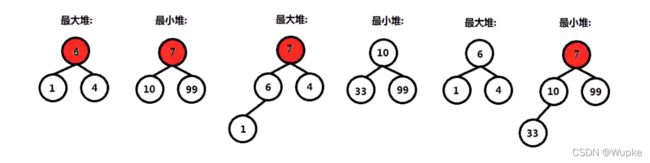
【数据结构与算法-栈、队列、堆经典例题汇总】
【数据结构与算法-栈、队列、堆经典例题汇总】
-
- 典例1、使用队列实现栈(easy)
- 典例2、使用栈实现队列(easy)
- 典例3、包含min函数的栈(easy)
- 典例4、合法的出栈顺序(medium)
- 典例5、简单的计算器(hard)
- 典例6、数组中第K大的数(medium)
- 典例7、寻找中位数(hard)
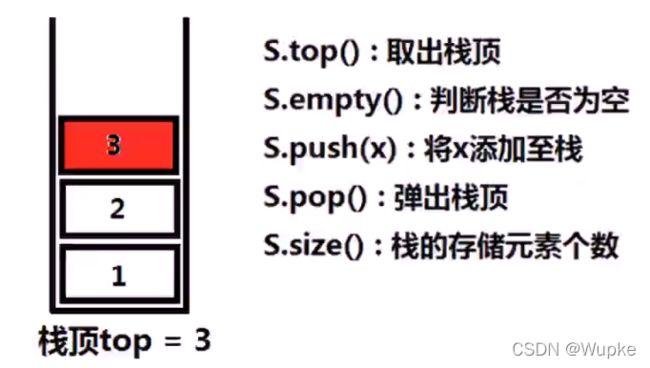
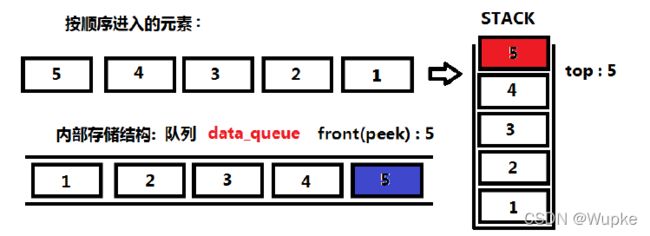
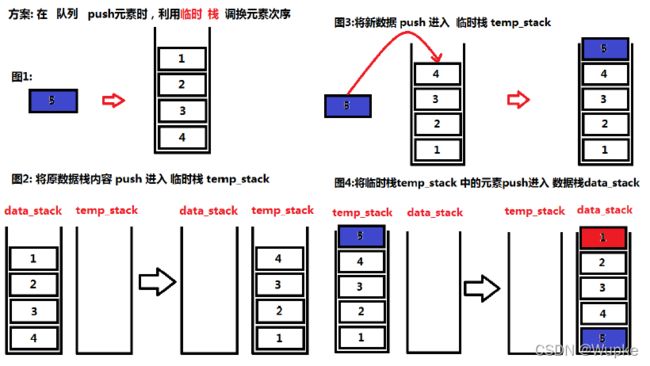
典例1、使用队列实现栈(easy)
- 题目描述:
-
LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
-
OJ测试代码实现:
class MyStack {
private:
std::queue<int> data; // 声明一个队列,其元素顺序与栈中元素出栈顺序一致
public:
MyStack() {
}
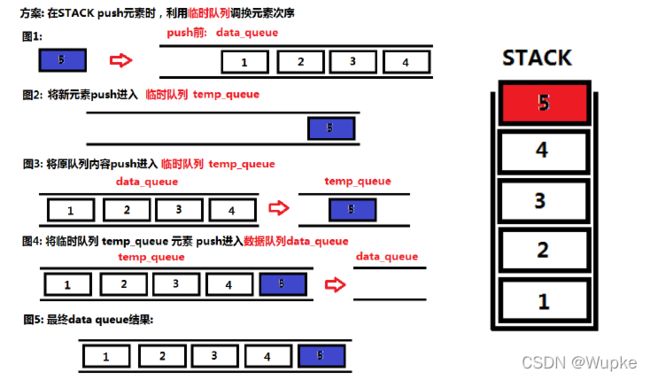
void push(int x) {
std::queue<int> temp_queue; // 声明一个队列 ,借助来调换顺序
temp_queue.push(x); // 先将新元素压入临时队列中
while(!data.empty()){
temp_queue.push(data.front()); // 将数据队列元素导入临时队列中
data.pop();
}
while(!temp_queue.empty()){
data.push(temp_queue.front()); //再将临时队列中的元素导入数据队列,完成顺序调整(与出栈的顺序一样)
temp_queue.pop();
}
}
int pop() {
int x = data.front(); //
data.pop();
return x;
}
int top() {
return data.front();
}
bool empty() {
return data.empty();
}
};
- 完整的本地代码:
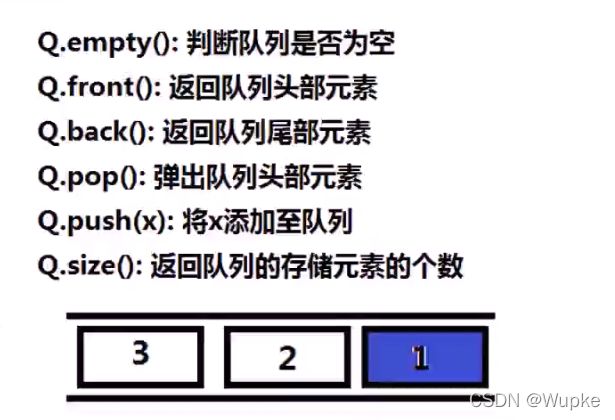
#include 典例2、使用栈实现队列(easy)
class MyQueue {
private:
std::stack<int> s; // 声明 一个 栈,其中存储的顺序 与队列顺序一致
public:
MyQueue() {
}
void push(int x) {
std::stack<int> temp_stack; // 声明 临时栈
while(!s.empty()){
temp_stack.push(s.top()); // 将数据栈中的数据push到临时栈中
s.pop(); // 依次删除存储栈中的元素
}
temp_stack.push(x); // 将新元素添加进临时栈中
while(!temp_stack.empty()){
s.push(temp_stack.top()); // 将临时栈中的元素重新依次push到存储栈中,完成顺序的调换
temp_stack.pop(); // 依次删除临时栈中的元素
}
}
int pop() { // 删除顶点元素
int x = s.top();
s.pop();
return x ;
}
int peek() { // 返回顶点元素
return s.top();
}
bool empty() { // 查询空否
return s.empty();
}
};
- 完整的本地代码:
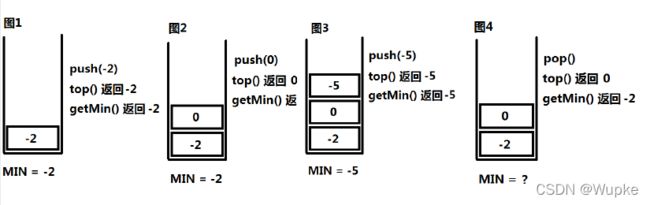
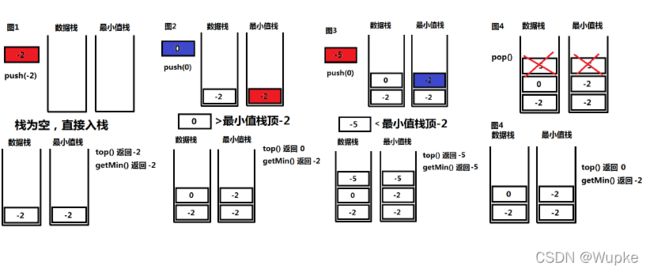
#include 典例3、包含min函数的栈(easy)
-
思路:使用辅助栈-记录状态的最小值栈 。
-
常数时间内,要求复杂度O(1),就是在确定最小值的时候,要有变量在记录这个最小值,查找的时候,可以直接取出这个变量;
-
LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
-
OJ测试代码实现:
class MinStack {
private:
std::stack<int> s; // 声明正常存储的栈
std::stack<int> min_s; // 声明存储对应最小值的栈
public:
MinStack() {
}
void push(int val) {
s.push(val); // 将数据压入正常存储的栈
if (min_s.empty()){
min_s.push(val); // 如果最小值栈为空,直接压入第一个元素值
}
else {
if (val>=min_s.top()){ // 比较当前数据与最小值栈栈顶的数值大小,选择最小的压入最小值栈
min_s.push(min_s.top());
}
else{
min_s.push(val);
}
}
}
void pop() {
// int x = s.top();
s.pop(); // 数据栈与最小值栈同时弹出
min_s.pop();
// return x;
}
int top() { // 获取栈顶
return s.top();
}
int getMin() { // 获取最小值栈的栈顶
return min_s.top();
}
};
- 完整的本地代码:
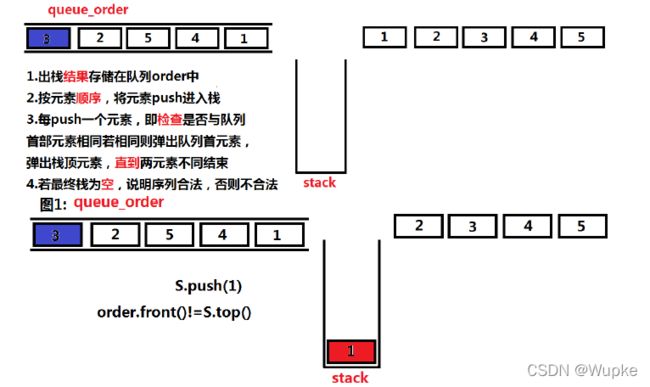
#include 典例4、合法的出栈顺序(medium)
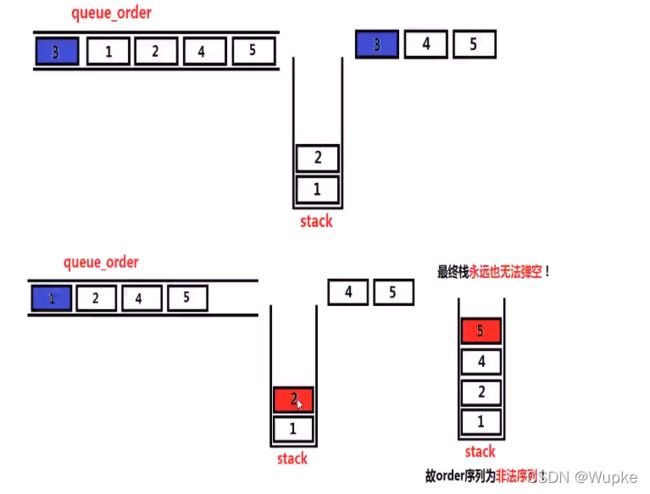
- 题目描述:
-
思路:使用栈与队列模拟入栈、出栈的过程 。
-
利用栈和队列进行模拟:
-
将元素顺序存入队列,然后同样的元素顺序依次入栈;
-
对比栈的首个元素与队列的首个元素是否相同:是,同时执行删除首个元素的操作;不同,则下个元素继续入栈;
-
最后,当栈为空,说明顺序合法;否则,即为不合法;
-
OJ测试提交代码逻辑:
bool check_is_valid_order(std::queue<int> &order){ // 出栈的结果保存在队列order中
std::stack<int> S; // 声明一个栈
int n = order.size();
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
S.push(i); // 按照元素顺序,依次将元素push进入栈中
while(!S.empty() && orde.front()==S.top()){ // 只要S不空,检查该元素是否与队列的首部元素相同
S.pop(); //相同则同时弹出队列首元素,栈的栈顶;不同则继续入栈下一个元素
order.pop();
}
}
if (!S.empty()){ //最终栈若是为空,说明元素序列合法;否则不合法
return false;
}
return true;
}
- 完整的本地代码:
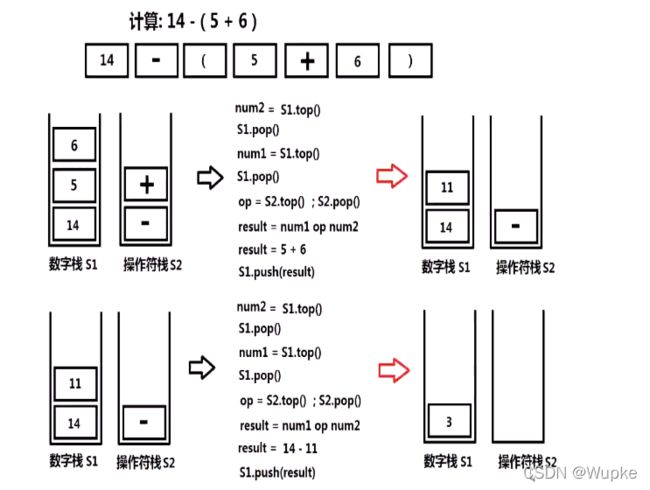
#include 典例5、简单的计算器(hard)
// 将字符串“12345”转化为整型12345
#include -
字符串处理思路:状态机判断处理
-
提示:第一个数可能是负数,为了减少边界判断,可先往 数值栈中 添加一个 0
-
为防止 () 内出现的首个字符为运算符,可将所有的空格去掉,并将 (- 替换为 (0-;(+ 替换为 (0+。
-
LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
-
OJ测试代码实现:
-
1 (-)
class Solution {
private:
void compute(std::stack<int> &number_stack,
std::stack<char> &operation_stack){
if (number_stack.size() < 2){
return;
}
int num2 = number_stack.top();
number_stack.pop();
int num1 = number_stack.top();
number_stack.pop();
if (operation_stack.top() == '+'){
number_stack.push(num1 + num2);
}
else if(operation_stack.top() == '-'){
number_stack.push(num1 - num2);
}
operation_stack.pop();
}
public:
int calculate(std::string s) {
static const int STATE_BEGIN = 0;
static const int NUMBER_STATE = 1;
static const int OPERATION_STATE = 2;
std::stack<int> number_stack;
// number_stack.push(0);
std::stack<char> operation_stack;
int number = 0;
int STATE = STATE_BEGIN;
int compuate_flag = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++){
if (s[i] == ' '){
continue;
}
switch(STATE){
case STATE_BEGIN:
if (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'){
STATE = NUMBER_STATE;
}
else{
STATE = OPERATION_STATE;
}
i--;
break;
case NUMBER_STATE:
if (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'){
number = number * 10 + (s[i] -'0');
}
else{
number_stack.push(number);
if (compuate_flag == 1){
compute(number_stack, operation_stack);
}
number = 0;
i--;
STATE = OPERATION_STATE;
}
break;
case OPERATION_STATE:
if (s[i] == '+' || s[i] == '-'){
operation_stack.push(s[i]);
compuate_flag = 1;
}
else if (s[i] == '('){
STATE = NUMBER_STATE;
compuate_flag = 0;
}
else if (s[i] >= '0' && s[i] <= '9'){
STATE = NUMBER_STATE;
i--;
}
else if (s[i] == ')'){
compute(number_stack, operation_stack);
}
break;
}
}
if (number != 0){
number_stack.push(number);
compute(number_stack, operation_stack);
}
if (number == 0 && number_stack.empty()){
return 0;
}
return number_stack.top();
}
};
- 2
class Solution {
public:
void calc(stack<int> &nums, stack<char> &ops) {
if(nums.size() < 2 || ops.empty())
return;
int b = nums.top(); nums.pop();
int a = nums.top(); nums.pop();
char op = ops.top(); ops.pop();
nums.push(op == '+' ? a+b : a-b);
}
void replace(string& s){
int pos = s.find(" ");
while (pos != -1) {
s.replace(pos, 1, "");
pos = s.find(" ");
}
}
int calculate(string s) {
// 存放所有的数字
stack<int> nums;
// 为了防止第一个数为负数,先往 nums 加个 0
nums.push(0);
// 将所有的空格去掉
replace(s);
// 存放所有的操作,包括 +/-
stack<char> ops;
int n = s.size();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char c = s[i];
if(c == '(')
ops.push(c);
else if(c == ')') {
// 计算到最近一个左括号为止
while(!ops.empty()) {
char op = ops.top();
if(op != '(')
calc(nums, ops);
else {
ops.pop();
break;
}
}
}
else {
if(isdigit(c)) {
int cur_num = 0;
int j = i;
// 将从 i 位置开始后面的连续数字整体取出,加入 nums
while(j <n && isdigit(s[j]))
cur_num = cur_num*10 + (s[j++] - '0');
// 注意上面的计算一定要有括号,否则有可能会溢出
nums.push(cur_num);
i = j-1;
}
else {
if (i > 0 && (s[i - 1] == '(' || s[i - 1] == '+' || s[i - 1] == '-')) {
nums.push(0);
}
// 有一个新操作要入栈时,先把栈内可以算的都算了
while(!ops.empty() && ops.top() != '(')
calc(nums, ops);
ops.push(c);
}
}
}
while(!ops.empty())
calc(nums, ops);
return nums.top();
}
};
- 完整的本地代码:
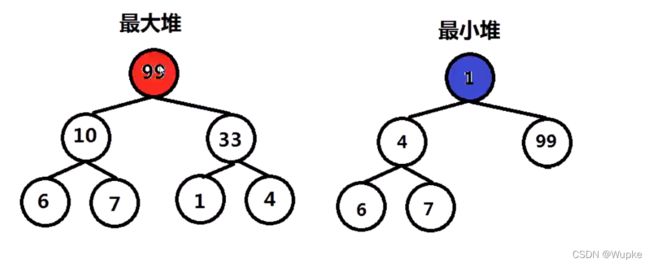
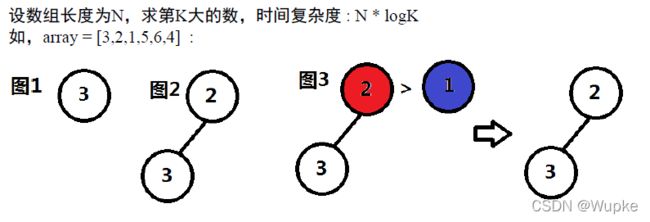
#include 典例6、数组中第K大的数(medium)
-
预备知识:二叉堆属性
-
插入复杂度:log n
-
思路:维护一个K 大小的最小堆,返回堆顶 。
-
最小堆的堆顶为堆中最小值;
-
堆中的元素个数维持为 K ;
-
当堆中的个数小于 k 时候,新元素直接进入堆;
-
LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
-
OJ测试代码实现:
class Solution {
private:
std::priority_queue<int,std::vector<int>,std::greater<int>> small_queue; // 声明最小堆
public:
int findKthLargest(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
for (int i= 0;i< nums.size();i++){ //遍历nums数组
if (small_queue.size()<k){ //如果堆中的元素个数小于k,直接push进入堆
small_queue.push(nums[i]);
}
else if(nums[i] > small_queue.top()){ //如果堆顶的元素比新元素小,弹出堆顶
small_queue.pop();
small_queue.push(nums[i]); // 新元素push进入堆,替换堆顶
}
}
return small_queue.top();
}
};
- 可本地测试的完整代码:
#include 典例7、寻找中位数(hard)
-
思路:直观的方法 VS 堆 。
-
直观方法:使用数组的存储结构,每次添加元素或者查找中位数的时候对数组进行排序,再计算结果。
若添加元素时排序,添加元素复杂度为O(n), 查找中位数为O(1);
若查询中位数时排序,添加元素复杂度为O(1), 查找中位数为O(nlogn);
若查找与增加时随机的,共n次操作,整体复杂度为:O(n*2) -
使用 堆 的方法:
-
同时维护一个最大堆和一个最小堆,各存储数据的一半(元素差值始终维持 <=1);
-
并且,维持最大堆的对顶小于最小堆的堆顶;
-
当堆的元素一样多,返回两堆顶之和;
-
LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
-
OJ测试代码实现:
class MedianFinder {
private:
std::priority_queue<double>big_queue; // 声明最大堆
std::priority_queue<double ,std::vector<double>,std::greater<double> > small_queue;//声明最小堆
public:
MedianFinder() {
}
void addNum(int num) {
if (big_queue.empty()){ // 往堆中添加元素,开始
big_queue.push(num);
return ;
}
if (big_queue.size()==small_queue.size()){ // 两堆元素一样多
if (num<=big_queue.top()){ //新加入的num值 小于最大堆的堆顶
big_queue.push(num);
}
else{ //新加入的num值 大于最大堆的堆顶
small_queue.push(num);
}
}
else if (big_queue.size()>small_queue.size()){ // 最大堆多一个
if (num>big_queue.top()){ //新加入的num值 大于最大堆的堆顶
small_queue.push(num);
}
else{//新加入的num值 小于最大堆的堆顶
small_queue.push(big_queue.top());
big_queue.pop();
big_queue.push(num);
}
}
else if (big_queue.size()<small_queue.size()){ //最小堆多一个
if (num<small_queue.top()){ //新加入的num值 小于最小堆的堆顶
big_queue.push(num);
}
else{
big_queue.push(small_queue.top());
small_queue.pop();
small_queue.push(num);
}
}
}
double findMedian() {
if (big_queue.size()==small_queue.size()){ // 两堆元素一样多
return (big_queue.top()+small_queue.top())/2;
}
else if (big_queue.size()>small_queue.size()){// 最大堆多一个
return (big_queue.top());
}
return small_queue.top();//最小堆多一个
}
};
- 可本地运行的测试代码:
#include