企业级日志系统分析——ELK详解
目录
前言
一、概述
1、组件说明
1.1 ElasticSearch
1.2 Kiabana
1.3 Logstash
1.4 Filebeat
1.5 缓存/消息队列(redis、kafka、RabbitMQ等)
1.6 Fluentd
2、思考:为什么要用ELK
3、完整日志系统的基本特征
4、ELK工作原理
二、部署ELK日志分析系统
1、服务器配置
2、关闭防火墙
3、ElasticSearch集群部署(需要部署两个节点,这里以node1为例说明)
3.1 环境准备
3.2 部署 ElasticSearch 软件
4、安装 Elasticsearch-head 插件(node1为例)
4.1编译安装 node
4.2 安装 phantomjs
4.3 安装 Elasticsearch-head 数据可视化工具
4.4 修改 Elasticsearch 主配置文件
4.5 启动 elasticsearch-head 服务
4.6 通过 Elasticsearch-head 查看 ES 信息
4.7插入索引
4.8 浏览器查看索引信息
5、ELK-Logstash 部署(在 Apache 节点上操作)
5.1 更改主机名
5.2 安装 Apache 服务(httpd)
5.3 安装 Java 环境
5.4 安装 logstash
5.5 测试 Logstash
5.6定义 logstash 配置文件
5.7访问测试
6、ELK-Kibana 部署(在 node1 节点上操作)
6.1 安装 Kibana
6.2 设置 Kibana 的主配置文件
6.3 启动 Kibana 服务
6.4 验证 Kibana
6.5 将 Apache 服务器的日志(访问的、错误的)添加到 ES 并通过 Kibana 显示
6 .6 浏览器访问
三、ELFK(Filebeat + ELK)
1、Filebeat 的作用
2、ELFK 工作流程
3、ELFK 的部署
3.1服务器配置
3.2 服务器环境
3.3 安装 filebeat
3.4 修改 filebeat 主配置文件
3.5 在 logstash 组件所在节点(apache节点)上新建一个 logstash 配置文件
3.6 浏览器验证
前言
ELK 平台是一套完整的日志集中处理解决方案,将 ElasticSearch、Logstash 和 Kibana 三个开源工具配合使用,完成更强大的用户对日志的查询、排序、统计需求。
一、概述
1、组件说明
1.1 ElasticSearch
ElasticSearch是基于Lucene(一个全文检索引擎的架构)开发的分布式存储检索引擎,用来存储各类日志。
Elasticsearch 是用 Java 开发的,可通过 RESTful Web 接口,让用户可以通过浏览器与 Elasticsearch 通信。
Elasticsearch是一个实时的、分布式的可扩展的搜索引擎,允许进行全文、结构化搜索,它通常用于索引和搜索大容量的日志数据,也可用于搜索许多不同类型的文档。
1.2 Kiabana
Kibana 通常与 Elasticsearch 一起部署,Kibana 是 Elasticsearch 的一个功能强大的数据可视化 Dashboard,Kibana 提供图形化的 web 界面来浏览 Elasticsearch 日志数据,可以用来汇总、分析和搜索重要数据。
1.3 Logstash
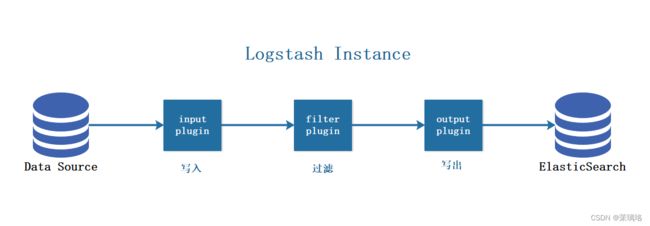
Logstash作为数据收集引擎。它支持动态的从各种数据源搜集数据,并对数据进行过滤、分析、丰富、统一格式等操作,然后存储到用户指定的位置,一般会发送给 Elasticsearch。
Logstash 由 Ruby 语言编写,运行在 Java 虚拟机(JVM)上,是一款强大的数据处理工具, 可以实现数据传输、格式处理、格式化输出。Logstash 具有强大的插件功能,常用于日志处理。
1.4 Filebeat
Filebeat 是一款轻量级的开源日志文件数据搜索器。通常在需要采集数据的客户端安装 Filebeat,并指定目录与日志格式,Filebeat 就能快速收集数据,并发送给 Logstash 进行解析,或是直接发给 ES 存储,性能上相比运行于 JVM 上的 Logstash 优势明显,是对它的替代。
filebeat 结合 logstash 带来好处
- 通过 Logstash 具有基于磁盘的自适应缓冲系统,该系统将吸收传入的吞吐量,从而减轻 Elasticsearch 持续写入数据的压力
- 从其他数据源(例如数据库,S3对象存储或消息传递队列)中提取
- 将数据发送到多个目的地,例如S3,HDFS(Hadoop分布式文件系统)或写入文件
- 使用条件数据流逻辑组成更复杂的处理管道
日志的集中化管理 beats 包括四种工具
- Packetbeat(搜索网络流量数据)
- Topbeat(搜索系统、进程和文件系统级别的 CPU 和内存使用情况等数据)
- Filebeat(搜集文件数据)
- Winlogbeat(搜集 Windows 时间日志数据)
1.5 缓存/消息队列(redis、kafka、RabbitMQ等)
可以对高并发日志数据进行流量削峰和缓冲,这样的缓冲可以一定程度的保护数据不丢失,还可以对整个架构进行应用解耦。
1.6 Fluentd
Fluentd是一个流行的开源数据收集器。由于 logstash 太重量级的缺点,Logstash 性能低、资源消耗比较多等问题,随后就有 Fluentd 的出现。相比较 logstash,Fluentd 更易用、资源消耗更少、性能更高,在数据处理上更高效可靠,受到企业欢迎,成为 logstash 的一种替代方案,常应用于 EFK 架构当中。在 Kubernetes 集群中也常使用 EFK 作为日志数据收集的方案。
在 Kubernetes 集群中一般是通过 DaemonSet 来运行 Fluentd,以便它在每个 Kubernetes 工作节点上都可以运行一个 Pod。 它通过获取容器日志文件、过滤和转换日志数据,然后将数据传递到 Elasticsearch 集群,在该集群中对其进行索引和存储。
2、思考:为什么要用ELK
答:
日志主要包括系统日志、应用程序日志和安全日志。系统运维和开发人员可以通过日志了解服务器软硬件信息、检查配置过程中的错误及错误发生的原因。经常分析日志可以了解服务器的负荷,性能安全性,从而及时采取措施纠正错误。
往往单台机器的日志我们使用grep、awk等工具就能基本实现简单分析,但是当日志被分散的储存不同的设备上。如果你管理数十上百台服务器,你还在使用依次登录每台机器的传统方法查阅日志。这样是不是感觉很繁琐和效率低下。当务之急我们使用集中化的日志管理,例如:开源的syslog,将所有服务器上的日志收集汇总。集中化管理日志后,日志的统计和检索又成为一件比较麻烦的事情,一般我们使用 grep、awk和wc等Linux命令能实现检索和统计,但是对于要求更高的查询、排序和统计等要求和庞大的机器数量依然使用这样的方法难免有点力不从心。
一般大型系统是一个分布式部署的架构,不同的服务模块部署在不同的服务器上,问题出现时,大部分情况需要根据问题暴露的关键信息,定位到具体的服务器和服务模块,构建一套集中式日志系统,可以提高定位问题的效率。
3、完整日志系统的基本特征
- 收集:能够采集多种来源的日志数据
- 传输:能够稳定的把日志数据解析过滤并传输到存储系统
- 存储:存储日志数据
- 分析:支持 UI 分析
- 警告:能够提供错误报告,监控机制
4、ELK工作原理
- AppServer 是一个类似于 Nginx、Apache 的集群,其日志信息由 Logstash 来收集
- 往往为了减少网络问题所带来的瓶颈,会把 Logstash 服务放入前者的集群内,减少网络的消耗
- Logstash 把收集到的日志数据格式化后输出转存至 ES 数据库内(这是一个将日志进行集中化管理的过程)
- 随后,Kibana 对 ES 数据库内格式化后日志数据信息进行索引和存储
- 最后,Kibana 把其展示给客户端
总结:logstash作为日志搜集器,从数据源采集数据,并对数据进行过滤,格式化处理,然后交由Elasticsearch存储,kibana对日志进行可视化处理。
二、部署ELK日志分析系统
1、服务器配置
| 服务器 | 配置 | 主机名 | ip地址 | 主要软件 |
| node1 节点 | 2C/4G | node1 | 192.168.223.37 | ElasticSearch、Kibana |
| node2 节点 | 2C/4G | node2 | 192.168.223.53 | ElasticSearch |
| apache 节点 | / | apache | 192.168.223.13 | Logstash、Apache |
2、关闭防火墙
systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld
setenforce 0
ntpdate ntp.aliyun.com
3、ElasticSearch集群部署(需要部署两个节点,这里以node1为例说明)
3.1 环境准备
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname node1
[root@localhost ~]# su
[root@node1 ~]# echo "192.168.223.37 node1" >> /etc/hosts
[root@node1 ~]# echo "192.168.223.53 node2" >> /etc/hosts
[root@node1 ~]# java -version #不建议使用 openjdk
# rpm 安装 jdk (方法一)
cd /opt
#将软件包传至该目录下
rpm -ivh jdk-8u201-linux-x64.rpm
vim /etc/profile.d/java.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_201-amd64
export CLASSPATH=.:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar
export PATH=$JAVA_HOME/bin:$PATH
#注释:
1.输出定义java的工作目录
2.输出指定java所需的类文件
3.输出重新定义环境变量,$PATH一定要放在$JAVA_HOME的后面,让系统先读取到工作目录中的版本信息
source /etc/profile.d/java.sh
java -version
java version "1.8.0_201"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_201-b09)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.201-b09, mixed mode)
# rpm 安装 jdk (方法二)
cd /opt
tar zxvf jdk-8u91-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/local
mv /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_91/ /usr/local/jdk
vim /etc/profile
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk
export JRE_HOME=${JAVA_HOME}/jre
export CLASSPATH=.:${JAVA_HOME}/lib:${JRE_HOME}/lib
export PATH=${JAVA_HOME}/bin:$PATH
source /etc/profile
java -version
3.2 部署 ElasticSearch 软件
1、安装 elasticsearch-rpm 包
[root@node1 ~]# cd /opt
[root@node1 opt]# rz -E
#上传elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm到/opt目录下
rz waiting to receive.
[root@node1 opt]# rpm -ivh elasticsearch-5.5.0.rpm
2、加载系统服务
systemctl daemon-reload && systemctl enable elasticsearch.service
3、修改 elasticsearch 主配置文件
[root@node1 opt]# cp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml.bak
#备份配置文件
[root@node1 opt]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
##17行,取消注释,指定群集名称
cluster.name: my-elk-cluster
##23行,取消注释,指定节点名称(node1节点为node1,node2节点为node2)
node.name: node1
##33行,取消注释,指定数据存放路径
path.data: /data/elk_data
##37行,取消注释,指定日志存放路径
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch/
##43行,取消注释,不在启动的时候锁定内存(前端缓存,与IOPS-性能测试方式,每秒读写次数相关)
bootstrap.memory_lock: false
##55行,取消注释,设置监听地址,0.0.0.0代表所有地址
network.host: 0.0.0.0
##59行,取消注释,ES服务的默认监听端口为9200
http.port: 9200
##68行,取消注释,集群发现通过单播实现,指定要发现的节点node1、node2
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["node1", "node2"]
[root@node1 opt]# grep -v "^#" /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
cluster.name: my-elk-cluster
node.name: node1
path.data: /data/elk_data
path.logs: /var/log/elasticsearch/
bootstrap.memory_lock: false
network.host: 0.0.0.0
http.port: 9200
discovery.zen.ping.unicast.hosts: ["node1", "node2"]
-------------------------------------------------------
scp /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml [email protected]:/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
#将配置好的文件用 scp 传至 node2,后续只用去改个节点名字即可
4、创建数据存放路径并授权
[root@node1 opt]# mkdir -p /data/elk_data
[root@node1 opt]# chown elasticsearch:elasticsearch /data/elk_data/
5、启动 elasticsearch
[root@node1 opt]# systemctl start elasticsearch.service
[root@node1 opt]# netstat -natp | grep 9200 #启动较慢,需等待
tcp6 0 0 :::9200 :::* LISTEN 4216/java
注:必须在解压后的 elasticsearch-head 目录下启动服务,进程会读取该目录下的 gruntfile.js 文件,否则可能启动失败。6、查看节点信息
浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:9200、http://192.168.223.53:9200 查看节点 node1、node2 的信息
浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:9200/_cluster/health?pretty、http://192.168.223.53:9200/_cluster/health?pretty查看群集的健康情况,可以看到status值为green(绿色),表示节点健康运行
浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:9200/_cluster/state?pretty、http://192.168.223.53:9200/_cluster/state?pretty 检查群集状态信息
4、安装 Elasticsearch-head 插件(node1为例)
ES 在 5.0 版本后,插件需要作为独立服务进行安装,需要使用 npm 工具(NodeJS 的包管理工具)安装。安装 Elasticsarch-head 需要提前安装好依赖软件 node 和 phantomjs。
- node是一个基于 Chrome V8 引擎的 JavaScript 运行环境。
- phantomjs是一个基于 webkit 的 JavaScriptAPI,可以理解为一个隐形的浏览器,任何基于 webkit 浏览器做的事情,它都可以做到。
4.1编译安装 node
[root@node1 ~]# cd /opt
[root@node1 opt]# rz -E
#上传软件包node-v8.2.1.tar.gz到/opt目录
rz waiting to receive.
[root@node1 opt]# yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ make
[root@node1 opt]# tar zxvf node-v8.2.1.tar.gz
[root@node1 opt]# cd node-v8.2.1/
[root@node1 node-v8.2.1]# ./configure
[root@node1 node-v8.2.1]# make -j 4 && make install
#编译时间很长
4.2 安装 phantomjs
[root@node1 node-v8.2.1]# cd /opt
[root@node1 opt]# rz -E
#上传软件包phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2到/opt目录
rz waiting to receive.
[root@node1 opt]# tar jxvf phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64.tar.bz2 -C /usr/local/src
[root@node1 opt]# cd /usr/local/src/phantomjs-2.1.1-linux-x86_64/bin
[root@node1 bin]# cp phantomjs /usr/local/bin
4.3 安装 Elasticsearch-head 数据可视化工具
[root@node1 bin]# cd /opt
[root@node1 opt]# rz -E
#上传软件包elasticsearch-head.tar.gz到/opt目录
rz waiting to receive.
[root@node1 opt]# tar zxvf elasticsearch-head.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/
[root@node1 opt]# cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# npm install
4.4 修改 Elasticsearch 主配置文件
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# vim /etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.yml
##末行添加以下内容
http.cors.enabled: true ##开启跨域访问支持,默认为false
http.cors.allow-origin: "*" ##指定跨域访问允许的域名地址为所有
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# systemctl restart elasticsearch.service
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# netstat -antp | grep 9200
4.5 启动 elasticsearch-head 服务
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# cd /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head/
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# npm run start &
[1] 71012
> [email protected] start /usr/local/src/elasticsearch-head
> grunt server
Running "connect:server" (connect) task
Waiting forever...
Started connect web server on http://localhost:9100
^C
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# netstat -natp | grep 9100
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:9100 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 71022/grunt
注:必须在解压后的 elasticsearch-head 目录下启动服务,进程会读取该目录下的 gruntfile.js 文件,否则可能启动失败。
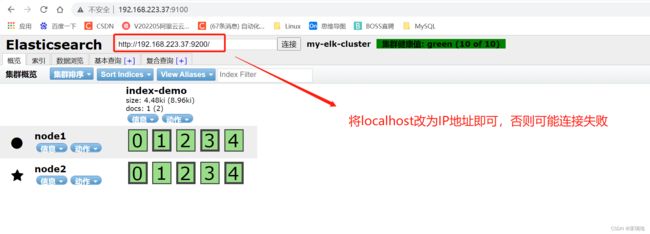
4.6 通过 Elasticsearch-head 查看 ES 信息
通过浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:9100 地址并连接群集。如果看到群集健康值为 green,代表群集很健康。
注意:有的时候显示未连接,这时将 localhost 改成 IP 地址即可
4.7插入索引
通过命令插入一个测试索引,索引为 index-demo,类型为 test
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# curl -X PUT 'localhost:9200/index-demo/test/1?pretty&pretty' -H 'content-Type: application/json' -d '{"user":"zhangsan","mesg":"hello world"}'
{
"_index" : "index-demo",
"_type" : "test",
"_id" : "1",
"_version" : 1,
"result" : "created",
"_shards" : {
"total" : 2,
"successful" : 2,
"failed" : 0
},
"created" : true
}
4.8 浏览器查看索引信息
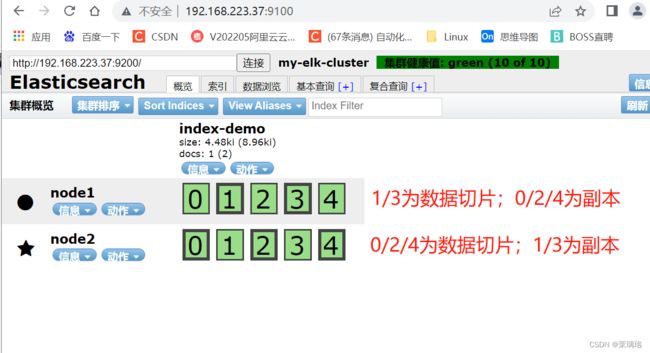
浏览器访问 http://129.168.223.37:9100 查看索引信息,可以看见索引默认被分片为 5 个,并且有一个副本。
点击 **数据浏览**,会发现在 node1 上创建的索引为 index-demo,类型为 test 的相关信息。
5、ELK-Logstash 部署(在 Apache 节点上操作)
- Logstash 一般部署在需要监控其日志的服务器。在本案例中,Logstash 部署在 Apache 服务器上,用于收集 Apache 的日志信息并发送到 Elasticsearch。
5.1 更改主机名
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname apache
[root@localhost ~]# su
[root@apache ~]#
5.2 安装 Apache 服务(httpd)
[root@apache ~]# yum install -y httpd
[root@apache ~]# systemctl start httpd && systemctl enable httpd
5.3 安装 Java 环境
cd /opt
tar zxvf jdk-8u91-linux-x64.tar.gz -C /usr/local
mv /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_91/ /usr/local/jdk
vim /etc/profile
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk
export JRE_HOME=${JAVA_HOME}/jre
export CLASSPATH=.:${JAVA_HOME}/lib:${JRE_HOME}/lib
export PATH=${JAVA_HOME}/bin:$PATH
source /etc/profile
java -version
5.4 安装 logstash
[root@apache ~]# cd /opt
[root@apache opt]# rz -E #上传安装包 logstash-5.5.1.rpm
[root@apache opt]# rpm -ivh logstash-5.5.1.rpm
[root@apache opt]# systemctl start logstash.service && systemctl enable logstash.service
[root@apache opt]# ln -s /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash /usr/local/bin/
5.5 测试 Logstash
1、 Logstash 命令常用选项
| Logstash 命令常用选项 | 说明 |
| -f | 通过这个选项可以指定 Logstash 的配置文件,根据配置文件配置 Logstash 的输入和输出流 |
| -e | 从命令行中获取,输入、输出后面跟着字符串,该字符串可以被当做 Logstash 的配置(如果是空,则默认使用 stdin 作为输入,stdout 作为输出) |
| -t | 测试配置文件是否正确,然后退出 |
2、定义输入和输出流
标准输入、输出:输入采用标准输入,输出采用标准输出(类似管道)
[root@apache opt]# logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{} }'
ERROR StatusLogger No log4j2 configuration file found. Using default configuration: logging only errors to the console.
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --p the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path //usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs to console
12:16:12.662 [main] INFO logstash.setting.writabledirectory - Creating directory {:setting=>"path.queue", :path=>"/usr/share/logstash/
12:16:12.667 [main] INFO logstash.setting.writabledirectory - Creating directory {:setting=>"path.dead_letter_queue", :path=>"/usr/shaueue"}
12:16:12.699 [LogStash::Runner] INFO logstash.agent - No persistent UUID file found. Generating new UUID {:uuid=>"20e5df40-1bc6-4e92-8r/share/logstash/data/uuid"}
12:16:12.997 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Starting pipeline {"id"=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>16, "pipeline.bat.delay"=>5, "pipeline.max_inflight"=>2000}
12:16:13.056 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Pipeline main started
The stdin plugin is now waiting for input:
12:16:13.110 [Api Webserver] INFO logstash.agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
www.test.com
2022-07-06T16:16:52.104Z apache www.test.com
www.baidu.com
2022-07-06T16:16:58.786Z apache www.baidu.com
www.aliyun.com
2022-07-06T16:17:12.959Z apache www.aliyun.com
^C12:17:16.405 [SIGINT handler] WARN logstash.runner - SIGINT received. Shutting down the agent.
12:17:16.417 [LogStash::Runner] WARN logstash.agent - stopping pipeline {:id=>"main"}
rubydebug 输出使:用 rubydebug 输出详细格式显示,codec 为一种编解码器
[root@apache opt]# logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { stdout{ codec=>rubydebug } }'
ERROR StatusLogger No log4j2 configuration file found. Using default configuration: logging only errors to the console.
WARNING: Could not find logstash.yml which is typically located in $LS_HOME/config or /etc/logstash. You can specify the path using --path.settings. Continuing using the defaults
Could not find log4j2 configuration at path //usr/share/logstash/config/log4j2.properties. Using default config which logs to console
12:17:43.470 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Starting pipeline {"id"=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>16, "pipeline.batch.size"=>125, "pipeline.batch.delay"=>5, "pipeline.max_inflight"=>2000}
12:18:39.514 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Pipeline main started
The stdin plugin is now waiting for input:
12:18:39.750 [Api Webserver] INFO logstash.agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
www.test.com
{
"@timestamp" => 2022-07-06T16:18:45.980Z,
"@version" => "1",
"host" => "apache",
"message" => "www.test.com"
}
^C12:18:52.237 [SIGINT handler] WARN logstash.runner - SIGINT received. Shutting down the agent.
12:18:52.260 [LogStash::Runner] WARN logstash.agent - stopping pipeline {:id=>"main"}
输出到 ES:使用 logstash 将写入到 ES 中
[root@apache opt]# logstash -e 'input { stdin{} } output { elasticsearch { hosts=>["192.168.223.37:9200"] } }'
12:20:47.760 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - Running health check to see if an Elasticsearch connection is working {:healthcheck_url=>http://192.168.223.37:9200/, :path=>"/"}
12:20:47.856 [[main]-pipeline-manager] WARN logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - Restored connection to ES instance {:url=>#}
12:20:47.859 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - Using mapping template from {:path=>nil}
12:20:48.074 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - Attempting to install template {:manage_template=>{"template"=>"logstash-*", "version"=>50001, "settings"=>{"index.refresh_interval"=>"5s"}, "mappings"=>{"_default_"=>{"_all"=>{"enabled"=>true, "norms"=>false}, "dynamic_templates"=>[{"message_field"=>{"path_match"=>"message", "match_mapping_type"=>"string", "mapping"=>{"type"=>"text", "norms"=>false}}}, {"string_fields"=>{"match"=>"*", "match_mapping_type"=>"string", "mapping"=>{"type"=>"text", "norms"=>false, "fields"=>{"keyword"=>{"type"=>"keyword", "ignore_above"=>256}}}}}], "properties"=>{"@timestamp"=>{"type"=>"date", "include_in_all"=>false}, "@version"=>{"type"=>"keyword", "include_in_all"=>false}, "geoip"=>{"dynamic"=>true, "properties"=>{"ip"=>{"type"=>"ip"}, "location"=>{"type"=>"geo_point"}, "latitude"=>{"type"=>"half_float"}, "longitude"=>{"type"=>"half_float"}}}}}}}}
12:20:48.083 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.outputs.elasticsearch - New Elasticsearch output {:class=>"LogStash::Outputs::ElasticSearch", :hosts=>[#]}
12:20:48.088 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Starting pipeline {"id"=>"main", "pipeline.workers"=>16, "pipeline.batch.size"=>125, "pipeline.batch.delay"=>5, "pipeline.max_inflight"=>2000}
12:20:48.138 [[main]-pipeline-manager] INFO logstash.pipeline - Pipeline main started
The stdin plugin is now waiting for input:
12:20:48.179 [Api Webserver] INFO logstash.agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
www.test.com
^C12:23:05.586 [SIGINT handler] WARN logstash.runner - SIGINT received. Shutting down the agent.
12:23:05.601 [LogStash::Runner] WARN logstash.agent - stopping pipeline {:id=>"main"}
结果不在标准输出显示,而是发送至 ES,可浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:9100 查看索引和数据
5.6定义 logstash 配置文件
Logstash 配置文件基本由三部分组成:input、output 以及 filter(可选,根据需要选择使用)
- input:表示从数据源采集数据,常见的数据源如Kafka、日志文件等
- filter:表示数据处理层,包括对数据进行格式化处理、数据类型转换、数据过滤等,支持正则表达式
- output:表示将Logstash收集的数据经由过滤器处理之后输出到Elasticsearch。
格式如下:
input {...}
output {...}
filter {...}
在每个部分中,也可以指定多个访问方式。例如:若要指定两个日志来源文件,则格式如下:
input {
file { path =>"/var/log/messages" type =>"syslog"}
file { path =>"/var/log/httpd/access.log" type =>"apache"}
}
修改 logstash 配置文件,让其收集系统日志 /var/log/messages,并将其输出到 ES 中
[root@apache opt]# chmod o+r /var/log/messages
#赋予读的权限,让 Logstash 可以获取到该文件的内容
[root@apache opt]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/system.conf
##该文件需自行创建,文件名可自定义
input {
file{
path =>"/var/log/messages"
##指定要收集的日志的位置
type =>"system"
##自定义日志类型标识
start_position =>"beginning"
##表示从开始处收集
}
}
output {
elasticsearch{
##输出到ES
hosts =>["192.168.223.37:9200", "192.168.223.53:9200"]
##指定ES服务器的地址和端口,为避免单机故障,建议写全
index =>"system-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
##指定输出到ES的索引格式
}
}
[root@apache opt]# systemctl restart logstash.service
5.7访问测试
浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:9100 查看索引信息
6、ELK-Kibana 部署(在 node1 节点上操作)
6.1 安装 Kibana
[root@node1 elasticsearch-head]# cd /opt
[root@node1 opt]# rz -E #上传软件包 kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm
[root@node1 opt]# rpm -ivh kibana-5.5.1-x86_64.rpm
6.2 设置 Kibana 的主配置文件
[root@node1 opt]# cp /etc/kibana/kibana.yml /etc/kibana/kibana.yml.bak
#备份配置文件
[root@node1 opt]# vim /etc/kibana/kibana.yml
##2行,取消注释,kibana服务的默认监听端口为5601
server.port: 5601
##7行,取消注释,设置kibana的监听地址,0.0.0.0代表所有地址
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
##21行,取消注释,设置和ES建立连接的地址和端口
elasticsearch.url: "http://192.168.223.37:9200"
##30行,取消注释,设置在ES中添加.kibana索引
kibana.index: ".kibana"
6.3 启动 Kibana 服务
[root@node1 opt]# systemctl start kibana.service && systemctl enable kibana.service
[root@node1 opt]# netstat -natp | grep 5601
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:5601 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 82765/node
6.4 验证 Kibana
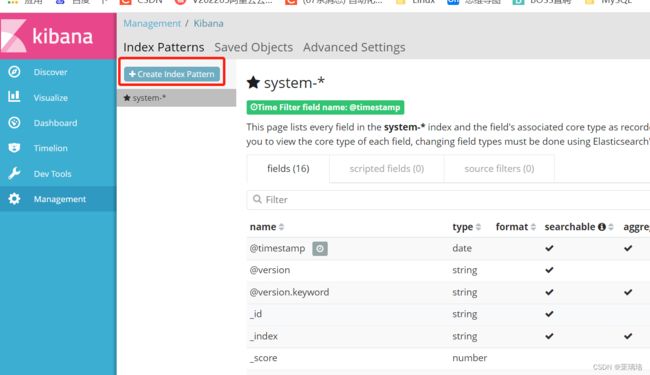
浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:5601
第一次登录需要添加一个 ES 索引
点击 create 创建
索引添加完成后,点击 Discover 按钮可查看图表信息及日志信息
数据展示可以分类显示,例如:在 Available Fileds 中的 host
6.5 将 Apache 服务器的日志(访问的、错误的)添加到 ES 并通过 Kibana 显示
apache 服务器
[root@apache opt]# vim /etc/logstash/conf.d/apache_log.conf
input {
file{
path => "/etc/httpd/logs/access_log"
type => "access"
start_position => "beginning"
}
file{
path => "/etc/httpd/logs/error_log"
type => "error"
start_position => "beginning"
}
}
output {
if [type] == "access" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.223.37:9200", "192.168.223.53:9200"]
index => "apache_access-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
if [type] == "error" {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.223.37:9200", "192.168.223.53:9200"]
index => "apache_error-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
}
}
[root@apache opt]# cd /etc/logstash/conf.d
[root@apache conf.d]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f apache_log.conf
······
23:42:13.199 [Api Webserver] INFO logstash.agent - Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9601}
6 .6 浏览器访问
浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:9100 查看索引是否创建可能你只看到了 apache-error,那是因为 access 需要访问 httpd 页面才能生成
浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:5601 登录 kibana,添加 apache_access-* 和 apache_error-* 索引,查看日志信息
三、ELFK(Filebeat + ELK)
1、Filebeat 的作用
- 由于 logstash 会大量占用系统的内存资源,一般我们会使用 filebeat 替换 logstash 收集日志的功能,组成 ELFK 架构
- 或用 fluentd 替代 logstash 组成 EFK(elasticsearch/fluentd/kibana),由于 fluentd 是由 Go 语言开发的,一般在 K8s 环境中使用较多
2、ELFK 工作流程
- filebeat 将日志收集后交由 logstash 处理
- logstash 进行过滤、格式化等操作,满足过滤条件的数据将发送给 ES
- ES 对数据进行分片存储,并提供索引功能
- Kibana 对数据进行图形化的 web 展示,并提供索引接口
3、ELFK 的部署
3.1服务器配置
| 服务器 | 配置 | 主机名 | ip地址 | 主要软件部署 |
| node1 节点 | 2C/4G | node1 | 192.168.223.37 | ElasticSearch、Kibana |
| node2 节点 | 2C/4G | node2 | 192.168.223.53 | ElasticSearch |
| apache 节点 | / | apache | 192.168.223.13 | Logstash、Apache |
| filebeat 节点 | / | filebeat | 192.168.223.33 | Filebeat |
在 ELK 的服务配置的基础上,增加一台 filebeat 服务器,其余不变(所以以下只说明部署Filebeat服务器)
3.2 服务器环境
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname filebeat
[root@localhost ~]# su
[root@filebeat ~]# systemctl stop firewalld && systemctl disable firewalld
[root@filebeat ~]# setenforce 0
3.3 安装 filebeat
#wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/beats/filebeat/filebeat-6.2.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
#wget http://101.34.22.188/ELK/filebeat-5.5.1-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -P /opt
[root@filebeat ~]# wget http://101.34.22.188/ELK/filebeat-6.2.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -P /opt
[root@filebeat ~]# cd /opt
[root@filebeat opt]# tar zxvf filebeat-6.2.4-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
[root@filebeat opt]# mv filebeat-6.2.4-linux-x86_64 /usr/local/filebeat
3.4 修改 filebeat 主配置文件
3.5 在 logstash 组件所在节点(apache节点)上新建一个 logstash 配置文件
[root@apache ~]# cd /etc/logstash/conf.d/
[root@apache conf.d]# vim logstash.conf
input {
beats {
port => "5044"
}
}
output {
elasticsearch {
hosts => ["192.168.223.37:9200", "192.168.223.53:9200"]
index => "%{[fields][service_name]}-%{+YYYY.MM.dd}"
}
stdout {
codec => rubydebug
}
}
[root@apache conf.d]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -f apache_log.conf
3.6 浏览器验证
浏览器访问 http://192.168.223.37:5601 登录 kibana, 添加 filebeat-* 索引后在 Discover 中查看 filebeat 日志收集情况。
参考文件如下
ELK 理论详解![]() https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51486343/article/details/114297277?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522163721971416780271569143%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fblog.%2522%257D&request_id=163721971416780271569143&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~blog~first_rank_v2~rank_v29-2-114297277.pc_v2_rank_blog_default&utm_term=ELK&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450
https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_51486343/article/details/114297277?ops_request_misc=%257B%2522request%255Fid%2522%253A%2522163721971416780271569143%2522%252C%2522scm%2522%253A%252220140713.130102334.pc%255Fblog.%2522%257D&request_id=163721971416780271569143&biz_id=0&utm_medium=distribute.pc_search_result.none-task-blog-2~blog~first_rank_v2~rank_v29-2-114297277.pc_v2_rank_blog_default&utm_term=ELK&spm=1018.2226.3001.4450
ELK 部署![]() https://xucf1.blog.csdn.net/article/details/114333700
https://xucf1.blog.csdn.net/article/details/114333700
ELK 详解![]() https://www.cnblogs.com/dingcong1201/p/15363199.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/dingcong1201/p/15363199.html
Zookeeper、Kafka集群与Filebeat+Kafka+ELK架构![]() https://www.cnblogs.com/dingcong1201/p/15365638.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/dingcong1201/p/15365638.html