【路径规划】基于粒子群算法机器人避障路径规划matlab源码含GUI
一、简介
1 粒子群算法的概念\ 粒子群优化算法(PSO:Particle swarm optimization) 是一种进化计算技术(evolutionary computation)。源于对鸟群捕食的行为研究。粒子群优化算法的基本思想:是通过群体中个体之间的协作和信息共享来寻找最优解.\ PSO的优势:在于简单容易实现并且没有许多参数的调节。目前已被广泛应用于函数优化、神经网络训练、模糊系统控制以及其他遗传算法的应用领域。
2 粒子群算法分析\ 2.1基本思想\ 粒子群算法通过设计一种无质量的粒子来模拟鸟群中的鸟,粒子仅具有两个属性:速度和位置,速度代表移动的快慢,位置代表移动的方向。每个粒子在搜索空间中单独的搜寻最优解,并将其记为当前个体极值,并将个体极值与整个粒子群里的其他粒子共享,找到最优的那个个体极值作为整个粒子群的当前全局最优解,粒子群中的所有粒子根据自己找到的当前个体极值和整个粒子群共享的当前全局最优解来调整自己的速度和位置。下面的动图很形象地展示了PSO算法的过程:\  \ 2 更新规则\ PSO初始化为一群随机粒子(随机解)。然后通过迭代找到最优解。在每一次的迭代中,粒子通过跟踪两个“极值”(pbest,gbest)来更新自己。在找到这两个最优值后,粒子通过下面的公式来更新自己的速度和位置。\
\ 2 更新规则\ PSO初始化为一群随机粒子(随机解)。然后通过迭代找到最优解。在每一次的迭代中,粒子通过跟踪两个“极值”(pbest,gbest)来更新自己。在找到这两个最优值后,粒子通过下面的公式来更新自己的速度和位置。\  \ 公式(1)的第一部分称为【记忆项】,表示上次速度大小和方向的影响;公式(1)的第二部分称为【自身认知项】,是从当前点指向粒子自身最好点的一个矢量,表示粒子的动作来源于自己经验的部分;公式(1)的第三部分称为【群体认知项】,是一个从当前点指向种群最好点的矢量,反映了粒子间的协同合作和知识共享。粒子就是通过自己的经验和同伴中最好的经验来决定下一步的运动。以上面两个公式为基础,形成了PSO的标准形式。\
\ 公式(1)的第一部分称为【记忆项】,表示上次速度大小和方向的影响;公式(1)的第二部分称为【自身认知项】,是从当前点指向粒子自身最好点的一个矢量,表示粒子的动作来源于自己经验的部分;公式(1)的第三部分称为【群体认知项】,是一个从当前点指向种群最好点的矢量,反映了粒子间的协同合作和知识共享。粒子就是通过自己的经验和同伴中最好的经验来决定下一步的运动。以上面两个公式为基础,形成了PSO的标准形式。\  \ 公式(2)和 公式(3)被视为标准PSO算法。\ 3 PSO算法的流程和伪代码\
\ 公式(2)和 公式(3)被视为标准PSO算法。\ 3 PSO算法的流程和伪代码\ 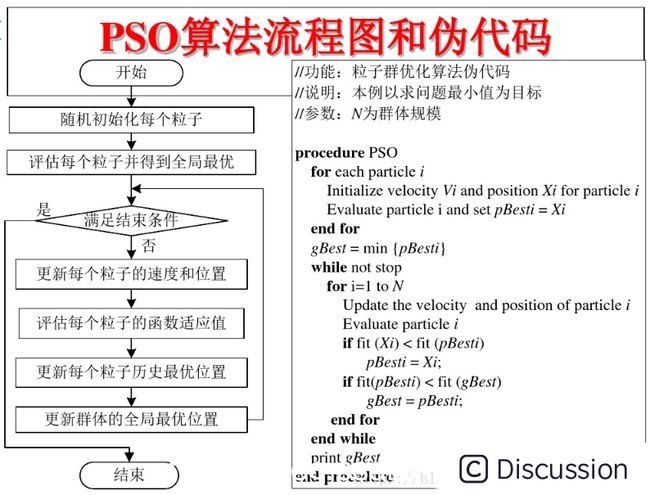
二、源代码
``` function varargout = GUIbiyeshiji(varargin) % GUIBIYESHIJI M-file for GUIbiyeshiji.fig % GUIBIYESHIJI, by itself, creates a new GUIBIYESHIJI or raises the existing % singleton. % % H = GUIBIYESHIJI returns the handle to a new GUIBIYESHIJI or the handle to % the existing singleton. % % GUIBIYESHIJI('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local % function named CALLBACK in GUIBIYESHIJI.M with the given input arguments. % % GUIBIYESHIJI('Property','Value',...) creates a new GUIBIYESHIJI or raises the % existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are % applied to the GUI before GUIbiyeshijiOpeningFunction gets called. An % unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application % stop. All inputs are passed to GUIbiyeshijiOpeningFcn via varargin. % % *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one % instance to run (singleton)". % % See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help GUIbiyeshiji
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 22-May-2021 03:05:52
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT guiSingleton = 1; guiState = struct('guiName', mfilename, ... 'guiSingleton', guiSingleton, ... 'guiOpeningFcn', @GUIbiyeshijiOpeningFcn, ... 'guiOutputFcn', @GUIbiyeshijiOutputFcn, ... 'guiLayoutFcn', [] , ... 'guiCallback', []); if nargin && ischar(varargin{1}) guiState.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{1}); end
if nargout [varargout{1:nargout}] = guimainfcn(guiState, varargin{:}); else guimainfcn(guiState, varargin{:}); end % End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before GUIbiyeshiji is made visible. function GUIbiyeshiji_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin) % This function has no output args, see OutputFcn. % hObject handle to figure % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) % varargin command line arguments to GUIbiyeshiji (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for GUIbiyeshiji handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes GUIbiyeshiji wait for user response (see UIRESUME) % uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line. function varargout = GUIbiyeshiji_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles) % varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT); % hObject handle to figure % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure varargout{1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1. function pushbutton1Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) clc;clear; %close(1);close(2);close(3);close(4); handles=guihandles; p1=get(handles.edit1,'String'); p=eval(p1); Objectnum=p;%%%障碍物的数目 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%随机产生障碍物点%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% num=Object_num; x=rand(num,1); y=rand(num,1); point=[x,y];
% % load('D:\MATLAB71\work\毕业设计\goodpoint.mat') % % x=point(:,1);y=point(:,2); %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%在点状图上画出障碍物环境%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
global photoll photocc photo; photoll=300;photocc=300; photo=ones(photoll,photocc); [photo_point,aaa]=plot2photo(point);
[photopointamount,aaa]=size(photopoint); for i=1:photopointamount photopointaround=square(photopoint(i,:),15);%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%画出的图形的大小 aaa=blackenphoto(photopoint_around); end
global photoconnectpoints; photoconnectpoints=photo;
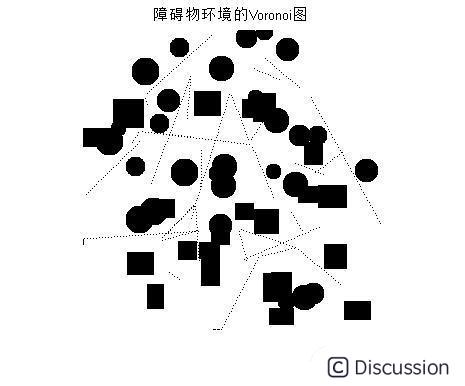
figure imshow(photo) title('障碍物环境')
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2. function pushbutton2Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) clc;clear; %close(1);close(2);close(3);close(4); handles=guihandles; p1=get(handles.edit1,'String'); p=eval(p1); Objectnum=p;%%%障碍物的数目 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%随机产生障碍物点%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% num=Object_num; x=rand(num,1); y=rand(num,1); point=[x,y];
% % load('D:\MATLAB71\work\毕业设计\goodpoint.mat') % % x=point(:,1);y=point(:,2); %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%在点状图上画出障碍物环境%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
global photoll photocc photo; photoll=300;photocc=300; photo=ones(photoll,photocc); [photo_point,aaa]=plot2photo(point);
[photopointamount,aaa]=size(photopoint); for i=1:photopointamount photopointaround=square(photopoint(i,:),15);%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%画出的图形的大小 aaa=blackenphoto(photopoint_around); end
global photoconnectpoints; photoconnectpoints=photo;
% % figure % % imshow(photo) % % title('障碍物环境')
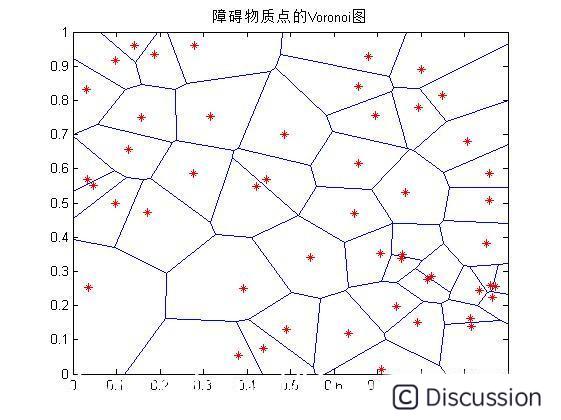
%%%%%%%%%%%获得其Voronoi图 figure voronoi(x,y) title('障碍物质点的Voronoi图') [connectpoint,roundpointcell]=voronoin(point); connectpoint(1,:)=[]; tri=delaunay(x,y); hold on plot(point(:,1),point(:,2),'r*'); hold off
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3. function pushbutton3Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles) % hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO) % eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB % handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA) clc;clear; %close(1);close(2);close(3);close(4); handles=guihandles; p1=get(handles.edit1,'String'); p=eval(p1); Objectnum=p;%%%障碍物的数目 %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%随机产生障碍物点%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% num=Object_num; x=rand(num,1); y=rand(num,1); point=[x,y];
% % load('D:\MATLAB71\work\毕业设计\goodpoint.mat') % % x=point(:,1);y=point(:,2); %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%在点状图上画出障碍物环境%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
global photoll photocc photo; photoll=300;photocc=300; photo=ones(photoll,photocc); [photo_point,aaa]=plot2photo(point);
[photopointamount,aaa]=size(photopoint); for i=1:photopointamount photopointaround=square(photopoint(i,:),20);%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%画出的图形的大小 aaa=blackenphoto(photopoint_around); end
global photoconnectpoints; photoconnectpoints=photo;
% % figure % % imshow(photo) % % title('障碍物环境')
%%%%%%%%%%%获得其Voronoi图 figure voronoi(x,y) close; % %% title('障碍物质点的Voronoi图') [connectpoint,roundpointcell]=voronoin(point); connectpoint(1,:)=[]; tri=delaunay(x,y); ```
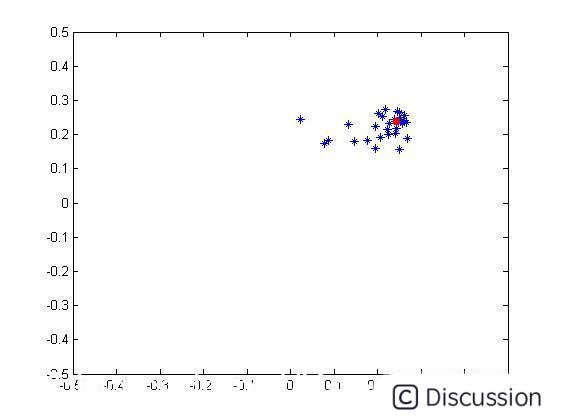
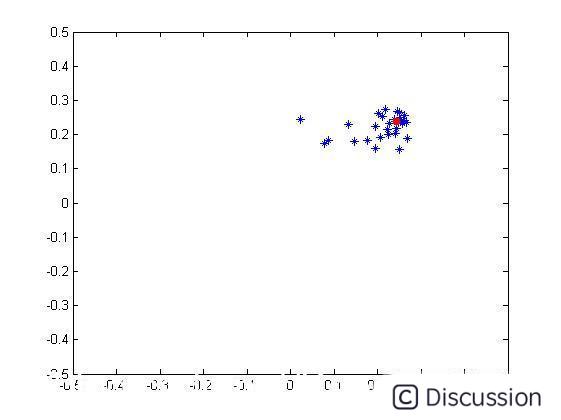
三、运行结果
四、备注
版本:2014a