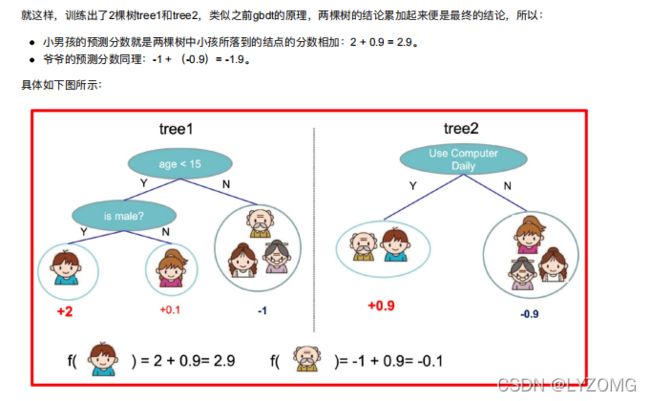
12.集成学习进阶一——xgboost
xgboost算法
XGBoost(Extreme Gradient Boosting)全名叫极端梯度提升树,XGBoost是集成学习⽅法的王牌,在Kaggle数据挖掘 ⽐赛中,⼤部分获胜者⽤了XGBoost。
最优模型的构建⽅法
XGBoost的⽬标函数推导
⽬标函数确定
CART树的介绍
树的复杂度定义
定义每课树的复杂度
树的复杂度例子
⽬标函数推导
XGBoost的回归树构建⽅法
计算分裂节点
停⽌分裂条件判断
XGBoost与GDBT的区别
xgboost算法api介绍
官网
pip3 install xgboost
通⽤参数(general parameters)
Booster 参数(booster parameters)
Parameters for Tree Booster
Parameters for Linear Booster
学习⽬标参数(task parameters)
xgboost案例–泰坦尼克号存活分析

案例
我们提取到的数据集中的特征包括票的类别,是否存活,乘坐班次,年龄,登陆home.dest,房间,船和性别等。
[数据](http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/wiki/pub/Main/DataSets/titanic.txt)

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.feature_extraction import DictVectorizer
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier, export_graphviz
# 1.获取数据
titan = pd.read_csv("http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/wiki/pub/Main/DataSets/titanic.txt")
titan
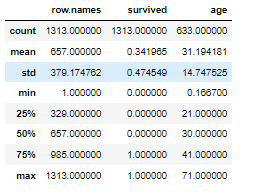
titan.describe()
# 2.数据基本处理
# 2.1 确定特征值,目标值
x = titan[["pclass", "age", "sex"]]
y = titan["survived"]
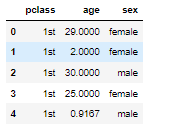
x.head()
y.head()
# 2.2 缺失值处理
x['age'].fillna(value=titan["age"].mean(), inplace=True)
x.head()
# 2.3 数据集划分
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(x, y, random_state=22, test_size=0.2)
# 3.特征工程(字典特征抽取)
x_train.head()
x_train = x_train.to_dict(orient="records")
x_test = x_test.to_dict(orient="records")
x_train
transfer = DictVectorizer()
x_train = transfer.fit_transform(x_train)
x_test = transfer.fit_transform(x_test)
# 4.xgboost模型训练
# 4.1 初步模型训练
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
xg = XGBClassifier()
xg.fit(x_train, y_train)
xg.score(x_test, y_test) #0.7832699619771863
# 4.2 对max_depth进行调优
depth_range = range(10)
score = []
for i in depth_range:
xg = XGBClassifier(eta=1, gamma=0, max_depth=i)
xg.fit(x_train, y_train)
s = xg.score(x_test, y_test)
print(s)
score.append(s)
# 4.3 调优结果可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot(depth_range, score)
plt.show()
xgboost案例–otto案例产品分类
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
数据获取
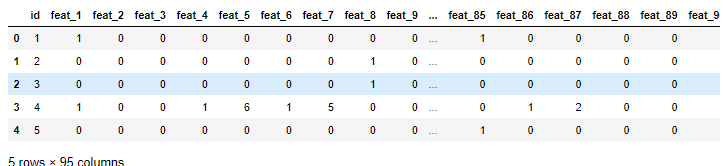
data = pd.read_csv("./data/otto/train.csv")
data.head()
data.shape #(61878, 95)
data.describe()
# 图形可视化,查看数据分布
import seaborn as sns
sns.countplot(data.target)
plt.show()
数据基本处理
数据已经经过脱敏,不再需要特殊处理
# 截取部分数据
new1_data = data[:10000]
new1_data.shape #(10000, 95)
# 图形可视化,查看数据分布
sns.countplot(new1_data.target)
plt.show()
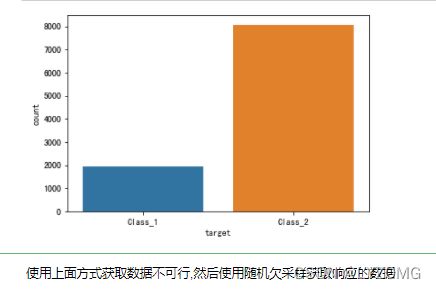
# 随机欠采样获取数据
# 首先需要确定特征值\标签值
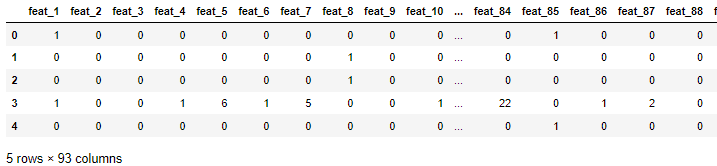
y = data["target"]
x = data.drop(["id", "target"], axis=1)
x.head()
y.head()
# 欠采样获取数据
from imblearn.under_sampling import RandomUnderSampler
rus = RandomUnderSampler(random_state=0)
X_resampled, y_resampled = rus.fit_resample(x, y)
x.shape, y.shape #((61878, 93), (61878,))
X_resampled.shape, y_resampled.shape #((17361, 93), (17361,))
# 图形可视化,查看数据分布
sns.countplot(y_resampled)
plt.show()
y_resampled.head()
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
le = LabelEncoder()
y_resampled = le.fit_transform(y_resampled)
y_resampled #array([0, 0, 0, ..., 8, 8, 8])
分割数据
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_resampled, y_resampled, test_size=0.2)
x_train.shape, y_train.shape #((13888, 93), (13888,))
x_test.shape, y_test.shape #((3473, 93), (3473,))
# 图形可视化
sns.countplot(y_test)
plt.show()
# 通过StratifiedShuffleSplit实现数据分割
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedShuffleSplit
sss = StratifiedShuffleSplit(n_splits=1, test_size=0.2, random_state=0)
for train_index, test_index in sss.split(X_resampled.values, y_resampled):
print(len(train_index)) #13888
print(len(test_index)) #3473
x_train = X_resampled.values[train_index]
x_val = X_resampled.values[test_index]
y_train = y_resampled[train_index]
y_val = y_resampled[test_index]
print(x_train.shape, x_val.shape) #(13888, 93) (3473, 93)
# 图形可视化
sns.countplot(y_val)
plt.show()
数据标准化
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(x_train)
x_train_scaled = scaler.transform(x_train)
x_val_scaled = scaler.transform(x_val)
数据PCA降维
x_train_scaled.shape #(13888, 93)
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
pca = PCA(n_components=0.9)
x_train_pca = pca.fit_transform(x_train_scaled)
x_val_pca = pca.transform(x_val_scaled)
print(x_train_pca.shape, x_val_pca.shape) #(13888, 65) (3473, 65)
# 可视化数据降维信息变化程度
plt.plot(np.cumsum(pca.explained_variance_ratio_))
plt.xlabel("元素数量")
plt.ylabel("表达信息百分占比")
plt.show()
模型训练
基本模型训练
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
xgb = XGBClassifier()
xgb.fit(x_train_pca, y_train)
# 输出预测值,一定输出带有百分占比的预测值
y_pre_proba = xgb.predict_proba(x_val_pca)
y_pre_proba
# logloss评估
from sklearn.metrics import log_loss
log_loss(y_val, y_pre_proba, eps=1e-15, normalize=True) #0.7845457684689274
xgb.get_params
模型调优
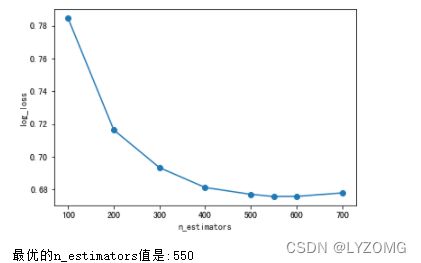
确定最优的estimators
scores_ne = []
n_estimators = [100, 200, 300, 400, 500, 550, 600, 700]
for nes in n_estimators:
print("n_estimators:", nes)
xgb = XGBClassifier(max_depth=3,
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=nes,
objective="multi:softprob",
n_jobs=-1,
nthread=4,
min_child_weight=1,
subsample=1,
colsample_bytree=1,
seed=42)
xgb.fit(x_train_pca, y_train)
y_pre = xgb.predict_proba(x_val_pca)
score = log_loss(y_val, y_pre)
scores_ne.append(score)
print("每次测试的logloss值是:{}".format(score))
# 图形化展示相应的logloss值
plt.plot(n_estimators, scores_ne, "o-")
plt.xlabel("n_estimators")
plt.ylabel("log_loss")
plt.show()
print("最优的n_estimators值是:{}".format(n_estimators[np.argmin(scores_ne)]))
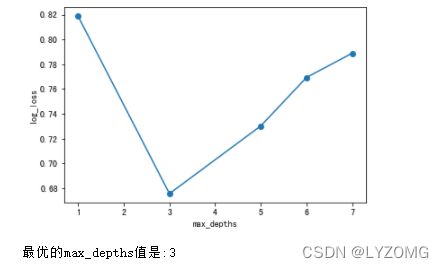
确定最优的max_depth
scores_md = []
max_depths = [1,3,5,6,7]
for md in max_depths:
print("max_depth:", md)
xgb = XGBClassifier(max_depth=md,
learning_rate=0.1,
n_estimators=n_estimators[np.argmin(scores_ne)],
objective="multi:softprob",
n_jobs=-1,
nthread=4,
min_child_weight=1,
subsample=1,
colsample_bytree=1,
seed=42)
xgb.fit(x_train_pca, y_train)
y_pre = xgb.predict_proba(x_val_pca)
score = log_loss(y_val, y_pre)
scores_md.append(score)
print("每次测试的logloss值是:{}".format(score))
# 图形化展示相应的logloss值
plt.plot(max_depths, scores_md, "o-")
plt.xlabel("max_depths")
plt.ylabel("log_loss")
plt.show()
print("最优的max_depths值是:{}".format(max_depths[np.argmin(scores_md)]))
**依据上面模式,运行调试下面参数
min_child_weights,
subsamples,
consample_bytrees,
etas**
xgb = XGBClassifier(learning_rate =0.1,
n_estimators=550,
max_depth=3,
min_child_weight=3,
subsample=0.7,
colsample_bytree=0.7,
nthread=4,
seed=42,
objective='multi:softprob')
xgb.fit(x_train_scaled, y_train)
y_pre = xgb.predict_proba(x_val_scaled)
print("测试数据的log_loss值为 : {}".format(log_loss(y_val, y_pre, eps=1e-15, normalize=True)))
测试数据的log_loss值为 : 0.5944022517380477