypress不识别ctrl shift ←→等键
document.addEventListener('keydpress',function(){
console.log('按下press');
})
// 执行顺序keydown->keypress->keyup
</script>
</body>
2.文本提示信息
<script>
var con=document.querySelector('.con');
var jd=document.querySelector('.jd');
jd.addEventListener('keyup',function(){
if(this.value=''){
con.style.display='none';
}else{
con.style.display='block';
con.innerText=this.value;
}
});
// 当失去焦点时,隐藏con盒子
jd.addEventListener('blur',function(){
con.style.display='none';
})
// 当获得焦点,显示con盒子
jd.addEventListener('focus',function(){
if(this.value!==''){
con.style.display='block';
}
})
</script>
</body>
第八章 BOM
1.BOM简介
2.窗口加载事件
<script>
// 传统
window.onload=function(){
var btn=document.querySelector('button');
btn.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('点击我');
})
}
// 新
window.addEventListener('load',function(){
var btn=document.querySelector('button');
btn.addEventListener('click',function(){
alert('点击我');
})
})
window.addEventListener('load',function(){
alert('load该注册事件可写多次但传统事件只能写一次');
})
document.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded',function(){
alert('DOMContentLoaded先加载');
})
// load等页面内容全部加载完毕 包含页面dom元素 图片 flash
// DOMContentLoaded是 DOM加载完毕,不包含flash css等就可以先执行 加载比load更快
</script>
</head>
<body>
<button>点击</button>
</body>
3.调整窗口大小事件
<body>
<script>
window.addEventListener('load',function(){
var div=document.querySelector('div');
window.addEventListener('resize',function(){
if(window.innerHeight<500){
div.style.display='none';
}else{
div.style.display='block';
}
})
})
</script>
<div style="width: 100px;height: 100px;background-color: red;"></div>
</body>
4.定时器
1.setTimeout定时器
<body>
<script>
// 1.用字符串表示一串代码
setTimeout('alert("2s弹出该方框");',2000);
// 2.传入一个匿名参数
setTimeout(function() {
alert('3s弹出该方款');
}, 3000);
// 3.传入函数名
setTimeout(fn,4000);
function fn(){
alert('4s弹出该方款');
}
</script>
</body>
2.clearTimeout停止定时器
<body>
<button>点击停止爆炸</button>
<script>
var btn=document.querySelector('button');
var boomtime=setTimeout(function(){
alert('爆炸了');
},5000)
btn.addEventListener('click',function(){
clearTimeout(boomtime);
})
</script>
</body>
3.setInterval定时器
<body>
<script>
// 每隔一秒调用一次函数
setInterval(function(){
alert('被使用了');
},1000)
</script>
</body>
4.clearterval清除定时器
<body>
<button class="begin">开启</button>
<button class="stop">关闭</button>
<script>
var begin=document.querySelector('.begin');
var stop=document.querySelector('.stop');
var timer=null; //全局变量
begin.addEventListener('click',function(){
timer=setInterval(function(){
alert('开启');
},5000)
})
stop.addEventListener('click',function(){
clearInterval(timer);
})
</script>
</body>
5.验证码定时器
<body>
手机号:<input type="number"><button>发送</button>
<script>
var btn=document.querySelector('button');
var time=5; //定义剩下的秒数
btn.addEventListener('click',function(){
btn.disabled=true;
var timer = setInterval(function(){
if(time==0){
// 清除定时器和复原按钮
clearInterval(time);
btn.disabled=false;
btn.innerHTML='发送';
}else{
btn.innerHTML='还剩下'+ time +'秒';
time--;
}
},1000)
})
</script>
</body>
![]()
5.this指向问题
<body>
<script>
// 1.在全局作用域或普通函数中 this指向全局window
console.log(this); //指向window
function fn(){
console.log(this);
}
window.fn(); //this指向window
// 2.在方法中 谁调用方法 this就指向谁
var o={
sayHi:function(){
console.log(this);
}
};
o.sayHi(); //sayHi中的this指向的是o这个对象
// 3.构造函数中的this指向的是新创建的实例
function fun(){
console.log(this);
}
var funs=new fun(); // fun中中的this指向的是新创建的实例funs
</script>
</body>
6.JavaScript执行机制
1.单线程:同一时间只能做一件事
2.同步和异步:同步则前一个任务结束后执行后一个任务(水开之后再去切菜炒菜)
异步则做一件事件的同时可以去处理其他事(烧水的同时切菜炒菜)
3.执行机制:先执行执行栈中同步任务再执行异步任务。
7.location对象
1.案例 5s后跳转页面
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
var div=document.querySelector('div');
var time=5;
setInterval(function(){
if(time==0){
location.href='http://www.baidu.com';
}else{
div.innerHTML='你将在'+time+'秒后跳转到首页';
time--;
}
},1000)
</script>
</body>
2.获取URL参数
login.html
<body>
<form action="index.html">
用户名:<input type="text" name="uname">
<input type="submit" value="登录">
</form>
</body>
index.html
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
console.log(location.search); //结果为:?uname=andy
// 1.去掉search中的问号
var params=location.search.substr(1);
console.log(params); //结果为:uname=andy
// 2.把字符串分割为数组
var arr=params.split('=');
console.log(arr); //结果为:["uname","andy"]
// 3.把数据写入div中
var div=document.querySelector('div');
div.innerHTML=arr[1]+'欢迎您';
</script>
</body>
在这里插入代码片
3.location的常用方法
| 方法 | 返回值 |
|---|---|
| location.assign() | 跟href一样,可以跳转页面 |
| location.replace() | 替换当前页面,因为不记录历史,所以不能后退页面 |
| location.reload() | 重新加载页面,相当于刷新按钮或者F5如果参数为true强制刷新ctrl+F5 |
8.navigator对象
一般通过window.navigator.userAgent来返回客户User-Agent头部的值
9.history对象
| history对象方法 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| back() | 可以后退功能 |
| forward() | 前进功能 |
| go(参数) | 前进后退功能 参数如果是1前进1个页面 如果是-1后退1个页面 |
第十章 jQuery(上)
1.jQuery的入口函数
<body>
<script>
// 1.等着DOM加载完毕在执行js代码
$(document).ready(function(){
$('div').hide();
})
// 2.等着DOM加载完毕在执行js代码 (简)
$(function(){
$('div').hide();
})
</script>
<div></div>
</body>
2.jQuery与DOM
<body>
<video src="123.mp4"></video>
<script>
// 1.DOM对象转换为jQuery对象
// (1)直接获取视频 得到的是jQuery对象
$('video');
// 用原生js获取DOM对象
var myvideo=document.querySelector('video');
// $(myvideo.play()); jQuery没有play这个方法
// 2.jQuery对象转换为DOM对象
$('video')[0].play()
$('video').get(0).play()
</script>
</body>
3.jQuery选择器
<body>
<div class="nav">nava</div>
<ul>
<li>我是li</li>
<li>我是li</li>
</ul>
<script>
$(function(){
console.log($(".nav")); //获取nav
console.log($("ul li")); //获取ul里的li
})
</script>
</body>
4.隐式迭代
遍历内部DOM元素的过程叫做隐式迭代
<body>
<div>哈哈</div>
<div>哈哈</div>
<div>哈哈</div>
<script>
$("div").css("background","green"); //对所有div操作
</script>
</body>
5.jQuery筛选选择器
<body>
<ul>
<li>我是li</li>
<li>我是li</li>
<li>我是li</li>
</ul>
<ol>
<li>我是li</li>
<li>我是li</li>
<li>我是li</li>
</ol>
<script>
$(function(){
// 索引都从0开始
$("ul li:first").css("color","red"); //ul里的li第一个变红
$("ul li:eq(2)").css("color","blue"); //ul里第三个li变蓝
$("ol li:odd").css("color","green"); //ol里索引为奇数的li变绿
$("ol li:even").css("color","skyblue"); //ol里索引为偶数的li变天空蓝
})
</script>
</body>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son">子</div>
</div>
<script>
$(function(){
console.log($(".son").parent()); //查找son的父亲
console.log($(".father").find("div")); //查找所有后代div
})
</script>
</body>
6.排他思想
<body>
<button>1</button>
<button>2</button>
<button>3</button>
<script>
// 1.隐式迭代 给所有按钮绑定点击事件
$("button").click(function(){
// 2.当前元素变化背景颜色
$(this).css("background","pink");
// 3.其余兄弟去掉背景颜色
$(this).siblings("button").css("background","");
});
</script>
</body>
7.链式编程
<body>
<button>1</button>
<button>2</button>
<button>3</button>
<script>
$("button").click(function(){
// 链式编程
// 我的颜色为粉 兄弟颜色为空
$(this).css("background","pink").siblings().css("color","");
// 我的颜色为空 兄弟颜色为红
$(this).siblings().css('color','red');
});
</script>
</body>
8.jQuery样式操作
<style>
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
<script>
$(function(){
$("div").css({
width:400,
height:400,
backgroundColor: "red"
})
})
</script>
</body>
1.类操作
<style>
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: pink;
}
.current{
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="current"></div>
<script>
$(function(){
// 1.添加类 addClass()
$("div").click(function(){
$(this).addClass("current");
});
// 2.删除类 removeClass()
$("div").click(function(){
$(this).removeClass("current");
})
// 3.切换类 toggleClass()
$("div").click(function(){
$(this).toggleClass("current");
})
})
</script>
</body>
9.jQuery动画
1.显示与隐藏效果
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| show([speed],[easing],fn[]]) | 显示与被隐藏的匹配元素 |
| hide([speed],[easing],fn[]]) | 隐藏已显示的匹配元素 |
| toggle([speed],[easing],fn[]]) | 元素显示与隐藏切换 |
2.滑动效果
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| slideDown([speed],[easing],fn[]]) | 向下滑动显示匹配元素 |
| hideUp([speed],[easing],fn[]]) | 向上滑动显示匹配元素 |
| toggleToggle([speed],[easing],fn[]]) | 在slideUp()和slideDown()两种效果间切换 |
3.停止动画
stop()方法
$(selector).stop(stopAll,gotoEnd)
4.淡入淡出
| 方法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| fadeIn([speed],[easing],fn[]]) | 淡入淡出显示匹配元素 |
| fadeOut([speed],[easing],fn[]]) | 淡入淡出隐藏匹配元素 |
| fadeTo([speed],opacity,[easing],fn[]]) | 在淡入淡出方式将元素调整到指定的透明度 |
| fadeToggle([speed],[easing],fn[]]) | 在fadeIn()和fadeout()两种效果间切换 |
5.自定义动画
$(selector).animate(params[, speed],[, easing],[, fn])