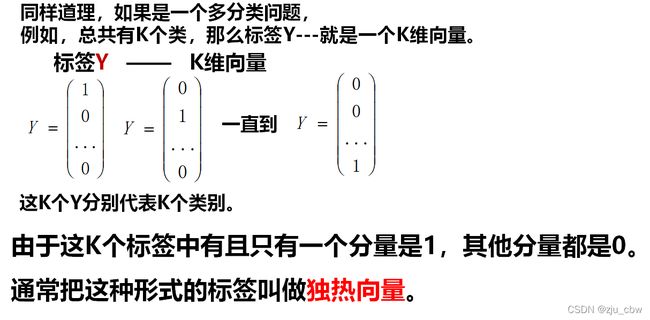
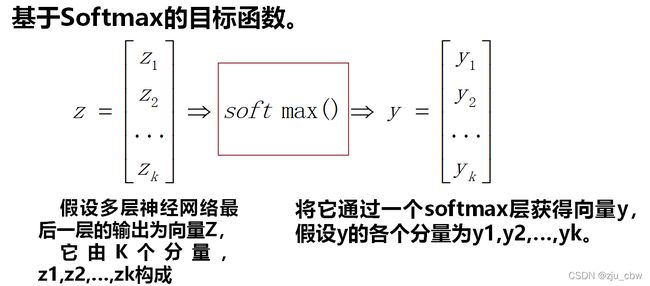
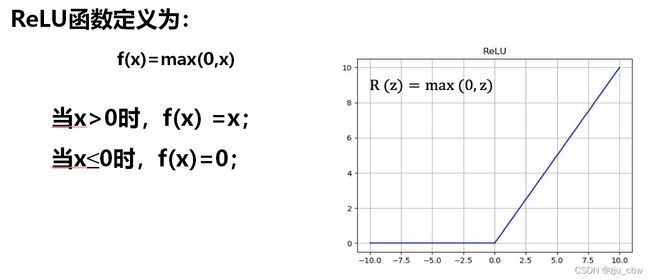机器学习(十三)——神经网络
人工神经网络(artificial neural network,ANN),简称神经网络(neural network,NN),是一种模仿生物神经网络的结构和功能的数学模型或计算模型。神经网络由大量的人工神经元联结进行计算。大多数情况下人工神经网络能在外界信息的基础上改变内部结构,是一种自适应系统。现代神经网络是一种非线性统计性数据建模工具,常用来对输入和输出间复杂的关系进行建模,或用来探索数据的模式。
神经网络概述
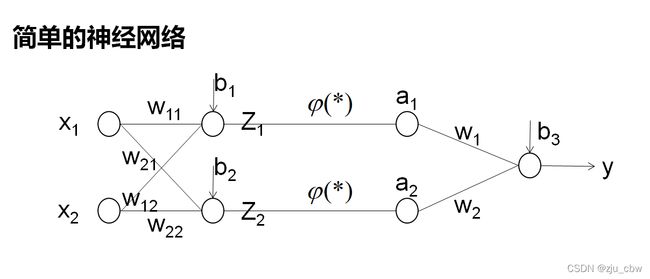
神经网络是一种运算模型,由大量的节点(或称“神经元”)和之间相互的联接构成。每个节点代表一种特定的输出函数,称为激励函数、激活函数(activation function)。每两个节点间的联接都代表一个对于通过该连接信号的加权值,称之为权重,这相当于人工神经网络的记忆。网络的输出则依网络的连接方式,权重值和激励函数的不同而不同。而网络自身通常都是对自然界某种算法或者函数的逼近,也可能是对一种逻辑策略的表达。
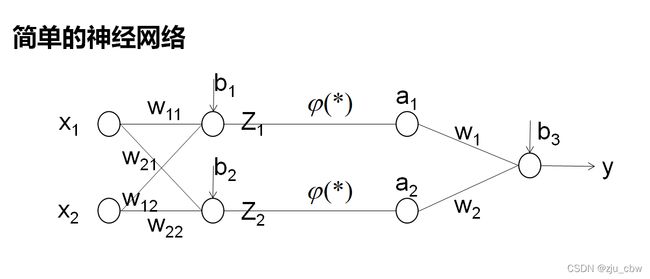
对于上面的神经网络我们需要估计以下参数:
(w11,w12,w21,w22,w1,w2,b1,b2,b3)
目标函数为:
Minimize: E(W,b) = 1/2(y-Y)2
参数估计
我们先以简单的神经网络为例。
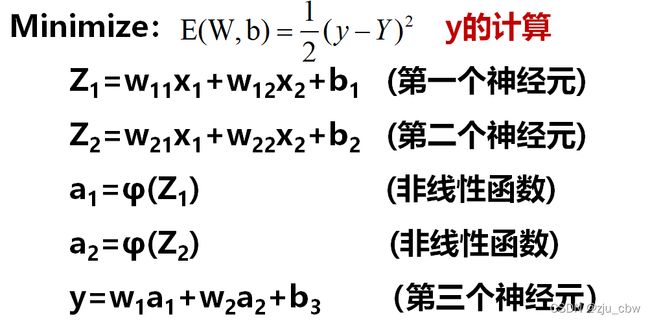
要求九个偏导数
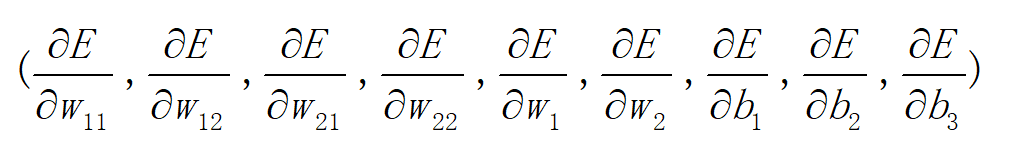
虽然我们可以逐一的计算这些偏导数,但是这样做的计算量太大,我们其实可以利用神经网络这种分层结构,来简化求解偏导数的计算,这个算法也被称为后向传播算法。
可以用已经算出的偏导数去计算还没有算出的另一些偏导数,这比直接计算9个偏导数要方便很多。
在这个网络中先计算Z1,Z2,y的偏导数。因为这三个点是整个网络的枢纽,其他偏导数都可以很容易地通过这三个点的偏导数算出来,接下来我们来计算这三个偏导数。
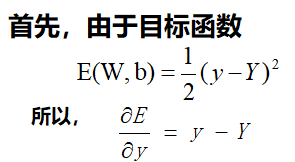




通过这三个关键位置的偏导数,很容易求出前面9个偏导数。
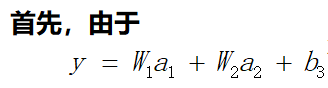
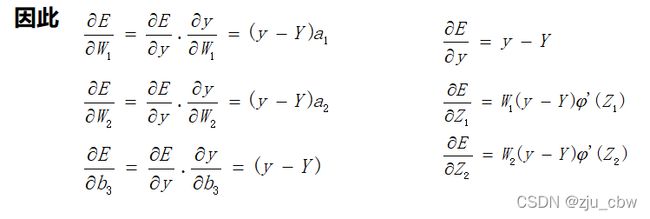
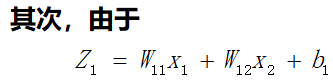
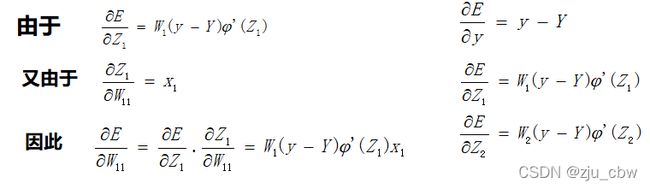
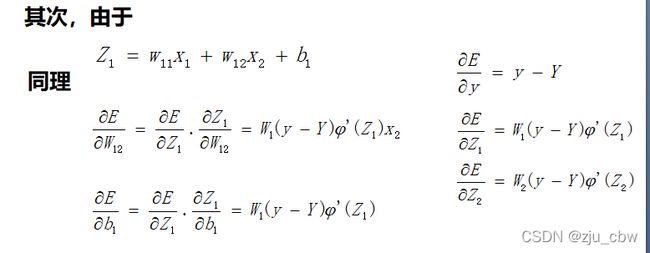
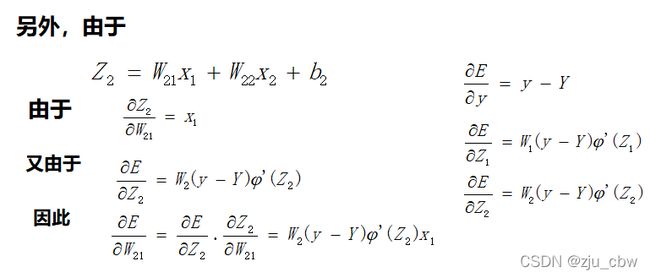
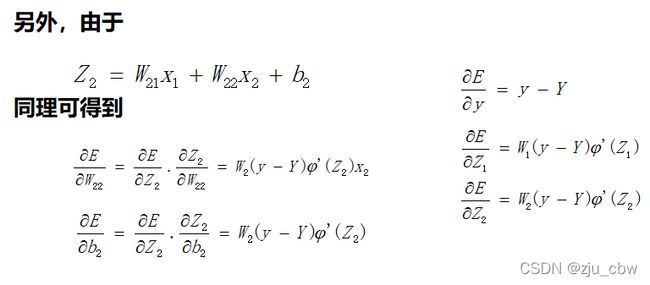

后向传播
更一般的神经网络
之前我们是通过简单的神经网络模型来推到后向传播的,下面我们通过更一般的神经网络进行后向传播。
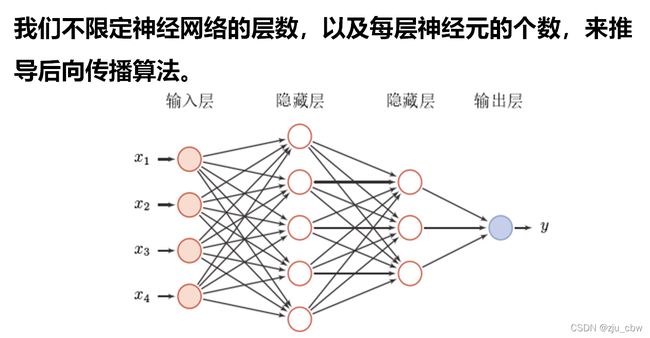
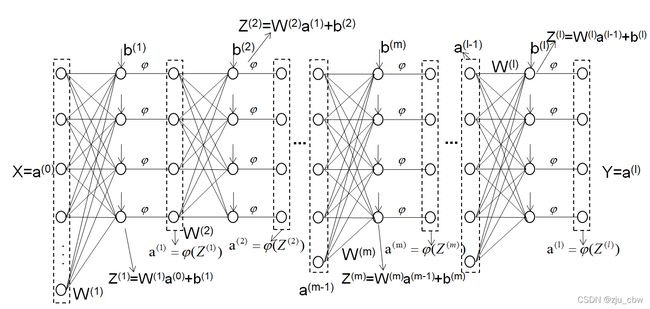


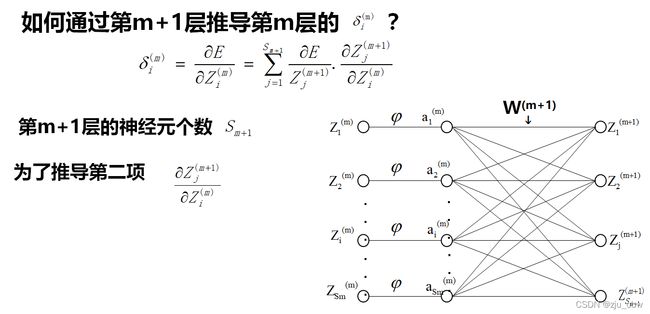
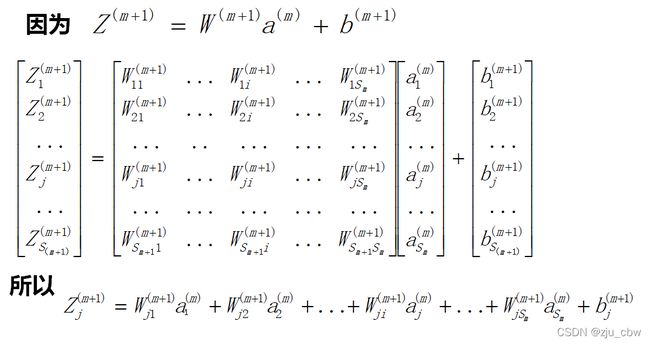
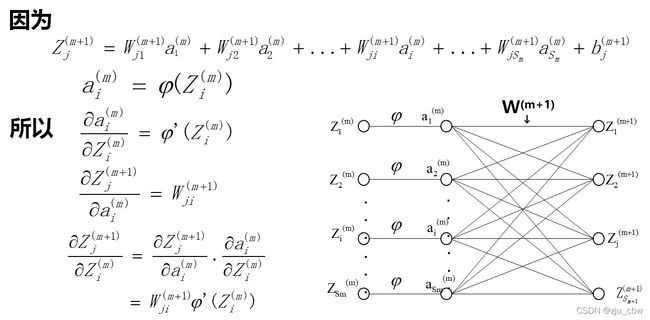
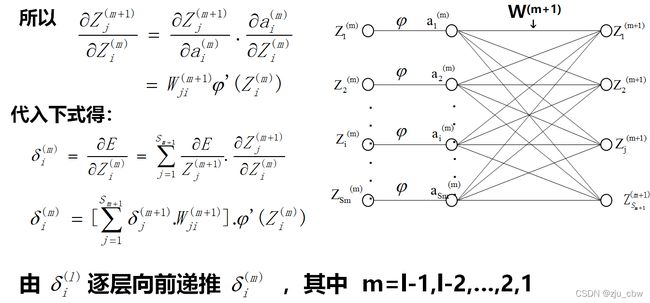
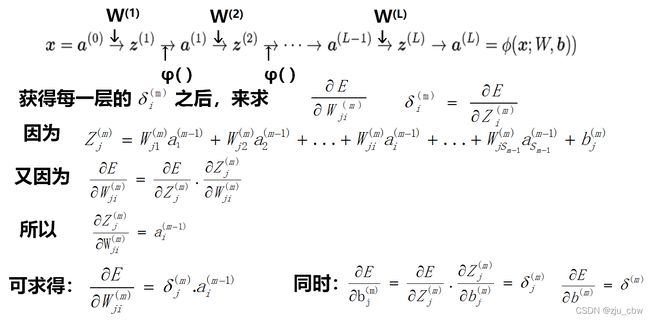


一般情况下,反向传播算法的算法流程:





神经网络的改进
对非线性(激活函数)的改进
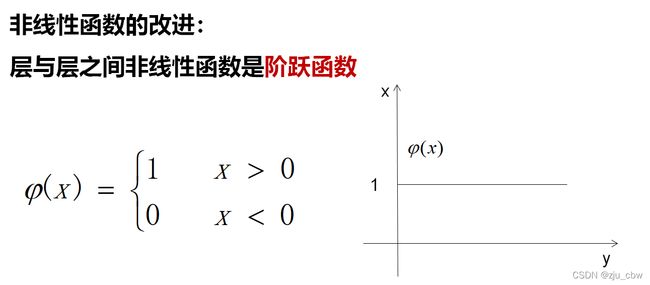
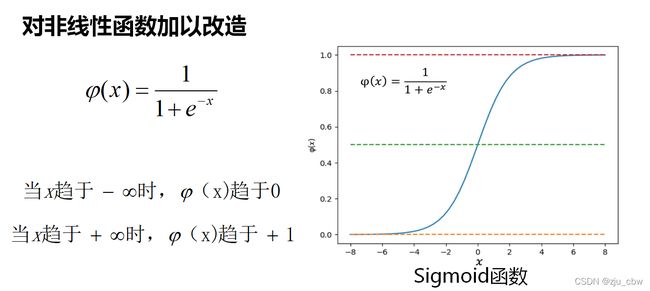
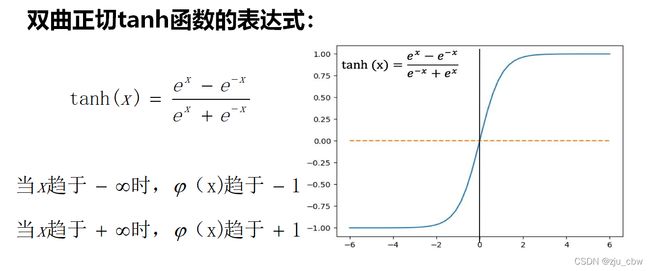
如果使用阶跃函数,导数就不是连续的了,所以我们对其进行改进,有以下几种选择。
目标函数
随机梯度下降法(SGD)
鸢尾花分类
Iris数据集是常用的分类实验数据集,由Fisher, 1936收集整理。Iris也称鸢尾花卉数据集,是一类多重变量分析的数据集。数据集包含150个数据集,分为3类,每类50个数据,每个数据包含4个属性。可通过花萼长度,花萼宽度,花瓣长度,花瓣宽度4个属性预测鸢尾花卉属于(Setosa,Versicolour,Virginica)三个种类中的哪一类。
- 属性:
Sepal.Length(花萼长度),单位是cm;
Sepal.Width(花萼宽度),单位是cm;
Petal.Length(花瓣长度),单位是cm;
Petal.Width(花瓣宽度),单位是cm; - 种类:
Iris Setosa(山鸢尾)(本例中使用数字‘0’表示)
Iris Versicolour(杂色鸢尾)(本例中使用数字‘1’表示)
Iris Virginica(维吉尼亚鸢尾)(本例中使用数字‘2’表示)
- 定义sigmoid函数
# define sigmoid function
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
- 神经网络结构确定
该函数主要是为了获取输入量x的矩阵大小,以及标签y的矩阵大小。
def layer_size(X, Y):
"""
:param X: input dataset of shape (input size, number of examples) (输入数据集大小(几个属性,样本量))
:param Y: labels of shape (output size, number of exmaples) (标签数据大小(标签数,样本量))
:return:
n_x: the size of the input layer
n_y: the size of the output layer
"""
n_x = X.shape[0]
n_y = Y.shape[0]
return (n_x, n_y)
- 权重和偏移量参数初始化
该函数主要是为了初始化我们的连接权重w和偏移量b。要注意的是确保参数矩阵大小正确。
def initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y):
"""
initialize_parameters
(参数初始化)
:param n_x: size of the input layer
:param n_h: size of the hidden layer
:param n_y: size of the output layer
:return:
W1: weight matrix of shape (n_h, n_x) (第1层的权重矩阵(n_h, n_x))
b1: bias vector of shape (n_h, 1) (第1层的偏移量向量(n_h, 1))
W2: weight matrix of shape (n_y, n_h) (第2层的权重矩阵(n_y, n_h))
b2: bias vector of shape (n_y, 1) (第2层的偏移量向量(n_y, 1))
"""
# np.random.seed(2) #Random initialization (随机种子初始化参数)
W1 = np.random.randn(n_h, n_x) * 0.01
b1 = np.zeros((n_h, 1))
W2 = np.random.randn(n_y, n_h) * 0.01
b2 = np.zeros((n_y, 1))
parameters = {
'W1': W1,
'b1': b1,
'W2': W2,
'b2': b2,
}
return parameters
- 正向传播计算
该函数为正向传播计算,需要注意的是,中间层的激活函数为tanh,输出层的激活函数为sigmoid。
def forward_propagation(X, parameters):
"""
forward_propagation
(正向传播)
:param X: input data of size (n_x, m) (输入数据集X)
:param parameters: python dictionary containing your parameters (output of initialization function) (字典类型,权重以及偏移量参数)
:return:
A2: The sigmoid output of the second activation (第2层激活函数sigmoid函数输出向量)
cache: a dictionary containing "Z1", "A1", "Z2" and "A2" (字典类型,包含"Z1", "A1", "Z2", "A2")
"""
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
Z1 = np.dot(W1, X) + b1
A1 = np.tanh(Z1) #第1层激活函数选择tanh
Z2 = np.dot(W2, A1) + b2
A2 = sigmoid(Z2) #第2层激活函数选择sigmod
assert (A2.shape == (1, X.shape[1])) #若A2的大小和((1, X.shape[1]))不同,则直接报异常
cache = {
'Z1': Z1,
'A1': A1,
'Z2': Z2,
'A2': A2,
}
return A2, cache
- 代价函数计算
该函数主要是为了计算代价函数,注意一个样本的期望输出和实际输出的误差的平方用来定义损失函数,在向量化的计算过程中,这里使用了代价函数。
交叉熵损失是分类任务中的常用损失函数,最后一层是sigmoid
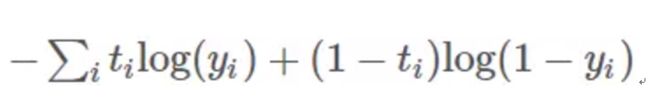
def compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters):
"""
compute cost(计算成本函数)
:param A2: The sigmoid output of the second activation, of shape (1, number of examples) (第2层激活函数sigmoid函数输出向量)
:param Y: "true" labels vector of shape (1, number of examples) (正确标签向量)
:param parameters: python dictionary containing your parameters W1, b1, W2 and b2 (字典类型,权重以及偏移量参数)
:return:
cost: cross-entropy cost
"""
m = Y.shape[1] # number of example
W1 = parameters['W1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
logprobs = np.multiply(np.log(A2), Y)
cost = - np.sum(np.multiply(np.log(A2), Y) + np.multiply(np.log(1. - A2), 1. - Y)) / m
# cost = np.sum(Y * np.log(A2) + (1 - Y) * np.log(1 - A2))/(-m)
cost = np.squeeze(cost) #squeeze()函数的功能是:从矩阵shape中,去掉维度为1的。例如一个矩阵是的shape是(5,1),使用过这个函数后,结果为(5,)。
assert (isinstance(cost, float)) #若cost不是float型 则直接报异常
return cost
- 反向传播计算
该函数为方向传播计算。
def backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y):
"""
backward propagation(反向传播)
:param parameters: python dictionary containing our parameters
:param cache: a dictionary containing "Z1", "A1", "Z2" and "A2"
:param X: input data of shape (2,number of examples)
:param Y: "ture" labels vector of shape (1, number of examples)
:return:
grads: python dictionary containing your gradients with respect to different parameters (字典类型,梯度微分参数)
"""
m = X.shape[1]
W1 = parameters['W1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
A1 = cache['A1']
A2 = cache['A2']
dZ2 = A2 - Y
dW2 = np.dot(dZ2, A1.T) / m
db2 = np.sum(dZ2, axis=1, keepdims=True) / m
dZ1 = np.dot(W2.T, dZ2) * (1 - A1 ** 2)
dW1 = np.dot(dZ1, X.T) / m
db1 = np.sum(dZ1, axis=1, keepdims=True) / m
grads = {
'dW1': dW1,
'db1': db1,
'dW2': dW2,
'db2': db2,
}
return grads
- 权重和偏移量参数更新
该函数为更新权重和偏移量参数。
def update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate):
"""
update parameters(更新权重和偏移量参数)
:param parameters: python dictionary containing your parameters
:param grads: python dictionary containing your gradients
:param learning_rate (学习速率)
:return:
:parameters: python dictionary containing your updated parameters
"""
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
dW1 = grads['dW1']
db1 = grads['db1']
dW2 = grads['dW2']
db2 = grads['db2']
W1 = W1 - learning_rate * dW1
b1 = b1 - learning_rate * db1
W2 = W2 - learning_rate * dW2
b2 = b2 - learning_rate * db2
parameters = {
"W1": W1,
"b1": b1,
"W2": W2,
"b2": b2,
}
return parameters
- BP神经网络
我们将上面的几个函数组合起来,就可以得到一个两层的BP神经网络模型。
def nn_model(X, Y, n_h, num_iterations, learning_rate, print_cost=False):
"""
Forward Neural Network model(前向神经网络模型)
:param X: input dataset of shape (input size, number of examples) (输入数据集大小(几个属性,样本量))
:param Y: labels of shape (output size, number of exmaples) (标签数据大小(标签数,样本量))
:param n_h: size of the hidden layer (隐层神经元数量)
:param num_iterations: Number of iterations in gradient descent loop (迭代次数)
:param learning_rate (学习速率)
:param print_cost: if True, print the cost every 1000 iterations (是否打印显示)
:return:
parameters: parameters learnt by the model. They can then be used to predict (训练完成后的参数)
"""
# np.random.seed(4)
n_x = layer_size(X, Y)[0]
n_y = layer_size(X, Y)[1]
parameters = initialize_parameters(n_x, n_h, n_y)
W1 = parameters['W1']
b1 = parameters['b1']
W2 = parameters['W2']
b2 = parameters['b2']
cost_list = []
for i in range(0, num_iterations):
A2, cache = forward_propagation(X, parameters)
cost = compute_cost(A2, Y, parameters)
cost_list.append(cost)
grads = backward_propagation(parameters, cache, X, Y)
parameters = update_parameters(parameters, grads, learning_rate)
if print_cost and i % 1000 == 0:
print("Cost after iteration %i: %f" % (i, cost))
return parameters, cost_list
- 鸢尾花分类测试
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
#from Forward_NeuralNetwork import *
def load_csv():
"""加载处理好存入csv格式的数据"""
tmp = np.loadtxt("iris.csv",dtype=np.str, delimiter=",")
data = tmp[1:, 1:5].astype(np.float)
label = tmp[1:, 5] #.astype(np.float)
# print(data.shape)
# print(label.shape)
label = label.reshape(150, 1)
return data.T, label.T
def normalized(X):
"""
:param X: 待归一化的数据
:return:
X:归一化后的数据
"""
Xmin, Xmax = X.min(), X.max()
XN = (X - Xmin) / (Xmax - Xmin)
return XN
def main():
X, Y = load_csv()
X = normalized(X)
for i in range(Y.shape[1]):
if Y[0][i]=='Iris-setosa':
Y[0][i] = '0'
if Y[0][i]=='Iris-versicolor':
Y[0][i] = '1'
if Y[0][i]=='Iris-virginica':
Y[0][i] = '2'
Y = Y.astype(np.float)
# print(Y)
Y = normalized(Y)
"""训练集90个数据"""
train_x = np.hstack((X[:, 0:30], X[:, 50:80], X[:, 100:130]))
train_y = np.hstack((Y[:, 0:30], Y[:, 50:80], Y[:, 100:130]))
"""测试集60个数据"""
test_x = np.hstack((X[:, 30:50], X[:, 80:100], X[:, 130:150]))
test_y = np.hstack((Y[:, 30:50], Y[:, 80:100], Y[:, 130:150]))
"""训练,中间层10个神经元,迭代10000次,学习率0.25"""
n_h = 10
parameter, cost_list = nn_model(train_x, train_y, n_h, num_iterations=10000, learning_rate=0.25, print_cost=True)
"""测试,代入测试集数据"""
A2, cache = forward_propagation(test_x, parameters=parameter)
TY = A2
TY[TY > 0.8] = 1
TY[TY < 0.2] = 0
TY[(TY >= 0.2) & (TY <= 0.8)] = 0.5
# print(A2,TY)
count = 0
for i in range(0, 60):
if TY[0, i] == test_y[0, i]:
count += 1
print("准确率为:%f %%" %(100*count/60))
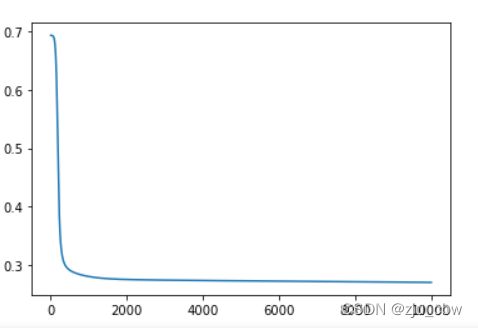
"""绘制梯度下降曲线"""
plt.plot(cost_list)
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
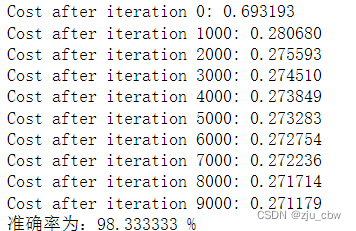
测试结果
测试中,将150个数划分成了90个训练数据,60个测试数据。神经网络的中间层为10个神经元,迭代次数为10000次,学习率为0.25。在训练和测试中,需要对数据进行归一化,其中包括对标签数据Y的归一化。
设置的三类鸢尾花的标签分别是0,1,2。通过归一化之后,获得的标签数据为0,0.5,1。对测试集获得的结果,进行归档,小于0.2的为0,大于0.8的为1,其余的均为0.5。
最终获得的分类结果的准确率是多少。
sklearn包神经网络的使用可以看这篇博客。